Possible Causes Of Bladder Cancer: Smoking
Smoking is the greatest known risk factor for bladder cancer smokers are four times more likely to get bladder cancer than nonsmokers. Harmful chemicals from cigarette smoke enter the bloodstream in the lungs and are ultimately filtered by the kidneys into the urine. This leads to a concentration of harmful chemicals inside the bladder. Experts believe that smoking causes about half of all bladder cancers in men and women.
Read Also: Can I Take Amoxicillin For A Bladder Infection
Surgery And Radiation Therapy
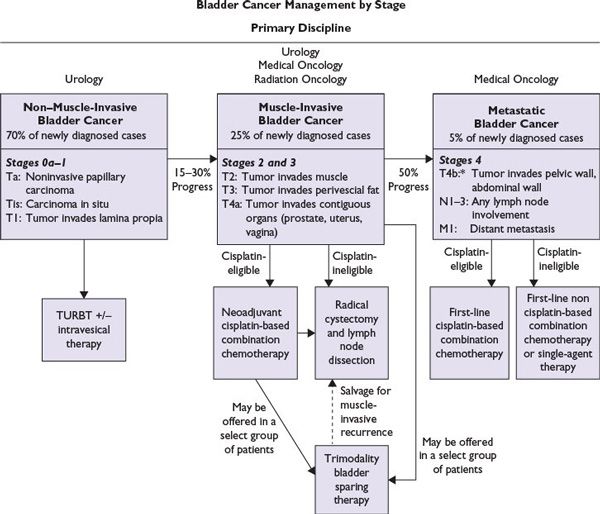
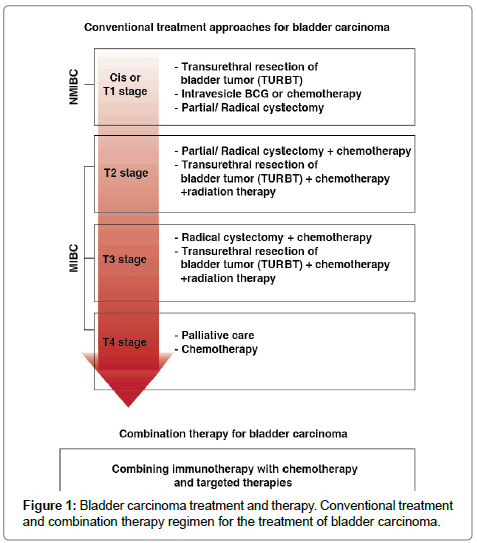
Endoscopic TURBT is the first-line treatment to diagnose, stage, and treat visible tumors. TURBT is not effective for CIS, because the disease is often so diffuse and difficult to visualize that complete surgical removal may not be feasible. It is critically important to surgically remove all nonmuscle-invasive disease prior to beginning intravesical therapy. When a combination of papillary tumor and CIS is present, the papillary tumor is removed before treatment of the CIS is initiated.
The EAU guidelines recommend the use of fluorescence-guided resection, as it is more sensitive than conventional white-light cystoscopy for detection of tumors. The added detection rate with fluorescence-guided cystoscopy is 20% for all tumors and 23% for CIS. The FDA has approved the use of blue-light cystoscopy with 5-aminolevulinic acid in patients suspected or known to have nonmuscle-invasive bladder cancer on the basis of prior cystoscopy.
As many as 20% of patients initially diagnosed with CIS may have unrecognized invasion beyond the lamina propria. Thus, they may not respond to intravesical therapy. These patients are candidates for radical cystectomy or radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy. Radiation therapy with or without chemotherapy is of limited benefit in patients with pure CIS but can be useful in some patients with muscle-invasive transitional cell carcinoma .
Lymph node dissection
Small cell carcinoma
Adenocarcinoma and lymphoma
Squamous cell carcinoma
The Tnm System Of Bladder Cancer Staging
The size of the tumor and whether it has spread are used to ascertain the stage. Cancer staging specifics are determined by guidelines set by the American Joint Committee on Cancers system, named the TNM staging system.
The TNM system has three parts:
- T stands for tumor. This number indicates how large the tumor is and how much it has grown into nearby tissues.
- N stands for nodes. This number indicates if the tumor has spread to lymph nodes, where the lymph nodes are located, and how many lymph nodes are impacted.
- M stands for metastasis. This number indicates if the tumor has spread to other organs.
Read Also: Hernia Of The Urinary Bladder
Remission And The Chance Of Recurrence
A remission is when cancer cannot be detected in the body and there are no symptoms. This may also be called having no evidence of disease or NED.
A remission may be temporary or permanent. This uncertainty causes many people to worry that the cancer will come back. While many remissions are permanent, it is important to talk with your doctor about the possibility of the cancer returning. Understanding your risk of recurrence and the treatment options may help you feel more prepared if the cancer does return. Learn more about coping with the fear of recurrence.
If the cancer returns after the original treatment, it is called recurrent cancer. It may come back in the same place , nearby , or in another place .
When this occurs, a new cycle of testing will begin again to learn as much as possible about the recurrence. After this testing is done, you and your doctor will talk about the treatment options.
