If Youre Concerned About Bladder Cancer Talk To Your Doctor About Cxbladder
Cxbladder is a cutting-edge genomic urine test that quickly and accurately detects or rules out bladder cancer. The test combines clinical risk factor markers with genetic information, measuring five biomarker genes to detect the presence or absence of bladder cancer in hematuria patients and those being monitored for recurrence.
Cxbladder comes as a suite of tests, each optimised for a different point in the patient journey:
- Cxbladder Triage: Incorporates known bladder cancer risk factors to help quickly rule out the disease.
- Cxbladder Detect: Designed to work alongside other tests to improve overall detection accuracy.
- Cxbladder Monitor: A non-invasive surveillance alternative that can reduce the need for frequent cystoscopies.
Cxbladder gives you peace of mind and will help your physician make informed treatment decisions.
Speak to your doctor or urologist to learn more about Cxbladder and which test might be right for you. You can also contact our Customer Service Team directly.Learn more about Cxbladder Contact us for more information
Timing Of Nac And Then Rc
In clinical practice there is debate on how much an invasive intervention such as RC should be delayed after NAC in order to maximize the patientâs recovery and ability to tolerate surgery without affecting the oncological outcomes and there is general agreement that RC should be delayed for a period after the last dose of NAC in order to maximize the patientâs blood counts and perhaps ability to tolerate surgery. In this context, RCTs investigating NAC provides more information on the time frame between RC and NAC .
A population based study form the Netherlands including 1,782 patients reported that a delay in RC greater than 3 months was not associated with OS notably 93% of the patients in the cohort underwent RC within 3 months thus limiting the number of patients with delayed treatment. Interestingly this study a separate subgroup analysis was performed for 105 patients who underwent neoadjuvant treatment and again failed to find association between timing to RC and OS . Investigation for the potential causes of delay in RC found that patients who were older than 75 years , treated in a university hospital and being referred from another hospital for RC were less likely to undergo RC within 3 months .
The Current Neoadjuvant Scenario In Uc
Historically, the standard of care for MIBC patients who are eligible has been platinum-based chemotherapy. For patients receiving three cycles of neoadjuvant methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin in stage T2-T4aN0 muscle-invasive bladder, pathologic complete response , defined as the absence of viable tumor in the resection specimen, has been reported in 38% of cases. Some of the significant adverse events for this chemotherapy regimen were grade 4 granulocytopenia and gastrointestinal toxicity, such as grade 3 nausea or vomiting, stomatitis, diarrhea, or constipation .15
Gemcitabine plus cisplatin the most widely used regimen in neoadjuvant MIBC has not been studied prospectively in the neoadjuvant setting. However, retrospective results for 935 patients across 19 centers for patients with clinical cT2-4aN0M0 showed a pCR of 23.9% for GC, compared with 24.5% for MVAC, with no difference on multivariable analysis for these regimens.16
Read Also: Shortness Of Breath And Loss Of Bladder Control
Data Collection And Analysis
We collected, validated and reanalysed updated data on all randomised patients from all available randomised trials, including 3005 patients from 11 RCTs. For all outcomes, we obtained overall pooled hazard ratios using the fixed effects model. To explore the potential impact of trial design we preplanned analyses that grouped trials by important aspects of their design that might influence the treatment effect. To investigate any differences in effect by predefined patient subgroups we used a stratified logrank analysis on the primary endpoint of survival.
Read Also: Causes Of Recurrent Bladder Infections
Stage Information For Bladder Cancer
The clinical staging of carcinoma of the bladder is determined by the depth of invasion of the bladder wall by the tumor. This determination requires a cystoscopic examination that includes a biopsy and examination under anesthesia to assess the following:
- Size and mobility of palpable masses.
- Degree of induration of the bladder wall.
- Presence of extravesical extension or invasion of adjacent organs.
Clinical staging, even when computed tomographic and/or magnetic resonance imaging scans and other imaging modalities are used, often underestimates the extent of tumor, particularly in cancers that are less differentiated and more deeply invasive. CT imaging is the standard staging modality. A clinical benefit from obtaining MRI or positron emission tomography scans instead of CT imaging has not been demonstrated.
Don’t Miss: Can You Use A Drain Bladder On A Toilet
Latest Treatment For Bladder Cancer
Intravesical therapy is a newer treatment for people who have bladder cancer. With intravesical therapy, the doctor puts a liquid medication right into your bladder rather than administering it orally or injecting it into your blood. The medication is put in through a catheter thats placed into your bladder through the urethra. The medication stays in your bladder for up to two hours, so it can affect the cells lining the inside of the bladder without having major effects on other parts of your body. Intravesical therapy is commonly used after transurethral resection of bladder tumor . Its often performed within 24 hours of the TURBT procedure. The goal is to kill any cancer cells that may be left in the bladder.
