Certain Factors Affect Prognosis And Treatment Options
The prognosis depends on the following:
- The stage of the cancer . Bladder cancer in the early stages can often be cured.
- The type of bladder cancer cells and how they look under a microscope.
- Whether there is carcinoma in situ in other parts of the bladder.
- The patients age and general health.
If the cancer is superficial, prognosis also depends on the following:
- How many tumors there are.
- The size of the tumors.
- Whether the tumor has recurred after treatment.
Treatment options depend on the stage of bladder cancer.
Bladder Cancer In Dogs Stages
Staging is a way to measure the primary tumor with X-rays or ultrasound to see how far the cancer may have spread and assess what level of risk there is to the dog.
Following the staging tests, your veterinarian may grade the tumor as low, intermediate, or high risk, depending on what stage it has reached. Unfortunately, most dogs with bladder tumors have intermediate to high-grade invasive TCC, which is high risk and difficult to treat.
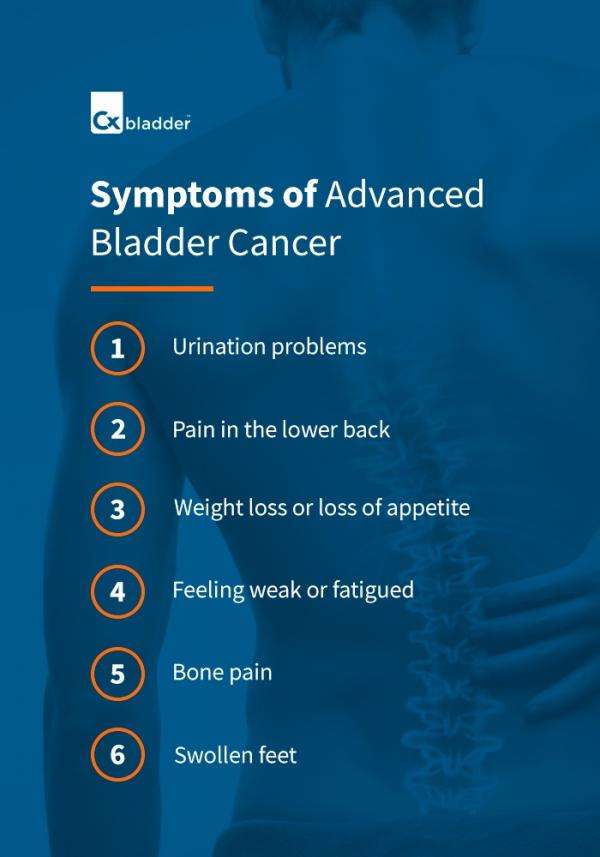
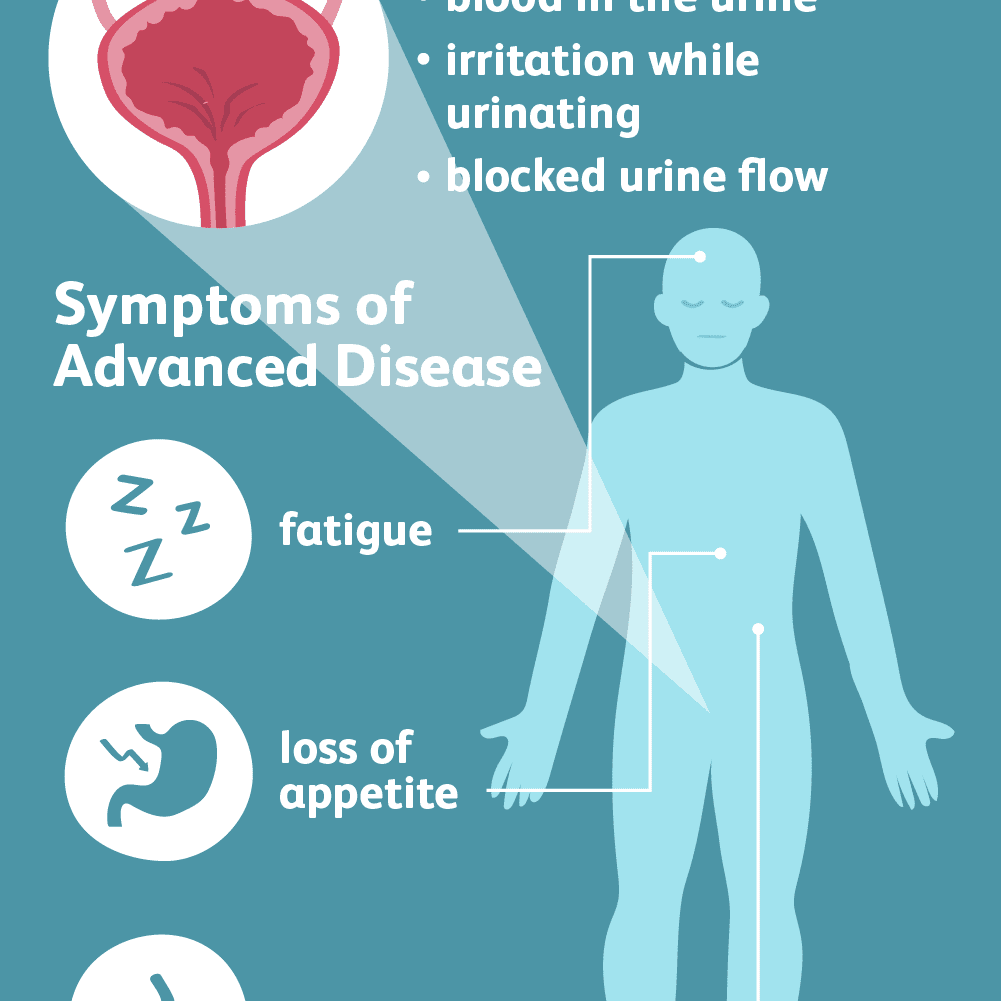
Early Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
The following are some of the early-stage bladder cancer symptoms you might experience:
1. Blood in the Urine
Blood in urine, often referred to as hematuria, is the most common symptom or sign of bladder cancer. With this symptom:
- You might have enough blood to change your urine color to pink, orange or, less often, dark red.
- Your urine color is sometimes normal, but a urine test , which the doctor performs during a general medical checkup or if you have other symptoms, can still detect small traces of blood.
- You may have blood one day and not the next, with your urine staying clear for weeks or maybe even months at a time.
Generally, the earlier stages of bladder cancer when the cancer is small and confined to your bladder only cause bleeding with either no pain or little pain.