People with recurrent cancer often experience emotions such as disbelief or fear. You are encouraged to talk with the health care team about these feelings and ask about support services to help you cope. Learn more about dealing with cancer recurrence.
Treatment Of Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage IV bladder cancer that has not spread to other parts of the body may include the following:
- Urinary diversion or cystectomy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
Treatment of stage IV bladder cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, such as the lung, bone, or liver, may include the following:
- External radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Urinary diversion or cystectomy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Aclinical trial of new anticancer drugs.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
You May Like: What Happens When You Have A Bladder Infection
Cancer Stages For Superficial Bladder Cancer
Ta: The most common superficial bladder cancer is stage Ta. This tumor looks like a cauliflower in the bladder, and it does not grow into any of the layers of the bladder. Further treatments for single Ta tumors are usually not needed. Patients do need to come back for regular cystoscopy to make sure the tumor does not come back. In patients with tumors that come back, or patients with many of these tumors at the initial surgery, medicine can be given inside the bladder to prevent cancer from coming back. Stage Ta cancers do come back with some regularity, but they rarely change into cancers that can grow into the bladder wall or go to other parts of the body.
Where Do These Numbers Come From
The American Cancer Society relies on information from the SEER* database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute , to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer.
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for bladder cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages . Instead, it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages:
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside of the bladder.
- Regional: The cancer has spread from the bladder to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as the lungs, liver or bones.
Recommended Reading: Cancer Stage 4 Life Expectancy
You May Like: How To Rid A Bladder Infection
How Do Healthcare Providers Diagnose Bladder Cancer
Healthcare providers do a series of tests to diagnose bladder cancer, including:
- Urinalysis: Providers use a variety of tests to analyze your pee. In this case, they may do urinalysis to rule out infection.
- Cytology: Providers examine cells under a microscope for signs of cancer.
- Cystoscopy: This is the primary test to identify and diagnose bladder cancer. For this test, providers use a pencil-sized lighted tube called a cystoscope to view the inside of your bladder and urethra. They may use a fluorescent dye and a special blue light that makes it easier to see cancer in your bladder. Providers may also take tissue samples while doing cystoscopies.
If urinalysis, cytology and cystoscopy results show you have bladder cancer, healthcare providers then do tests to learn more about the cancer, including:
Healthcare providers then use what they learn about the cancer to stage the disease. Staging cancer helps providers plan treatment and develop a potential prognosis or expected outcome.
Bladder cancer can be either early stage or invasive .
The stages range from TA to IV . In the earliest stages , the cancer is confined to the lining of your bladder or in the connective tissue just below the lining, but hasnt invaded the main muscle wall of your bladder.
Stages II to IV denote invasive cancer:
A more sophisticated and preferred staging system is TNM, which stands for tumor, node involvement and metastases. In this system:
Whats The Treatment For Stage 2 Bladder Cancer
Your treatment options will depend on a number of factors, such as your age and general health. Youll probably need a combination of treatments. Your doctor will monitor your progress and adjust therapy as needed. You may also need treatments to help control symptoms of cancer and side effects of treatment.
Read Also: Pain Radiating From Hip Down Leg
Recommended Reading: Cleveland Clinic Bladder Cancer Treatment
Treating Stage Iii Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the outside of the bladder and might have grown into nearby tissues or organs and/or lymph nodes . They have not spread to distant parts of the body.
Transurethral resection is often done first to find out how far the cancer has grown into the bladder wall. Chemotherapy followed by radical cystectomy is then the standard treatment.Partial cystectomy is rarely an option for stage III cancers.
Chemotherapy before surgery can shrink the tumor, which may make surgery easier. Chemo can also kill any cancer cells that could already have spread to other areas of the body and help people live longer. It can be especially useful for T4 tumors, which have spread outside the bladder. When chemo is given first, surgery to remove the bladder is delayed. The delay is not a problem if the chemo shrinks the cancer, but it can be harmful if it continues to grow during chemo. Sometimes the chemo shrinks the tumor enough that intravesical therapy or chemo with radiation is possible instead of surgery.
Some patients get chemo after surgery to kill any cancer cells left after surgery that are too small to see. Chemo given after cystectomy may help patients stay cancer-free longer, but so far its not clear if it helps them live longer. If cancer is found in nearby lymph nodes, radiation may be needed after surgery. Another option is chemo, but only if it wasn’t given before surgery.
Signs And Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
Sometimes bladder cancer doesnt have many symptoms. Signs or symptoms can include:
- blood in your urine
- pain or burning when passing urine
- not being able to pass urine when you need to.
Not everyone with these symptoms has bladder cancer. If you have any of these symptoms or are worried, always see your doctor.
Read Also: Womens Bladder Leakage Protection
Also Check: Natural Remedies For Bladder Cancer
There Are Three Ways That Cancer Spreads In The Body
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Risk Factors Of Prostate Cancer
Age is the most significant risk factor for prostate cancer. Your risk increases as you get older. Most men diagnosed with prostate cancer are over 50 years of age. If you are over the age of 50, talk to your GP about the PSA blood test which can indicate if your prostate is healthy or not.
