How Can I Prevent Bladder Cancer
Stopping smoking is the best way to prevent bladder cancer. You should also reduce your exposure to cancer-causing agents to help prevent bladder cancer. Other than these measures, decreasing your risk of invasive bladder cancer relies on early detection of symptoms and possibly screening if you are high-risk.
Tests For Bladder Cancer
Your doctor may do some tests to check for bladder cancer:
- internal examination the doctor may check inside your bottom or vagina with their finger, using gloves
- urine tests your urine will be checked for signs of bladder cancer
- blood tests to check your general health
- ultrasound a scan on the outside of your abdomen to check for cancer
- cystoscopy the doctor puts a small camera into your bladder to see inside
- biopsy the doctor takes a small sample of the cells from the bladder to check for signs of cancer.
Your doctor might ask you to have further tests. These can include:
- CT scan and x-rays scans that take pictures of the inside of the body, sometimes also called a CT-IVP or a triple phase abdominal-pelvic CT scan
- MRI scan a scan that uses magnetism and radio waves to take pictures of the inside of the body
- bone scan a scan that uses dye to show changes in your bones
- FDG-PET scan a scan that uses an injection of liquid to show cancer cells.
Causes Of Bladder Cancer
Most cases of bladder cancer appear to be caused by exposure to harmful substances, which lead to abnormal changes in the bladder’s cells over many years.
Tobacco smoke is a common cause and it’s estimated that more than 1 in 3 cases of bladder cancer are caused by smoking.
Contact with certain chemicals previously used in manufacturing is also known to cause bladder cancer. However, these substances have since been banned.
Read more about the causes of bladder cancer.
Don’t Miss: Botox Dose For Overactive Bladder
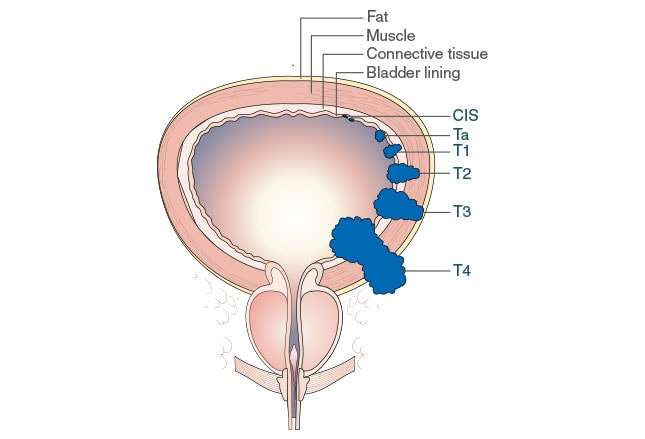
After Bladder Cancer Has Been Diagnosed Tests Are Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Bladder Or To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out if cancer has spread within thebladder lining and muscle or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment. The following tests and procedures may be used in the staging process:
Signs Of Bladder Cancer In Dogs
Dogs with urinary tract infections and tumors within the bladder, prostate, kidneys, or urethra may present with similar symptoms:
- Straining to urinate.
- Constipation as a result of dehydration.
- Loss of appetite and weight loss.
If your pets have abdominal pain or are straining to urinate, this is not to be ignoredseek veterinary advice. Straining to urinate and being unable to pass urine for more than 24 hours is a medical emergency. Consider arranging for the dog to have a test for cancer cells if you notice blood in the urine.
Also Check: Heavy Feeling In Bladder And Frequent Urination
Dog Bladder Cancer Clinical Trials
There is a close similarity between TCC in dogs and high-grade invasive bladder tumors in humans therefore, canine bladder cancer is an area of research interest for doctors and veterinarians alike . As such, you may be asked if you would like your dog to be part of a veterinary clinical trial, which can give you access to experimental treatments that are otherwise unavailable.
Do I Need New Clothes After A Urostomy
Loose-fitting clothes may be more comfortable at first, but you should be able to switch back to many of your regular clothes in time. Ostomy wraps or bands can help reduce any bulge and keep it in place. You may need to give up belts that press on the stoma or clothes that are tight over it, though.
