Medicine For Stress Incontinence
If stress incontinence does not significantly improve with lifestyle changes or exercises, surgery will usually be recommended as the next step.
However, if you’re unsuitable for surgery or want to avoid an operation, you may benefit from an antidepressant medicine called duloxetine. This can help increase the muscle tone of the urethra, to help keep it closed.
You’ll need to take duloxetine tablets twice a day and will be assessed after 2 to 4 weeks to see if the medicine is beneficial or causing any side effects.
Possible side effects of duloxetine can include:
- nausea
- constipation
Do not suddenly stop taking duloxetine, as this can also cause unpleasant side effects. A GP will reduce your dose gradually.
Duloxetine is not suitable for everyone, however, so a GP will discuss any other medical conditions you have to determine if you can take it.
Medications For Urinary Incontinence
If medications are used, this is usually in combination with other techniques or exercises.
The following medications are prescribed to treat urinary incontinence:
- Anticholinergics calm overactive bladders and may help patients with urge incontinence.
- Topical estrogen may reinforce tissue in the urethra and vaginal areas and lessen some of the symptoms.
- Imipramine is a tricyclic antidepressant.
When To Seek Medical Advice
See a GP if you have any type of urinary incontinence. Urinary incontinence is a common problem and you should not feel embarrassed talking to them about your symptoms.
This can also be the first step towards finding a way to effectively manage the problem.
Urinary incontinence can usually be diagnosed after a consultation with a GP, who will ask about your symptoms and may do a pelvic or rectal examination, depending on whether you have a vagina or a penis.
The GP may also suggest you keep a diary in which you note how much fluid you drink and how often you have to urinate.
Find out about diagnosing urinary incontinence.
Also Check: What Does Overactive Bladder Feel Like
Who Is Most At Risk
In addition to the causes mentioned above, there are some things that can increase your risk of developing urinary incontinence without directly being the cause of the problem. These are known as risk factors.
Some of the main risk factors for urinary incontinence include:
- family history there may be a genetic link to urinary incontinence, so you may be more at risk if other people in your family have experienced the problem
- increasing age urinary incontinence becomes more common as you reach middle age and is particularly common in people over 80
- having lower urinary tract symptoms a range of symptoms that affect the bladder and urethra
Different Types Of Incontinence
Incontinence is generally categorized as:
Functional IncontinencePatients with functional incontinence have mental or physical disabilities that keep them from urinating normally, although the urinary system itself is structurally intact. Conditions that can lead to functional incontinence include Parkinson’s Disease, Alzheimer’s Disease and other forms of dementia.
Urge incontinencePeople that leak urine after a strong, sudden urge to urinate, have urge incontinence. Its caused by over activity of the bladder muscles and can be caused by a range of conditions like mental stress, nerve damage , infections, tumors or bladder stones. A thorough assessment of the underlying causes is, therefore, essential for treatment. Urge incontinence often starts with the consistent urge to urinate although the urine can be held. It progresses to the point where the urge cannot be controlled any longer. Urge incontinence can be treated with medication that helps regulate the activity of the bladder as well as exercises, to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and bladder training for the extension of urination intervals to aid improved bladder capacity and reduced frequency.
Mixed IncontinenceMixed incontinence refers to a combination of stress and urge incontinence. Many patients experience symptoms of both types. A thorough examination of the causes is essential for effective treatment.
- Brands
Also Check: I Feel A Lot Of Pressure On My Bladder
What Your Treatment Will Involve
Your healthcare providers recommended treatment plan will depend on the cause of your incontinence. An underlying medical condition may require medication, surgery, or other treatments.
You may also be encouraged to do certain exercises, such as pelvic floor exercises or bladder training, which can help to increase your bladder control.
In certain situations, your healthcare provider may not be able to cure your bladder incontinence. In these cases, there are steps you can take to manage your condition.
