Intravesical Therapy For Bladder Cancer
With intravesical therapy, the doctor puts a liquid drug right into your bladder rather than giving it by mouth or injecting it into your blood. The drug is put in through a soft catheter that’s put into your bladder through your urethra. The drug stays in your bladder for up to 2 hours. This way, the drug can affect the cells lining the inside of your bladder without having major effects on other parts of your body.
Initial Experience In Treating Bcg Failures With Non
Like todays failure patient, patients who developed recurrent high-grade non-muscle invasive disease after BCG posed a big challenge to treating urologists, namely due to the large disparity in treatment options. Radical cystectomy could be pursued but risked the possibility of overtreatment given that the disease remained non-muscle invasive, as well as significant perioperative morbidity and mortality . Conversely, repeat intravesical therapy risked poor efficacy and the development of metastatic disease, bypassing the ability for a potentially curative procedure . The first study of further intravesical instillations for failure patients was reported by Haaff et al. who found that repeat BCG induction was effective in eradicating disease in 56% of patients . Two larger series of 60 and 57 patients found similar recurrence-free survival rates of 53% and 59.6% , respectively, with repeat BCG therapy when followed for more than 3 years .
When To See A Doctor
There are a few side effects that can be especially dangerous, so make sure to talk to your doctor if you notice that you:
- Have a severe skin rash
- Are wheezing or having difficulty breathing
- Are finding swallowing to be difficult
- Have a high fever that isnt lowered with Tylenol or other over-the-counter fever reducers
Recommended Reading: Poise Impressa Incontinence Bladder Supports
Clinical Outcomes Of The Gemdoce Combination Were Promising Approaching 50 Percent Recurrence
A better approach? Kates and colleagues have begun investigating a combination of two chemotherapy drugs, gemcitabine and docetaxel , delivered directly in the bladder in the same way that BCG is instilled for newly diagnosed bladder cancer patients. In previously published work at the Brady, as part of a multi-institutional study, Kates and Trinity Bivalacqua, M.D., Ph.D., evaluated patients who were given GEMDOCE when bladder tumors recurred after BCG. Clinical outcomes of the GEMDOCE combination were promising, says Kates, approaching 50 percent recurrence-free survival at two years when used with monthly maintenance. Based on these promising results, Kates has opened a Phase 2 clinical trial to evaluate this combination for newly diagnosed patients who have not had previous BCG. We will also be looking for a biomarker that can predict response to GEMDOCE, which would help us guide newly diagnosed patients either to intravesical chemotherapy or BCG immunotherapy, based on their tumor biology. More information on this clinical trial can be found here.
Even more exciting: We identified unique immune gene expression signatures found only in patients with CIS, says Hahn. Next, the team plans to investigate whether these new CIS signatures are associated with response to BCG and other forms of bladder cancer immune therapy.
Defining Bcg Unresponsive Disease
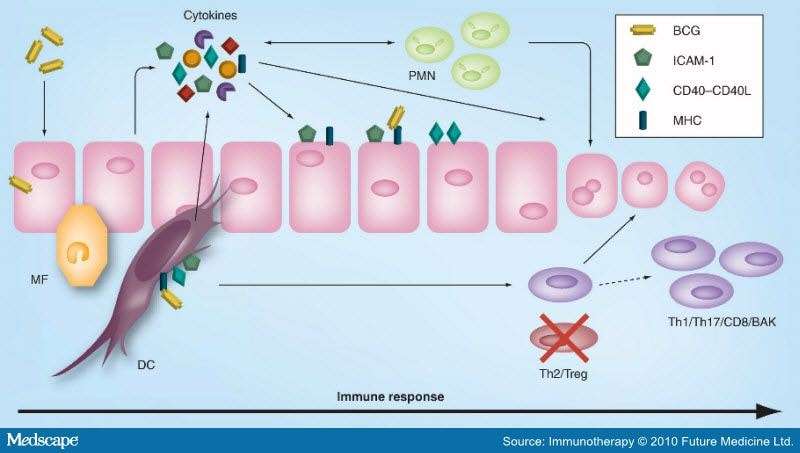
So what truly constitutes BCG unresponsive disease? In defining this, we should first consider the reasoning for creating such a definition. The goal with any intravesical therapy is to prevent recurrence, progression, and metastatic disease, as these require dramatic changes in management and put the patient at high risk of poor long-term survival . Identifying the point at which BCG is less likely to be effective at preventing these outcomes is crucial so as not to delay delivery of alternative agents or radical surgery that can confer an improved survival benefit. In formulating this definition, many different disease-specific elements must be considered which affect the likelihood of disease recurrence and progression. In an attempt to identify these variables, Herr et al. examined 221 men with non-muscle invasive disease treated with BCG and followed for 2 years. The investigators considered both disease-independent and disease-dependent variables prior to intravesical therapy, at the 3-month surveillance cystoscopy and at the 6-month surveillance cystoscopy. Variables found to be predictive of progression included stage T1 disease at all time points and disease duration of less than 1 year . This early study highlighted two of the key elements of BCG unresponsive disease, disease stage and timing of recurrence. Other factors not considered in this study, but critical to consider, include patient age, the number of prior BCG courses and extent of disease .
