How Does Recurrence Of Bladder Cancer Affect Survival Rate
Recurrent bladder cancer is cancer that has returned after initial treatment. Recurrence rates for bladder cancer depend on the stage of the original tumor, with 5-year recurrence rates of approximately 65% in patients with non-invasive or in situ tumors and 73% in patients with slightly more advanced disease at first diagnosis.16
Many patients with non-invasive bladder cancer have recurrences that are typically not life threatening however, the prognosis is generally worse if the disease has spread into deeper layers of the bladder wall or beyond to the lymph nodes or other organs.
Signs & Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer In Women
Blood in your urine is often the first and most common early symptom of bladder cancer you experience. It could be a slight amount, or it can turn your urine color to pink, orange or darker red.
You could notice blood one day and not the next day. The blood will eventually come back if you have bladder cancer. Sometimes you wonât even see blood in your urine. The only way the doctor would be able to detect it is if they give you a urine test.
Other potential early signs of bladder cancer in women to look out for are:
- Your urine changes color.
- You need to urinate more frequently than usual.
- You feel burning or pain when urinating.
- You still feel like you need to urinate, despite your bladder not being full.
- You urinate very little or canât urinate.
If you notice any of these symptoms, donât panic, but contact your doctor as soon as possible. These symptoms donât necessarily mean you have cancer. You could be dealing with a bladder infection, urinary tract infection or another less severe condition.
After bladder cancer has begun spreading, you might notice:
- You canât urinate, even if you feel like you need to.
- Youâre not as hungry as you usually are.
- Your lower back hurts.
- Youâre not trying, but are losing weight.
- You frequently feel very weak or tired.
- You have swollen feet
Again, contact your doctor if you notice any of these symptoms. They most likely could indicate you have something else going on other than bladder cancer.
Rare Forms Of Bladder Cancer
Adenocarcinomas account for less than 2% of primary bladder tumors. These lesions are observed most commonly in exstrophic bladders and are often associated with malignant degeneration of a persistent urachal remnant.
Other rare forms of bladder cancer include leiomyosarcoma, rhabdosarcoma, carcinosarcoma, lymphoma, and small cell carcinoma. Leiomyosarcoma is the most common sarcoma of the bladder. Rhabdomyosarcomas most commonly occur in children. Carcinosarcomas are highly malignant tumors that contain a combination of mesenchymal and epithelial elements. Primary bladder lymphomas arise in the submucosa of the bladder. Except for lymphomas, all these rare bladder cancers carry a poor prognosis.
Small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder is a poorly differentiated, malignant neoplasm that originates from urothelial stem cells and has variable expression of neuroendocrine markers. Morphologically, it shares features of small cell carcinoma of other organs, including the lung.
Recommended Reading: Revive Reusable Bladder Control Support
What Are The Treatment Options For Bladder Cancer
There are four types of treatment for patients with bladder cancer. These include:
- Surgery
Sometimes, combinations of these treatments will be used.
Surgical options
Surgery is a common treatment option for bladder cancer. The type of surgery chosen will depend on the stage of the cancer.
- Transurethral resection of the bladder is used most often for early stage disease . It is done under general or spinal anesthesia. In this procedure, a special telescope called a resectoscope is inserted through the urethra into the bladder. The tumor is then trimmed away with the resectoscope, using a wire loop, and the raw surface of the bladder is then fulgurated .
- Partial cystectomy is the removal of a section of the bladder. At times, it is used for a single tumor that invades the bladder wall in only one region of the bladder. This type of surgery retains most of the bladder. Chemotherapy or radiation therapy is often used in combination. Only a minority of patients will qualify for this bladder-sparing procedure.
- Radical cystectomy is complete removal of the bladder. It is used for more extensive cancers and those that have spread beyond the bladder .
This surgery is often done using a robot, which removes the bladder and any other surrounding organs. In men, this is the prostate and seminal vesicles. In women, the ovaries, uterus and a portion of the vagina may be removed along with the bladder.
