Can I Lower My Risk Of Getting A Second Cancer
There are steps you can take to lower your risk and stay as healthy as possible. For example, prostate cancer survivors should do their best to stay away from all tobacco products and tobacco smoke. Smoking can increase the risk of bladder cancer, as well as increase the risk of many other cancers.
To help maintain good health, prostate cancer survivors should also:
- Get to and stay at a healthy weight
- Keep physically active and limit the time you spend sitting or lying down
- Follow a healthy eating pattern that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and limits or avoids red and processed meats, sugary drinks, and highly processed foods
- Not drink alcohol. If you do drink, have no more than 1 drink per day for women or 2 per day for men
These steps may also lower the risk of some other health problems.
See Second Cancers in Adults to learn a lot more about the causes of second cancers.
Our team is made up of doctors and oncology certified nurses with deep knowledge of cancer care as well as journalists, editors, and translators with extensive experience in medical writing.
Bostrom PJ, Soloway MS. Secondary cancer after radiotherapy for prostate cancer: Should we be more aware of the risk? Eur Urol. 2007 52:973-982.
Moon K, Stukenborg GJ, Keim J, Theodorescu D. Cancer incidence after localized therapy for prostate cancer. Cancer. 2006 107:991-998.
Last Revised: June 9, 2020
Also Check: Zinc Prostate Cancer
What Is The Prognosis Of Urothelial Carcinoma
The general 5-year survival rate for people with bladder cancer is 77%. However, survival rates depend on many factors, including the type and stage of bladder cancer that is diagnosed. The 5-year survival rate of people with bladder cancer that has not spread beyond the inner layer of the bladder wall is 96%.
Early Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
The following are some of the early-stage bladder cancer symptoms you might experience:
1. Blood in the Urine
Blood in urine, often referred to as hematuria, is the most common symptom or sign of bladder cancer. With this symptom:
- You might have enough blood to change your urine color to pink, orange or, less often, dark red.
- Your urine color is sometimes normal, but a urine test , which the doctor performs during a general medical checkup or if you have other symptoms, can still detect small traces of blood.
- You may have blood one day and not the next, with your urine staying clear for weeks or maybe even months at a time.
Generally, the earlier stages of bladder cancer when the cancer is small and confined to your bladder only cause bleeding with either no pain or little pain.
Itâs important to note that blood in your urine doesnât necessarily indicate bladder cancer. The cause of blood may be due to another factor. In fact, many healthy individuals may have some unseen blood in their urine at some stage . And, for most individuals, the cause isnât cancer.
In many situations, the cause is due to other things like benign tumors, medications or foods, infection, bladder or kidney stones or another benign kidney disease. Still, you should have your doctor check it out.
If youâre concerned about cancer, ask them about Cxbladder, a non-invasive genomic urine test that quickly and accurately detects or rules out bladder cancer.
You May Like: How To Make A Weak Bladder Stronger
Where Can I Find A Support Group
To find a local group, talk to your healthcare provider. Local and Zoom meeting lists are also available through organizations such as CancerCare.
Joining a support group of people dealing with advanced cancer may help provide camaraderie and knowledge. You can connect with people who understand what you’re going through.
Treating cancer means looking after your whole self. This includes keeping an active lifestyle, eating healthy, practicing mindfulness, and socializing with family and friends to improve your mood and overall health. If you smoke cigarettes or use nicotine products, this is a good time to try to quit or cut down.
It’s also important to look after your mental health. Meeting with a therapist can help you navigate intense emotions and provide you with tools to feel more in control of your daily life.
Palliative care may also be beneficial. Your palliative care provider can help you learn about pain management options. Palliative care providers can also assist with finding mental health services, such as counseling.
Risk Factors For Kidney Cancer
There are some things that can make you more likely to develop kidney cancer. These are called risk factors and they include:
- smoking chemicals in cigarettes can cause kidney cancer. Around one in three cases of kidney cancer may be due to smoking
- obesity excess body fat may cause changes in certain hormones that can lead to kidney cancer
- high blood pressure
- kidney failure people with end-stage kidney disease
- family history people who have family members with kidney cancer, especially a sister or brother
- exposure to toxic substances at work the risk may be higher after regular exposure to some chemicals, such as some metal degreasers, arsenic or cadmium.
Having these risk factors doesnt mean you will develop kidney cancer. Often there is no clear reason for getting kidney cancer. If you are worried about your risk factors, ask your doctor for advice.