Also Check: Ways To Treat Bladder Infection At Home
Predictors Of Efficacy Of Intravesical Bcg Therapy
As another promising predictor, cytokine gene polymorphism has been investigated. Although some results are still contradictory, polymorphisms of IL-6, IL-8, and TNF- might be a candidate. More recently, Wei et al. reported that polymorphism of oxidative stress genes in NMIBC patients might affect response to BCG therapy.
What To Expect During Bcg Treatment
First, make sure you havent had any fluids for four hours before the treatment. Right before you go into the treatment room your doctor or nurse will have you empty your bladder.
Youll lie on your back, and the medical professional will insert a catheter into your urethra and into your bladder, likely using some local numbing, and use this tube to infuse the treatment.
Once the treatment is infused, your doctor or nurse will remove the catheter. Theyll have you lie on your back, each side, and your stomach for 15 minutes each. The BCG mycobacteria needs to touch the bladder cancer cells to activate the immune system. Youll then be free to go but will need to hold off on peeing for another hour.
Verywell / Alex Dos Diaz
For at least six hours after your infusion, youll need to disinfect your pee to ensure none of the mycobacteria spread to anyone else. Pour an equal amount of bleach into the toilet after you pee and let it sit for 15 minutes before flushing.
Also, people with a penis who undergo BCG treatment should avoid sex for 48 hours to ensure they dont pass the mycobacteria to their partners.
You will likely need multiple BCG treatments. They may be given weekly for a few weeks, then less often for months or years to prevent cancer from coming back.
Also Check: Heavy Feeling In Bladder And Frequent Urination
What Conditions Are Treated With Bcg Treatment
BCG treatment is used to address early-stage bladder cancer. This includes bladder cancers that havent invaded your bladder wall muscle, such as carcinoma in situ bladder cancers and non-muscle invasive bladder cancers . BCG treatment isnt effective against bladder cancer that has metastasized .
Clinical trials are currently underway to explore BCG treatment for fibromyalgia and diabetes. Experts believe that BCG treatment may increase cytokines , which could potentially benefit people with these conditions. More research is needed in these areas, though.
Section : Clinical Questions Related To The Intravesical Bcg Immunotherapy
Question 13: What are the contraindications of intravesical BCG immunotherapy?
Recommendation: Intravesical BCG immunotherapy is contraindicated to patients with visible haematuria, symptomatic urinary tract infection, recent history of traumatic catheterization, active tuberculosis, severe immunosuppression , allergy to BCG, and operations within two weeks of TURBT. .
Evidence summary: We referred to the recommendations from the EAU guideline , NCCN guideline , and Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Urology and Andrology in China .
Question 14: Is intravesical BCG immunotherapy prior to intravesical chemotherapy in patients with NMIBC?
Recommendations: For patients with high-risk tumors, intravesical BCG immunotherapy is recommended. . For patients with intermediate-risk tumors, intravesical chemotherapy or intravesical BCG immunotherapy is recommended.
Implementation consideration: Treatment schemes for intravesical BCG immunotherapy: starting intravesical BCG instillation within 24 weeks after TURBT The patients should first be given BCG induction instillation for 68 weeks , followed by BCG maintenance instillation for 13 years , and then repeat the treatment every 6 months .
Question 15: Is a standard dose of BCG immunotherapy superior to a low dose of BCG immunotherapy for the patients with intermediate-risk and high-risk NMIBC?
Question 18: What is the treatment option after the intravesical BCG immunotherapy failed?
Table 2 Management of BCG side effects
Don’t Miss: Immunology Treatment For Bladder Cancer
When You Go Home
Some hospitals allow you to go home with the medicine in your bladder if you live close by and are okay with the treatment. Your team will let you know if you can do this. You should follow the advice on what to do when you pass urine.
