Which Bacteria Cause Uti
Escherichia coli is the most common cause of UTI and is responsible for about 80 to 85% of all UTIs. Other bacteria involved in UTIs include Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas and Enterococcus. UTIs are rarely due to viral, fungal and parasitic infections.
It is thought that in women who experience recurrent bacterial UTI that the normal healthy bacteria that live in the vagina are replaced by uropathogenic bacteria from the bowel. Uropathogenic bacteria have features that make it easier for them to enter, breed and survive in the urinary tract.
How Are Utis Treated
UTIs are usually treated with antibiotics. To help avoid the recurrence of a UTI, it is important to ensure that the full antibiotic course is completed.
Can UTI symptoms linger after antibiotic treatment?
If antibiotic treatment has been effective, UTI symptoms should be fully resolved. When symptoms persist at completion of the prescribed antibiotic course, further tests and treatment will be necessary. This may involve culturing a urine sample to determine which antibiotic types are effective against the infecting bacteria, and the use of diagnostic imaging to check the urinary tract.
How long can a UTI go untreated?
If you ever see blood in your urine or are concerned about other UTI signs and symptoms, contact your doctor. Seeking treatment promptly not only decreases the chance of UTI-related complications, but also helps to avoid extended periods of misdiagnosis if your symptoms are not being caused by a UTI.
If symptoms such as back pain, fever, and nausea/vomiting are present always seek urgent treatment, because of the risk of permanent kidney damage and/or life-threatening complications.
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections In Women: Diagnosis And Management
CHARLES M. KODNER, MD, University of Louisville School of Medicine, Louisville, Kentucky
EMILY K. THOMAS GUPTON, DO, MPH, Primary Care Medical Center, Murray, Kentucky
Am Fam Physician. 2010 Sep 15 82:638-643.
Recurrent urinary tract infections are common in women and associated with considerable morbidity and health care use. The clinical features, diagnostic testing, and causative organisms are often similar to those of single cases of UTI, although there are additional treatment strategies and prevention measures to consider with recurrent UTIs.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
A urine culture with greater than 102 colony-forming units per mL is considered positive in patients who have symptoms of UTI.
| Clinical recommendation | Evidence rating | References |
|---|---|---|
|
Continuous and postcoital antimicrobial prophylaxis have demonstrated effectiveness in reducing the risk of recurrent UTIs. |
||
|
Cranberry products may reduce the incidence of recurrent symptomatic UTIs. |
||
|
Use of topical estrogen may reduce the incidence of recurrent UTIs in postmenopausal women. |
||
|
Treatment of complicated UTIs should begin with broad-spectrum antibiotic coverage, with adjustment of antimicrobial coverage guided by culture results. |
||
|
Prophylactic antimicrobial therapy to prevent recurrent UTIs is not recommended for patients with complicated UTIs. |
UTI = urinary tract infection.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
UTI = urinary tract infection.
You May Like: How Long Can You Live With Aggressive Bladder Cancer
Preventing Bladder Infections In Women
|
In women who experience three or more bladder infections in a year, these measures may help:
|
How Are Urinary Abnormalities Diagnosed
It’s important for a doctor to rule out any underlying problems in the urinary system when a child gets UTIs repeatedly. Kids with recurrent infections should see a pediatric urologist to see what is causing the infections.
Some problems can be found before birth. Hydronephrosis that develops before birth can be seen in an ultrasound as early as 16 weeks. In rare cases, doctors may consider neonatal surgery if hydronephrosis affects both kidneys and is a risk to the fetus. Most of the time, though, doctors wait until after birth to treat the condition, because almost half of all cases seen prenatally disappear by the time a baby is born.
Doctors will closely watch the blood pressure of a newborn thought to have hydronephrosis or another urinary system abnormality, because some kidney problems can cause high blood pressure. Another ultrasound may be done to get a closer look at the bladder and kidneys. If the condition appears to be affecting both kidneys, doctors usually will order blood tests to check kidney function.
Also Check: Losing Control Of Your Bladder
When Should I Call The Doctor
As soon as you think that your child has a UTI, call your doctor. The doctor may recommend another urine test after treatment to be sure that the infection has cleared.
If your child has from recurrent UTIs, consult a pediatric urologist, who can do a thorough evaluation and order tests for urinary system abnormalities. In the meantime, follow your doctor’s instructions for treating a UTI.
