When Might Peripheral Neuropathy Be Diagnosed
Peripheral neuropathy may be diagnosed because you may notice some of the symptoms described above and see your doctor because of this. Sometimes it may be discovered if your doctor examines you for another reason for example, if you have a cut on your foot.
At other times peripheral neuropathy is diagnosed at a routine check-up for your diabetes.
Different Types Of Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy may affect:
- several nerves
- all the nerves in the body
Polyneuropathy is the most common type and starts by affecting the longest nerves first, so symptoms typically begin in the feet.
Over time it gradually starts to affect shorter nerves, so feels as if it’s spreading upwards, and later affects the hands.
Page last reviewed: 24 April 2019 Next review due: 24 April 2022
What Is The Bladder
The bladder is a hollow organ located in the pelvis, or lower abdomen. The bladder has two important functions:
- It stores urine.
- It removes urine from the body through a complex communication circuit in the spinal cord and brain.
Urinary incontinence occurs when a person cannot control the flow of urine. The storage of urine can be a problem if the bladder is unable to empty fully or if it begins to empty itself before the person reaches the bathroom . Leakage can occur if the bladder cannot empty , if the sphincter controlling urination doesnt work , or if bladder spasms cause the bladder to shrink before the person reaches the toilet .
You May Like: Cranberry Juice Cure Bladder Infection
Bladder Control Loss Which Is Often Caused By Diabetic Neuropathy
Nerve damage can comprise bladder control, leading to an overactive bladder, underactive bladder, or incontinence. Diabetic neuropathy is the most common cause of this condition, but it is also seen in people with Guillain-Barré syndrome, HIV and AIDS, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, and amyloid neuropathy.
Treatments include bladder-relaxing medication, such as Ditropan , Detrol LA , or Pro Banthine ones that stimulate bladder nerves, such as bethanechol botulinum toxin GABA supplements and anti-epileptic drugs.
What Causes Neurogenic Bladder
Neurogenic bladder can be congenital . Birth defects that can cause neurogenic bladder include:
- Spina bifida : This disorder occurs when the fetus’ spine does not completely develop during the first month of pregnancy. Babies born with myelomeningocele often have paralysis or weakness that affects how the bladder works.
- Sacral agenesis: This is a condition in which parts of the lower spine are missing.
- Cerebral palsy: Cerebral palsy is a group of chronic disorders that weaken a person’s ability to control body movement and posture. These disorders result from injury to the motor areas of the brain. The problem causing cerebral palsy may occur while the infant is still in the womb or after birth. Cerebral palsy is not always found during a child’s first year of life.
Various medical conditions can cause neurogenic bladder, including the following:
- Stroke
- Heavy metal poisoning
Don’t Miss: How Many Radiation Treatments For Bladder Cancer
The 5 False Facts Your Doctor Mistakenly Promotes Bladder Problems Due To Peripheral Neuropathy
The medical community is largely responsible for this misinformation being passed on to the suffering patient. In my view it is the job and responsibility of the family doctor to teach the patient about their neuropathy problem. It is also the doctors job to train the patient in what they can do to improve and manage their neuropathy case successfully.
===> How To End Peripheral Neuropathy < < <
Many neuropathy patients, suffering with foot or hand pain, tingling, numbness, burning, and other evasive and hard to describe neuropathy symptoms, dont even know the name of their condition! And while others do, that is essentially all they know. With this in mind I want to address some of the most commonly INCORRECT facts that suffering neuropathy patients have been told, or come to understand, due to the lack of patient education by the medical community.
1. Neuropathy comes with age, and there is nothing you can do about it.This statement is only partially correct, inasmuch as aging can contribute to the increased onset and intensity of the neuropathy condition. There are however, many simple techniques and procedures that any person can learn which will offset many of these effects of aging as they relate to peripheral neuropathy.
4. Neuropathy just gets worse with time, and you have to accept that you are stuck with it.
Peripheral Neuropathy And Lupus
Peripheral neuropathy is nerve damage that impairs of the communication between our central nervous system and the rest of the body. How is this condition implicated in lupus?
Introduction
Our central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord the centers where we coordinate, regulate and interpret and ultimately control most of our other bodily functions and occasionally some thinking! The CNS takes the signals that come from all over the body , interprets them and then sends messages back so that the body can move or react appropriately. Our peripheral nervous system consists of all of the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord and as such, mediates the CNS with the rest of the body and the outside world.
The peripheral nervous system has two main parts the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system .
