Palliative Or Supportive Care
If your cancer is at an advanced stage and can’t be cured, your medical team should discuss how the cancer will progress and which treatments are available to ease the symptoms.
You can be referred to a palliative care team, who can provide support and practical help, including pain relief.
Page last reviewed: 01 July 2021 Next review due: 01 July 2024
Lymphadenectomy: Role And Extent
Controversies in evaluating the clinical significance of lymphadenectomy are related to two main aspects of nodal dissection: therapeutic procedure and/orstaging instrument.
Two important autopsy studies have been performed for RC so far. The firststudy showed that in 215 patients with MIBC and nodal dissemination, the frequency ofmetastasis was 92% in regional , 72% in retroperitoneal, and 35% inabdominal LNs. There was also a significant correlation between nodal metastases andconcomitant distant metastases . Approximately 47% of the patients had bothnodal metastases and distant dissemination and only 12% of the patients had nodaldissemination as the sole metastatic manifestation .
The second autopsy study focused on the nodal yield whensuper-extended pelvic LND was performed. Substantial inter-individual differences were foundwith counts ranging from 10 to 53 nodes . These findingsdemonstrate the limited utility of node count as a surrogate for extent of dissection.
Regional LNs have been shown to consist of all pelvic LNsbelow the bifurcation of the aorta . Mapping studiesalso found that skipping lesions at locations above the bifurcation of the aorta withoutmore distally located LN metastases is rare .
Radiotherapy With A Radiosensitiser
Radiotherapy is given by a machine that beams the radiation at the bladder . Sessions are usually given on a daily basis for 5 days a week over the course of 4 to 7 weeks. Each session lasts for about 10 to 15 minutes.
A medicine called a radiosensitiser should also be given alongside radiotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. This medicine affects the cells of a tumour, to enhance the effect of radiotherapy. It has a much smaller effect on normal tissue.
As well as destroying cancerous cells, radiotherapy can also damage healthy cells, which means it can cause a number of side effects. These include:
- diarrhoea
- tightening of the vagina , which can make having sex painful
- erectile dysfunction
- tiredness
- difficulty passing urine
Most of these side effects should pass a few weeks after your treatment finishes, although there’s a small chance they’ll be permanent.
Having radiotherapy directed at your pelvis usually means you’ll be infertile .
After having radiotherapy for bladder cancer, you should be offered follow-up appointments every 3 months for the first 2 years, then every 6 months for the next 2 years, and every year after that. At these appointments, your bladder will be checked using a cystoscopy.
You may also be offered CT scans of your chest, abdomen and pelvis after 6 months, 1 year and 2 years. A CT scan of your urinary tract may be offered every year for 5 years.
You May Like: Can A Ct Urogram Detect Bladder Cancer
Histopathological And Clinical Markers
The most important histopathological prognostic variables after RC and LNdissection are tumour stage and LN status . In addition, otherhistopathological parameters of the RC specimen have been associated with prognosis.
The value of lymphovascular invasion was reported in asystematic review and meta-analysis including 78,000 patients from 65 studies treated withRC for BC . Lymphovascular invasion was present in 35% of thepatients and correlated with a 1.5-fold higher risk of recurrence and CSM, independent ofpathological stage and peri-operative chemotherapy. This correlation was even stronger inthose patients with node-negative disease .
In a systematic review andmeta-analysis including 23 studies and over 20,000 patients, the presence of concomitantCIS in the RC specimen was associated with a higher odds ratio of ureteralinvolvement . Concomitant CIS was not independentlyassociated with OS, recurrence-free survival and DSS in all patients, but inpatients with organ-confined disease concomitant CIS was associated with worse RFS and CSM .
Tumour location has been associated with prognosis. Tumours located at thebladder neck or trigone of the bladder appear to have an increased likelihood of nodalmetastasis and have been associated with decreasedsurvival .
Improving Outcomes Of Cisplatin
Another potential solution to optimize cisplatin-based NAC is the addition of ICI in the adjuvant setting . In the first reported study of this approach, atezolizumab did not meet its primary endpoint of improved disease-free survival compared with observation, as reported in a press release no further data are currently available. Three other phase 3 trials are currently underway in this setting including pembrolizumab vs observation , durvalumab , and nivolumab vs placebo .