Intravesical chemotherapy is used to treat non-invasive bladder cancer. It is used for these early-stage cancers because medication given this way mostly affects the cells lining the inside of the bladder. It has little to no effect on cells elsewhere. This means any cancer cells outside of the bladder lining are not treated by intravesical chemotherapy.
What Are The 5
In 2020, approximately 17,980 deaths in the United States are predicted to be attributed to bladder cancer1. This represents the eighth most common cause of cancer deaths in men.
The general 5-year survival rate for people with bladder cancer is 77%, while the 10-year survival rate is 70% and the 15-year survival rate is 65%1. Notably, as each patient and cancer are different, it is not possible to definitely know the disease course for an individual patient.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of Bladder Spasms
Cellular Classification Of Bladder Cancer
More than 90% of bladder cancers are transitional cell carcinomas derived from the uroepithelium. About 2% to 7% are squamous cell carcinomas, and 2% are adenocarcinomas. Adenocarcinomas may be of urachal origin or nonurachal origin the latter type is generally thought to arise from metaplasia of chronically irritated transitional epithelium. Small cell carcinomas also may develop in the bladder. Sarcomas of the bladder are very rare.
Pathologic grade of transitional cell carcinomas, which is based on cellular atypia, nuclear abnormalities, and the number of mitotic figures, is of great prognostic importance.
References
Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy For Bladder Cancer
Seth P. Lerner, MDOncology
Occult distant micrometastasis at the time of radical cystectomy leads predominantly to distant failures in patients with locally advanced muscle-invasive transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Cisplatin-based combination chemotherapy enhances survival in patients with metastatic urothelial cancer. Studies evaluating adjuvant chemotherapy have been limited by inadequate statistical power. However, randomized clinical trials have demonstrated a survival benefit for neoadjvuant cisplatin-based combination chemotherapy, which should be considered a standard of care. In addition, neoadjuvant therapy may assist in the rapid development of novel systemic therapy regimens, since pathologic complete remission appears to be a powerful prognostic factor for long-term outcomes. Patients who are either unfit for or refuse radical cystectomy may benefit from neoadjuvant chemotherapy with or without radiation to enable bladder preservation.
Risk Factors for Recurrence Following Radical Cystectomy
A postoperative nomogram was developed by the International Bladder Cancer Nomogram Consortium, based on > 9,000 postoperative patients and including age, sex, time from diagnosis to surgery, pathologic tumor stage and grade, tumor histologic subtype, and regional lymph node status. The predictive accuracy of the nomogram was significantly better than standard staging or standard pathologic subgroupings .
Systemic Chemotherapy for Metastatic Urothelial Cancer
Don’t Miss: Surgery To Remove Bladder Tumor
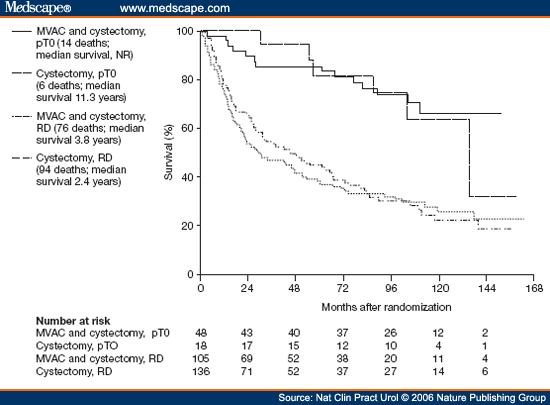
Cmv And Mvac As Standard Nac Regimens
The first of these phase III trials randomized 976 patients with high-grade cT2-T4a N0-NX M0 bladder cancer to receive either CMV chemotherapy for three cycles or no chemotherapy, followed by local therapy with either cystectomy or radiotherapy. Long-term follow-up revealed an OS advantage at 10 years for patients receiving NAC . There was a statistically significant 16 percent reduction in the risk of death for patients receiving CMV prior to local therapy.