Check If It’s A Urinary Tract Infection
Symptoms of a UTI may include:
- pain or a burning sensation when peeing
- needing to pee more often than usual during the night
- pee that looks cloudy
- needing to pee suddenly or more urgently than usual
- needing to pee more often than usual
- lower tummy pain or pain in your back, just under the ribs
- a high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a very low temperature below 36C
You May Like: Men’s Overactive Bladder Treatment
Cranberry Juice And Tablets
Cranberry juice and tablets have been shown to reduce RUTIs as they contain a compound called tannin, or proanthocyanidin, which reduces E. coli vaginal colonisation., Although earlier, smaller studies have shown that consuming cranberry juice or tablets can prevent RUTIs, an updated Cochrane review showed that evidence for its benefit in preventing UTIs is small therefore, cranberry juice cannot be recommended any longer for UTI prevention.,
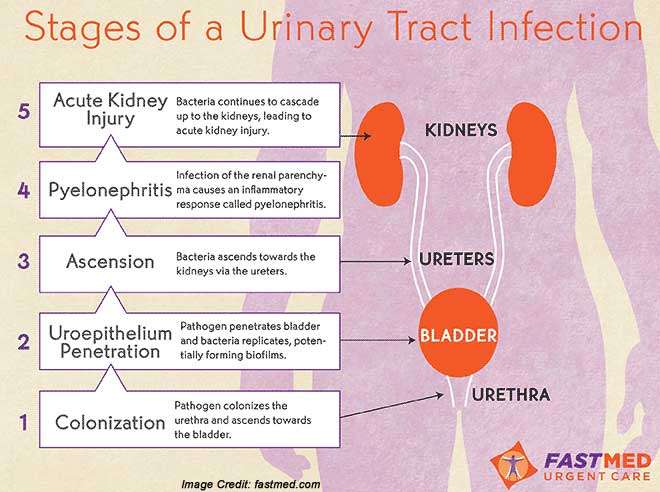
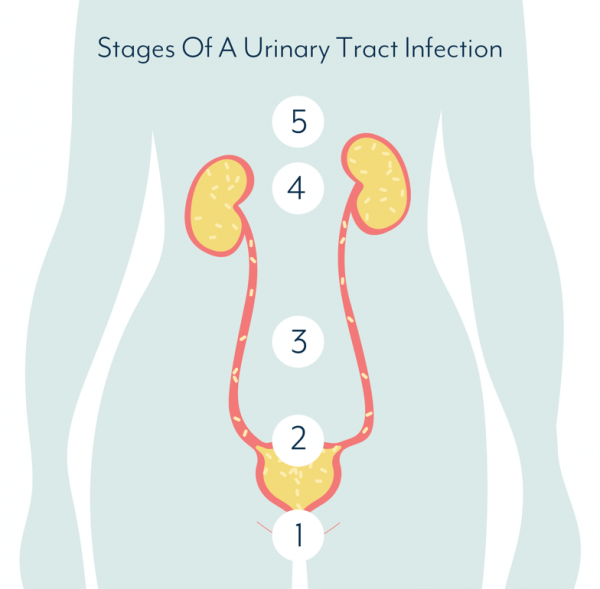
What Causes Urinary Tract Infection
The vast majority of urinary tract infections are caused by the bacteria Escherichia coli , which is usually found in the digestive system. However, other pathogens may cause a UTI. These include:
- Klebsiella pneumonia
- Enterococcus faecalis
- Staphylococcus saprophyticus
The bacteria may infect any part of the urinary tract bladder, urethra or kidneys. Depending on where the infection occurs, the UTIs are often known as:
- Cystitis infection of the bladder
- Urethritis infection of the urethra
- Pyelonephritis infection of the kidneys
The infection in urethra and bladder is usually not very serious and clears up with treatment. Similarly, ureters very rarely get infected. However, if a UTI reaches the kidneys, it may lead to kidney infections and a person may have to go to the hospital for treatment.
Also Check: Overactive Bladder At Night Time Only
Causes Of Chronic Utis
A whole slew of things can cause chronic UTIs, but these are some of the biggest causes.