It’s important to note that blood in your urine doesn’t necessarily indicate bladder cancer. The cause of blood may be due to another factor. In fact, many healthy individuals may have some unseen blood in their urine at some stage . And, for most individuals, the cause isn’t cancer.
In many situations, the cause is due to other things like benign tumors, medications or foods, infection, bladder or kidney stones or another benign kidney disease. Still, you should have your doctor check it out.
If you’re concerned about cancer, ask them about Cxbladder, a non-invasive genomic urine test that quickly and accurately detects or rules out bladder cancer.
Also Check: Best Over The Counter Bladder Control Medication
Dog Bladder Cancer: What To Expect
Look out for these common symptoms, especially if you are the owner of Scottish Terriers or Shetland Sheepdogs:
- Bloody urine
- Painful urination or other urinary tract infection signs.
- Abdominal pain.
When you seek veterinary help, expect that your veterinarian may recommend a urinary catheter to help your pet relieve themselves, should they be suffering from a blocked urinary tract.
Ask your vet if they believe there is a harmless urinary infection, and consider a Cadet BRAF test if there are suspicions of a serious disease.
If the Cadet BRAF and other urinary tests determine cancer cells are present, talk to your veterinarian about a biopsy and ultrasound. This will ensure your dog is fully diagnosed by assessing if the bladder tumors have spread to the lymph nodes, the lungs, the kidneys, or the urinary tract.
With advanced bladder tumors, expect that chemotherapy may be recommended, which can have nasty side effects for your dog. Consider ways of making your pet as comfortable as you can.
Stages Of Bladder Cancer
Cancer staging is typically determined by the extent to which a cancer has grown or spread. A staging system is a way for professionals to specifically describe how much a cancer has progressed. Typically, the TNM system is used for bladder cancer and represents the following:
- T describes how far the main tumor has grown
- N reveals any cancer spread to lymph nodes near the bladder
- M reveals whether the cancer has spread to other locations away from the bladder.