Recommended Reading: Can Candida Cause Bladder Infection
Comorbidity Scales Anaesthetic Risk Classification Andgeriatric Assessment
A range of comorbidity scales has been developed , seven of which have been validated . The Charlson Comorbidity Index ranges from 0 to30 according to the importance of comorbidity described at four levels and is calculated byhealthcare practitioners based on patients medical records. The score has been widelystudied in patients with BC and found to be an independent prognostic factor forperi-operative mortality , overallmortality , and CSM . Only the age-adjusted version of the CCI wascorrelated with both cancer-specific and other-cause mortality . The age-adjusted CCI is the most widely usedcomorbidity index in cancer for estimating long-term survival and is easily calculated .
Health assessment of oncology patients must be supplemented by measuringtheir activity level. Extermann et al. have shown thatthere is no correlation between morbidity and competitive activity level . The Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performancestatus scores and Karnofsky index have been validated to measure patient activity . Performance score is correlated with patient OS after RC and palliative chemotherapy .
Table 5.2: Calculation of the Charlson Comorbidity Index
|
Number of points |
Both patient and tumour characteristics guide treatment decisions andprognosis of patients with MIBC.
Treatment Of Stage I Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage I bladder cancer may include the following:
- Transurethral resection with fulguration. This may be followed by one of the following:
- Intravesicalchemotherapy given right after surgery.
- Intravesical chemotherapy given right after surgery and then regular treatments with intravesical BCG or intravesical chemotherapy.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Also Check: How Long Is Bladder Surgery
Small Cell Carcinoma Of The Bladder
This aggressive form of the disease begins in small nerve-like cells in the bladder called neuroendocrine cells. Small cell carcinoma makes up about 1 percent of bladder cancers. It is often detected at an advanced stage, after it has spread to other parts of the body. It usually requires a combination of treatments, including chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation therapy.
Case Authors Lament Scant Information On Treatments Or Outcomes
byKate Kneisel, Contributing Writer, MedPage Today April 26, 2021
A 59-year-old man presents to a hospital in Yokohama, Japan, after being referred by his local medical provider for further workup regarding gross hematuria. He has no other symptoms.
Clinicians perform cystoscopy, followed by CT and MRI scans, which identify a nodular tumor that occupies the patient’s bladder — it is 8 cm in diameter.
Aside from being a tobacco smoker, the patient’s medical history is unremarkable. Laboratory tests are performed but fail to identify any abnormalities. The patient undergoes transurethral resection of the bladder tumor, which is sent to histology for analysis.
The pathology report reveals the tumor as the sarcomatoid variant of urothelial carcinoma with a heterologous osteosarcomatous element of osteosarcoma and high-grade spindle cells. The patient refuses to undergo the radical cystectomy proposed by clinicians, opting instead to undergo another transurethral resection of the tumor.
The specimen from the second surgery reveals the same elements, with evidence of invasion to the muscle. Based on these findings, clinicians schedule the patient for two courses of neoadjuvant chemotherapy with gemcitabine and cisplatin they recommend that this be followed by a radical cystectomy.
At that point, the patient is unable to undergo radical cystectomy. Six months after his initial consultation, the patient succumbs to cancer of the bladder.
Discussion
Disclosures
Don’t Miss: Treatment Of Overactive Bladder In Males
Transurethral Resection Of Bladder Tumour
Transurethral resection of bladder tumour alone in MIBC patients is onlypossible as a therapeutic option if tumour growth is limited to the superficial muscle layerand if re-staging biopsies are negative for residual tumour . In general, approximately 50% of patients will still have toundergo RC for recurrent MIBC with a disease-specific mortality rate of up to 47% withinthis group . A disease-free status at re-staging TURB appearsto be crucial in making the decision not to perform RC . A prospective study by Solsona et al. including 133 patients with radical TURB andre-staging negative biopsies, reported a 15-year follow-up .Thirty per cent of patients had recurrent NMIBC and went on to intravesical therapy, and 30% progressed, of which 27 died of BC. After five, ten, and fifteen years, the resultsshowed CSS rates of 81.9%, 79.5%, and 76.7%, respectively and PFS rates with an intactbladder of 75.5%, 64.9%, and 57.8%, respectively.
In conclusion, TURB alone should only be considered as atherapeutic option for muscle-invasive disease after radical TURB, when the patient is unfitfor cystectomy, or refuses open surgery, or as part of a multimodality bladder-preservingapproach.