Also Check: Not Being Able To Hold Bladder
Chemotherapy After A Turbt
After surgery, you might be given one or more courses of chemotherapy. You will have your first course when you have recovered from the effects of the general anaesthetic. A type of chemotherapy called intravesical chemotherapy is used. It involves placing a liquid solution of chemotherapy medication directly into your bladder using a catheter. The solution will be kept in your bladder for about an hour before being drained away.
Some residue of the chemotherapy medication may be left in your urine, so be careful not to splash yourself or the toilet seat with urine, because it could irritate your skin. After having a wee, wash your genitals, and your hands, with soap and water.
The advantage of intravesical chemotherapy is that because the medication is placed inside your bladder , you will not experience the side effects that are most commonly associated with chemotherapy, such as feeling sick, tiredness and hair loss. The most common side effect of intravesical chemotherapy is irritation and inflammation of the bladder lining. This can sometimes make you feel like you need to wee a lot, or make weeing painful. Dont worry, these side effects should pass within a few days.
Cystoscopy With Cautery Destruction Of The Bladder Tumor
Cystoscopy is an outpatient procedure during which a thin, lighted tube with a camera is passed through the urethra into the bladder, allowing your doctor to see the inside of the bladder.
Most modern cystoscopes are also equipped with channels that permit small instruments to be passed into the bladder. During a cystoscopy, your doctor may use these instruments to remove tissue, stop bleeding with a special electrical device called an electrocautery or even perform laser treatment. If the bladder cancer tumor is small enough, this cautery may be used to remove the cancer.
Also Check: What Are The Symptoms Of Advanced Bladder Cancer
Dog Bladder Cancer: What To Expect
Look out for these common symptoms, especially if you are the owner of Scottish Terriers or Shetland Sheepdogs:
- Bloody urine
- Painful urination or other urinary tract infection signs.
- Abdominal pain.
When you seek veterinary help, expect that your veterinarian may recommend a urinary catheter to help your pet relieve themselves, should they be suffering from a blocked urinary tract.
Ask your vet if they believe there is a harmless urinary infection, and consider a Cadet BRAF test if there are suspicions of a serious disease.
If the Cadet BRAF and other urinary tests determine cancer cells are present, talk to your veterinarian about a biopsy and ultrasound. This will ensure your dog is fully diagnosed by assessing if the bladder tumors have spread to the lymph nodes, the lungs, the kidneys, or the urinary tract.
With advanced bladder tumors, expect that chemotherapy may be recommended, which can have nasty side effects for your dog. Consider ways of making your pet as comfortable as you can.
Treatments For Bladder Cancer
If you have bladder cancer, your healthcare team will create a treatment plan just for you. It will be based on your health and specific information about the cancer. When deciding which treatments to offer for bladder cancer, your healthcare team will consider:
- stage
- other medical problems you have
- what you prefer or want
You May Like: How Long Is Bladder Surgery
Bladder Cancer In Dogs
The most common form of dog bladder cancer is a malignant cancer tumor called transitional cell carcinoma .
The tumor is developed from the cells lining the bladder . Therefore, such tumors are usually found in the inside lining of the bladder.
As the tumor grows, it takes over the space that is used for holding urine. As you can imagine, this obstructs the flow of urine from the kidneys to the outside of the body.
Canine transitional cell carcinoma is fairly aggressive. In one out of every 10 instances, it spreads to other sites of the body, such as the lungs, the bones, or the lymph nodes near the bladder.
What About Other Treatments That I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments can be vitamins, herbs, special diets, and other things. You may be curious about these treatments.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to be helpful. A few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor about anything you’re thinking about using, whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
Don’t Miss: What Should I Do If I Have A Bladder Infection
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if bladder cancer spreads to the bone, the cancer cells in the bone are actually bladder cancer cells. The disease is metastatic bladder cancer, not bone cancer.
Tests That May Be Done
Physical exam: The doctor will check you for signs of bladder cancer and other health problems. This might include a rectal exam, during which a gloved finger is put into your rectum. If you are a woman, a pelvic exam might also be done. During these exams, the doctor can sometimes feel a bladder tumor.
Urine tests: For these tests, you’ll be asked to pee in a cup. Your urine is then tested for cancer cells, blood, or certain proteins .