Basic anatomy in itself may be the single biggest risk factor for UTIs, urologist Elodi Dielubanza, M.D., assistant professor of surgery at Harvard Medical School and associate surgeon at Brigham and Womens Hospital, tells SELF.
The reason is simple: The bacteria E. coli, which causes the majority of UTIs, is naturally present in your GI tract , but it can cause an infection if it gets to your urinary tract. The genital anatomy of someone with a vagina is conveniently set up in a way that makes this trip very quick and easy for that bacteria. Basically, the distance between the anus and the urethra is extremely short , as is the length of the urethra, which basically acts as a ladder that E. coli can climb up into the bladder, Dr. Dielubanza says. In comparison, people with penises tend to have a greater distance between their anus and their urethra, which makes these infections less likely .
Being sexually active is a UTI risk factor, the Mayo Clinic explains.
Because UTIs are sometimes thought of being a problem for young people, older people may be surprised to find they start getting more UTIs after they go through menopause, Dr. Vasavada says. This is thanks to a postmenopausal decline in estrogen. This estrogen deficiency alters the urinary tract in a way that can increase the risk of UTIs, according to the Mayo Clinic.
What Causes Chronic Bladder Infections In Dogs
Most dogs get UTIs when normal skin and gastrointestinal tract flora get past the urinary tract’s defenses. These bacteria then colonize the urinary tract, leading to an infection. E. coli is the most common bacterial cause of UTIs, but several bacteria and even some fungi can cause infections.
Besides, why does my dog keep getting bladder infections?
Recurrent urinary tract infections are common in dogs compared to cats. Common causes of a UTI relapse include inappropriate antibiotic use, persistence of the UTI within a urinary tract nidus , and emergence of drug-resistant pathogens.
Beside above, what can I give my dog for a urinary tract infection? It is suggested, for small dogs, to add a teaspoon of apple cider vinegar to their water or food. For a big dog, one to two tablespoons can be added. You can give this remedy up to twice a day for seven to ten days depending on the severity of the infection.
Also to know is, how do you prevent bladder infections in dogs?
Supplementation with B vitamins and antioxidants in times of stress, as well as offering cooling foods such as raw fruits, vegetables, and yogurt to reduce the symptoms of urinary tract infection. Foods that are known to aggravate UTIs include asparagus, spinach, raw carrots, tomatoes, and dairy products.
What causes bladder infections in female dogs?
You May Like Also
Read Also: How To Take Care Of A Bladder Infection At Home
Help My Dog Has Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections
If your dog has recurrent urinary tract infections , you are certainly concerned about their persistence. Urinary tract infections in dogs can be very unsettling to dogs. UTI’s lead to dogs peeing frequently and in small amounts, burning sensations and accidents around the home. Veterinarian Dr. Ivana shares what to do if your dog has recurrent urinary tract infections.
Urinary tract infections in dogs are painful, complex, and potentially dangerous issues occurring in as much as 27 percent of the dog population.
When a housebroken dog starts having accidents around the house, it is a red flag for a urinary tract infection. Straining while urinating, blood speckles in the urine, and licking the genitals are other red flags.
Best-case scenario, urinary tract infections are uncomfortable, and worst-case scenario, if left untreated, are life-threatening.
Dogs suspected of having a urinary tract infection or manifesting changes in standard urinating patterns need to be closely examined by a veterinarian.
How Is A Chronic Urinary Tract Infection Diagnosed
If you have a chronic UTI, you probably had a UTI in the past.
Performing lab tests on a sample of urine is the most common method doctors use to diagnose UTIs. A medical professional will examine the sample of urine under a microscope, looking for signs of bacteria.
In a urine culture test, a technician places a urine sample in a tube to encourage the growth of bacteria. After one to three days, theyll look at the bacteria to determine the best treatment.
If your doctor suspects kidney damage, they may order X-rays and kidney scans. These imaging devices take pictures of parts inside your body.
If you have recurring UTIs, your doctor may want to perform a cystoscopy. In this procedure, theyll use a cystoscope. Its a long, thin tube with a lens at the end used to look inside your urethra and bladder. Your doctor will look for any abnormalities or issues that could cause the UTI to keep coming back.