Bladder Cancer Stages
The following is an example of bladder cancer stages and the TNM system:
Stage 0a : The cancer is non-invasive papillary carcinoma and has not invaded the connective tissue or bladder wall muscle. Stage 0is : Cancerous cells in the inner lining tissue of the bladder only.Stage I : Tumor has spread onto the bladder wall.Stage II : Tumor has penetrated the inner wall and is present in muscle of the bladder wall. Stage III : Tumor has spread through the bladder to fat around the bladder.Stage IV applies to one of the following: : Tumor has grown through the bladder wall and into the pelvic or abdominal wall.Any T, N1, M0: The tumor has spread to the nearby lymph nodes.Any T, any N, M1: The tumor has spread to distant lymph nodes or to sites such as bones, liver, or lungs.
Read Also: Men’s Overactive Bladder Treatment
Changes In Bladder Habits Or Symptoms Of Irritation
Bladder cancer can sometimes cause changes in urination, such as:
- Having to urinate more often than usual
- Pain or burning during urination
- Feeling as if you need to go right away, even when your bladder isn’t full
- Having trouble urinating or having a weak urine stream
- Having to get up to urinate many times during the night
These symptoms are more likely to be caused by a urinary tract infection , bladder stones, an overactive bladder, or an enlarged prostate . Still, its important to have them checked by a doctor so that the cause can be found and treated, if needed.
What Is Advanced Prostate Cancer
When prostate cancer spreads beyond the prostate or returns after treatment, it is often called advanced prostate cancer.
Prostate cancer is often grouped into four stages, with stages III and IV being more advanced prostate cancer.
- Early Stage | Stages I & II: The tumor has not spread beyond the prostate.
- Locally Advanced | Stage III: Cancer has spread outside the prostate but only to nearby tissues.
- Advanced | Stage IV: Cancer has spread outside the prostate to other parts such as the lymph nodes, bones, liver or lungs.
When an early stage prostate cancer is found, it may be treated or placed on surveillance . Advanced prostate cancer is not curable, but there are many ways to treat it. Treatment can help slow advanced prostate cancer progression.
There are several types of advanced prostate cancer, including:
Biochemical Recurrence
With biochemical recurrence, the prostate-specific antigen level has risen after treatment using surgery or radiation, with no other sign of cancer.
Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Non-Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer that no longer responds to hormone treatment and is only found in the prostate. This is found by a rise in the PSA level, while the testosterone level stays low. Imaging tests do not show signs the cancer has spread.
Metastatic Prostate Cancer
- Lymph nodes outside the pelvis
- Bones
- Other organs, such as liver or lungs
Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer
Read Also: Reasons For Lack Of Bladder Control
Sex After Bladder Cancer Treatment
Surgery can damage sensitive nerves, making sex more difficult. Some men may have trouble having an erection, though for younger patients, this often improves over time. When the prostate gland and seminal vesicles are removed, semen can no longer be made. Women may also have trouble with orgasm, and may find sex less comfortable. Be sure to discuss treatment options with your doctor.
Five Types Of Standard Treatment Are Used:
Surgery
One of the following types of surgery may be done:
- Transurethral resection with fulguration: Surgery in which a cystoscope is inserted into the bladder through the urethra.A tool with a small wire loop on the end is then used to remove thecancer or to burn the tumor away with high-energy electricity. This is known as fulguration.
- Radical cystectomy: Surgery to remove the bladder and anylymph nodes and nearby organs that contain cancer. This surgery may bedone when the bladder cancer invades the muscle wall, or when superficialcancer involves a large part of the bladder. In men, the nearby organs that areremoved are the prostate and the seminal vesicles. In women, the uterus, theovaries, and part of the vagina are removed. Sometimes, when the cancer hasspread outside the bladder and cannot be completely removed, surgery to removeonly the bladder may be done to reduce urinarysymptoms caused by the cancer.When the bladder must be removed, the surgeon creates another way for urine toleave the body.
- Partial cystectomy: Surgery to remove part of thebladder. This surgery may be done for patients who have a low-grade tumor thathas invaded the wall of the bladder but is limited to one area of the bladder.Because only a part of the bladder is removed, patients are able to urinate normally afterrecovering from this surgery. This is also called segmental cystectomy.
- Urinary diversion: Surgery to make a new way forthe body to store and pass urine.
Radiation therapy
Chemotherapy
You May Like: How Do I Treat A Bladder Infection At Home
What Are The Risks Of Bladder Cancer
No single factor is directly connected to bladder cancer, but factors that can increase the risk include:
- Age: Bladder cancer typically affects people age 55 and older.