7.5.1.1.Guideline for transurethralresection of bladder tumour
|
Recommendation |
Strength rating |
|
Do not offer transurethral resection of bladdertumour alone as a curative treatment option as most patients will not benefit. |
Strong |
HCP = healthcare professional.
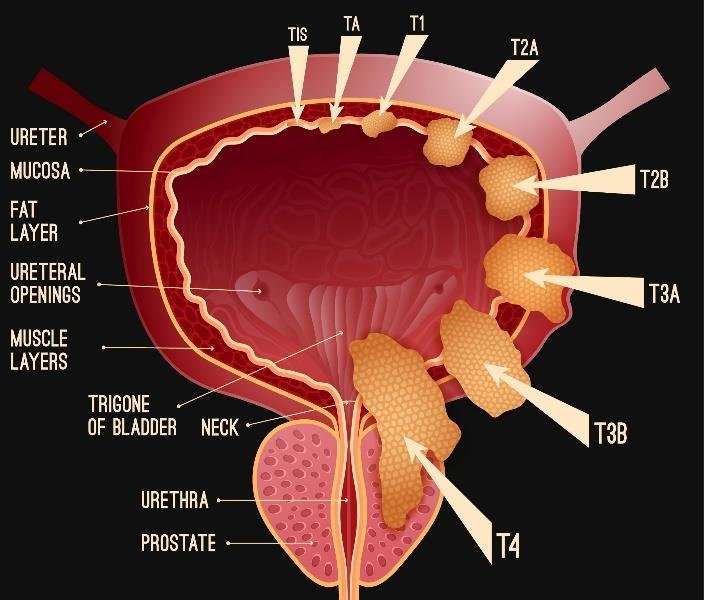
Imaging For Staging Of Mibc
In clinical practice, tumour stage and histopathological grade are used toguide treatment and determine prognosis .
Computed tomography and MRI are the imaging techniquesmost commonly used for tumour staging. If the correct choice of treatment is to be made,staging must be accurate.
The goal of imaging patients with bladder cancer is to determine:
- extent of local tumour invasion, ideally differentiating T1 from T2 tumours as thetreatment is different
- tumour spread to LNs
- tumour spread to the upper UT and other distant organs .
Read Also: Best Over The Counter Bladder Control Medication
How Is Gallbladder Cancer Usually Treated
Treatment for gallbladder cancer may include
- Surgery: It can be used to remove the gallbladder. If cancer has spread, then surgery can also be used to remove the surrounding tissue, lymph nodes and parts of other organs.
- Cancer found in the wall of the gallbladder can be completely removed by surgery.
- Unresectable cancer cannot be removed completely by surgery. Most patients with gallbladder cancer have unresectable cancer.
- Recurrent cancer is cancer that has recurred after it has been treated. GBC may come back in the gallbladder or in other parts of the body.
Treatmentof Patients With Bone Metastases
The prevalence of metastatic bone disease in patients withadvanced/metastatic UC is 3040% . Skeletal complicationsdue to MBD have a detrimental effect on pain and QoL and are also associated with increasedmortality . Bisphosphonates such as zoledronic acid reduce anddelay skeletal-related events due to bone metastases by inhibiting bone resorption,as shown in a small pilot study . Denosumab, a fully humanmonoclonal antibody that binds to and neutralises RANKL , was shown to be non-inferior to zoledronic acid in preventing ordelaying SREs in patients with solid tumours and advanced MBD, including patients with UC. Patients with MBD, irrespective of the cancer type, should beconsidered for bone-targeted treatment .
Patients treated with zoledronic acid or denosumab should be informed aboutpossible side effects including osteonecrosis of the jaw and hypocalcaemia. Supplementationwith calcium and vitamin D is mandatory. Dosing regimens of zoledronic acid should followregulatory recommendations and have to be adjusted according to pre-existing medicalconditions, especially renal function . For denosumab, no doseadjustments are required for variations in renal function.
You May Like: Where Do You Feel Bladder Pain
What Can Cause Adenocarcinoma
Though the exact cause of adenocarcinoma is not fully understood, researchers have identified a variety of risk factors that are associated with this type of cancer:
- Family history of cancer
- Environmental toxins
- Beta carotene supplements
Smoking is the most common risk factor associated with all types of cancers. It is important to note that these risk factors will not necessarily lead to lung cancer. Similarly, an individual may develop lung cancer without having any of these risk factors.
