You Have An Enlarged Prostate
The urethra connects the bladder to the outside world. In women, its that simple. But in men, the tube goes through the prostate, which expands with age. As it expands, it can put undue pressure on the bladder and urethra. The bladder responds by becoming overactive and sensitive to even small amounts of urine, making you feel like you have to go even when your tank is relatively empty, explains Brahmbhatt.
Read More: What All Men Should Know About Taking Care Of Their Prostate
This is typically an issue in men over the age of 50, Brahmbhatt says. Still, strictures and chronic prostatitis can have similar side effects in younger guys.
What Is The Treatment For An Inability To Urinate
If urinary retention is thought to be acute, severe, or painful, a Foley catheter may be inserted through the urethra into the bladder. This is a small, flexible rubber or silicone tube. Once it has reached the bladder, urine will drain out into a bag and the balloon is inflated to keep the catheter in place.
If a catheter cannot reach your bladder because of an obstruction in the urethra, an alternative procedure can be tried.
- The most common reason for the obstruction is a narrowing or stricture within the urethra. In this setting, a cystoscopy can often identify the area of narrowing, and a small wire can be passed through the narrowed area, and the area can be dilated with special dilators that pass over the wire and a catheter placed.
- In the situation in which a catheter cannot be placed through the urethra, the catheter can be placed through your skin, over your pubic bone, and through the lower abdominal wall directly into your bladder. This is called the suprapubic route. This procedure is generally performed by urologists. The tube will provide temporary drainage until the situation can be managed via a cystoscopic procedure.
In the last few years, devices have become available that can help some people with chronic urinary retention. For example, an implantable device is available that stimulates the nerves that control the bladder. These devices are typically placed by a urologist and/or urogynecologist for select indications.
How Common Is Urinary Retention
Urinary retention in men becomes more common with age.
- In men 40 to 83 years old, the overall incidence of urinary retention is 4.5 to 6.8 per 1,000 men.
- For men in their 70s, the overall incidence increases to 100 per 1,000 men.
- For men in their 80s, the incidence of acute urinary retention is 300 per 1,000 men.
Urinary retention in women is less common, though not rare. The incidence of urinary retention in women has not been well studied because researchers have primarily thought of urinary retention as a man’s problem related to the prostate.
- weakened bladder muscles
Obstruction of the Urethra
Obstruction of the urethra causes urinary retention by blocking the normal urine flow out of the body. Conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasia — also called BPH — urethral stricture, urinary tract stones, cystocele, rectocele, constipation, and certain tumors and cancers can cause an obstruction.
As the prostate enlarges, the gland presses against and pinches the urethra. The bladder wall becomes thicker. Eventually, the bladder may weaken and lose the ability to empty completely, leaving some urine in the bladder.
Surgery to correct pelvic organ prolapse, such as cystocele and rectocele, and urinary incontinence can also cause urethral stricture. The urethral stricture often gets better a few weeks after surgery.
Nerve Problems
- pelvic injury or trauma
- heavy metal poisoning
Medications
Weakened Bladder Muscles
Also Check: What Does Overactive Bladder Feel Like
Whats The Best Way To Recover From A Gallbladder Removal
Recovery after gallbladder removal tip 1: Get out of bed and walk around Light activity after surgery, such as walking, can aid in your recovery. After a laparoscopic gallbladder removal, some of the carbon dioxide used during surgery might have remained in your abdomen, causing pain in your stomach and shoulders.
How Does Bladder Cancer Impact The Bladder Lining
Bladder cancer usually starts growing in the thin layer of cells that line the inside of the bladder. The cancer cells can gather together to form tumors in the bladder lining. In non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer, the tumors are only located in the bladder lining.
In muscle-invasive bladder cancer, the cancer is more advanced and the tumors may have grown deeper into the muscles of the bladder wall. If the bladder cancer has metastasized, it means that the cancer cells have spread to other parts of the body beyond the bladder. The symptom of being unable to urinate is more common among patients who have more advanced bladder cancer than in patients with early stage bladder cancer.