You May Like: Is Bladder Cancer Fast Or Slow Growing
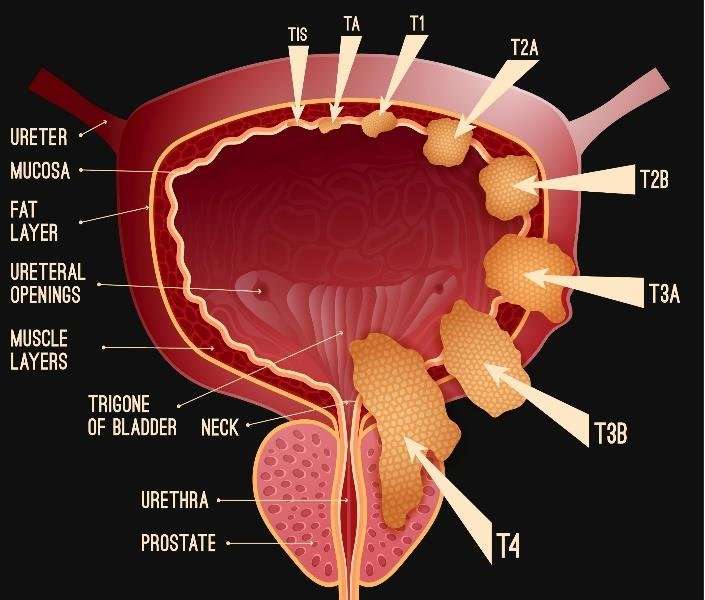
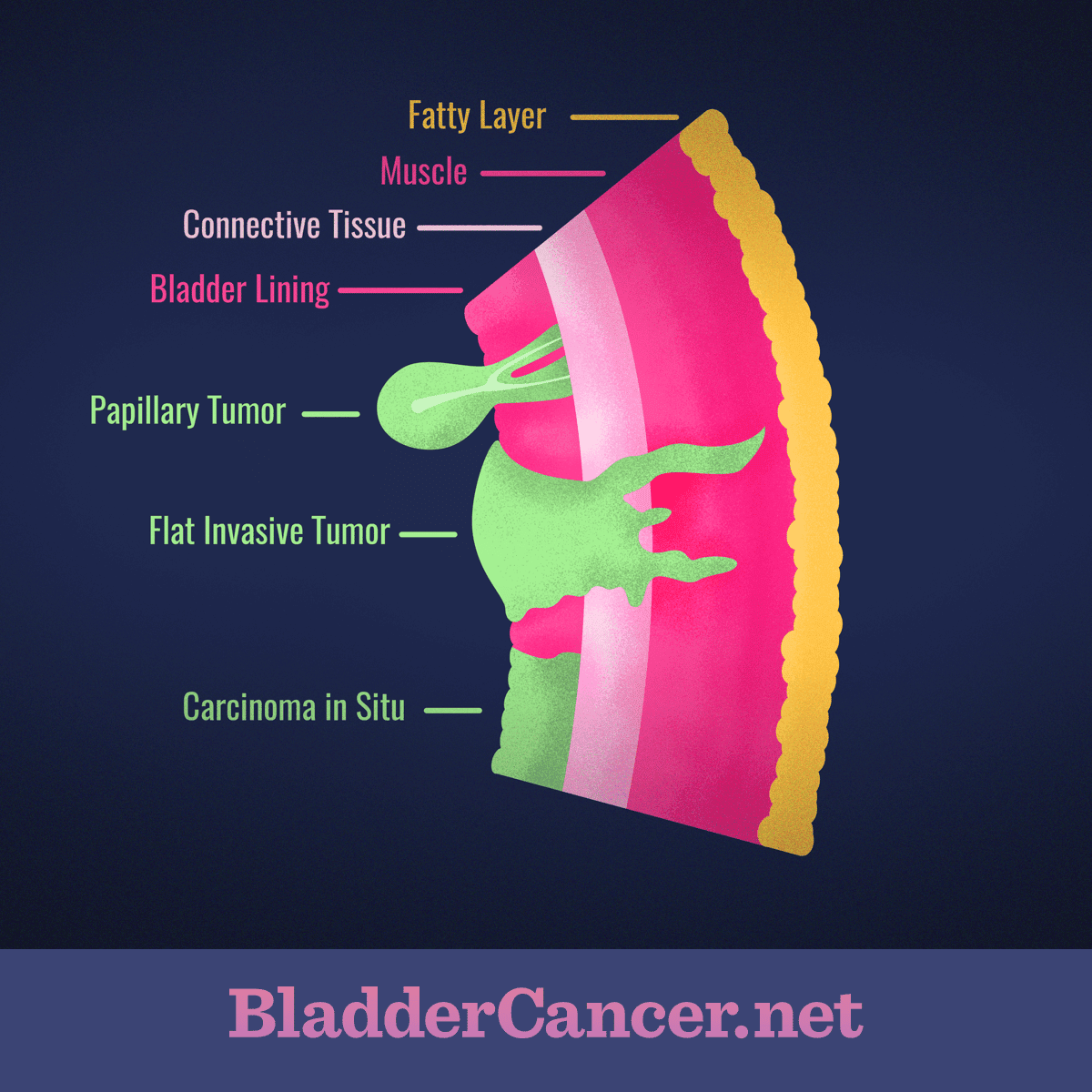
What Are The Stages Of Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer can be either early stage or invasive .
The stages range from TA to IV . In the earliest stages , the cancer is confined to the lining of the bladder or in the connective tissue just below the lining, but has not invaded into the main muscle wall of the bladder.
Stages II to IV denote invasive cancer:
- In Stage II, cancer has spread to the muscle wall of the bladder.
- In Stage III, the cancer has spread to the fatty tissue outside the bladder muscle.
- In Stage IV, the cancer has metastasized from the bladder to the lymph nodes or to other organs or bones.
A more sophisticated and preferred staging system is known as TNM, which stands for tumor, node involvement and metastases. In this system:
- Invasive bladder tumors can range from T2 all the way to T4 .
- Lymph node involvement ranges from N0 to N3 .
- M0 means that there is no metastasis outside of the pelvis. M1 means that it has metastasized outside of the pelvis.
Where Is The Bladder Located
The bladder is a hollow organ that stores urine before it leaves your body. It sits in the lowest part of your belly, called your pelvis. Urine is made in your kidneys. Tubes called ureters connect your kidneys to the bladder. Urine flows through the ureters and into your bladder, where its stored. When you urinate , the bladder squeezes the urine out through a tube called the urethra.
Also Check: Tissue Salts For Overactive Bladder
Will Treatment Cause Erectile Dysfunction
Radical prostatectomy is a surgery to remove the prostate gland. When your surgeon removes the gland, they may damage the nerves and blood vessels that run along it. If theyre damaged enough, you wont be able to get an erection following the procedure.
Today, doctors can do nerve-sparing surgery, which helps prevent permanent ED. Your surgeon can still touch those nerves and blood vessels, causing ED as a temporary side effect. Many men have trouble getting an erection for a few weeks, months, or even years after their procedure.
Radiation therapy also damages blood vessels and the nerves that control erection. Up to half of men who have radiation for prostate cancer experience ED afterward. In some men, this symptom will improve with time. Sometimes radiation side effects dont appear until a few months after the treatment. If ED starts late, it may not be as likely to go away.
A few treatments can help with ED until youre able to have erections on your own again.
Additional treatments include the following:
Recommended Reading: Foods Good For Bladder Control
Treatment Of Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage IV bladder cancer that has not spread to other parts of the body may include the following:
- Urinary diversion or cystectomy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
Treatment of stage IV bladder cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, such as the lung, bone, or liver, may include the following:
- External radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Urinary diversion or cystectomy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- A clinical trial of new anticancer drugs.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
You May Like: What Do Bladder Spasms Feel Like
What Can I Do
First, work with your doctor to figure out how to best treat it. Even if it canât be cured, you may be able to slow it down and manage your symptoms with surgery, medicine, and other treatments.
You can also do a lot on your own to feel better physically and emotionally:
Pace yourself. Cancer, and even some of its treatments, can wipe you out. Try to keep your days simple and save your energy for the important activities. And donât be shy about resting when you need to.
Speak your symptoms. Your doctor can help with all kinds of common problems from cancer and its treatments, like constipation, upset stomach, and pain. But only if you say something about them. Check in with your doctor often to get the care you need.
Stay active. Exercise lifts your energy and helps you fight off anxiety, depression, and stress. Ask your doctor whatâs safe for you to do.
Tend to your body. Along with regular exercise, try to stick to a healthy diet and get the rest you need. If you donât feel like eating much, a dietitian might be able to help.
Find ways to relax. Itâll keep your mood and energy up. Take time to read a book, go for a walk, call a friend, get a massage, or try some meditation. Or all of the above. Go with works best for you.
Work with your doctor, and try to stay positive. There are more ways to treat the condition than ever before. Your doctor can help you think about which ones are best for you.
Show Sources
Dont Miss: How Do They Inject Botox Into The Bladder
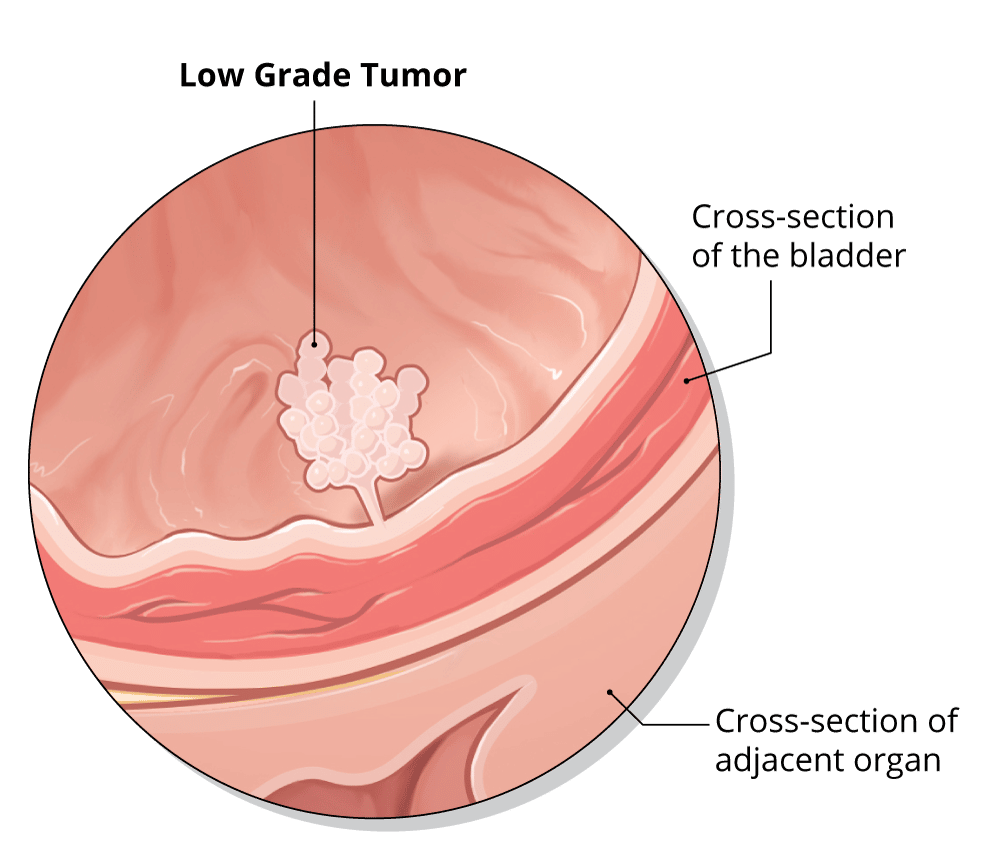
Stage 0 Bladder Cancer
Stage 0 describes non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. It is found only on the surface of the inner lining of the bladder. This stage is also known as in situ. Stage 0 bladder cancer is typically treated with transurethral resection , followed by either close follow-up without further treatment or intravesical therapy using bacillus Calmette-Guérin therapy to try to keep the cancer from coming back.
Don’t Miss: Do You Need Antibiotics For Bladder Infection
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if bladder cancer spreads to the bone, the cancer cells in the bone are actually bladder cancer cells. The disease is metastatic bladder cancer, not bone cancer.
How Do I Know If I Have Bladder Cancer
Many people with bladder cancer do not exhibit symptoms. A bladder cancer diagnosis is often made when red blood cells are detected in a urine test . Urologists are generally the doctors who diagnose and treat bladder cancer. Their specialty is the urinary tract, which includes the bladder, kidneys, ureters, and urethra.
Common Symptoms of Bladder Cancer
Blood in the urine
In many cases, blood in the urine is an early sign of bladder cancer. The blood may change the color of the urine to pink, orange, or dark red. The color of the urine could even be normal, and small amounts of blood may be discovered during the urine test . Blood may be there one day and gone the next. The urine could remain clear for months. However, if the patient has bladder cancer, the blood will eventually reappear.
