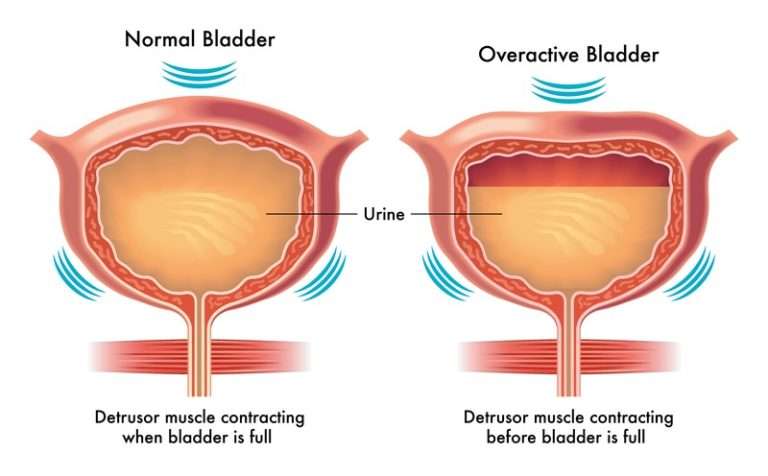
What Causes Overactive Bladder
An overactive bladder can be caused by several things, or even a combination of causes. Some possible causes can include:
- Weak pelvic muscles: Pregnancy and childbirth can cause your pelvic muscles to stretch and weaken. This can cause the bladder to sag out of its normal position. All of these factors can cause leakage.
- Nerve damage: Sometimes signals are sent to the brain and bladder to empty at the wrong time. Trauma and diseases can cause this to happen. These can include:
- Pelvic or back surgery.
- Stroke.
Often, there may be no specific explanation for why this is occurring.
Section : Patient Presentation
Symptoms. When symptoms of urinary frequency and urgency, with or without urgency incontinence, are self-reported as bothersome the patient may be diagnosed with overactive bladder .27 Additionally, a caregiver or partner may perceive these symptoms as bothersome and lead the patient to seek care. It is common for patients to have suffered with their symptoms for an extended time before seeking medical advice.
Differentiation. OAB symptoms may occur only at night, causing a single symptom of nocturia. The differential of nocturia includes nocturnal polyuria ,28 low nocturnal bladder capacity or both. In nocturnal polyuria, nocturnal voids are frequently normal or large volume as opposed to the small volume voids commonly observed in nocturia associated with OAB. Sleep disturbances, vascular and/or cardiac disease and other medical conditions are often associated with nocturnal polyuria. As such, it is often age-dependent, increasing in prevalence with aging and with poorer general health.
What Behavioral Changes Can I Make To Help With Overactive Bladder
There are many techniques and changes to your typical behavior that you can try to help with an overactive bladder. These can include:
Keeping a log: During a typical day, write down your fluid intake, the number of times you urinate, the number of accidents and when they occur. Make a note about what happened when the accident happened, like when you:
- Cough.
- Laugh.
- Were unable to reach the bathroom in time.
Monitoring your diet: Eliminate or decrease foods or beverages that may worsen your bladder symptoms. These could include:
- Tea.
- Spicy and acidic foods and drinks.
- Foods and drinks that contain artificial sweeteners.
Maintaining bowel regularity: Constipation can place added pressure on the bladder and have a negative effect on your bladder function. By keeping healthy bowel habits, you may be able to avoid constipation and help to lessen bladder symptoms. The following are some suggestions for maintaining bowel regularity:
- Increase your fiber intake by eating foods like beans, pasta, oatmeal, bran cereal, whole wheat bread, and fresh fruit and vegetables.
- Every morning, take 2 tablespoons of this mixture: 1 cup apple sauce, 1 cup unprocessed wheat bran, and ¾ cup prune juice.
- Exercise regularly to maintain regular bowel movements.