Don’t Miss: Botox Injection For Bladder Incontinence
Can A Uti Be A Sign Of Cancer Or Other Problems
Dr. Rx
If you have more than three UTIs in a year, you should be evaluated by a urologist. When infections occur in rapid succession, it can be a sign of an underlying problem with bladder or kidney drainage. Sometimes, when no specific cause is found, a low dose daily preventive antibiotic is used to prevent infection over a period of months. Dr. Mindrup
The vast majority of UTIs are not a sign of a serious disease. Yet when they keep coming back, you should see a doctor. They will rule out other causes such as kidney stones, poor drainage of the kidney or bladder, or tumors, all of which are rare causes of UTI.
In rare instances, recurrent UTIs can lead to a life threatening condition called urosepsis or bladder cancer.
Antibiotic Prevention Is Another Option
This means taking a low dose of an antibiotic regularly. One dose each night will usually reduce the number of bouts of cystitis. A six-month course of antibiotics is usually given.
You may still have bouts of cystitis if you take antibiotics regularly but the episodes should be much less often. If a bout does occur, it is usually caused by a germ which is resistant to the antibiotic you are taking regularly. A urine sample is needed to check on which bacterium is causing any bout of cystitis. You may then need a temporary change to a different antibiotic.
Read Also: Doterra Oils For Bladder Infection
How A Chronic Uti Develops
Why Are Women And Older Adults More At Risk
E. coli or other bacteria cause UTIs, which are infections in your kidneys, bladder, ureters or urethra. Unfortunately, women are more likely to get them mainly because of their anatomy.
A womans urethra is shorter than a mans and closer to the anus. The urethra is also close to the vagina, which can collect bacteria during sex. So bacteria from both the anus and vagina have easy access to a womans urinary tract.
Post-menopausal women are also at higher risk because pH changes in the vagina make it more susceptible to infection.
Both men and women are more likely to get UTIs as they age. Certain medical conditions, such as bladder prolapse in women and enlarged prostate in men, cause incomplete bladder emptying in older adults. Urine that stays in your bladder too long can encourage bacteria to grow.
Some newer diabetic drugs can also promote sugar in the urine and create conditions ideal for a UTI, Dr. Vasavada adds.
Don’t Miss: Will Overactive Bladder Go Away
Living With Urinary Tract Infections
If you have 3 or more urinary tract infections each year, your doctor may want you to begin a preventive antibiotic program. A small dose of an antibiotic taken every day helps to reduce the number of infections. If sexual intercourse seems to cause infections for you, your doctor many suggest taking the antibiotic after intercourse.
Things You Can Do Yourself
To help ease pain:
- takeparacetamolup to 4 times a day to reduce pain and a high temperature for people with a UTI, paracetamol is usually recommended over NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or aspirin
- you can give childrenliquid paracetamol
- rest and drink enough fluids so you pass pale urine regularly during the day, especially during hot weather
It’s important to follow the instructions on the packet so you know how much paracetamol you or your child can take, and how often.
It may also help to avoid having sex until you feel better.
You cannot pass a UTI on to your partner, but sex may be uncomfortable.
Taking cystitis sachets or cranberry products has not been shown to help ease symptoms of UTIs.
Also Check: How To Fix Bladder Leakage After Pregnancy
Why Are Women More Commonly Affected By Utis
Women are more commonly affected by UTIs because of:
- The female anatomy
- The female urethra is short which allows easier entry of skin and surface bacteria into the bladder.
- The female urethra is close to the vagina and back passage that normally contain bacteria and makes it easier for bacteria to enter the urinary system.
What Is A Uti
Before we talk about recurrent UTIs, lets talk about UTIs in general.
A UTI is an infection in any part of your urinary tract, the Mayo Clinic explains. The infection usually starts when bacteria normally found in your bowels get into the urethra, where pee exits from. Instead of urine flushing out the bacteria or your immune system fending it off like its supposed to, the bacteria begin to colonize the urinary tract, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases . Most UTIs stay in the urethra and bladder , per the Mayo Clinic.
Sometimes a UTI keeps coming back, which is called a recurrent UTI or a chronic UTI. Most people would say a true recurrent UTI is either two within six months or three within a year, Sandip Vasavada, M.D., urologic director of the Center for Female Urology and Reconstructive Pelvic Surgery at the Cleveland Clinic within the Glickman Urological Institute, tells SELF.
You May Like: I Feel A Lot Of Pressure On My Bladder