Recommended Reading: How Long Can You Live With Aggressive Bladder Cancer
Medication For Urinary Problems
Your doctor may suggest various medications to help ease your urinary problems, including:
- medications to reduce the tone of the muscles of the urethra and prostate to minimise any constriction to urine flow caused when these muscles contract
- medication to reduce the size of the prostate gland. These medications work by blocking the action of male hormones produced by the prostate gland
- medications to relax the bladder, making unwanted contractions less likely and reducing the symptoms of urgency and frequency of urination
- the over-the-counter preparation ‘saw palmetto’ is sometimes used. This may help some men, especially if frequent urination at night is a problem.
However, recent reviews of the evidence for using saw palmetto as a treatment for mild or moderate urinary symptoms did not show any improvement, compared to no treatment, in men with BPH.
Information For Healthcare Providers On Bladder Control Problems
The content on this page will be of most use to clinicians, such as nurses, doctors, pharmacists, specialists and other healthcare providers.
The following signs and symptoms are cause for concern and require referral to a specialist for further investigation:
| Red flags for referral in people with incontinence |
|
Males with urinary incontinence and any of the following factors should be referred to an appropriate specialist within 2 weeks:
|
|
Consideration for referral to a urologist should be given to patients with the following factors:
|
Read Also: Overactive Bladder At Night Time Only
Urination Difficulty At A Glance:
- Having trouble urinating also referred to as voiding difficulty is caused by an underlying mechanical problem with the coordination between the urethra and the bladder muscle that allows urine to freely pass.
- Urination problems include difficulty initiating urination and impaired bladder emptying, as well as urinary incontinence.
- Urine voiding problems in women can be caused by a variety of conditions, including urinary retention, prolapsed bladder, urinary tract infections, and the effects of menopause and pregnancy.
- Symptoms are painful urination, difficulty starting the urine stream, a sense of incomplete bladder voiding, and sometimes an inability to urinatean emergency situation known as acute urinary retention that requires immediate treatment.
- Treatments for voiding problems depend upon the underlying cause, but may include bladder muscle conditioning, medications, implant devices and surgery.
What Exams And Tests Assess The Causes Of Urinary Retention
Medical evaluation for urinary retention includes a medical and physical examination as well as laboratory tests to find the cause of the problem.
On physical examination, the bladder may be visible and/or palpable . A rectal examination in a male may demonstrate an enlarged prostate, an enlarged prostate with hard areas suspicious for prostate cancer, or prostate tenderness suggestive of prostatitis. A penile examination can identify abnormalities of the penile skin and the meatus, the opening at the tip of the penis that urine passes through, or signs of prior penile surgery such as prior hypospadias repair. Examination of the genitalia in a female may demonstrate a large cystocele . A rectal examination in both males and females may reveal fecal impaction.
A bladder scan is often used to determine how much urine is in the bladder to confirm the diagnosis of urinary retention.
A renal and bladder ultrasound may be helpful to determine if there is hydronephrosis or bladder stones.
A pelvic ultrasound or CT of the abdomen/pelvis may be indicated to check for pelvic, abdominal, or retroperitoneal conditions.
A catheter can be placed in the urethra. This is a thin, flexible tube. It goes up the bladder and drains the urine into a bag.
Other lab tests may be done, depending on your doctor’s conclusions from your medical interview and exam.
Don’t Miss: Doterra Oils For Bladder Infection
What Causes Bladder Pressure
Doctors arent sure what exactly causes IC. What they do know is that the bladder normally fills and then tells your brain to use the bathroom. It communicates this through the nerves in your body.
With IC, these signals get mixed up. You may feel like you need to urinate more frequently but without a lot of urine at each bathroom trip.
Bladder pressure may also be caused by:
- a defect in the lining of the bladder
- an autoimmune reaction
IC is more common in women than in men. Some people who have IC, also have other health issues such as irritable bowel syndrome and fibromyalgia. Other pain syndromes are also possible.
People who have both fair skin and red hair also have a greater risk of IC.
IC is primarily diagnosed in people in their 30s or older.