The somatic nervous system is divided into motor and sensory systems. As such, it is responsible for most of our voluntary muscle movement , and for processing external stimuli such as the traditional five senses as well as all the other senses such as motion, position, and equilibrium. The SNS is also responsible for the involuntary muscle movements we have when we do things such as jerk our hand away when we touch a hot stove or kick our leg when our reflexes are tested.
Classifying Peripheral Neuropathy
What are the symptoms of peripheral neuropathy?
What causes peripheral neuropathy?
Diagnosis
Treatment
In Conclusion
Don’t Miss: Can You Have Intercourse While Having A Bladder Infection
Specific Secondary Or Associated Conditions And Complications
Both supraspinal and suprapontine injuries result in detrusor overactivity and incontinence. In spinal cord pathologies the simultaneous presence of reduced bladder wall compliance and DSD cause increased bladder pressure, which leads to structural bladder wall changes such as trabeculations and diverticuli.6
Vesicoureteral reflux and hydronephrosis may develop with increased bladder pressures .1 This can lead to renal impairment and even end stage renal disease.1,6 Patients with SCI are prone to upper tract damage and renal disease.6
Genitourinary tract infections, such as cystitis or pyelonephritis, are common. Bladder stones may develop.6
Treatment Options For Neurological Bladder Problems
Treatment for neurological problems affecting the bladder is highly individualised to the specific patient. Many factors have to be taken into consideration when determining the best treatment for the individual including:
- The patients quality of life and aims for treatment
- The specific neurological condition and its prognosis or likelihood of progressive disability
- The patients mobility and level of independence and self-care
- The patients hand and eye function and potential ability to perform intermittent self catheterisation
- The patients cognitive function
- Carer support and assistance in continence management
- The severity of the neurological abnormality affecting the bladder and its potential to cause deterioration in kidney function and bladder function
Combinations of treatment are very commonly used in management of neurological problems affecting the urinary tract due to the combinations of problems affecting both the bladder and the urinary sphincter.
Read Also: Bladder Leakage Pads For Men
Can I Prevent Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy can often be avoided if you manage your blood glucose vigilantly. To do this, be consistent in:
- monitoring your blood glucose levels
- taking medications as prescribed
- managing your diet
- being active
If you do develop diabetic neuropathy, work closely with your doctor and follow their recommendations for slowing its progression. With proper care, you can reduce the damage to your nerves and avoid complications.
Identifying The Cause Of A Neuropathy
Your GP can usually identify the underlying cause of a peripheral neuropathy.
If diabetes is suspected, they can usually make a confident diagnosis based on your symptoms, a physical examination and checking the levels of glucose in your blood and urine.
If you’re taking a medication known to cause peripheral neuropathy, your GP may temporarily stop or reduce your dose to see whether your symptoms improve.
If the cause is uncertain, you may be referred to a neurologist for more extensive blood tests to check:
- whether you have a rare acquired cause that may be responsible
- whether you have a genetic abnormality, such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
You may need a lumbar puncture to test the cerebrospinal fluid for inflammation.
Also Check: How To Fix Bladder Leakage Naturally
Disease Progression Including Natural History Disease Phases Or Stages Disease Trajectory
New onset/acute:
Many central neurologic disorders temporarily result in an areflexic bladder.
Suprapontine lesions: Detrusor areflexia often develops immediately post-stroke. Urinary incontinence is common. Uninhibited detrusor overactivity and urge incontinence may develop.8
Suprasacral lesions: During the spinal shock period , patients with SCI have a competent bladder neck, but there is detrusor acontractility/underactivity. Urinary retention is common, and incontinence occurs when there is overflow. The return of the bulbocavernosus reflex marks the recovery from spinal shock, at which time detrusor activity gradually returns.7
Infrasacral lesions: In cauda equina syndrome , early symptoms of bladder dysfunction can be subtle, such as difficulty in initiating the urinary stream.9 Early stage bladder dysfunction in diabetes may present with bladder hypertrophy, remodeling and increased contractility.10
Subacute and chronic:
Suprapontine lesions: Post-stroke incontinence is multifactorial. Detrusor overactivity is the most common UDS finding in stroke patients. Urinary incontinence is more prevalent in post-stroke patients with impaired awareness and cognition, poor lower limb motor function and depression. Many patients show improvement in voiding dysfunction by one year post-stroke. Persistence of urinary incontinence at 1 year is a poor prognostic factor for mortality, functional recovery and institutionalization.8
What Is Neurogenic Bladder

Neurogenic bladder is when a problem in your brain, spinal cord, or central nervous system makes you lose control of your bladder. You may pee too much or too little. You could have symptoms of both overactive bladder and underactive bladder . You may not be able to fully empty it.
Itâs normal to have some stress and anxiety if you canât control when you urinate. Talk to your doctor about whatâs going on as soon as possible so you can start on a treatment to help manage your symptoms.
