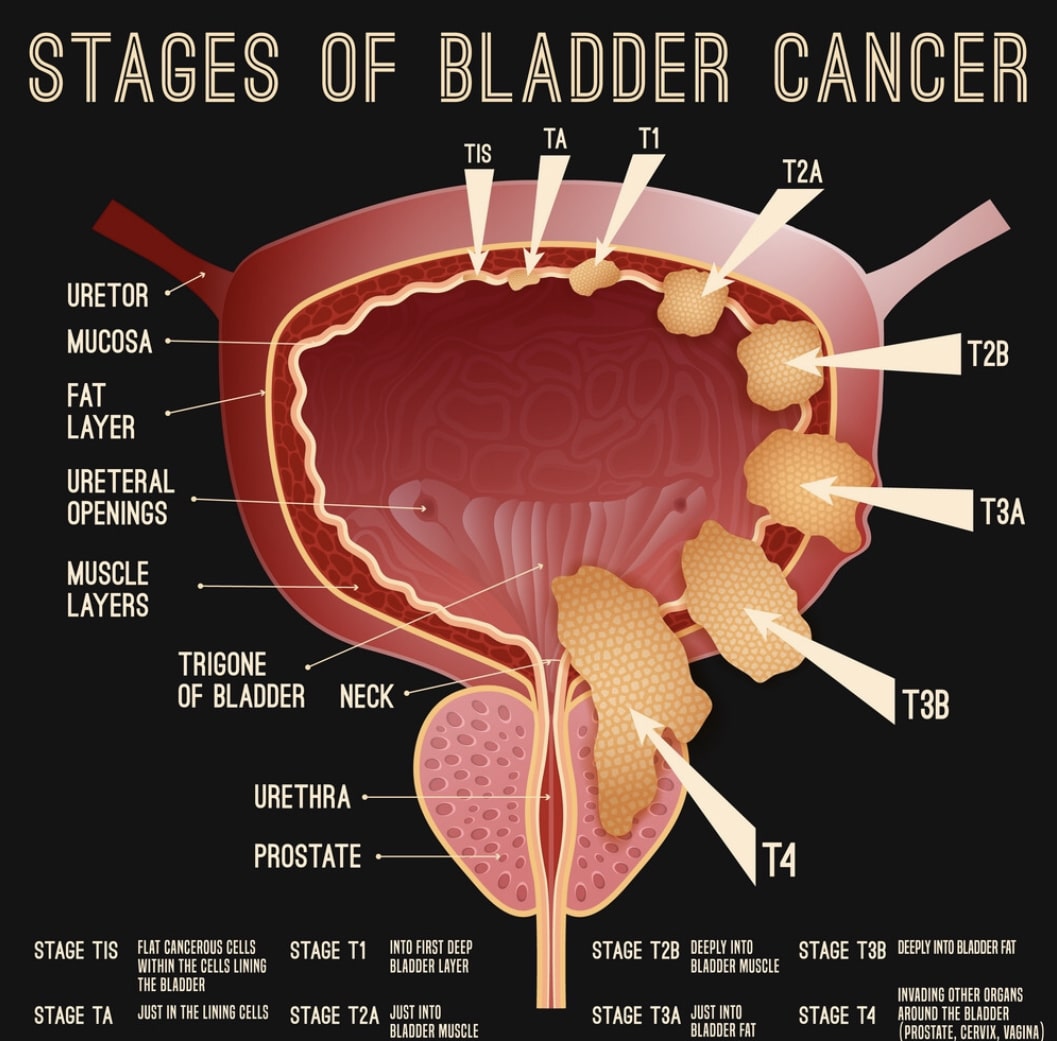
Correlation With Dominant Tumor Location
Dominant lesions on RP: 50 R lobe, 44 L lobe, 31 bilateral. 15/50 R lobe and 18/44 L lobe dominant tumors had LN metastasis on the contralateral side. Only 4% of cases were associated with anterior dominant tumors. 3040% of LN metastases occur contralateral to the dominant tumor. LN metastasis is overwhelmingly associated with high grade, high stage and large volume disease. LN positivity is rarely associated with anterior dominant tumors.
Keywords:
Evaluation For Metastatic Disease
Complete blood count, blood chemistry tests , liver function tests, chest radiography, and CT or magnetic resonance imaging of the abdomen and pelvis should be included in the metastatic workup for invasive bladder cancer.12 A bone scan may be performed if the alkaline phosphatase level is elevated or if symptoms suggesting bone metastasis are present.
Lymph Node Evaluation On Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging
MRI of the of the abdomen and pelvis is an alternative, but less commonly utilized, modality for evaluating lymph nodes in patients with suspected or known bladder cancer . When consideration is made as to whether or not to obtain an MRI, the potential benefits of multiparametric assessment of nodal characteristics, should be weighed against a number of potential contraindications, including the patientâs ability to lie still for a prolonged period of time, claustrophobia, the presence of regional orthopedic hardware, and potential MR incompatibility of any implantable medical devices that the patient may have .