What Is Urinary Retention
Urinary retention is a condition where your bladder doesnt empty all the way or at all when you urinate. Your bladder is like a storage tank for urine. Urine is made up of waste thats filtered out of your blood by your kidneys. Once filtered, the urine moves to your bladder where it waits till its time to move through the urethra and out of the body.
When you have urinary retention, it can be acute or chronic . Acute means that it comes on quickly and it could be severe. Chronic urinary retention means that youve had the condition for a longer period of time.
The acute form of urinary retention is an emergency. In this case, youll need to see a healthcare provider right away. The chronic form happens most of the time in older men, but it can also occur in women.
You May Like: How To Relieve Bladder Spasms With Catheter
Free Just Cant Wait Toilet Card
The most common cause of difficult urination in men is a blockage due to an enlarged prostate restricting the outlet from the bladder. For women one of the common causes of difficulty in urination is an anterior prolapse/bladder prolapse which can distort the urethra and restrict the flow of urine.
Overactive Bladder And Gender
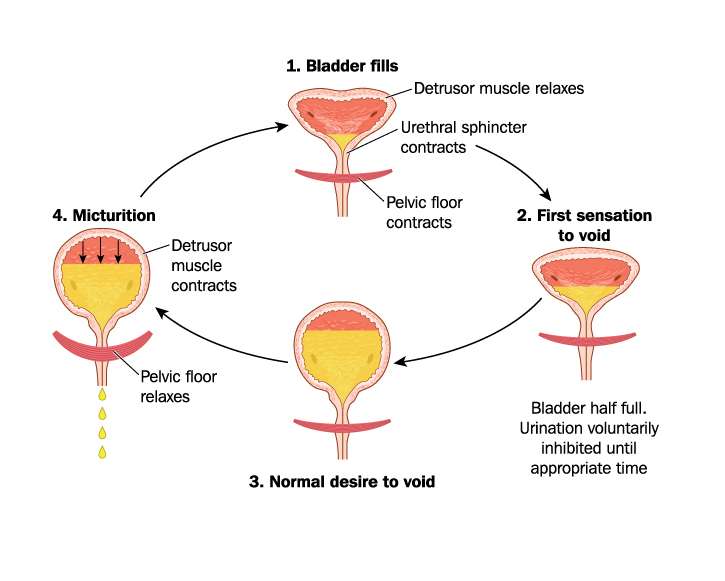
Normally, the brain says time to go when your bladder is about half full. To urinate, the bladder wall squeezes inward as a valve called the urinary sphincter relaxes open so the bladder can drain into the urethra.
But with overactive bladder, the bladder muscles start to quiver whether your bladder is full or not. As a result, you experience a powerful urge to urinate. The result can anything from a small leak to soaked garments.
In women, childbirth or menopause can weaken muscles in the bladder or pelvic floor, causing overactive bladder and incontinence. In men, overgrowth of the prostate gland, or benign prostatic hyperplasia , can put pressure on the bladder and trigger various urinary problems, including overactive bladder. Neuromuscular disorders , stroke, and diabetes are also associated with overactive bladder.
Sometimes the cause of overactive bladder is unclear, but that wont prevent you from finding a treatment that helps.
You May Like: Will Overactive Bladder Go Away
Mistake : Not Emptying Fully
When youre in a rush, incomplete bladder emptying can cause issues far more problematic than taking the extra minute or so in the bathroom. Similar to urine-holding, incomplete bladder emptying allows a reservoir of urine to collect that can potentially cause urinary infections. It can also increase the odds of developing another painful problembladder stones, which are salt crystals that sometimes form when urinary concentration or stasis develops.
Incomplete emptying isnt something you are always aware you’re doing, but its a good idea to make an effort to ensure you are emptying your bladder, says Dr. Brito. He says this is a particular problem for older men with prostate issues. For them, incomplete bladder emptying can lead to a smaller functional bladder capacity and subsequent urinary frequency and urgency problems.
Often as men get older, they will not completely empty their bladder. The problem there is, if your bladder’s full and you empty it halfway and then drink fluids like you normally would, it fills up more quickly, says Dr. Brito.