You need to drink lots of fluid after this treatment for 24 hours. It helps clear your system of the BCG.
You should not have sex for 24 hours after each treatment. During your course of treatment and for a week afterwards, you should wear a condom during sex.
Having bladder cancer and its treatment can be difficult to cope with. Tell your doctor or nurse about any problems or side effects that you have. The nurse will give you telephone numbers to call if you have any problems at home.
Induction Of Immune Responses
As shown in Table , various types of cytokines are detectable in the urine after BCG instillation. The cytokines in the urine indicate an immunological response specific for BCG instillation, although not completely. Most of the cytokines are detected after the second BCG instillation, and their concentrations increase after BCG instillations., Macrophages and activated lymphocytes are thought to be major sources of these cytokines. In contrast, some cytokines such as interleukin -1, IL-6, and IL-8 are detected after the first BCG instillation., Miyazaki et al. reported that cultured urothelial cells release IL-6 and IL-8 directly in response to BCG. Although this urothelial cell reaction is not specific to BCG, urothelial cells are supposed to be involved in the early phase of mucosal cytokine network induction by BCG. In addition to Th1 and Th2 cytokines, recently, several investigations showed that IL-17 plays a crucial role in generation of Th1-cell responses in BCG vaccination. At present, clinical data about IL-17 is limited, but in a mouse model, increases in IL-17 family genes and urinary IL-17 concentrations are reported. Recently, Takeuchi et al. reported that IL-17-producing T cells induced recruitment of neutrophils to the bladder.
Also Check: Harbor Freight Drain Cleaning Bladder
Induction Of Antitumor Effects
The antitumor effect of BCG has been recognized as dependent on T-cells. In particular, the role of Th1 cell-mediated immunity including CD4+ T cells and CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes is well known. Ratlieff et al. showed that the athymic nude mouse did not undergo BCG-induced tumor rejection. However, the actual antitumor effector mechanism is still unclear. In addition to the acquired immunity, the innate immune response plays a role in the antitumor effect of BCG. Brandau et al. reported that BCG therapy was completely ineffective in natural killer -cell deficient beige mice and in mice treated with an anti-NK cell monoclonal antibody. More recently, several investigations demonstrated the antitumor effect of neutrophils, which comprise the major cell subset in the leukocyturia observed after BCG instillation, or TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand produced by neutrophils. Macrophages and other types of innate immune cells are also reported to be involved in the antitumor effect of BCG.,
Bacillus Calmetteguerin Immunotherapy For Bladder Cancer: Current Understanding And Perspectives On Engineered Bcg Vaccine
Department of Urology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Tsukuba, Tokyo, Japan
To whom correspondence should be addressed.
Hideyuki Akaza
Department of Strategic Investigation on Comprehensive Cancer Network, Research Center for Advanced Science and Technology, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
Department of Urology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Tsukuba, Tokyo, Japan
To whom correspondence should be addressed.
Hideyuki Akaza
Department of Strategic Investigation on Comprehensive Cancer Network, Research Center for Advanced Science and Technology, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
Don’t Miss: Best Pain Relief For Bladder Infection
Current Clinical Use Of Intravesical Bcg Therapy
At initial diagnosis, approximately 70% of bladder cancer patients are diagnosed with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer , which include tumor stages Ta , T1 , and carcinoma in situ . The remaining patients have muscle-invasive tumor , which usually requires radical cystectomy. In contrast, most visible NMIBC lesions can be removed by endoscopic surgery, i.e., transurethral resection . For complete resection, a second TUR within 6 weeks after the initial resection is advised for T1 tumor. One problem in the management of NMIBC is the high intravesical recurrence rates ranging from 30% to nearly 80%, depending on the risk profile. Several mechanisms for intravesical recurrence have been proposed including microscopic persistence of tumor, cancer cell implantation, and new tumor formation. More importantly, NMIBC may progress to muscle-invasive cancer during repeated episodes of intravesical recurrence. Urothelial CIS, unlike CIS in other organs, has high malignant potential. CIS has over 50% risk of progression to muscle-invasive cancer.