Maintaining a healthy weight: Being overweight can add pressure on your bladder, which may contribute to bladder control problems. If you are overweight, weight loss can reduce the pressure on your bladder.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Rid Of Overactive Bladder
Overactive Bladder In The Vulnerable Elderly
Accepted for publication 26 June 2014
3 October 2014Volume 2014:6 Pages 131138
Introduction
Urinary symptoms such as urgency/frequency and incontinence become increasingly prevalent with aging.1,2 A large multinational population-based survey estimated the prevalence of overactive bladder in Europe and Canada to be 12.8% in women and 10.8% in men.2 The NOBLE study showed similar trends in the USA, with OAB being twice as prevalent in individuals over 65 years of age than in those aged 45 years or younger.3 Urinary symptoms have a considerable negative impact on quality of life and health in the elderly,4,5 and have been shown to be associated with increased risk of falls and fractures.6,7 Costs associated with urinary symptoms in the aged are significant.8,9 With the aging of the population, it is estimated that by 2025 there will be 52 million adults in the USA with lower urinary tract symptoms.10 Thus, the burden of these symptoms on society is increasing.
Overactive bladder
Vulnerable or frail elderly
Evaluating OAB in the vulnerable elderly
|
Figure 1 Conceptual relationship of clinical factors.Notes: Symptoms, measurable function, and morbidity related pathophysiology, their evaluation and any treatments are related concerns which must be identified, clarified, and prioritized. While this sometimes-subtle distinction is always important, it assumes greater importance in the vulnerable elderly. |
Who is the patient?
What are feasible treatment options?
Antimuscarinics
Drugs For Overactive Bladder
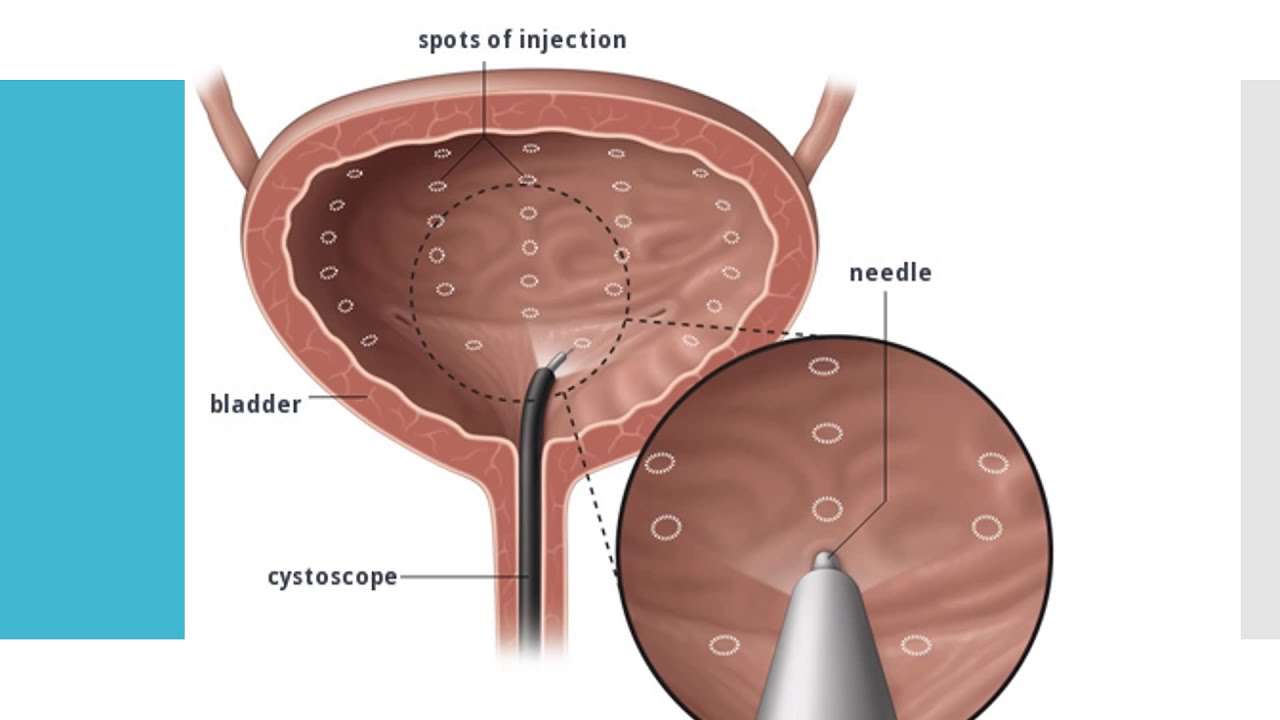
In people with overactive bladder, muscles in the bladder wall contract at the wrong time. A group of drugs called anticholinergics combat this problem by blocking the nerve signals related to bladder muscle contractions. Research suggests that these drugs also might increase bladder capacity and decrease the urge to go.