- Smoking: Carcinogens from tobacco smoke come in contact with the lining of the bladder. Smokers are three times as likely as non-smokers to get bladder cancer.
- Family history: There is evidence that bladder cancer may have a genetic component.
- Industrial chemicals: Chemicals known as aromatic amines are often used in the dye industry. Workers who have daily exposure to them, such as painters, machinists and hairdressers, may be at a higher risk for bladder cancer.
- Drinking contaminated water: This includes water that has been treated with chlorine or drinking water with a naturally high level of arsenic, which occurs in many rural communities in the United States,.
- Taking certain herb: Supplements such as Aristolochia fangchi, a Chinese herb, sometimes used for weight loss has been linked to higher rates of bladder cancer.
Living With Bladder Cancer
Cancer is a life-changing experience. And although there’s no surefire way of preventing a recurrence, you can take steps to feel and stay healthy. Eating plenty of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and keeping to modest portions of lean meat is a great start. If you smoke, stop. Limit alcohol to one drink a day for women and up to two drinks a day for men. Daily exercise and regular checkups will also support your health and give you peace of mind.
You May Like: Recurrent Bladder Infections And Cancer
What Is Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
Muscle invasive bladder cancer is a cancer that spreads into the detrusor muscle of the bladder. The detrusor muscle is the thick muscle deep in the bladder wall. This cancer is more likely to spread to other parts of the body.
In the U.S., bladder cancer is the third most common cancer in men. Each year, there are more than 83,000 new cases diagnosed in men and women. About 25% of bladder cancers are MIBC. Bladder cancer is more common as a person grows older. It is found most often in the age group of 75-84. Caucasians are more likely to get bladder cancer than any other ethnicity. But there are more African-Americans who do not survive the disease.
What is Cancer?
Cancer is when your body cells grow out of control. When this happens, the body cannot work the way it should. Most cancers form a lump called a tumor or a growth. Some cancers grow and spread fast. Others grow more slowly. Not all lumps are cancers. Cancerous lumps are sometimes called malignant tumors.
What is Bladder Cancer?
When cells of the bladder grow abnormally, they can become bladder cancer. A person with bladder cancer will have one or more tumors in his/her bladder.
How Does Bladder Cancer Develop and Spread?
The bladder wall has many layers, made up of different types of cells. Most bladder cancers start in the urothelium or transitional epithelium. This is the inside lining of the bladder. Transitional cell carcinoma is cancer that forms in the cells of the urothelium.
New And Experimental Treatments
Several new treatments may prove useful in treating bladder cancer. Photodynamic therapy, used in early stage cancers, uses a laser light to activate a chemical that kills cancer cells. Some gene therapies use lab-created viruses to fight cancer. And targeted therapies aim to control the growth of cancer cells. You may be eligible to participate in a clinical trial of these or other cutting-edge treatments.
21) Carol & Mike Werner / Visuals Unlimited / Corbis
American Urological Association: “Bladder Cancer.”
American Urological Association Foundation: “Hematuria.”
Journal of the American Medical Association: Association Between Smoking and Risk of Bladder Cancer Among Men and Women.
Occupational & Environmental Medicine: Bladder cancer among hairdressers: a meta-analysis.
British Journal of Cancer: Occupation and bladder cancer: a cohort study in Sweden.
National Cancer Institute: “Staging,” “Bladder Cancer Treatment,” “Drugs Approved for Bladder Cancer,” “SEER Stat Fact Sheets: Bladder.”
NIH Research Matters: “Smoking and Bladder Cancer.”
ScienceDaily: “Cigarette Smoking Implicated in Half of Bladder Cancers in Women Bladder Cancer Risk from Smoking Is Higher Than Previously Estimated, Study Confirms.”
Stanford Cancer Institute: “Information About Bladder Cancer.”
World Health Organization: “Tobacco Free Initiative — Cancer.”
Read Also: What Causes An Overactive Bladder In Males
Bladder Cancer Treatment: Surgery
Transurethral Resection
Early-stage cancers are most commonly treated by transurethral surgery. An instrument with a small wire loop is inserted through the urethra and into the bladder. The loop removes a tumor by cutting or burning it with electrical current, allowing it to be extracted from the bladder.
Partial and Radical Cystectomy
Partial cystectomy includes the removal of part of the bladder. This operation is usually for low-grade tumors that have invaded the bladder wall but are limited to a small area of the bladder. In a radical cystectomy, the entire bladder is removed, as well as its surrounding lymph nodes and other areas that contain cancerous cells. If the cancer has metastasized outside of the bladder and into neighboring tissue, other organs may also be removed such as the uterus and ovaries in women and the prostate in men.