You May Like: Does Overactive Bladder Go Away
When To See A Doctor
- A cut or sore on your foot that is infected or won’t heal
- Burning, tingling, weakness or pain in your hands or feet that interferes with daily activities or sleep
- Changes in digestion, urination or sexual function
- Dizziness and fainting
The American Diabetes Association recommends that screening for diabetic neuropathy begin immediately after someone is diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, and five years after diagnosis for someone with type 1 diabetes. After that, screening is recommended annually.
How Is Neurogenic Bladder Diagnosed
A doctor will do an exam and may order several tests of the nervous system and the bladder to diagnose neurogenic bladder: These include:
- Urodynamic studies: These bladder function tests measure how much urine the bladder can hold, the pressure within the bladder, how well urine flows, and how well the bladder empties when it is full. Special sensors may be placed on the skin near the urethra or rectum to see if the muscles and nerves in those parts of the body are working properly.
- Cystoscopy: The doctor may perform this procedure to examine the inside of the bladder and urethra with the use of a small telescope .
- X-rays
Also Check: Why Does My Bladder Hurt When I Pee
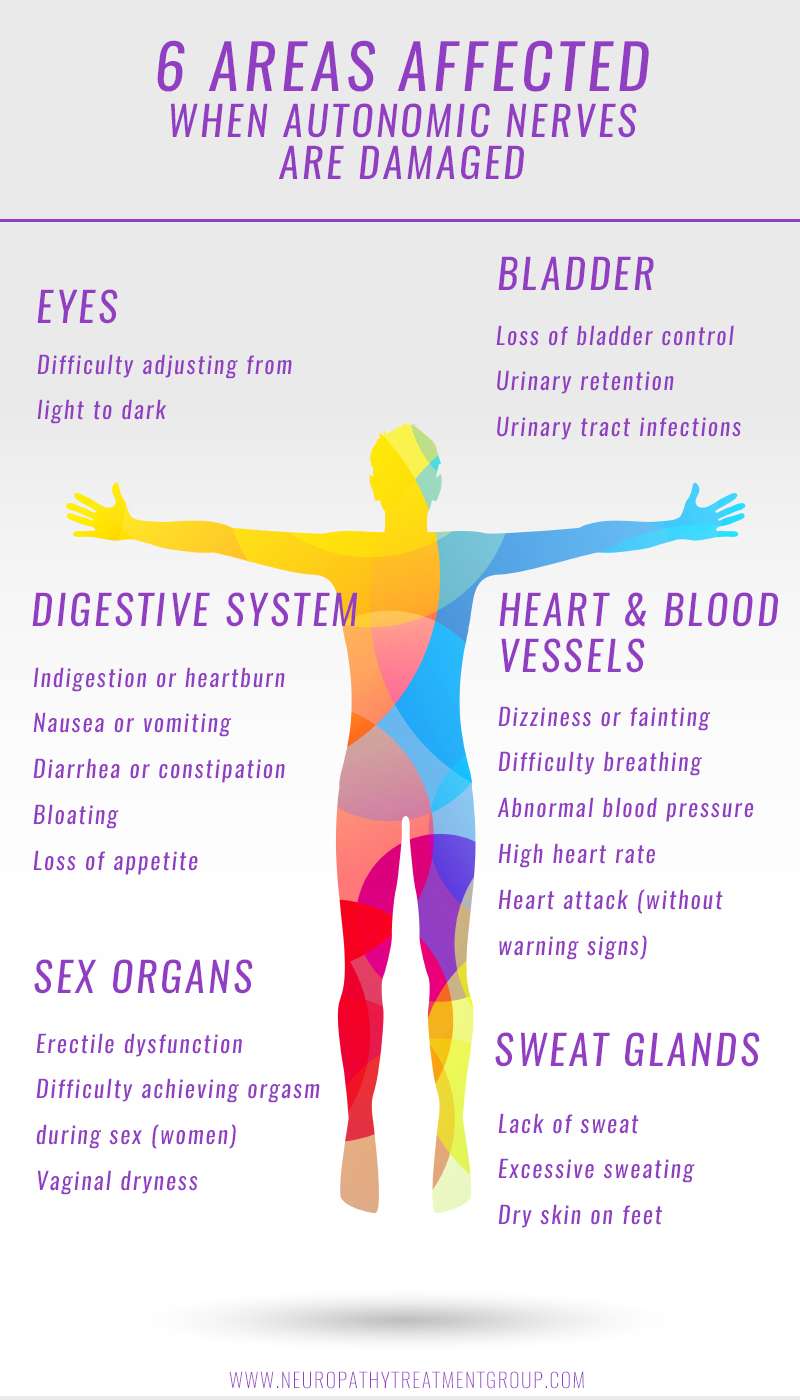
Symptoms Of Autonomic Neuropathy
General symptoms of this condition may include:
- Inability to sweat properly, leading to heat intolerance
- Loss of bladder control, leading to infection or incontinence
- Dizziness, lightheadedness or fainting because of a loss of control over blood pressure
- Diarrhea, constipation or incontinence related to nerve damage in the intestines or digestive tract
- Difficulty eating or swallowing
- Life-threatening symptoms, such as difficulty breathing or irregular heartbeat
Often, the symptoms affect a certain system in the body:
Cardiovascular Symptoms of Autonomic Neuropathy
Autonomic neuropathy can damage the nerves of the cardiovascular system, affecting heart rate and blood pressure:
- Blood pressure may drop sharply after you sit or stand, causing a feeling of lightheadedness.