Anticholinergic drugs include:
Oxytrol for women is the only drug available over the counter. Overall, these drugs work about the same in treating overactive bladder, and generally people tolerate all of them well. The main side effect is dry mouth, but anticholinergics also can cause constipation, blurred vision, and increased heartbeat.
Anticholinergics aren’t right for everyone. Some people with glaucoma, urinary retention, or gastrointestinal disease should avoid using anticholinergic drugs.
The drugs mirabegron and vibegron called beta-3 adrenergic agonists. These medications work by activating a protein receptor in bladder muscles that relaxes them and helps the bladder fill and store urine.
Another type of drug for overactive bladder is the tricyclic antidepressantimipramine hydrochloride , which also relaxes bladder muscles.
Doctors also treat men with drugs that relax a muscle at the bladder neck and prostate to help with emptying. They include:
You May Like: Can A Ct Urogram Detect Bladder Cancer
Anticholinergic Medications That Can Help With Overactive Bladder But Cause Dementia
That line may sound like making a deal with the devil: You get a decent payoff but end up paying dearly for it in the long run. I agree with that, and so does the American Urogynecologic Society .
In their consensus statement on the use of anticholinergic medications for OAB, they state that evidence shows significant associations between these meds and increased risk of cognitive impairment and dementia. AUGS goes on to recommend providers counsel their patients on these risks and to consider other options or the lowest doses possible.
The brand names of anticholinergic medications are Ditropan XL, Detrol LA, Vesicare, Enablex, Toviaz and Sanctura XR. They act by inhibiting one of the bodys cholinergic receptors that is the main trigger for bladder contraction. They are also used as antidepressants and antihistamines much more often than they are used for OAB, which accounts for only about 10 percent of these drugs users.
These anticholinergic medications produce side effects such as dry mouth, dizziness and constipation. Because of those side effects found in anticholinergic medications, most people stop using them, with adherence rates after a year down to 9 percent and less with some of the drugs. And now we know they have another more serious side effect, the possibility of dementia.
- Reduced brain glucose activity.
- Evidence of temporal lobe and whole-brain atrophy.
- An association with progression to mild cognitive impairment and/or Alzheimers disease.
Treatment Options For Overactive Bladder
There are a number of treatment options available, but some are better for seniors than others. More times than not, a combination of different methods is the best treatment option. A lot depends on your physical and cognitive ability, so take that into consideration when determining the best choice for you. Speaking with your doctor, getting educated, and together working to find the best method can help with your OAB.
Behavior Intervention – Behavior intervention methods are typically the first choice for treating OAB because they have no side effects. Some of these options will not work for those that cannot control their muscles or cant maintain a mental state.
Kegel Exercises – Kegel exercises are used to strengthen your pelvic floor muscles and urinary sphincter. It is best to have someone teach you how to do them correctly, and with continued use throughout the day and for a few weeks, your symptoms should begin to reside.
Scheduled Toilet Trips – Scheduling trips to the bathroom during specific times of the day should help to reduce the sudden urge to urinate. Go at the same time every day even if you dont have to go.