For example, your healthcare provider may advise you to:
- adjust your diet or fluid intake
- maintain a clear and well-lit path to the bathroom
It Could Be A Sign Of An Underlying Condition
Naturally, later in life, people can experience incontinence because of increased production of urine related to aging kidneys. Bladder function is also heavily impacted by changing bladder capacity and chronic medical conditions like diabetes, says Fairchild. Chronic straining, coughing and/or constipation can all put stress on the bladder, she explains.
But leakage can also be sign of a more serious, underlying health condition, according to a 2018 National Poll on Healthy Aging.” For example, poor heart function could be the culprit behind frequent urination while sleeping.
If fluid is pooling in your legs during the day, when you lay down, that fluid redistributes and increases urine production, says Fairchild.
Although bladder leakage is common, discuss your particular symptoms with your doctor.
Read Also: New Treatments For Neurogenic Bladder
Loss Of Control Of Urine In Men
Welcome to this Guide about Loss of Urine Control for men.
Loss of urine or bladder control is a surprisingly common problem, especially in older men. It’s estimated that 1.5 to five percent of men under age 65 experience problems with urine control. After age 65 this number increases to between 15 and 30 percent, and up to half of people in nursing homes lose control of their bladder for some or all of the time.
Loss of urine control may develop for a number of reasons. Problems with the bladder and prostate gland are probably the most common, but in many men the cause lies outside of the urinary tract. For example, severe constipation and certain medications can reduce bladder control. In some men, more than one problem is present.
It’s also important to realize that some causes of incontinence are quite simple, while others are very serious. In the same way, some causes of incontinence may be easy to treat, while others may be long-lasting.
Men who experience new loss of urine control should see their doctor. This guide is intended to provide helpful information while you are awaiting further evaluation, or to add to what you may have already learned after an evaluation by your doctor. Please keep in mind that this information cannot replace a face-to-face evaluation with your own health care provider.
Have you had recent surgery or a medical procedure that involves the urinary tract? Examples include
Managing Bladder Or Urinary Incontinence
Sometimes urinary incontinence can last a short time, depending on what’s causing it. But sometimes incontinence can be long-term and uncomfortable, making some everyday activities difficult to manage.
Your health care team will ask you questions to determine the type of bladder incontinence you might have. Then, you might need tests to verify the type and learn the cause of it which will help them know the best way to manage it.
- Pelvic floor muscle strengthening may be recommended. A physical therapist that specializes in pelvic floor muscle exercises can help. This might help muscle strength and bladder control get better by doing exercises that tighten and relax muscles that control the flow of urine.
- Bladder training canhelp manage how often you need to urinate throughout the day, by assigning certain time intervals to empty your bladder.
You May Like: Recurrent Bladder Infections And Cancer
What Are The Treatments For Urinary Incontinence
Treatment depends on the type and cause of your UI. You may need a combination of treatments. Your provider may first suggest self-care treatments, including:
- Lifestyle changes to reduce leaks:
- Drinking the right amount of liquid at the right time
- Being physically active
- Staying at a healthy weigh
- Avoiding constipation
- Not smoking
If these treatments do not work, your provider may suggest other options such as:
- Medicines, which can be used to
- Relax the bladder muscles, to help prevent bladder spasms
- Block nerve signals that cause urinary frequency and urgency
- In men, shrink the prostate and improve urine flow
How To Stop Urine Leakage When Coughing
Its important to know that you have the power to control, or learn how to control, your pelvic floor muscles, and train them to do what you want.
This is not something youre taught how to do after potty training because your body is naturally supposed to know how to do this. Most often it does, however, sometimes we can lose the ability to do it.
If it becomes a problem for you later in life, then thats something you need to deal with on your own and to assume youre the only one suffering from this issue. That is false and should never be taken for granted.
However, your physical and mental health is in your hands and how you treat your body and whether you accept this as normal or as a problem is something that is also up to you.
Prevention is key, so even if you dont suffer from stress incontinence at all, knowing how to use your pelvic floor muscles is very important.
Pelvic Floor Exercises
Research shows some of the strongest evidence in fighting back against stress incontinence is pelvic floor muscle exercises.
You can find exercises online about how to retrain your pelvic floor. However, you can also see a pelvic floor physiotherapist, and gain more personalized help and techniques, which is a very beneficial thing to do.