Cystoscopy: For this exam, a doctor called a urologist looks at the inside of your bladder using a tool called a cystoscope. This is a thin tube with a tiny light and camera on its end. It’s put through the opening of your urethra and moved up into your bladder.
Blue light cystoscopy: Sometimes, special drugs are put into the bladder during the exam. Cancer cells soak up these drugs and then glow when the doctor shines a blue light through the scope. This can help the doctor see cancer cells that might have been missed with the normal light.
Bladder biopsy: This is needed to know for sure if you have bladder cancer. For this test, a cystoscope is used it to take a tiny piece of the bladder . More than one sample may be taken because sometimes cancer starts in more than one part of the bladder. Salt water washings of the inside of your bladder may also be collected to look for cancer cells. Any samples are sent to a lab and tested to see if there are cancer cells in them.
Recommended Reading: Treatment Of Overactive Bladder In Males
How Is Bladder Cancer Diagnosed
Anyone with blood in the urine should have other testing done. Often, the first thing that is done is a urine cytology, which looks at the urine under a microscope to find abnormal appearing cells. If these cells are seen, a diagnosis of cancer may be made. However, the test does not detect all cases of bladder cancer.
- An X-ray of the upper urinary tract may be done to diagnose bladder cancer or to see if these structures contain cancer.
- Ultrasound can be used to study the kidneys.
- A CT scan is used to look at the entire urinary tract.
- An intravenous pyelogram can be used to study the urinary tract. An IVP puts a dye into a patient’s vein and then an x-ray is done a short time later. The dye exits the body via the kidneys and urine and can be seen on the x-ray, showing the kidney collecting system, ureters, and often the bladder.
Though the above tests are useful, the most important test for diagnosis and staging is a cystoscopy. A fiberoptic camera is placed into the bladder, going through the urethra. Cystoscopy allows the provider to see the entire bladder and biopsy any suspicious lesions. If the biopsy reveals cancer, a repeat cystoscopy and resection is done to see the whole tumor and if it has started to spread.
If you are diagnosed with cancer, you will also have a complete physical done. Your provider will tell you what tests you need to have done to help determine the extent of the cancer and if it has spread.
Sex After Bladder Cancer Treatment
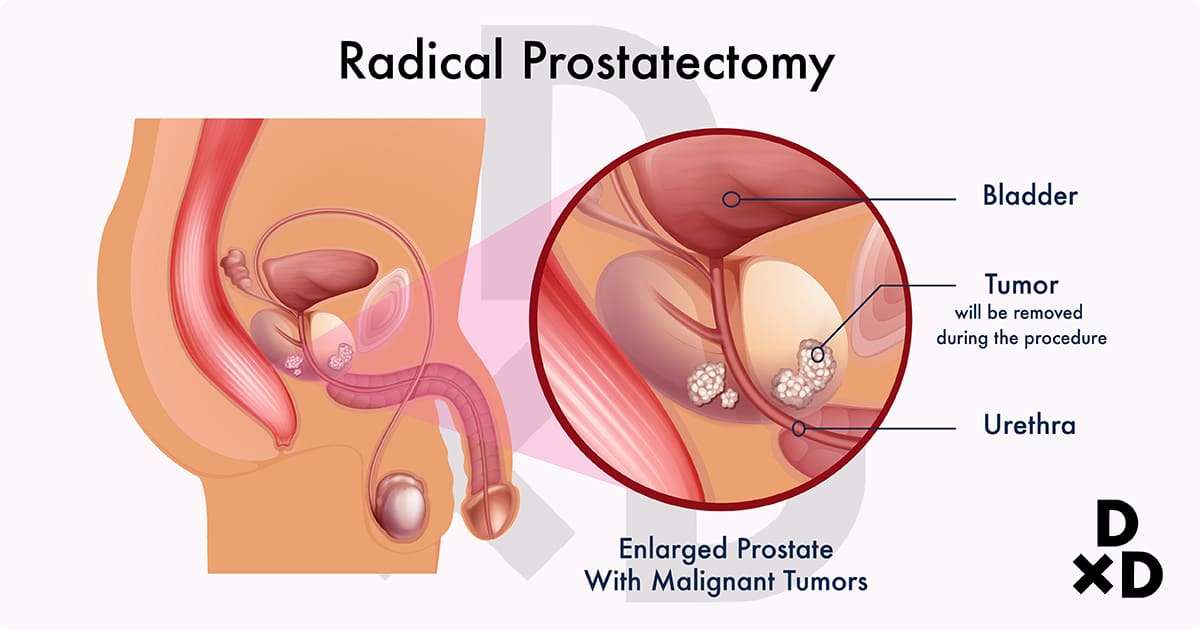
Surgery can damage sensitive nerves, making sex more difficult. Some men may have trouble having an erection, though for younger patients, this often improves over time. When the prostate gland and seminal vesicles are removed, semen can no longer be made. Women may also have trouble with orgasm, and may find sex less comfortable. Be sure to discuss treatment options with your doctor.
Read Also: Reasons For Lack Of Bladder Control
Sexual Dysfunction After A Cystectomy
After a cystectomy both men and women can have an altered sexual life. This concern is the source of many patient questions, and Dr. Wilson thoroughly addresses this concern.
To reduce the prospect of such issues, Dr. Wilson provides nerve sparing cystectomies whenever possible to preserve sexual function. She also uses the latest surgical techniques to further reduce those risks.
If an ileal conduit procedure was performed, it can also affect a persons sex life. Emptying the pouch prior to sexual intercourse can reduce the chances of leakage. During intercourse it may be easier to wear a tight shirt or put on a smaller pouch to keep the daily pouch out of the way. A person may also need to try other sexual positions to keep their partners weight from rubbing against the pouch.
Treating Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the pelvic or abdominal wall , may have spread to nearby lymph nodes , and/or have spread to distant parts of the body . Stage IV cancers are very hard to get rid of completely.
Chemotherapy is usually the first treatment if the cancer has not spread to distant parts of the body . The tumor is then rechecked. If it appears to be gone, chemo with or without radiation or cystectomy are options. If there are still signs of cancer in the bladder, chemo with or without radiation, changing to another kind of chemo, trying an immunotherapy drug, or cystectomy may be recommended.
Chemo is typically the first treatment when bladder cancer has spread to distant parts of the body . After this treatment the cancer is rechecked. If it looks like it’s gone, a boost of radiation to the bladder may be given or cystectomy might be done. If there are still signs of cancer, options might include chemo, radiation, both at the same time, or immunotherapy.
In most cases surgery cant remove all of the cancer, so treatment is usually aimed at slowing the cancers growth and spread to help people live longer and feel better. If surgery is a treatment option, it’s important to understand the goal of the operation whether it’s to try to cure the cancer, to help a person live longer, or to help prevent or relieve symptoms from the cancer.
Because treatment is unlikely to cure these cancers, many experts recommend taking part in a clinical trial.
Recommended Reading: Where Do You Feel Bladder Pain
Why Would You See A Urologist
A urologist might treat bladder problems, urinary tract infections , bladder and kidney cancer, kidney blockage, and kidney stones.
ishonest
Men might also see them for:
- Erectile dysfunction
Women might also see a urologist for
- Problems holding your pee after pregnancy
- Pelvic organ prolapse
Children might need to see a urologist if they have an abnormal urinary tract problem like bedwetting.
Treatment Of Recurrent Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of recurrentbladder cancer depends on previous treatmentand where the cancer has recurred. Treatment for recurrent bladder cancer mayinclude the following:
- Radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- A clinical trial of a new treatment.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Also Check: Men’s Overactive Bladder Treatment
What Is The Bladder
The bladder is an organ found in the lower part of the belly near the pelvic bones. It acts as a holding area for urine. The bladder expands and can hold about half of a liter of urine, but a person usually feels the urge to urinate when the bladder is 25% full. The bladder will contract and become smaller when it is empty. The ureters are two tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder. They empty urine from the kidneys into the bladder. The urethra is a tube that connects the bladder to the outside of the body and releases urine.
The bladder wall consists of 4 main layers of tissue.
- The innermost layer is called the urothelium, or transitional epithelium. It is made up of cells called urothelial or transitional cells.
- Beneath the urothelium is a thin layer called the lamina propria, made up of connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves.
- The next layer is called the muscularis propria, made of muscle.
- The last layer is a layer of fatty tissue that separates the bladder from other surrounding organs.