- A family history of cancer
A family history means that you have someone in your family who has cancer. Generally, if you have a father or brother diagnosed with prostate cancer, you are 2 to 3 times more likely to get prostate cancer yourself, compared to the average man.
The risk is much higher for men with several affected relatives, particularly if their relatives were young when the cancer was found. It is always worth knowing about your family history.
Several inherited gene changes seem to raise prostate cancer risk, but they probably account for only a small percentage of cases overall. For example, inherited mutations of the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes raise the risk of breast and ovarian cancers in some families. Mutations in these genes may also increase prostate cancer risk in some men.
Prostate cancer is more common in black Caribbean and black African men than in white or Asian men. Asian men have half the risk of white men.
- A previous cancer
Recommended Reading: Stage 4 Ovarian Cancer What To Expect
Don’t Miss: Bladder Infection Not Going Away After Antibiotics
How You Have It
You have chemotherapy into a vein . This means you have treatment through a thin short tube that goes into a vein in your arm each time you have treatment.
You usually have chemotherapy as cycles of treatment. Each cycle is either a 2, 3 or 4 week period. The cycle length varies in time depending on the chemotherapy you are having.
You usually have 3 cycles of chemotherapy before surgery or radiotherapy. After surgery or radiotherapy, you might have 6 or more cycles.
Your specialist will explain how you have treatment, and how long they expect your treatment course to be.
What Happens During Treatment
A urinary catheter is inserted through your urethra and into your bladder. Then the BCG solution is injected into the catheter. The catheter is clamped off so the solution stays in your bladder. Some doctors may remove the catheter at this time.
You have to hold the medicine in your bladder. Youll be instructed to lie on your back and to roll from side to side to make sure the solution reaches your entire bladder.
After about two hours, the catheter is unclamped so the fluid can be drained. If the catheter was already removed, youll be asked to empty your bladder at this time.
Read Also: How Long Does Overactive Bladder Last
Don’t Miss: Bladder Infection Symptoms Home Remedies
What Affects Survival Rate And What Treatment Options Are Available
After diagnosing bladder cancer, your doctor will try to determine if it has advanced and if it has, how far. Doctors use a staging process to describe how far the tumor has penetrated the surrounding tissue and muscle, and to what extent it has spread to other parts of the body or metastasized. The staging process helps the doctor decide on the best way to treat it.
The American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM system is the most widely used staging system for bladder cancer. It relies on three critical factors:
- T: The letter T stands for tumor and describes the degree to which the tumor has grown through the wall of your bladder and into neighboring tissue and muscles.
- N: The letter N stands for nodes and notes if the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are groups of immune system cells about the size of beans. When cancer starts to spread, it frequently spreads to the lymph nodes nearest the bladder first.
- M: The letter M stands for metastasized, which means the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver, lungs or other lymph nodes farther from the bladder.
The American Cancer Society provides a detailed breakdown of the TNM system. Letters or numbers after T, N and M offer more detail related to the progression of the cancer.
Extended Treatment With Alpha1h Ongoing Study
The positive effects on the tumor and the absence of side effects compared to placebo, even at the higher dose, now make it possible to add a second round of treatment after the patients have undergone the first treatment according to the original protocol in the current study. The goal of prolonging the treatment is to optimize the effect on the tumor by introducing repeated treatment, which better corresponds to the future clinical reality. The treatment will be tested in a smaller number of patients and will not delay the regulatory process.
Don’t Miss: Can A Bladder Ultrasound Detect Cancer
Take Charge Of Your Health With Cxbladder
Early detection saves lives and is a crucial factor when it comes to the treatment of bladder cancer. Cxbladder is a clinically proven cutting-edge genomic urine test that quickly and accurately detects or rules out bladder cancer in patients presenting with blood in the urine and those being monitored for recurrence. The test works at a molecular level, measuring five biomarker genes to detect the presence or absence of bladder cancer.
Cxbladder is discreet, quick, non-invasive and painless, typically giving you meaningful results within five working days. It comes as a suite of test options, each optimized for a different point in the patient journey.
- Triage: Incorporates known bladder cancer risk factors to help rapidly rule out the disease.
- Detect: Designed to work alongside other tests to improve overall detection accuracy.
- Monitor: Optimised for bladder cancer surveillance, reducing the need for further invasive tests
Cxbladder gives you peace of mind and will help your doctor make informed treatment decisions. Speak to your general practitioner or urologist to learn more about Cxbladder and which test might be right for you. You can also contact our Customer Service Team directly.Contact us for more information
Patients Can Enter Clinical Trials Before During Or After Starting Their Cancer Treatment
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCIs clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Also Check: Can A Bladder Infection Go Away
Catheterizable Continent Diversion Pouch
This is a reservoir of bowel with a stoma that is catheterizable for emptying the bladder. The urine is siphoned out of the urinary reservoir with a small catheter every four to six hours. The catheterizable pouch may require surgical repair at some point after surgery due to the wear and tear of frequent catheterization. This type of reconstruction is not performed on patients with a history of bowel disease.