Chemotherapy
- Methotrexate
Intravesical therapy
Radiation therapy
Side Effects Of Treatment For Bladder Cancer
All cancer treatments can have side effects. Your treatment team will discuss these with you before you start treatment. Talk to your doctor or nurse about any side effects you are experiencing. Some side effects can be upsetting and difficult, but there is help if you need it.
or email to speak with a caring cancer nurse for support.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Better Bladder Control
Cancerous Tumours Of The Bladder
A cancerous tumour of the bladder can grow into nearby tissue and destroy it. It can also spread to other parts of the body. Cancerous tumours are also called malignant tumours.
Bladder cancer is often divided into 3 groups based on how much it has grown into the bladder wall.
- Non-invasive bladder cancer is only in the inner lining of the bladder .
- Nonâmuscle-invasive bladder cancer has only grown into the connective tissue layer .
- Muscle-invasive bladder cancer has grown into the muscles deep within the bladder wall and sometimes into the fat that surrounds the bladder.
Donât Miss: Can Too Much Sugar Cause A Bladder Infection
How Do You Prevent Bladder Cancer
Unfortunately, there is no one way to prevent bladder cancer. Some things like age, race, gender and genetics or family history cant be controlled. However, people can take steps to reduce their risk.
Tips for bladder cancer prevention include:
- Quit or dont start smoking
- Limit chemical exposure on the job
- Drink plenty of fluids, especially water
- Eat a diet high in fruits and vegetables
Read Also: Home Cure For Bladder Infection
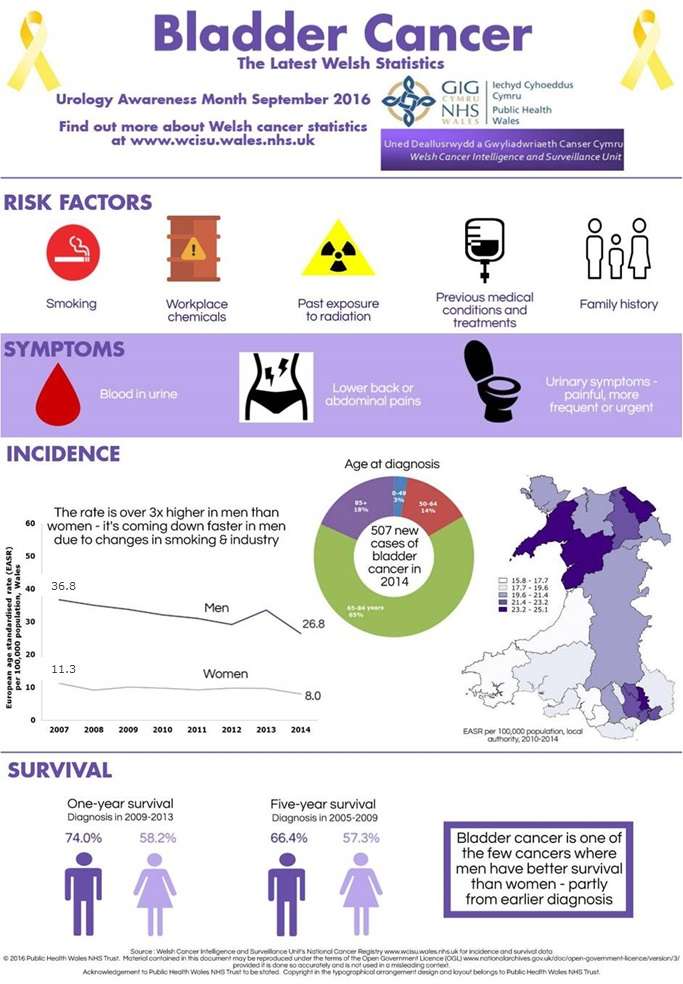
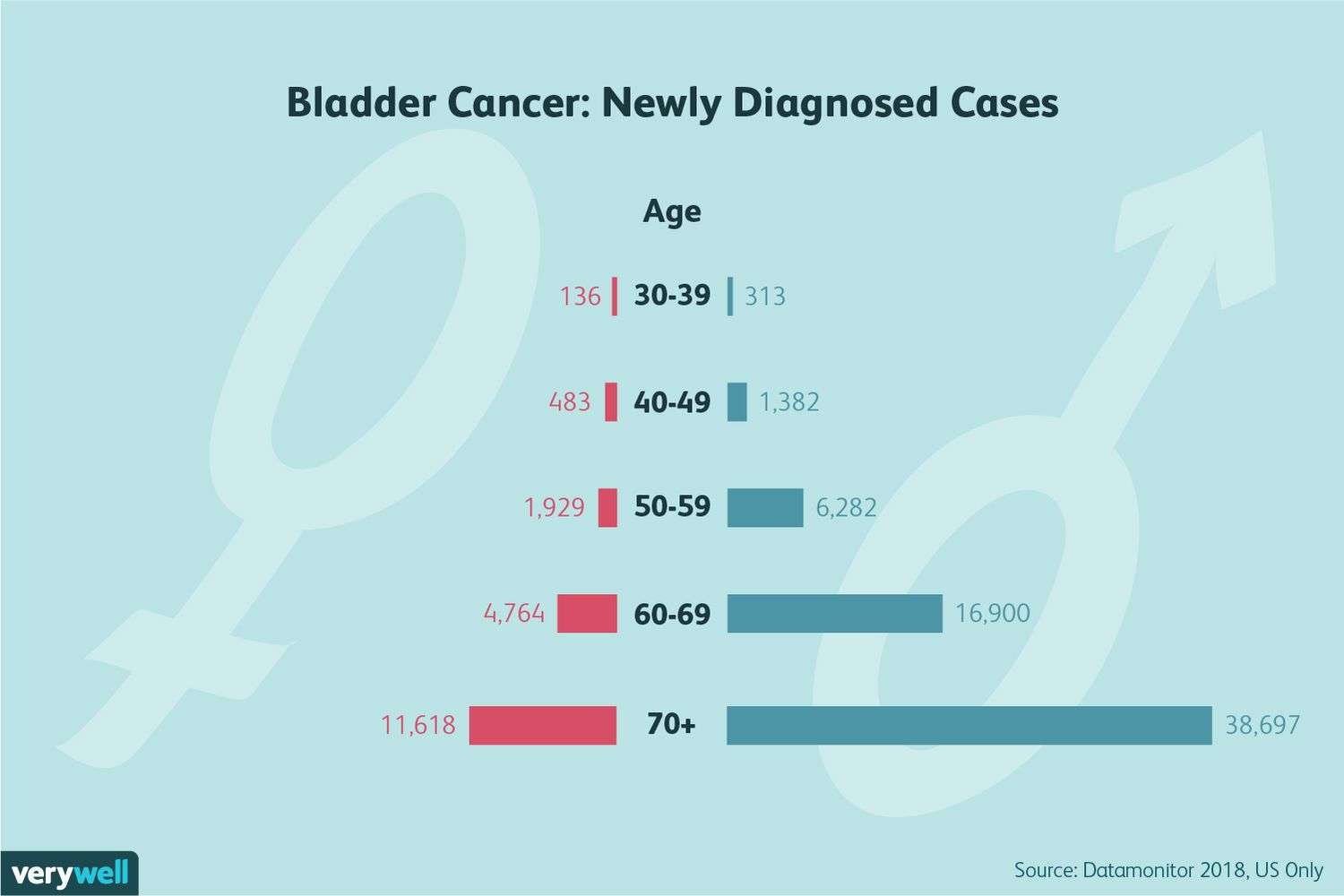
How Common Is Bladder Cancer
The American Cancer Societys estimates for bladder cancer in the United States for 2022 are:
- About 81,180 new cases of bladder cancer
- About 17,100 deaths from bladder cancer
The rates of new bladder cancers and deaths linked to bladder cancer and have been dropping slightly in women in recent years. In men, incidence rates have been decreasing, but death rates have been stable.
Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men, but it’s less common in women.
Evaluation Of Upper Urinary Tract
Additional workup for all patients with bladder cancer includes evaluation of the upper urinary tract with intravenous urography , renal ultrasonography, computed tomography urography, or magnetic resonance urography.21,22 Renal ultrasonography alone is insufficient to complete the evaluation of hematuria in a patient with bladder cancer because it cannot delineate details of the urinary collecting system. Traditional IVU has been largely replaced by CT urography because of increased detail and data combined in the CT .