Weight Loss – Losing weight can reduce the stress put on your bladder, therefore reducing your symptoms.
Double Voiding – Double voiding is a method used to hopefully completely void your bladder. This is done by using the bathroom, and then waiting a few minutes and trying again.
Also Check: Homeopathic Medicine For Bladder Weakness
Section : Research Needs And Future Directions
Figure 4: OAB Patient Groups
Epidemiology. Studies assessing how OAB develops and its natural history and progression are required. The timing and circumstances around which OAB develops and associated risk factors are not yet well-understood. While not specifically targeting epidemiology of OAB, there are large community-based studies that assess prevalence of lower urinary tract symptoms and urinary incontinence.280, 281 By longitudinally studying these community cohorts, these investigators have developed a new hypothesis that lower urinary tract symptoms are likely related to other systemic diseases/conditions.282, 283 Continuation of these types of studies could lead to potential preventive interventions for OAB symptoms and/or utilization of treatments that target the associated systemic conditions rather than the bladder. Epidemiologic studies provide a better cross sectional estimation of the overall population impact of OAB-type symptoms.284
Clinical studies should use validated standardized measures to report subjective outcomes. Objective outcomes should include frequency, nocturia, urgency, incontinence episode frequency and reporting of the variance for each of these measures. Furthermore, the Guideline Panel’s meta-analytic efforts were hampered by lack of consistent reporting of variance information for baseline and post-treatment measurements.
How Can Nerve Stimulation Help Overactive Bladder
There are several treatments that involve stimulating your nerves to help improve overactive bladder. Your nerves help communicate the message that your bladder needs to be emptied to your brain. By treating the nerves, your healthcare provider can improve your bladder control. Nerve stimulation is a reversible treatment that is considered when conservative treatments have not worked or have not been tolerated. Conservative treatments include behavioral therapies and medications.
There are several types of nerve stimulation treatments. These can include:
Don’t Miss: What Vitamins Are Good For Bladder Health
Overactive Bladder Treatment For Seniors
Overactive Bladder Treatment for Seniors
Overactive bladder is a huge inconvenience to seniors because it gets in the way of everyday life. There are about 33 million Americans suffering from the condition. You search for the restroom whenever you get somewhere, or you might not even go because your symptoms may get in the way. You may start to realize that many of your relationships are strained. The problem is that many do not talk to their doctor about it because they are either embarrassed, or they do not think there are treatments available for them. OAB is not just a part of getting older it is a group of urinary symptoms that affect millions of Americans.
Other Treatments To Try
In rare cases when all OAB treatment fails and overactive bladder is severe, doctors may recommend one of several types of surgery.
A procedure called bladder augmentation uses part of the bowel to increase bladder capacity. Or, urinary diversion, an alternate route for bladder drainage for severe, complicated OAB patients.
Sacral nerve stimulation. Another procedure implants a small device, similar to a pacemaker, under the skin. The device is connected to a wire, which sends small electrical pulses to nerves around the pelvic floor that control the bladder and muscles surrounding it. This helps build bladder control. Itâs often called a bladder pacemaker. The main limitation with this treatment is that it keeps you from having a spinal MRI.
Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation. The doctor places a needle on nerves near your ankle that affect bladder control. Youâll have one session a week for 12 weeks and then maintenance treatments as needed. This procedure is done in the office.
An overactive bladder doesnât have to get in the way of your daily life. With a little time, patience, and the right treatment, you can regain control — and peace of mind. Whatever treatment for overactive bladder you and your doctor decide upon, it’s important that you stick with it. If you do, chances are your condition will improve in time.
Show Sources
Don’t Miss: Can Candida Cause Bladder Infection
Precautions And Proper Diagnosis
The main symptoms of OAB can also occur in other health conditions like bladder cancer, urinary tract infection and enlarged prostate. Seeing blood in your urine is not a symptom of OAB.