The role of MRI in assessment of nodal involvement is an area of active investigation . Similar to CT, metastatic lymph nodes are conventionally identified when short axis diameter lymph node exceeds 8â10 mm however, assessment of nodal size by MRI suffers from the same limitations as CT, in that normal sized lymph nodes may still harbor metastatic disease .
Figure 6Figure 7Figure 8Figure 9
Also Check: Prescription Medication For Bladder Infection
Whats Usually The First Symptom Of Bladder Cancer
Blood in your pee is the most common bladder cancer symptom. That said, simply having blood in your pee isnt a sure sign of bladder cancer. Other conditions cause this issue, too. But you should contact a healthcare provider whenever you spot blood in your pee. Other bladder cancer symptoms include:
- Visible blood in your pee : Healthcare providers can also spot microscopic amounts of blood in pee when they do a urinalysis.
- Pain when you pee : This is a burning or stinging sensation that you may feel when you start to pee or after you pee. Men and DMAB may have pain in their penises before or after peeing.
- Needing to pee a lot: Frequent urination means youre peeing many times during a 24-hour period.
- Having trouble peeing: The flow of your pee may start and stop or the flow may not be as strong as usual.
- Persistent bladder infections: Bladder infections and bladder cancer symptoms have common symptoms. Contact your healthcare provider if you have a bladder infection that doesnt go away after treatment with antibiotics.
Evaluation Of Upper Urinary Tract
Additional workup for all patients with bladder cancer includes evaluation of the upper urinary tract with intravenous urography , renal ultrasonography, computed tomography urography, or magnetic resonance urography.21,22 Renal ultrasonography alone is insufficient to complete the evaluation of hematuria in a patient with bladder cancer because it cannot delineate details of the urinary collecting system. Traditional IVU has been largely replaced by CT urography because of increased detail and data combined in the CT .
For patients unable to undergo contrast injection , magnetic resonance urography may be used to evaluate the upper urinary tract. These tests are useful for disease staging and excluding other causes of hematuria. Pelvic imaging should be performed before transurethral resection to improve staging accuracy because postoperative inflammation mimics the appearance of tumor infiltration.21 Pelvic imaging also may detect synchronous upper tract urothelial cancer, which can occur in 5 percent of patients with bladder cancer.22
Recommended Reading: Kidney Bladder Or Prostate Cancer Symptoms
Symptoms Of Recurrent Bladder Cancer
Although seven of every 10 cases of bladder cancer are diagnosed at an early stage when the cancer is treatable, post-treatment recurrence is a particular risk, and the disease has a recurrence rate of about 70%19. Because of this, individuals who have had bladder cancer will require surveillance for years following treatment.
Recurrence happens when you have smaller areas of cancer cells that stay in your body undetected. These cells, over time, might increase in number and eventually cause symptoms or show up on test results. Your doctor, who knows your medical history, will discuss your risk of recurrence during follow-up care.
Symptoms of recurrent bladder cancer often resemble those of early or advanced cancer. Let your doctor know if you develop any new symptoms like frequent urination, blood in your urine, immediate need to urinate or pain while urinating. These symptoms could be signs of bladder cancer recurrence or signs of another health condition.
Knowing the symptoms and signs of bladder cancer, no matter if it’s early, advanced or recurrent, is important and your first step to diagnosis and treatment.
When Does Cancer Spread To The Lymph Nodes
The rate that cancer spreads to a persons lymph nodes may depend on the cancer they have.
Some cancers can spread more quickly to the lymph nodes. Other cancers are slow to develop, and may spread at a slower rate.
Certain cancers may only spread to lymph nodes on rare occasions. Research indicates that osteosarcomas, a form of bone cancer, only spread to the lymph nodes in 411% of cases.
Cancer can affect people in different ways, so it can be hard to predict how it may spread.
When a doctor discusses a persons cancer with them, they may refer to the stage it is at. Different stages of cancer indicate how far it has spread from its original location.
The National Cancer Institute states that the stages of cancer are:
- Stage 0: Stage 0 cancer, also called carcinoma in situ , is when abnormal cells are present, but have not spread.
- Stage 1, 2, and 3: Stages 1 to 3 indicate that there is cancer present. The higher the stage, the larger and more spread out the cancer is.
- Stave 4: Stage 4 cancer is when the cancer has spread to areas that are distant from the original tumor.
Healthcare professionals also break stage 3 into multiple categories, including 3a, b, and c. The stage at which cancer has spread to the lymph nodes varies. According to the United Kingdoms National Health Service, the cancer may have spread to the lymph nodes at stage 3.
| Number beside the N |
Read Also: Can Stress And Anxiety Cause Overactive Bladder
Remission And The Chance Of Recurrence
A remission is when cancer cannot be detected in the body and there are no symptoms. This may also be called having no evidence of disease or NED.