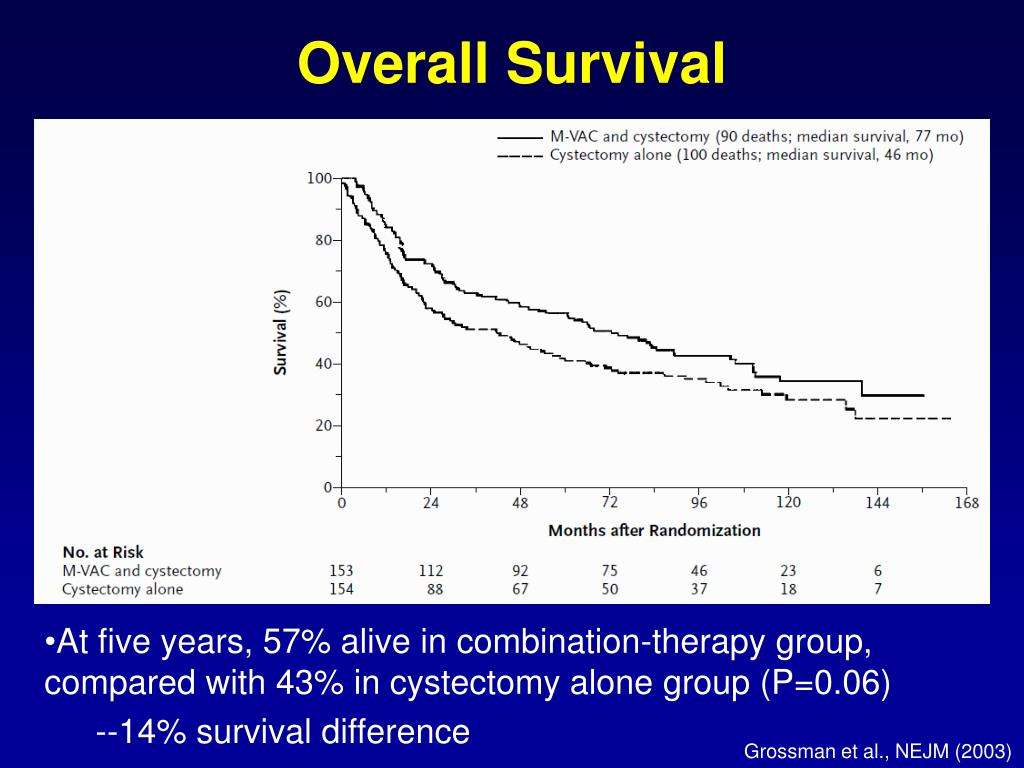
Another major trial initiated by SWOG used MVAC as the NAC regimen prior to radical cystectomy. It included 317 patients enrolled from 1987 to 1998 with stage cT2-T4a muscle-invasive bladder cancer who were intended to undergo radical cystectomy. Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive either three cycles of MVAC followed by radical cystectomy or radical cystectomy alone.
Intention-to-treat analysis revealed median OS in the MVAC plus cystectomy group to be 77 months as compared to 46 months in the cystectomy group . More patients in the MVAC plus cystectomy group had pathologic complete response at the time of cystectomy compared to patients who only had cystectomy . Pathologic complete response was associated with 85 percent disease-free status rate at five years.
Muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma
Read Also: How Do You Fix Overactive Bladder
Immunotherapy In Advanced Uc
PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in UC were first studied in patients with unresectable or metastatic disease. Significant activity was demonstrated for all the previously mentioned drugs.
Pembrolizumab was studied in first-line setting in 370 patients with an overall objective response rate of 24% and complete response of 5%. Subgroup analysis using the PD-L1 combined positive score , defined as the percentage of cells expressing PD-L1 in a tumor biopsy, showed an ORR of 39% in those with CPS> 10%, 20% for CPS between 1% and 10%, and 11% for those with CPS scores below 1%.9
Similarly, Atezolizumab was studied in 486 patients in the second-line setting, showing an overall ORR of 15%, while CR was reported in 5% of patients. Subgroup analysis by the percentage of PD-L1-positive immune cells in the tumor microenvironment IC0 , IC1 , and IC2/3 , showed an ORR of 8%, 10%, and 26% respectively.10
Additionally, in a phase I/II study including 191 patients, Durvalumab showed an ORR of 17.8%. The rate was 27.6% for patients with high PD-L1 expression and 5.1% for those with low or negative PD-L1 expression . CR for Durvalumab was seen in 3.7% of the overall studied population.11
Another immune checkpoint inhibitor , Nivolumab, was assessed in 265 patients in the second-line setting, after platinum-based chemotherapy, showing an overall ORR of 19.6% and CR in 2% of patients. Subgroup analysis by PD-L1 expression 5%, > 1% and < 1% indicated an ORR of 28.4%, 23.8% and 16.1%, respectively.12
Read Also: What Herbs Are Good For Bladder Control
Treatment Of Bladder Cancer By Stage
Most of the time, treatment of bladder cancer is based on the tumors clinical stage when it’s first diagnosed. This includes how deep it’s thought to have grown into the bladder wall and whether it has spread beyond the bladder. Other factors, such as the size of the tumor, how fast the cancer cells are growing , and a persons overall health and preferences, also affect treatment options.
Bladder Reconstructions And Stomas
If you have had your bladder removed, the way you pass urine will change. There are several options that your treatment team will talk to you about:
- Urostomy is where doctors create a new hole in your abdomen called a stoma. Urine drains from the stoma to the outside of your abdomen into a special bag.
- Neobladder is where a new bladder made from your small bowel forms a pouch inside your body to store urine. You will pass urine by squeezing your abdominal muscles. You will also pass a small tube into the neobladder each day to help drain the urine.
- Continent urinary diversion is a pouch made from your small bowel inside your body to store urine. The urine empties through a hole called a stoma to the outside of your abdomen into a special bag.
A bladder reconstruction is a big change in your life. You can speak with a continence or stomal therapy nurse for help, support and information. You can also call Cancer Council (. You may be able to speak with a trained Cancer Council volunteer who has had cancer for tips and support. If you find it difficult to adjust after your bladder reconstruction, it may help to be referred to a psychologist or counsellor.
Note: If you have a stoma, you can join a stoma association for support and free supplies. For more information about stoma associations, visit the Australian Council of Stoma Associations.
Also Check: Sodium Bicarbonate For Bladder Infection
Survival For All Stages Of Bladder Cancer
Generally, for people diagnosed with bladder cancer in England:
- around 75 out of every 100 survive their cancer for 1 year or more after diagnosis
- almost 55 out of every 100 survive their cancer for 5 years or more after they are diagnosed
- around 45 out of every 100 survive their cancer for 10 years or more after diagnosis
Cancer survival by stage at diagnosis for England, 2019Office for National Statistics
These statistics are for net survival. Net survival estimates the number of people who survive their cancer rather than calculating the number of people diagnosed with cancer who are still alive. In other words, it is the survival of cancer patients after taking into account that some people would have died from other causes if they had not had cancer.
What Causes Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer occurs when cells within the lining of the bladder wall begin to grow in a disordered, uncontrolled way.
Exactly what prompts this disordered growth is not fully known. However, several factors associated with a higher risk of bladder cancer have been identified, including:
- Age – most people diagnosed with bladder cancer are older than 55 years.
- Sex – compared to women, men are 4 times more likely to develop bladder cancer.
- Smoking – smoking is associated with around half of all bladder cancers in men and women.
- Race – in the United States, White Americans have the highest rate of bladder cancer.
- Previous bladder cancer – people who have had bladder cancer may have a recurrence.
- Workplace exposures – certain chemicals in some workplaces may contribute to higher rates of bladder cancer in workers. For example, painters, hairdressers, and truck drivers are at increased risk.
- Arsenic in drinking water.
- Certain types of medication.
Read Also: What Medications Are Used For Overactive Bladder
What Is A 5
A relative survival rate compares people with the same type and stage of bladder cancer to people in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of bladder cancer is 90%, it means that people who have that cancer are, on average, about 90% as likely as people who dont have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
How Is Bladder Cancer Treated
Treatment for bladder cancer depends on
- The stage of cancer.
- If cancer has spread beyond the lining of the bladder.
- The extent of cancer spread.
Treatment options based on tumor grade
- High-grade bladder cancer: High-grade cancers that are life-threatening and spread quickly need to be treated with chemotherapy, radiation or surgery.
- Low-grade cancers: Less aggressive cancers have a low chance of becoming high grade and do not require aggressive treatments, such as radiation or bladder removal.
Treatment options may vary depending on the tumor stage.
Also Check: Why Does My Bladder Leak
Association Of Treatment Options With Acm And Bcsm Of Patients
Treatment options were associated with ACM and BCSM of patients. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year ACM of patients were as follows: 41.9, 75, and 82.6% for RC, and 57.2, 87.9, and 91.3% for TMT, respectively. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year BCSM of patients were as follows: 37, 71.5, and 75% for RC, respectively, and 54.2, 85.6, and 88.8% for TMT, respectively .
Table 2. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year all-cause mortality and bladder cancer-specific mortality of patients after radical cystectomy and trimodal therapy.
Figure 2. Adjusted survival curves for all-cause mortality and bladder cancer-specific mortality by radical cystectomy and trimodal therapy treatment options after weighting.
Overall, multivariate and propensity matched score adjustment analyses found that the patient’s age of diagnosis, T, N, M stage, and treatment were related to prognosis . Compared to RC, TMT was associated with higher ACM . Similarly, in the competitive risk model, there was a difference in BCSM between patients treated with TMT and RC .
Table 3. Proportional hazards regression model for the all-cause mortality and bladder cancer-specific mortality according to treatment type.
We further analyzed age by subgroup. Among patients aged 60 years and 6179 years, TMT was associated with higher ACM and higher BCSM , compared to RC. However, among patients aged 80 years, there was no difference in prognosis between the TMT and RC groups .
Study Of People Who Underwent A Radical Cystectomy
In 2017, a group of researchers looked at the long-term outcomes of 1652 patients who underwent a radical cystectomy and removal of lymph nodes to treat their bladder cancer. These patients were treated at 3 different centers and had their surgeries between 1988 and 2012. None of these patients had post-surgery chemotherapy or biologic agents, also known as neoadjuvant therapy, which could change the results of the data.
Recommended Reading: Can Overactive Bladder Start Suddenly