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if bladder cancer spreads to the bone, the cancer cells in the bone are actually bladder cancer cells. The disease is metastatic bladder cancer, not bone cancer.
Read Also: Turbt Treatment For Bladder Cancer
Surgery For Stage Ii Or Iii
Most patients with stage II or stage III bladder cancer will have part or all of their bladder removed. This is called a cystectomy. A partial cystectomy is when only a part of the bladder is removed. A radical cystectomy is a surgery to remove all of the bladder:
- In men, the surgery removes the entire bladder as well as the prostate and seminal vesicles.
- In women, the bladder is removed along with the uterus, ovaries, and part of the vagina.
- Some stage IV patients may be offered surgery.
Your surgeon will reconstruct your urinary tract if your bladder is removed.
Before you have bladder removal and reconstruction:
- Find a surgeon who performs the surgeries often.
- Ask questions like: How will your reconstruction work? How long will you be in the hospital? What complications may you experience? How long will it take to recover? How may the surgery affect your sexual functioning?
- Talk to your doctor about the lifelong follow-up you will need. Your health care team will check your reconstruction and address bladder stones or other health problems.
- Be aware that you may experience incontinence or urine leakage, no matter what reconstruction you choose.
- Get support as you learn to use your new bladder. Specialized urology nurses and wound/ostomy nurses can help you in recovery.
- Join an in-person or online support group to connect with other bladder cancer patients.
Expert Review And References
- Al-Ahmadie H, Lin O, Reuter VE. Pathology and cytology of tumors of the urinary tract. Scardino PT, Lineham WM, Zelefsky MJ, Vogelzang NJ . Comprehensive Textbook of Genitourinary Oncology. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2011: 16:295-316.
- American Society of Clinical Oncology. Bladder Cancer. 2017: .
- Feldman AS, Efstathiou JA, Lee RJ, Dahl DM, Michaelson MD, Zietman AL. Cancer of the bladder, ureter, and renal pelvis. DeVita VT Jr, Lawrence TS, Rosenberg SA. Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2015: 65:896-916.
- Martini FH, Timmons MJ, Tallitsch RB. Human Anatomy. 7th ed. San Francisco: Pearson Benjamin Cummings 2012.
- Penn Medicine. All About Bladder Cancer. University of Pennsylvania 2017: .
Recommended Reading: Can Lower Back Pain Cause Bladder Problems
How Is Adenocarcinoma Treated
Treatment of adenocarcinoma depends on the anatomical site and its manifestations. Below are treatment options for adenocarcinoma.
- Surgery: The primary treatment after diagnosis is usually to remove the tumor and the tissue around it. Usually, the tissue is sent to pathology lab to determine the aggressiveness of the cancer. Depending on the pathology result, an individual might need to combine other treatments with surgery.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs used in chemotherapy can kill adenocarcinoma cells, slow their growth, or even cure the disease.
- Radiation: Generally, high-energy X-rays or other types of rays are exposed to the cancerous site to kill the cancer cells.
Cancer treatment can have side effects which include vomiting and weakness doctors usually treat these side effects with medications.
Symptoms In Men And Women
Bladder cancer symptoms in men and women are the same. Men are more likely to get bladder cancer, but they are also more likely to have it diagnosed earlier, according to Moffitt Cancer Center.
Women are more likely to mistake bladder cancer symptoms for urinary tract infections or menstruation.
Rarely, bladder cancer may also be misdiagnosed as interstitial cystitis in women. IC is a painful, inflammatory bladder condition that affects more women than men.
In one study, doctors found bladder cancer in about one percent out of 600 patients referred to them for IC treatment, according to an article in Urology Times.
You May Like: How Do I Treat A Bladder Infection At Home
Distantmetastases At Sites Other Than Lymph Nodes
Prior to any curative treatment, it is essential to evaluate the presenceof distant metastases. Computed tomography and MRI are the diagnostic techniques of choiceto detect lung and liver metastases , respectively. Bone and brain metastases are rare at the timeof presentation of invasive BC. A bone scan and additional brain imaging are therefore notroutinely indicated unless the patient has specific symptoms or signs to suggest bone orbrain metastases . Magneticresonance imaging is more sensitive and specific for diagnosing bone metastases than bonescintigraphy .