A remission may be temporary or permanent. This uncertainty causes many people to worry that the cancer will come back. While many remissions are permanent, it is important to talk with your doctor about the possibility of the cancer returning. Understanding your risk of recurrence and the treatment options may help you feel more prepared if the cancer does return. Learn more about coping with the fear of recurrence.
If the cancer returns after the original treatment, it is called recurrent cancer. It may come back in the same place , nearby , or in another place .
When this occurs, a new cycle of testing will begin again to learn as much as possible about the recurrence. After this testing is done, you and your doctor will talk about the treatment options.
People with recurrent cancer often experience emotions such as disbelief or fear. You are encouraged to talk with the health care team about these feelings and ask about support services to help you cope. Learn more about dealing with cancer recurrence.
Also Check: Not Able To Control Bladder
What Are Bone Metastases With Prostate Cancer
The ACS describes bone metastases as areas of bone containing cancer cells that have spread from another place in the body. In the case of prostate cancer, the cells have spread beyond the prostate gland. Since the cancer cells originated in the prostate gland, the cancer is referred to as metastatic prostate cancer.
The cancer cells spread to the bones by breaking away from the prostate gland and escaping attack from your immune system as they travel to your bones.
These cancer cells then grow new tumors in your bones. Cancer can spread to any bone in the body, but the spine is most often affected. Other areas cancer cells commonly travel to, according to the ACS, include the pelvis, upper legs and arms, and the ribs.
You May Like: How To Relax The Bladder Naturally
Also Check: Bcg Treatment For Bladder Cancer Mayo Clinic
What Causes Bladder Cancer
Healthcare providers and researchers dont know exactly why certain bladder cells mutate and become cancerous cells. Theyve identified many different risk factors that may increase your chance of developing bladder cancer, including:
- Cigarette smoke: Smoking cigarettes more than doubles your risk of developing bladder cancer. Smoking pipes and cigars and being exposed to second-hand smoke may also increase your risk.
- Radiation exposure: Radiation therapy to treat cancer may increase your risk of developing bladder cancer.
- Chemotherapy: Certain chemotherapy drugs may increase your risk.
- Exposure to certain chemicals: Studies show that people who work with certain chemicals used in dyes, rubber, leather, paint, some textiles and hairdressing supplies may have an increased risk.
- Frequent bladder infections: People who have frequent bladder infections, bladder stones or other urinary tract infections may be at an increased risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
- Chronic catheter use: People who have a chronic need for a catheter in their bladder may be at risk for squamous cell carcinoma.
What Lymph Nodes Does Prostate Cancer Spread To
While the prostate is the most common site for prostate cancer, the disease can spread to other areas of the body. This is called metastatic spread. It occurs when cancer cells break away from the primary tumor and travel through the bloodstream and lymphatic system to other locations. If metastasis is suspected, the patient should speak with their doctor about treatment options.
Lymph nodes are tiny organs that filter lymph fluid in the body. When prostate cancer spreads outside the prostate gland, it can affect lymph nodes in other parts of the body. The cancer cells can block the drainage of lymph fluid from the body, which causes swelling in the legs. This swelling, known as lymphoedema, is caused by the cancer cells in the lymph nodes.
Prostate cancer can spread to other areas of the body, including the bones. While some cancers spread to bones, others remain localized. The difference between localized cancer and metastatic cancer is that localized cancer can be cured. The cancer cells break away from the prostate and travel through the bloodstream and lymphatic system. They eventually stop in a blood vessel or capillary, where they can spread to other parts of the body.
Also Check: How Do They Do A Prostate Biopsy
Also Check: High Grade Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
Find The Best Treatment For An Enlarged Prostate You Have Options
There are various treatment options available, depending on the severity of symptoms. The options range from medication to shrink the prostate, to removal of prostate tissue in surgery.
At any stage, or as a long-time solution, your doctor might recommend symptom relief with the use of a catheter. This is a good option as it empties the bladder completely every time. Resulting in that you wont have to go to the toilet in the middle of the night or have to worry about embarrassing leaks.
What If You Have Metastatic Castration
This means you have a type of metastatic prostate cancer thatââ¬â¢s able to grow and spread after you had hormone therapy to lower your testosterone levels.
Still, most people with mCRPC stay on androgen deprivation therapy because it might still be effective against some prostate cancer cells.
Your doctor may recommend adding other treatments like:
- Treatments to ease symptoms like pain
You could also find out if a clinical trial might be right for you.
Some people with mCRPC simply choose to try active surveillance or watchful waiting.