The early stages of bladder cancer often cause bleeding but with very little pain or discomfort. Its important to note that blood in the urine does not always indicate that you have bladder cancer. More often than not, its caused by benign tumors, an infection, bladder stones, or another non-cancerous ailment. Its still critical to be seen by a doctor if you have blood in the urine.
Bladder habit changes
While bladder symptoms are more often the result of conditions unrelated to cancer, bladder cancer may cause changes to bladder habits, including:
Needing to urinate with little or no results Having to urinate more than usual Painful urination
Also Check: Bladder Cancer Prognosis In Elderly
When Bladder Cancer Spreads To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer cells break away from where they started to grow and start spreading to other parts of the body, it is called metastasis. Metastatic bladder cancer is the name for bladder cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, such as the lungs, the liver, or the bones. Even if the cancer cells are first discovered in the bones, for example, if they first started growing in the bladder it is still called metastatic bladder cancer.1
Lymphatic Drainage Of The Bladder
The lymphatic drainage from the bladder involves many regions within and beyond the pelvis . The specific route of lymphatic spread from the bladder is complex and impacted by the primary location of the tumor . Roth et al. performed a prospective study of 60 patients to assess the primary lymphatic landing site from the bladder and showed that while the major lymphatic landing sites are regional lymph nodes, a small majority of cases showed drainage initially to more distant lymph nodes, such as the common iliac or paraortic regions . Given this pattern, it is not surprising that the most commonly effected sites of nodal involvement are the obturator and internal iliac regions .
Recommended Reading: Bladder Infection Or Kidney Stone
How Long Does It Take For Bladder Cancer To Spread
As many as 50% of patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer may have occult metastases that become clinically apparent within 5 years of initial diagnosis and around 5% will have distant metastasis at the time of initial diagnosis. Most patients with overt metastatic disease die within 2 years despite chemotherapy.
What Kind Of Treatment Will I Need
There are many ways to treat bladder cancer. You might want to get a second opinion about the best treatment plan for you.
Bladder cancer is most often treated with:
Sometimes more than one type is used. The treatment plan thats best for you depends on:
- The stage and grade of the cancer
- Whether the cancer has spread into the bladder wall
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Other health problems you have
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
Read Also: What Do They Give You For Bladder Infection
After Bladder Cancer Has Been Diagnosed Tests Are Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Bladder Or To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out if cancer has spread within thebladder lining and muscle or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment. The following tests and procedures may be used in the staging process:
What Is Invasive High Grade Papillary Urothelial Carcinoma
An invasive papillary urothelial carcinoma is a tumour that has spread into the layers of tissue below the urothelium. These layers include the lamina propria, muscularis propria, and perivesical soft tissue. Unlike non-invasive tumours, invasive tumours are able to spread to other parts of the body.
Read Also: Prognosis Of Bladder Cancer In Males
Bladder Cancer Clinical Trials
What about Clinical Trials?
You may hear about clinical trials for your bladder cancer. Clinical trials are research studies that test if a new treatment or procedure is safe and effective.
Through clinical trials, doctors find new ways to improve treatments and the quality of life for people with disease. Trials are available for all stages of cancer. The results of a clinical trial can make a major difference to patients and their families. Please visit our clinical trials research webpage to learn more.
Tests That May Be Done
Physical exam: The doctor will check you for signs of bladder cancer and other health problems. This might include a rectal exam, during which a gloved finger is put into your rectum. If you are a woman, a pelvic exam might also be done. During these exams, the doctor can sometimes feel a bladder tumor.
Urine tests: For these tests, you’ll be asked to pee in a cup. Your urine is then tested for cancer cells, blood, or certain proteins .
Cystoscopy: For this exam, a doctor called a urologist looks at the inside of your bladder using a tool called a cystoscope. This is a thin tube with a tiny light and camera on its end. It’s put through the opening of your urethra and moved up into your bladder.
Blue light cystoscopy: Sometimes, special drugs are put into the bladder during the exam. Cancer cells soak up these drugs and then glow when the doctor shines a blue light through the scope. This can help the doctor see cancer cells that might have been missed with the normal light.
Bladder biopsy: This is needed to know for sure if you have bladder cancer. For this test, a cystoscope is used it to take a tiny piece of the bladder . More than one sample may be taken because sometimes cancer starts in more than one part of the bladder. Salt water washings of the inside of your bladder may also be collected to look for cancer cells. Any samples are sent to a lab and tested to see if there are cancer cells in them.
Don’t Miss: I Feel A Bladder Infection Coming On