For patients unable to undergo contrast injection , magnetic resonance urography may be used to evaluate the upper urinary tract. These tests are useful for disease staging and excluding other causes of hematuria. Pelvic imaging should be performed before transurethral resection to improve staging accuracy because postoperative inflammation mimics the appearance of tumor infiltration.21 Pelvic imaging also may detect synchronous upper tract urothelial cancer, which can occur in 5 percent of patients with bladder cancer.22
You May Like: Different Types Of Bladder Infections
Treatment Of Recurrent Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of recurrentbladder cancer depends on previous treatmentand where the cancer has recurred. Treatment for recurrent bladder cancer mayinclude the following:
- Radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- A clinical trial of a new treatment.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Read Also: Reasons For Lack Of Bladder Control
What Is Bladder Cancer
The bladder, a hollow organ in the lower part of the abdomen, serves as a reservoir for urine until it is discharged out of the body through the urethra.
There are different types of bladder cancer. The cancer cell type can be transitional cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma or adenocarcinomaeach named for the types of cells that line the wall of the bladder where the cancer originates.
- Most bladder cancers start from the transitional cells, which occupy the innermost lining of the bladder wall. The cancers, which originate in these cells lining the bladder can, in some instances, invade into the deeper layers of the bladder , the thick muscle layer of the bladder, or through the bladder wall into the fatty tissues that surround the bladder.
- Squamous cells are thin flat cells that line the urethra and can form in the bladder after long bouts of bladder inflammation or irritation. Squamous cell carcinoma makes up about 5 percent of bladder cancers.
- Adenocarcinoma is a very rare type of bladder cancer that begins in glandular cells in the lining of the bladder. Only 1 percent to 2 percent of bladder cancers are adenocarcinoma.
Read Also: Lower Back Pain Bladder Cancer
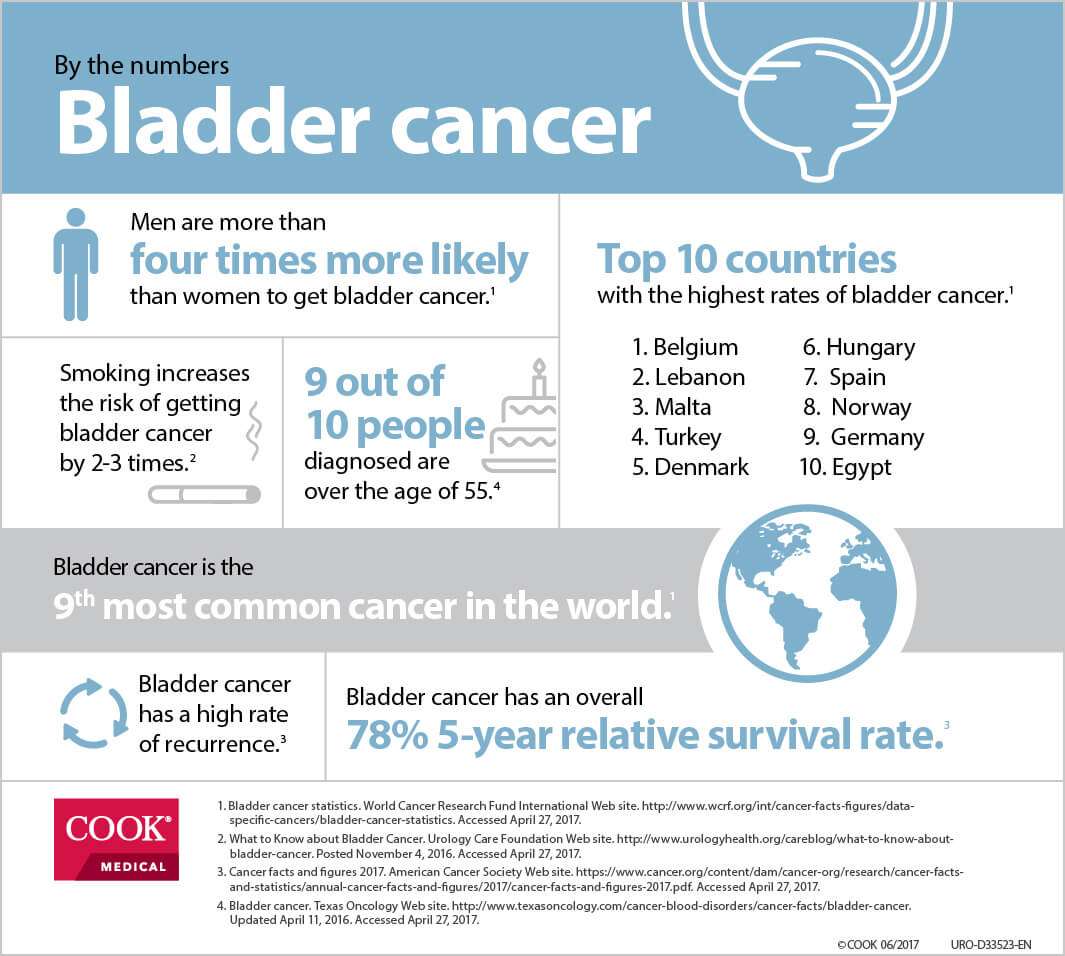
Risk Of Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer occurs mainly in older people. About 9 out of 10 people with this cancer are over the age of 55. The average age of people when they are diagnosed is 73.