Overall, what we want to accomplish is teaching your brain and your bladder to communicate in times such as coughing, what to do and what not to do.
Kegel Exercises
Make Scheduled Bathroom Visits a Habit
Also Check: How Long Can You Live With Aggressive Bladder Cancer
When Should I See A Health Care Professional
See a health care professional if you have symptoms of a bladder problem, such as trouble urinating, a loss of bladder control, waking to use the bathroom, pelvic pain, or leaking urine.
Bladder problems can affect your quality of life and cause other health problems. Your health care professional may be able to treat your UI by recommending lifestyle changes or a change in medicine.
Types Of Bladder Control Problems

Anyone can have bladder control problems or incontinence. Incontinence caused by cancer or cancer treatment can last a short time or a long time, and it can be mild or severe. There are different types of bladder control problems.
Stress incontinence. Urine leaks out during activities such as coughing, laughing, sneezing, or exercising.
Overflow incontinence. Urine leaks out when your bladder is full.
Urge incontinence. You feel the urge to go to the bathroom right away and urine leaks before you can get to the bathroom.
Continuous incontinence. Urine leaks out constantly, and you cannot control it.
These bladder problems can make you feel uncomfortable or embarrassed. Sometimes, people avoid activities they enjoy because of bladder problems. That can affect your quality of life. These are reasons why it is important to tell your health care provider about your experiences. They can help you treat incontinence. The treatment of side effects is an important part of your cancer care and treatment, called palliative care or supportive care. Talk with your health care team about how to treat or manage incontinence.
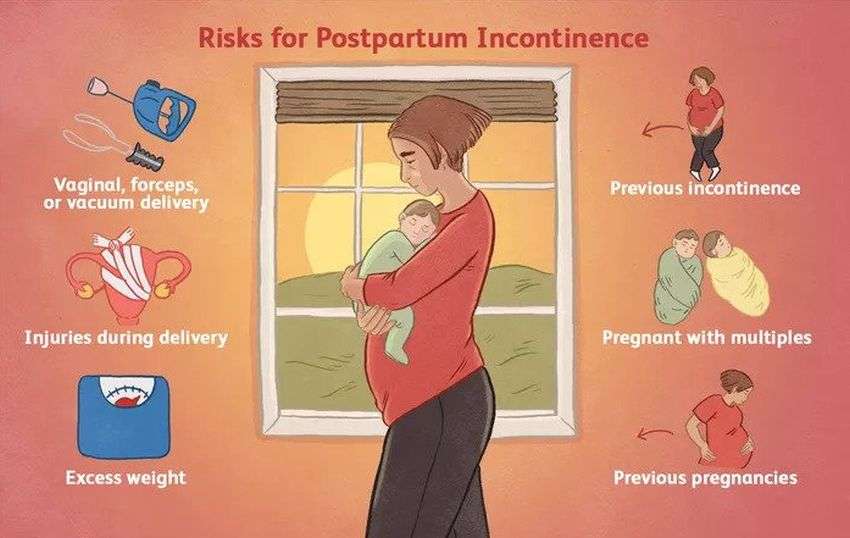
Read Also: How To Fix Bladder Leakage After Pregnancy
My Experience With Loss Of Bladder Control
I know first hand what it feels like the first time your shortness of breath causes you to lose control of your bladder in public. In my early years with COPD I was like many of you who are new to COPD are: unaware incontinence is a consequence of having severe COPD. I will never forget how embarrassed and ashamed I felt at the checkout counter in Walmart, and the look on the faces of the people around me. I was so SOB, I was already the object of everyone’s stares, and losing control of my bladder and standing in a puddle of my own urine, my pants soaked made me want to die.
Treatments For Stress Incontinence
Stress incontinence occurs when weakened pelvic floor muscles cant hold up to the pressure on the bladder and urethra. These muscles may have weakened due to age, vaginal birth, or obesity.