Tests To Determine Stage And Grade
Bladder cancer is classified by stage and grade. The stage is determined by the cancer growth in the bladder wall and how far it has spread to nearby tissues and other organs, such as the lungs, the liver, or the bones. The grade of bladder cancer is determined by how the cancer cells look in comparison with normal bladder cells.
Your doctor finds out the stage and grade of your bladder cancer by gathering information from several tests, including:
- Biopsies from the cystoscopy.
- An intravenous pyelogram or CT urogram to look for a mass near the kidneys, ureters, or bladder.
- Ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging . These help find out if the cancer has spread to lymph nodes, the lungs, the liver, or other abdominal organs.
- CT scan. This finds out if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
- Chest X-ray. This finds out if the cancer has spread to the lungs.
- Bone scan. This finds out if the cancer has spread to the bones.
Knowing the stage and grade of your cancer is important in choosing the right treatments.
Also Check: Will Overactive Bladder Go Away
Types Of Bladder Cancer
The main types of bladder cancer are named for the type of cells that become cancerous. The most common is urothelial carcinoma , which begins in the cells that line the inside of the bladder.
Squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma are much less common.
Stage 0: Cancer stays in the inner lining.Stage I: Cancer has spread to the bladder wall.Stage II: Cancer has reached the muscle of the bladder wall.Stage III: Cancer has spread to fatty tissue around the bladder and possibly certain nearby lymph nodes. It may also have spread to the prostate in men or the uterus or vagina in women.Stage IV: Cancer has spread to the pelvic or abdominal wall, lymph nodes, or distant sites such as bone, liver, or lungs.
Possible Causes Of Bladder Cancer: Smoking
Smoking is the greatest known risk factor for bladder cancer smokers are four times more likely to get bladder cancer than nonsmokers. Harmful chemicals from cigarette smoke enter the bloodstream in the lungs and are ultimately filtered by the kidneys into the urine. This leads to a concentration of harmful chemicals inside the bladder. Experts believe that smoking causes about half of all bladder cancers in men and women.
Recommended Reading: Overactive Bladder At Night Time Only
What Breeds Of Dogs Get Bladder Cancer
Several breeds, in particular Terriers, are more likely to develop bladder cancer. Owners of Scottish Terriers should be aware the breed has an 18 fold higher chance of being diagnosed with TCC than other dogs .
Shetland Sheepdogs, Beagles, West Highland White Terriers, and Wire Hair Fox Terriers are also more at risk of developing TCC than other breeds. It is unclear why these breeds are prone to urinary tract cancer, although these breeds are less resilient to TCC and other urinary tract mutations, therefore the bloodlines of these dogs have significance.
Are There Other Early Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
Other early symptoms of bladder cancer that may be experienced are:
- Urinary irritation
- Changes in bladder habits
If youve noticed any of these symptoms and are concerned about bladder cancer, speak to your doctor as soon as possible and ask them about Cxbladder, a non-invasive genomic urine test that quickly and accurately detects or rules out bladder cancer.Learn more about Cxbladder
Recommended Reading: What Should I Do If I Have A Bladder Infection
Do The Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer Differ In Males And Females
In both males and females, blood in the urine is the most common symptom of bladder cancer and often the first sign that is noticed. However, while bladder cancer is more frequently diagnosed in men than in women, females often present with advanced tumors and their outcomes may be accordingly poorer.
A major reason for women presenting with more advanced bladder tumors is often the delay in receiving a diagnosis. This delay may occur because:
- Blood in the urine , the most common symptom of bladder cancer, may be discounted by women as being related to menstruation or post-menopausal bleeding.
- When blood in the urine and urinary irritation is reported to a doctor it may be initially misdiagnosed as a urinary tract infection , which has similar initial symptoms to bladder cancer .
- UTIs and bladder cancer can occur at the same time, in which case the UTI will be the logical first diagnosis.
- If a woman subsequently presents after treatment failure for a misdiagnosed UTI, further antibiotics may be prescribed rather than carrying out a complete urological evaluation.
Because of this confusion, a definitive diagnosis of bladder cancer may be delayed in some women. Of concern in these situations is the risk that bladder cancer becomes more advanced and may therefore be more difficult to treat.