A sudden and frequent need to urinate is common in both OAB and a UTI. How can you tell the difference between these two urinary health issues? Unlike OAB, a UTI also comes with other symptoms such as discomfort while urinating. In addition, OAB symptoms are continuous while UTI symptoms are sudden and may also include a fever.
Overflow incontinence is characterized by the involuntary release of urine from an overfull urinary bladder, often in the absence of any urge to urinate. This condition is not associated with OAB. It typically occurs in people who have a blockage of the bladder outlet, which can occur with benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostate cancer or a narrowing of the urethra. Overflow incontinence can also occur when the muscle responsible for removing urine from the bladder is too weak to empty the bladder in a normal way.
It is very important to see a doctor to ensure a proper diagnosis if you experience any changes in your urine and/or urination habits.
I Recommend Other Overactive Bladder Treatment Options
We want to move women away from overactive bladder treatments that have dementia and Alzheimers disease as side effects. As always at CU Urogynecology, we start with the simplest treatment options before moving to more complex ones. Women and their physicians should consider the following options.
Pelvic floor therapy can have good results on OAB. A recent study of 32 women who undertook 6-9 pelvic floor muscle rehabilitation therapy sessions over 2 weeks showed:
- 22.9 percent reduction in the number of urinations in a 24-hour period.
- 21.3 percent reduction during the day.
- 34.7 percent reduction at night.
- Improved quality of life and significant improvements lasting 6 months.
Non-anticholinergic medications are an option. Drugs known as beta-3 agonists, such as mirabegron can help. Beta-3 agonists are recommended for women at high risk for side effects of anticholinergic medications.
Botox injections can reduce OAB symptoms. It relaxes bladder muscles while increasing the bladders storage capacity. Bulking agents are injected into the area around the urethra or into the bladder.
Vaginal estrogen treatment in topical cream, tablet or ring application can reduce urinary frequency and urinary urgency in women with OAB. It should be discussed as an option, though studies on its effectiveness are inconclusive.
Recommended Reading: New Drug For Overactive Bladder
Medical Treatments For Nocturia
Your doctor may prescribe medications when preventive measures and lifestyle changes fail to reduce the frequency of your nighttime urination. Doctors prescribe a class of drugs called anticholinergics to treat symptoms of OAB, if thats the cause of your nocturia. They reduce bladder spasms that create the urge to go.
Your doctor may suggest you take a diuretic for regular urine production. A diuretic can itself cause nocturia. But if you take it early enough in the day, it may help you get rid of excess fluid while youre awake. This should decrease your urine production at night.
Other drugs that may help are:
- desmopression in cases of diabetes insipidus to cause the kidneys to produce less urine
- tamsulosin , finasteride , or dutasteride to treat prostate enlargement
- antibiotics if you have a urinary tract infection
Your doctor may also adjust your diabetic medications to lower your blood sugar if theyre causing nocturia.
Sexual Differences In Incidence
In the NOBLE study, the prevalence of OAB was similar in women and men . However, the prevalence of incontinence associated with OAB differed. Among women, 9.3% reported having OAB with incontinence 7.6% reported having OAB without incontinence. In contrast, more men reported having OAB without incontinence than with incontinence . In women, the prevalence of OAB with urgency urinary incontinence increased with increasing body mass index , whereas in men, no difference was found.
Milsom et al, in a population-based survey of 16,776 men and women aged 40 years or older from the general population in Europe, found the overall prevalence of OAB symptoms to be 16.6%. The main outcome measures included the prevalence of urinary frequency , urinary urgency, and urgency incontinence.
Frequency was the most common symptom , followed by urgency and urgency incontinence . The prevalence of OAB increased with age, and rates in men and women were similar. Symptoms of urinary urgency and frequency were similar between both sexes, but urgency incontinence was more prevalent in women than in men.
OAB in men is often related to obstruction therefore, it may be important to differentiate between obstruction and irritative symptoms before the initiation of treatment.
Also Check: New Treatments For Neurogenic Bladder