Sometimes educating patients to take their time in the bathroom and ensure their bladder is as empty as possible can help, says Dr. Brito. Other times, patients may need medications or surgery to help the bladder empty better.
Possible Reasons Why Your Bladder Always Feels Full
Posted on
If youre someone whose bladder always feels full, you might be wondering why youre saddled with so many trips to the bathroomand frustrated by the inconvenience.
Theres a natural connection between hydration and urination, of course, but thats only one factor that determines how many times you relieve your bladder each day.
One excuse you can rule out: a tiny bladder. While theres some variation in size, most bladders generally hold about two cups of fluid, says Jamin Brahmbhatt, M.D., board-certified urologic surgeon. So nope, your bladder isnt special.
On average, people empty their bladders about six-to-eight times daily, and as they age, this may include an additional one-to-two times per night. If youre going more than this, here are seven potential reasons why.
Don’t Miss: Botox Injection For Bladder Incontinence
What Are The Symptoms Of Urinary Retention
The signs can vary. Some people with the chronic form have a hard time starting the flow of urine. Some have a weak flow once they start. Others may feel the need to go but cant start. Others have to go a lot, while others still feel the need to go right after going. You may leak urine when you arent going because the bladder is full.
With the acute form, youre all of a sudden not able to go at all, or only able to go very small amounts. This occurs even though you have a full bladder. See a healthcare provider right away if this happens to you.
What Is Bladder Fullness
Bladder fullness is a sensation that the bladder is filled to capacity and there is a need to urinate. This is also known as urinary or bladder urging. It is normal sensation that every person experiences as the bladder fills close to its maximum capacity. It serves as a signal that a person needs to find the appropriate facility to urinate. Although the sensation can be ignored for a period of time if the situation is not suitable, the sensation gradually intensifies until a person can no longer bear it or a person may end up urinating involuntarily.
However, sometimes the bladder fullness sensation occurs even after passing urine or with there being only small amounts of urine contained within the bladder compared to its normal capacity. In these cases the sensation is abnormal and most likely a symptom of some underlying disease of the bladder. It is more correctly known as urinary or vesical tenesmus. Although the causes of this bladder fullness sensation is largely the same for both males and females, there are some conditions which are specific to each gender that results in this abnormal feeling.
You May Like: New Treatments For Neurogenic Bladder
Cause Of Urinary Problems As Men Age
Many men experience urinary symptoms as they age, which may be caused by inflammation of the prostate gland . In older men, symptoms may be due to a blockage in the tubes due to a benign enlargement of the prostate gland . The most common symptom is difficulty emptying your bladder. Urinary symptoms may become bothersome enough that they require treatment. Not all urinary symptoms are due to changes to the prostate. Also, some men have enlarged prostates and yet experience few, if any, symptoms.
How Is Chronic Urinary Retention Diagnosed
History and physical exam: During the diagnosis process, your healthcare provider will ask about your signs and symptoms and how long you have had them. He or she will also ask about your medical history and your drug use. A physical exam of the lower abdomen may show the cause or give your provider additional clues. After this, certain tests may be needed. Men may have a rectal exam to check the size of their prostate.
Your urine may be saved and checked to look for infection.
Ultrasound of the bladder: The amount of urine that stays in your bladder after urinating may be measured by doing an ultrasound test of the bladder. This test is called a postvoid residual or bladder scan.
Cystoscopy: Cystoscopy is a test in which a thin tube with a tiny camera on one end is put into your urethra. This lets the doctor look at pictures of the lining of your urethra and bladder. This test may show a stricture of the urethra, blockage caused by a stone, an enlarged prostate or a tumor. It can also be used to remove stones, if found. A computed tomography scan may also help find stones or anything else blocking the flow of urine.
Urodynamic testing: Tests that use a catheter to record pressure within the bladder may be done to tell how well the bladder empties. The rate at which urine flows can also be measured by such tests. This is called urodynamic testing.
Recommended Reading: How Do Bladder Infections Happen