Don’t Miss: What Is Best For Bladder Infection
What Does It Mean For Prostate Cancer To Spread
Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body. If this occurs, doctors say the cancer has metastasized or spread.
Areas of the body to which prostate cancer can spread include:
- the lymph nodes, usually those around the pelvis
A doctor will typically recommend imaging scans and tissue samples to test for the presence of cancerous cells.
According to the Prostate Cancer Foundation, age is the biggest contributing factor to the risk for prostate cancer. An estimated 65 percent of all prostate cancers are diagnosed in men older than 65 years of age.
Additional risk factors for prostate cancer include:
- Family history: Men who have a father or brother with prostate cancer are twice as likely to get prostate cancer as men who do not.
- Race: African-American men face the greatest risk of prostate cancer.
- Smoking: A history of smoking is associated with a higher risk of aggressive prostate cancer.
Researchers are also studying a link between diet and increased prostate cancer risk. Diets low in vegetables or high in calcium have been linked to an increased risk of aggressive prostate cancer.
The prostate is very close to the point at which urine drains from the body. As a result, many prostate cancer symptoms affect the urination process. Examples of these symptoms include:
Some of these symptoms are associated with aging and an enlarged prostate. As a result, some men may ignore these symptoms instead of seeking medical attention.
Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
Stage IV cancer is the most advanced form of bladder cancer. It is called metastatic. This means the cancer has spread to distant lymph nodes or organs. Cancers that have spread beyond the bladder into the wall of the abdomen or pelvis are also considered Stage IV. Stage IV cancer is usually treated with chemotherapy and, more recently, with immunotherapy as well.
People with bladder cancer of all stages may be able to participate in a clinical trial. Clinical trials are research studies that test new treatments to see how well they work.
Recommended Reading: Can Sugar Cause Bladder Infection
Read Also: Side Effects Of Bladder Cancer Chemotherapy
Pain In Other Areas Of Your Body
Advanced bladder cancer may spread to these areas of the body:
As cancer metastasizes, it may infiltrate bones throughout your body. This can result in bone pain or tenderness at night or during activity. Your bones may also be more susceptible to breakage.
Cancer that has spread to your lungs may cause chest pain. It may also make it hard for you to breathe, cause a chronic cough, or cause your voice to sound different.
Cancer that has spread to your abdomen or liver may cause stomach pain.
Whats The Treatment For Stage 3 Bladder Cancer
The standard treatment for stage 3 bladder cancer is surgery, usually in combination with other therapies.
Be sure to discuss your treatment goals with your doctor. Assess all the potential benefits and risks of each therapy. Some treatments aim for a cure. Others work to slow progression or relieve symptoms. The recommended treatment may depend on your overall health.
If cancer continues to progress or comes back during treatment, you may have to reconsider your options.
Also Check: Natural Ways To Control Overactive Bladder
Iliac Lymph Nodes Cancer Treatment
There is no one standard treatment for iliac lymph nodes cancer, as the best course of action depends on the individual patients situation. However, common treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Surgery is often the first line of treatment, and may involve the removal of the affected lymph nodes. Radiation therapy may be used to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors, while chemotherapy is a systemic treatment that uses drugs to kill cancer cells.
Pet/mri Accurately Predicts Risk Of Prostate Cancer Recurrence After Prostatectomy
Journal of Nuclear Medicine
In men recently diagnosed with intermediate or high-grade prostate cancer, prostate specific membrane antigen , PET/MRI can successfully determine whether their cancer is likely to return within two years of a prostatectomy. Armed with this information, physicians can identify patients who could benefit from additional treatment and/or frequent surveillance. This research was published in the December issue of the Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
Prostate cancer is known to have very variable behavior and outcomes. While many cases of localized prostate cancer can be treated successfully, some patients experience a rapid progression even after prostatectomy or radiation therapy. Therefore, initial risk stratification is important to determine treatment decisions and subsequent management of prostate cancer patients.
Clinicians currently use biopsy findings and clinical information, such as prostate-specific antigen levels, to predict if prostate cancer is slow-growing or if it will spread quickly and require aggressive treatments, said Andrei Iagaru, MD, professor of RadiologyNuclear Medicine and chief of the Division of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging at Stanford University Medical Center in Stanford, California. However, functional imaging, such as PET/MRI, is increasingly being considered as a way to identify patients at risk for persistent or recurrent disease.
More information:Journal of Nuclear MedicineJournal information:
Also Check: Get Rid Of Bladder Infection Naturally
Figure Out The Stage Of Endometrial Cancer In Lymph Nodes
When endometrial cancer moves into lymph nodes in uterus, it starts to weaken the nodes with time. You may feel a little problem in the early stages, but with time, lymphatic nodes start swelling and cause serious health issues. In other stages, uterine cancer spreads away from lymph nodes in other organs. Here are the stages of endometrial uterine cancer: