Bladder Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Bladder
The bladder is a hollow organ in the lower part of the abdomen. It is shaped like a small balloon and has a muscular wall that allows it to get larger or smaller to store urine made by the kidneys. There are two kidneys, one on each side of the backbone, above the waist. Tiny tubules in the kidneys filter and clean the blood. They take out waste products and make urine. The urine passes from each kidney through a long tube called a ureter into the bladder. The bladder holds the urine until it passes through the urethra and leaves the body.
There are three types of bladder cancer that begin in cells in the lining of the bladder. These cancers are named for the type of cells that become malignant :
- Transitional cell carcinoma: Cancer that begins in cells in the innermost tissue layer of the bladder. These cells are able to stretch when the bladder is full and shrink when it is emptied. Most bladder cancers begin in the transitional cells. Transitional cell carcinoma can be low-grade or high-grade:
- Low-grade transitional cell carcinoma often recurs after treatment, but rarely spreads into the muscle layer of the bladder or to other parts of the body.
- High-grade transitional cell carcinoma often recurs after treatment and often spreads into the muscle layer of the bladder, to other parts of the body, and to lymph nodes. Almost all deaths from bladder cancer are due to high-grade disease.
See the following PDQ summaries for more information:
En Bloc Transurethral Resection Of Bladder Tumors
En bloc transurethral resection of bladder tumors is newer technique in which the tumor and the surrounding normal urothelium are removed as a single unit. A meta-analysis of seven trials found that ETURBT was associated with shorter hospital stays and catheterization time,fewer complications, and a lower recurrence-free rate than conventional TURBT. In a separate systematic review of 17 studies, the results were comparable to conventional TURBT. Both papers cited the ability to provide high-qualityspecimens for histological assessment as a significant advantage of ETURBT over TURBT.
A prospective, non-randomized interventional study was performed to compare ETURBT to TURBT in the setting of NMBIC, in terms of progression and recurrence. Cohort groups were comparable with 21 patients undergoing ETURBT vs 24 TURBT, with results being notable for significantly decreased recurrence rate and recurrence-free survival while progression rate and progression-free survival rate were not significantly different.
Interesting, Uphadhyay et al. found that with non-pedunculated bladder tumors 2-4 cm in size that were resected via ETURBT vs TURBT, a greater yield of detrusor muscle was found in histopathological examination of specimens obtained with ETURBT .
While these results are attractive, there are several limitations of ETURBT to consider :
Tumours On The Lateral And Anterior Walls
Resection of lateral wall tumours may result in stimulation of ONR resulting in increased risk of perforation . Strategies that have been shown to reduce the likelihood of ONR would include avoidance of bladder overfilling, reduced cutting current, use of short intermittent burst current , use of bipolar electrocautery, and use of neuromuscular blockade .
Tumours on the anterior wall could be challenging to resect and may require suprapubic depression by an assistant as well as proper resectoscope angles. More effective resection might be achieved by using open-angled loops.
Also Check: Can A Ct Urogram Detect Bladder Cancer
There Are Different Types Of Treatment For Patients With Bladder Cancer
Different types of treatment are available for patients with bladder cancer. Some treatments are standard , and some are being tested in clinical trials. A treatment clinical trial is a research study meant to help improve current treatments or obtain information on new treatments for patients with cancer. When clinical trials show that a new treatment is better than the standard treatment, the new treatment may become the standard treatment. Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
Enhancing The Quality Of Transurethral Resection: The Importance Of A Complete Turbt And The En Bloc Resection
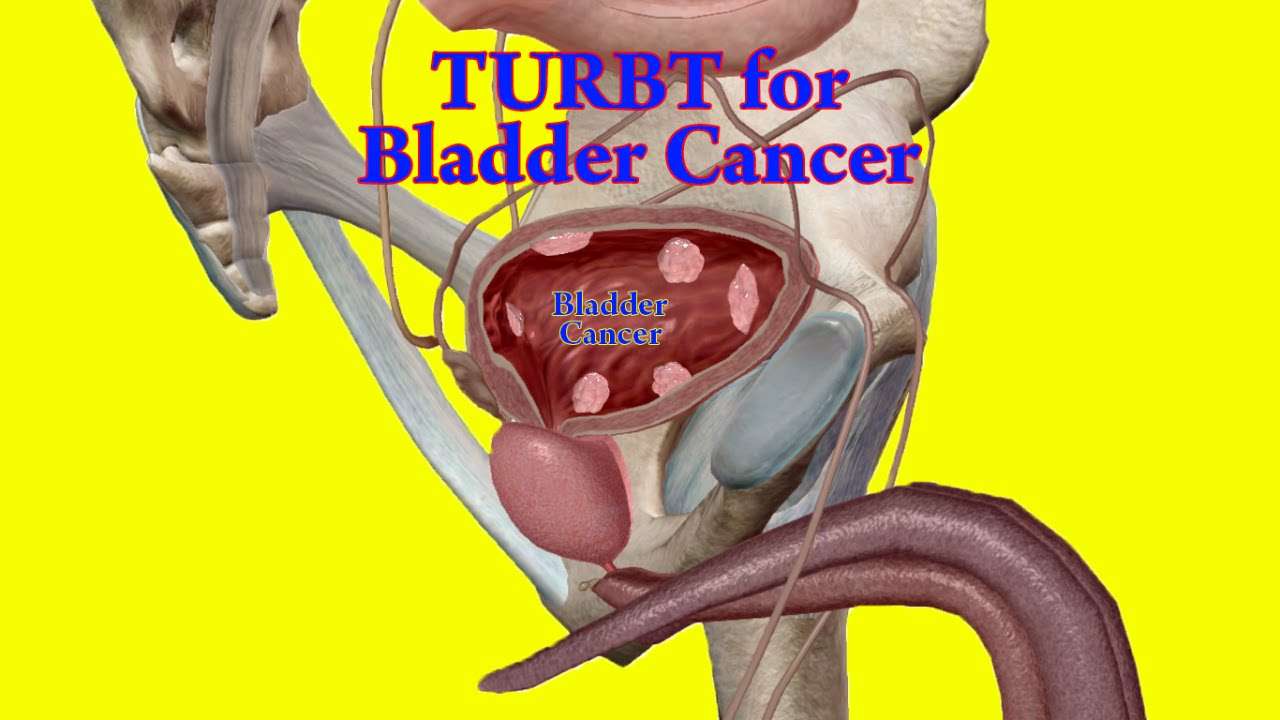
While TURBT has been the most widely used technique for resection of bladder tumour over several decades, it has been fraught with multiple concerns that need to be addressed. The resection is performed in a piecemeal fashion also known as âincise and scatteringâ technique. Essentially it is against oncological principles as it will breach surgical margins and increase the risk of potential seeding and implantation by tumour fragmentation. This could then affect oncological outcomes with potentially higher rate of recurrence and progression. There is also a risk of perioperative morbidities such as ONR, and bladder perforation. Furthermore, accurate histological assessment might not be possible due to fragmentation and cautery artefact as well as high rate of incomplete resection or absent detrusor muscle. Due to relatively high risk of recurrence and progression there is a need for improved accuracy and novel resection techniques have been developed with encouraging results. The one of the most notable technical advances in endoscopic management of bladder tumours in the last decade is en bloc resection of bladder tumour as an alternative to conventional TURBT . It may overcome these shortcomings, representing the best surgical technique to perform a âGood-quality TURBTâ.
You May Like: How To Prevent Bladder Infection After Intercourse
Treating Stage Iii Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the outside of the bladder and might have grown into nearby tissues or organs and/or lymph nodes . They have not spread to distant parts of the body.
Transurethral resection is often done first to find out how far the cancer has grown into the bladder wall. Chemotherapy followed by radical cystectomy is then the standard treatment.Partial cystectomy is rarely an option for stage III cancers.
Chemotherapy before surgery can shrink the tumor, which may make surgery easier. Chemo can also kill any cancer cells that could already have spread to other areas of the body and help people live longer. It can be especially useful for T4 tumors, which have spread outside the bladder. When chemo is given first, surgery to remove the bladder is delayed. The delay is not a problem if the chemo shrinks the cancer, but it can be harmful if it continues to grow during chemo. Sometimes the chemo shrinks the tumor enough that intravesical therapy or chemo with radiation is possible instead of surgery.
Some patients get chemo after surgery to kill any cancer cells left after surgery that are too small to see. Chemo given after cystectomy may help patients stay cancer-free longer, but so far its not clear if it helps them live longer. If cancer is found in nearby lymph nodes, radiation may be needed after surgery. Another option is chemo, but only if it wasn’t given before surgery.
Tumours In Bladder Diverticulae
Tumours within bladder diverticula are also considered to be difficult to obtain complete clearance due to suboptimal access and resection in particular if the diverticular neck is narrow and lack of muscularis propria layer. This would pose an increased risk of perforation and the inherent limitations in the assessment of the depth of tumour invasion. In view of this, while small, low grade tumours can be carefully resected, diverticulectomy, partial or radical cystectomy is considered to deal with large, high grade tumours in the diverticulum .
You May Like: Can Lower Back Pain Cause Bladder Problems
Treating Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the pelvic or abdominal wall , may have spread to nearby lymph nodes , and/or have spread to distant parts of the body . Stage IV cancers are very hard to get rid of completely.
Chemotherapy is usually the first treatment if the cancer has not spread to distant parts of the body . The tumor is then rechecked. If it appears to be gone, chemo with or without radiation or cystectomy are options. If there are still signs of cancer in the bladder, chemo with or without radiation, changing to another kind of chemo, trying an immunotherapy drug, or cystectomy may be recommended.
Chemo is typically the first treatment when bladder cancer has spread to distant parts of the body . After this treatment the cancer is rechecked. If it looks like it’s gone, a boost of radiation to the bladder may be given or cystectomy might be done. If there are still signs of cancer, options might include chemo, radiation, both at the same time, or immunotherapy.
In most cases surgery cant remove all of the cancer, so treatment is usually aimed at slowing the cancers growth and spread to help people live longer and feel better. If surgery is a treatment option, it’s important to understand the goal of the operation whether it’s to try to cure the cancer, to help a person live longer, or to help prevent or relieve symptoms from the cancer.
Because treatment is unlikely to cure these cancers, many experts recommend taking part in a clinical trial.
Palliative Or Supportive Care
If your cancer is at an advanced stage and can’t be cured, your medical team should discuss how the cancer will progress and which treatments are available to ease the symptoms.
You can be referred to a palliative care team, who can provide support and practical help, including pain relief.
Page last reviewed: 01 July 2021 Next review due: 01 July 2024
Also Check: How To Take Care Of A Bladder Infection At Home
Selection Process And Data Abstraction
Two reviewers reviewed the titles, abstracts, and full text independently according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Disputes arising during the title and abstract screening phase were directly incorporated into the full text assessment to ensure that all relevant papers were not omitted. In the full text stage, the differences were resolved by negotiation between 2 reviewers. If there was no agreement, a third reviewer is consulted.
The 2 reviewers independently extracted relevant data with a predesigned data extraction table. Baseline data extracted included: first author and publication year, country, study type, surgical methods, sample size, follow-up time, outcomes, and quality score. Outcome indexes can be divided into intraoperative indexes and postoperative indexes. Intraoperative indicators include operation time, incidence of obturator nerve reflex, incidence of perforation, and detrusor muscle acquisition rate. Postoperative outcome indicators included: hospitalization time, catheterization time, bladder irrigation rate, incidence of urethral stricture, 12-month recurrence rate, and 24-month recurrence rate. The median, range, and sample size data provided in the literature were all converted into the data types required for the statistics in this study by the method described by Hozo et al. .
Inclusion And Exclusion Criteria
The inclusion criteria were: the types of studies were RCT or cohort studies and clinical case-control studies the study subjects were primary NMIBC patients with a clear pathological diagnosis and postoperative bladder perfusion therapy, followed up for more than 1 year interventions included all laser types of transurethral laser surgery studies involved the comparison of transurethral laser surgery and TURBT and outcome indicators included at least one of the following: operation time, incidence of obturator nerve reflex, incidence of bladder perforation, detrusor muscle acquisition rate, hospitalization time, catheterization time, bladder irrigation rate, incidence of urethral stricture, and recurrence rate.
The exclusion criteria were: the subjects included patients with recurrent or muscle-invasive bladder cancer ta lack of relevant outcome indicators the patient had undergone other transurethral procedures and unclear outcomes and missing data and republished literature.
Also Check: Hard To Urinate When Bladder Full
Trimodality Therapy Treatment Approach
TMT includes the combination of maximal tumor debulking and concurrent chemoradiotherapy. The optimal radiation target volume, radiation fractionation, chemotherapy, and sequencing remain areas of active study. In general, the patient undergoes a maximal, preferably visually complete TURBT, ideally with bladder mapping , followed by the delivery of cisplatin-based chemoradiotherapy to a dose of approximately 40â45Gy. If no evidence of disease or minimal residual disease is noted at cystoscopic reassessment, the final consolidative phase of chemoradiotherapy is initiated. If progressive or unresponsive disease is found, the patient proceeds to radical cystectomy. After completion of therapy, patients are closely surveilled with cystoscopy and urine cytology.
Sequencing of trimodality therapy for bladder preservation
Patients undergoing TMT for bladder preservation undergo a maximal TURBT followed by induction chemoradiation. Patients with a CR to induction therapy proceed to consolidative chemoradiation, whereas evidence of progression results in immediate cystectomy. Following therapy, a strict schedule of surveillance is undertaken. Evidence of invasive recurrence is treated with cystectomy. Non-invasive recurrences are managed with TURBT and intravesicle therapy.
Articles On Bladder Cancer Treatments
If you have bladder cancer, there are several available treatment options. Your doctor will help you decide which treatment is best for you. This will depend on a number of things, including your age, how much the cancer has spread , and any other health conditions you have.
Many people with bladder cancer need surgery. But in some cases, it canât remove all of the disease. So youâll need other treatments along with, or instead of, an operation. These could include chemotherapy, radiation, and immunotherapy.
Don’t Miss: Treatment Of Overactive Bladder In Males
Sex After Bcg Treatment
Men should use a condom during sex for the first week after each BCG treatment. If you are a woman having the treatment, your partner should use a condom during this time. This protects your partner from any BCG that may be present in semen or vaginal fluid. Your doctor or specialist nurse can give you more information about this.
Doctors do not yet know how BCG may affect an unborn baby. They will recommend you do not become pregnant or make someone pregnant while having it. You should use effective contraception during treatment. Your doctor or specialist nurse can give you more information about this.
Treatments For Early Stage Bladder Cancer
The following are treatment options for bladder cancer. Early stage bladder cancer is only in the inner lining or thin connective tissue layer of the bladder . This includes stage 0a, stage 0is and stage 1 bladder cancers. Your healthcare team will suggest treatments based on the . They will work with you to develop a treatment plan.
Sometimes bladder cancer comes back after it has been treated or initial treatments dont work. If the cancer is still non-invasive or non-muscle invasive, the following treatments can be used.
Don’t Miss: How Long Is Bladder Surgery
What Is The Role Of Transurethral Resection Of Bladder Tumor In The Treatment Of Bladder Cancer
Endoscopic TURBT is the first-line treatment to diagnose, stage, and treat visible tumors. TURBT is not effective for CIS, because the disease is often so diffuse and difficult to visualize that complete surgical removal may not be feasible. It is critically important to surgically remove all nonmuscle-invasive disease prior to beginning intravesical therapy. When a combination of papillary tumor and CIS is present, the papillary tumor is removed before treatment of the CIS is initiated.
The Following Stages Are Used For Bladder Cancer:
Stage 0
In stage 0, abnormalcells are found in tissue lining the inside of the bladder. These abnormal cells may become cancer and spread into nearby normal tissue. Stage 0 is divided into stages 0a and 0is, depending on the type of the tumor:
- Stage 0a is also called noninvasive papillary carcinoma, which may look like long, thin growths growing from the lining of the bladder.
- Stage 0is is also called carcinoma in situ, which is a flat tumor on the tissue lining the inside of the bladder.
Stage I
In stage I, cancer has formed and spread to the layer of connective tissue next to the inner lining of the bladder.
Stage II
In stage II, cancer has spread to the layers of muscle tissue of the bladder.
Stage III
Stage III is divided into stages IIIA and IIIB.
- In stage IIIA:
- cancer has spread from the bladder to the layer of fat surrounding the bladder and may have spread to the reproductive organs and cancer has not spread to lymph nodes or
- cancer has spread from the bladder to one lymph node in the pelvis that is not near the common iliac arteries .
Stage IV
Stage IV is divided into stages IVA and IVB.
- In stage IVA:
- cancer has spread from the bladder to the wall of the abdomen or pelvis or
- cancer has spread to lymph nodes that are above the common iliac arteries .
Recommended Reading: How Can I Relax My Bladder Naturally
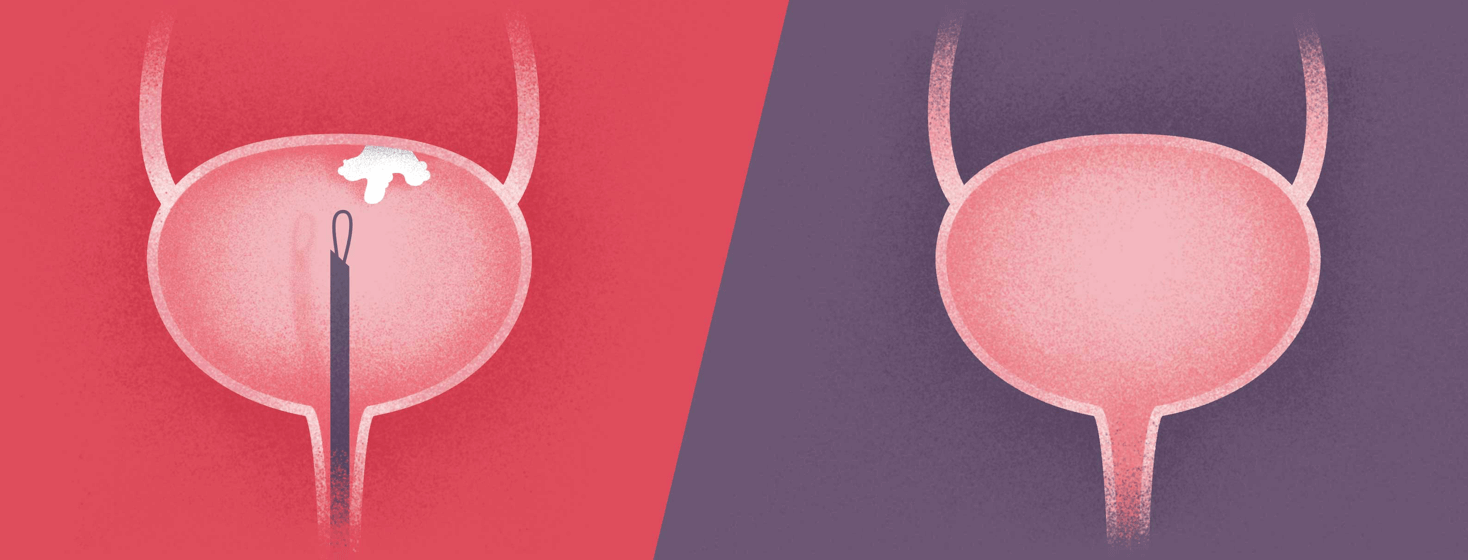
What Is Transurethral Resection Of Bladder Tumor
TURBT is the procedure done to diagnose and to treat early stage bladder cancer at the same time. The initials stand for transurethral resection of a bladder tumor. This procedure is the first-line diagnostic test and treatment for bladder cancer. Men are almost four times more likely than women to be diagnosed with this type of cancer.
The majority of people have bladder cancer that hasnt invaded the muscle wall when first diagnosed. Almost everyone diagnosed with bladder cancer will undergo bladder tumor biopsy and resection.
A biopsy is a procedure in which a doctor takes a tissue sample from the area where cancer may exist. During the biopsy procedure, the doctor also will try to remove the cancerous growth. This is called resectioning. The entire procedure for bladder tumor biopsy and resection is known as transurethral resection of bladder tumor .