If the issue may be related to weight, well talk about weight loss. As little as an 8 percent weight loss can decrease incontinence by half. I also recommend that patients work with a physical therapist who specializes in pelvic floor exercises. These exercises strengthen the muscles that control urination.
Another option is a pessary, which is a device that supports the walls of your vagina and lifts the bladder and urethra. Its a non-surgical fix. If were still not finding relief after trying a pessary, the surgical option is a urethral sling, which is a type of mesh thats placed under the urethra.
When you cough, for example, and the urethra moves, the mesh provides extra support for the muscles that arent doing their job.
When To Contact A Medical Professional
Talk to your provider about incontinence. Providers who treat incontinence are gynecologists and urologists that specialize in this problem. They can find the cause and recommend treatments.
- Difficulty talking, walking, or speaking
- Sudden weakness, numbness, or tingling in an arm or leg
- Loss of vision
- Loss of consciousness or confusion
- Loss of bowel control
- Cloudy or bloody urine
- Frequent or urgent need to urinate
- Pain or burning when you urinate
- Trouble starting your urine flow
- Fever
Is Urinary Incontinence Just Part Of Growing Older
No. But changes with age can reduce how much urine your bladder can hold. Aging can make your stream of urine weaker and can cause you to feel the urge to urinate more often. This doesnt mean youll have urinary incontinence just because youre aging. With treatment, it can be controlled or cured.
Learn More About Urinary Incontinence
There are 5 types of urinary incontinence, described below.
What Is Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence refers to a loss or leaking of urine due to faulty bladder control. An estimated 25% to 33% of people in the United States suffer from urinary incontinence. That means millions of people live with the condition. There are many different types of urinary incontinence. Although both men and women suffer from the condition, several factors unique to women increase the risk of urinary incontinence in females. It’s a common misconception that this is a normal part of aging. It is not. Thankfully, there are lots of ways to manage urinary incontinence and minimize the effect it has on your life.
Wide-Ranging Consequences
Urinary incontinence is more than a health concern. It affects people on a social, psychological, and emotional level. People who have urinary incontinence may avoid certain places or situations for fear of having an accident. Urinary incontinence can limit life, but it doesn’t have to. The concern is treatable once the underlying cause is identified and addressed.
What Causes Loss Of Bladder Control
A loss of bladder control can be very embarrassing, and unfortunately is caused by a number of conditions. The most common cause of a loss of bladder control is pregnancy, though the condition can also be related to an infected or enlarged prostate. In addition, some prescription medications are to blame for a decrease in bladder control, specifically those which work as muscle relaxants. Neurological conditions, like stroke, epilepsy, and other similar diseases, may also contribute. Often, individuals who experience this condition are encouraged to undergo physical or occupational therapy to learn how to better control bladder function.
Pregnancy is one of the most common conditions linked to a loss of bladder control. Often, women who are pregnant experience a decrease in the strength of the bladder and urethra, due to increased weight. While loss of bladder control often disappears with child birth, some women may continue to experience the condition long after the baby has been born. This is most often the case in women who have had several pregnancies, which has repeated stress on these parts of the body.
Additional Treatments For Urinary Incontinence
Nerve Stimulation
If behavioral and lifestyle interventions do not bring relief of urinary incontinence, electrical nerve stimulation may be an option to consider. Small devices implanted near the tibial nerve in the ankle or the sacral nerve in the lower back deliver impulses that help relieve urinary incontinence symptoms. Stimulation of the tibial nerve interrupts the impulses from the bladder that go to the brain. Stimulation of the sacral nerve may improve blood flow to the bladder and make pelvic muscles that control the bladder stronger. Nerve stimulation may also trigger the relief of chemicals that block pain.
Other Procedures
In some cases of urinary incontinence unresponsive to other treatments, a physician may inject bulking agents near the urinary sphincter to help close the bladder opening. A mixture of collagen and carbon beads are injected under local anesthesia. About 40% of those who undergo the procedure have a successful outcome. If a neurological condition is contributing to the issue, Botox injections to the bladder may provide relief by decreasing bladder contractions. In cases where weak or prolapsed pelvic organs play a role, surgery may be required.