Overall, the chance men will develop this cancer during their life is about 1 in 27. For women, the chance is about 1 in 89.
Whites are more likely to be diagnosed with bladder cancer than African Americans or Hispanic Americans.
Survival Statistics For Bladder Cancer
Survival statistics for bladder cancer are very general estimates and must be interpreted very carefully. Because these statistics are based on the experience of groups of people, they cannot be used to predict a particular persons chances of survival.
There are many different ways to measure and report cancer survival statistics. Your doctor can explain the statistics for bladder cancer and what they mean to you.
Read Also: How Can I Treat A Bladder Infection
Who Gets Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is four times more common in men than women. This form of cancer is also associated with older individuals. More than 90 percent of people diagnosed with bladder cancer are over the age of 55, and the average age of diagnosis is 73.
The most common risk factor associated with this form of cancer is smoking, which is seen in about 50 percent of cases.
Occurrence In The United States
The American Cancer Society estimates that 81,180 new cases of bladder cancer will be diagnosed in the United States in 2022 and that 17,100 people will die of the disease. The incidence of bladder cancer increases with age, with the median age at diagnosis being 73 years bladder cancer is rarely diagnosed before age 40 years.
Bladder cancer is about 4 times more common in men than in women. The male predominance in bladder cancer in the United States reflects the prevalence of transitional cell carcinoma . With small cell carcinomain contrast to TCCthe male-to-female incidence ratio is 1:2.
Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men in the United States, after prostate, lung, and colorectal cancer, but it is not among the top 10 cancers in women. Accordingly, more men than women are expected to die of bladder cancer in 2022, with 12,120 deaths in men versus 4980 in women. Nevertheless, women generally have a worse prognosis than men.
The incidence of bladder cancer is twice as high in White men as in Black men in the United States. However, Blacks have a worse prognosis than Whites.
Limited data indicate that small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder probably has the same epidemiologic characteristics as urothelial carcinoma. Patients are more likely to be male and older than 50 years.
Also Check: Overactive Bladder Only At Night
Do Benign Tumors Need To Be Removed
It depends, says Dr. Guru. Benign bladder masses usually grow very slowly and will not spread to other tissues or organs in the body. In some cases, we will just monitor patients on a regular basis. However, some benign masses can bleed or grow very large and cause problems by taking up too much space in your bladder or pressing on other organs in your body. In that case, we usually remove or treat benign masses, using a TURBT procedure.
If you are ever unsure about your bladder symptoms or your bladder tumor diagnosis, we recommend an appointment with our multidisciplinary cancer care experts at Roswell Park.
What Causes Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer forms when the DNA in cells in the bladder mutate or change, disabling the functions that control cell growth. In many cases, these mutated cells die or are attacked by the immune system. But some mutated cells may escape the immune system and grow out of control, forming a tumor in the bladder.
While the exact cause of bladder cancer is not known, certain risk factors are linked to the disease, including tobacco smoking and exposure to certain chemicals and gases. Also, people with a family history of bladder cancer have a high risk of developing the disease.