| Definition | |
|---|---|
| Any combination of T1 and/or G3 and/or CIS | TURBT+ intravesical BCG with induction and maintenance |
| Immediate radical cystectomy should be considered for high grade, multiple T1 tumors T1 tumors located at a site difficult to resect residual T1 tumors on resection high-grade tumors with CIS |
| Local |
|---|
| Pneumonitis |
Differences In Strains Efficacy
Interestingly, despite decades of administration and widespread use, there are only few clinical trials directly comparing the efficacy of different trains. We could identify seven RCTs and one observational study . Two studies showed a statistically significant difference in terms of RFS in favor of BCG Connaught when compared to BCG TICE, but only if no maintenance cycle was given . An explanation could be found in the mice model proposed by Rentsch et al. Indeed, authors found that intravesical BCG Connaught had a stronger immune system stimulation and greater cellular recruitment compared to BCG TICE . The observation of Witjes et al. that maintenance cycles of BCG TICE can achieve a better RFS compared to maintenance with BCG Connaught generates the hypothesis that the optimal efficacy of different strains may be dependent of different maintenance protocols .
Table 1
Only in one of all RCTs, patients were treated with maintenance therapy . Since maintenance has shown to achieve better outcomes when compared to induction alone and is, therefore, the standard of care , results from trials in which maintenance was not administered should be interpreted with caution and are only hypothesis generating.
Table 2
Also Check: Bladder Leakage Pads For Women
When Do Doctors Use Bcg
Doctors most commonly use BCG to treat superficial bladder cancer. The vaccine stimulates the immune system to attack cancer cells in the bladder. It can be used with intravesical chemotherapy for advanced stages of bladder cancer.
It is not recommended for those who have weakened immune systems. While BCG treatment for bladder cancer can be effective, it is not a cure. It can help prevent cancer from recurring.
Association Between Antibiotic Treatment And The Efficacy Of Intravesical Bcg Therapy In Patients With High
- 1Department of Urology, Center for Urologic Cancer, National Cancer Center, Goyang, South Korea
- 2Department of Urology, Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea
- 3Biometrics Research Branch, Research Institute, National Cancer Center, Goyang, South Korea
- 4Division of Tumor Immunology, Research Institute, National Cancer Center, Goyang, South Korea
- 5Department of Pathology, National Cancer Center, Goyang, South Korea
Objective: To investigate the association between antibiotic therapy and the efficacy of intravesical BCG therapy in patients with high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer .
Methods: This study involved the retrospective review of medical records of patients who underwent transurethral resection of bladder tumors for high-risk NMIBC followed by intravesical BCG therapy between 2008 and 2017. Patients were categorized as none, short- , and long-course use based on the duration of antibiotic treatment concurrent with or initiated 30 days before BCG therapy. Oncologic outcomes, including recurrence-free survival and progression-free survival, were analyzed.
Long-course antibiotic treatment concurrently with or prior to intravesical BCG adversely influenced disease recurrence and progression outcomes in patients with high-risk NMIBC. Careful use of antibiotics may be required to enhance the efficacy of intravesical BCG therapy. Further mechanistic and prospective studies are warranted.
Don’t Miss: Air Bladder To Open Car Door
Treatment Of Superficial Bladder Cancer
The treatment of bladder cancer in general depends on numerous factors, including stage and grade of the disease, patient age, and their co-morbidity. The standard treatment of superficial bladder cancer is a transurethral resection, this initial resection usually removes the tumour but it is known that they have a great propensity to recur. It is important to realise that some tumours progress, and in those which do it is vital that they are recognised so that further treatment can be instigated. A significant breakthrough in the last decade has been the clear definition of prognostic factors, which determine later recurrence. Using these factors it is possible to identify different patient subgroups and tailor their treatment and subsequent follow up accordingly. The most important factors are easily assessed at transurethral resection and are listed in box 1.
Sex After Bcg Treatment
Men should use a condom during sex for the first week after each BCG treatment. If you are a woman having the treatment, your partner should use a condom during this time. This protects your partner from any BCG that may be present in semen or vaginal fluid. Your doctor or specialist nurse can give you more information about this.
Doctors do not yet know how BCG may affect an unborn baby. They will recommend you do not become pregnant or make someone pregnant while having it. You should use effective contraception during treatment. Your doctor or specialist nurse can give you more information about this.
Read Also: How Is Bladder Cancer Staged
Bcg Attachment And Internalization Assay
We used PCR to detect BCG attachment and internalization. After incubating and washing out non-attached BCG, the cell monolayers were washed twice with Hanks BSS . Cells were then harvested using Cell Disassociation Solution . Genomic DNA was extracted according to manufacturer’s instruction of the Dneasy Blood and Tissue kit .