Known risk factors for bladder cancer include:
Recommended Reading: What Does Carcinoma In Situ Of Bladder Mean
Living With Bladder Cancer
Cancer is a life-changing experience. And although there’s no surefire way of preventing a recurrence, you can take steps to feel and stay healthy. Eating plenty of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and keeping to modest portions of lean meat is a great start. If you smoke, stop. Limit alcohol to one drink a day for women and up to two drinks a day for men. Daily exercise and regular checkups will also support your health and give you peace of mind.
How Is Superficial Bladder Cancer Diagnosed
The road to diagnosis usually involves a number of tests, which may include:
- Urine test : A pathologist will examine a sample of your urine under a microscope to look for cancer cells.
- CT urogram: This is an imaging test that provides a detailed view of your urinary tract to check for signs of cancer. During the procedure, a contrast dye will be injected into a vein in your hand. X-ray images will be taken as the dye reaches your kidneys, ureters, and bladder.
- Retrograde pyelogram: For this test, your doctor will insert a catheter through the urethra into your bladder. After contrast dye is injected, X-ray images can be taken.
- Cystoscopy: In this procedure, the doctor inserts a narrow tube called a cystoscope through your urethra into your bladder. The tube has a lens so your doctor can examine the inside of your urethra and bladder for abnormalities.
- Biopsy: Your doctor can take a tissue sample during a cystoscopy . The sample will then be sent to a pathologist for examination under a microscope.
If the biopsy confirms bladder cancer, other imaging tests may be used to determine if the cancer has spread. These may include:
If the cancer hasnt spread outside the lining of the bladder, the diagnosis is superficial, or stage 0 bladder cancer.
Next, the tumor is assigned a grade. Low-grade, or well-differentiated tumors, are similar in appearance to normal cells. They tend to grow and spread slowly.
Donât Miss: How To Do Kegel Exercises For Overactive Bladder
You May Like: Why Do I Keep Getting Bladder Infections After Intercourse
Patients Can Enter Clinical Trials Before During Or After Starting Their Cancer Treatment
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCIs clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Drugwatchcom Has Been Empowering Patients For More Than A Decade
Drugwatch.com has provided reliable, trusted information about medications, medical devices and general health since 2008. Weve also connected thousands of people injured by drugs and medical devices with top-ranked national law firms to take action against negligent corporations.
Our team includes experienced medical writers, award-winning journalists, researchers and certified medical and legal experts. Drugwatch.com is HONCode certified. This means the high-quality information we provide comes from credible sources, such as peer-reviewed medical journals and expert interviews.
The information on Drugwatch.com has been medically and legally reviewed by more than 30 expert contributors, including doctors, pharmacists, lawyers, patient advocates and other health care professionals. Our writers are members of professional associations, including American Medical Writers Association, American Bar Association, The Alliance of Professional Health Advocates and International Society for Medical Publication Professionals.
Read Also: Stage 4 Bladder Cancer Symptoms
What Are Bladder Tumors
Bladder tumors are abnormal growths that occur in the bladder. If the tumor is benign, its noncancerous and wont spread to other parts of your body. This is in contrast to a tumor thats malignant, which means its cancerous.
There are several types of benign tumors that can develop within the bladder.
In The World Of Bladder Tumors: Size Does Matter
Article type: Research Article
Authors: Loloi, Justina | Allen, Jordan L.a | Schilling, Amberb | Hollenbeak, Christopherc | Merrill, Suzanne B.a | Kaag, Matthew G.a | Raman, Jay D.a *
Affiliations: Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, Penn State Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, The Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine, Hershey, PA, USA | Division of Outcomes Research and Quality, Department of Surgery, The Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine, Hershey, PA, USA | Department of Health Policy and Administration, The Pennsylvania State University, State College, PA, USA
Correspondence: Correspondence to: Jay D. Raman, M.D., F.A.C.S., Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, Division of Urology, 500 University Drive, BMR Building c4830B, Hershey, PA 17033-0850, USA. Tel.: +1 717 531 6979 Fax: +1 717 531 4475 E-mail: .
Keywords: Bladder, TURBT, cancer, tumor, size, resection, complication, postoperative
DOI: 10.3233/BLC-200273
Journal: Bladder Cancer, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 195-200, 2020
Abstract
Read Also: Does Bladder Infection Cause Fever