- Heart rate may remain high or too low instead of fluctuating with body functions and exercise.
Gastrointestinal Symptoms of Autonomic Neuropathy
Damage to the nerves of the digestive system can cause:
- Constipation
- Difficulty swallowing
- Gastroparesis, a condition in which the stomach empties too slowly, causing nausea, vomiting, bloating and loss of appetite. This condition can cause blood sugar levels to fluctuate greatly.
Urinary and Sexual Symptoms of Autonomic Neuropathy
A person with autonomic neuropathy can have problems with urination and sexual function:
Vision-Related Symptoms of Autonomic Neuropathy
Sweating Due to Autonomic Neuropathy
Neurogenic Bladder Treatment And Home Remedies
Your care will depend on whatâs causing your symptoms and how serious they are. Thereâs no cure for neurogenic bladder, but you can manage your symptoms and get control.
If you have OAB, you may need to:
- Train your bladder. You can do this by squeezing your pelvic floor muscles during the day or when you need to pee .
- Hold it, if you can. Delayed voiding is when you wait a few minutes to urinate after you feel the urge. The goal is to extend this time to a few hours.
- Pee on a schedule. You might avoid accidents if you urinate at certain times of the day.
- Take medicine. Some medications can relax bladder muscles and stop spasms.
- Keep a healthy weight. Extra body mass can add pressure to your bladder.
- Change your diet. Things like caffeine, alcohol, spicy foods, dairy, artificial sweeteners, chocolate, and citrus fruit can irritate your system.
- Use electrical stimulation. A device under your skin sends electricity to the nerve that controls your bladder. These painless pulses help stop overactive signals that tell your brain to pee.
- Get Botox. Your doctor can inject this neurotoxin into your bladder to temporarily stop it from contracting too much. If you have problems emptying your bladder or have urinary tract infections often, this treatment isn’t an option.
If you have UAB, you may need to:
Columbia University Irving Medical Center: âNeurogenic Bladder.â
Urology Care Foundation: âWhat is Neurogenic Bladder?â
Recommended Reading: Bladder Exercises For Overactive Bladder
When Nerve Damage Causes Bladder Problems: Neurogenic Bladder
Until a few short years ago, Rob, who is in his 80s, had been relatively free of health problems. He was an active guy, skiing and hiking in his beloved Washington State mountains. Husband, father and grandfather, he was living a happy retirement from Boeing Aircraft. Then what he thought was a small nagging problem was diagnosed as a complex medical problem.
When ongoing heartburn was keeping him awake at night, he went to a GI doctor for help. A scan showed Robs bladder was so enlarged it was pushing against his stomach, causing the heartburn. One doctor visit after another revealed more than one medical issue. Rob began a series of tests and surgeries to treat bladder cancer, prostate cancer and an aortic aneurysm.
His cancers were removed, but nerve damage from his surgery left Rob unable to fully empty his bladder. Today, he relies on using a straw-like tube, called a catheter, to help empty his bladder completely. Rob has neurogenic bladderand he isnt alone. Millions of Americans have this health issue. Neurogenic bladder is when a person lacks bladder control due to damage to the nerves carrying messages between the bladder and the brain. This damage may be the result of a spinal cord injury, an infection of the brain or spinal cord, heavy metal poisoning or diseases affecting the nerves, such as stroke, multiple sclerosis, Parkinsons disease or diabetes. People born with problems of the spinal cord, such as spina bifida, are also at risk for neurogenic bladder.
Mitochondrial Neurogastrointestinal Encephalopathy Disease
Mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalopathy disease is characterized by progressive gastrointestinal symptoms, cachexia, ptosis, ophthalmoplegia/ophtalmoparesis, central and peripheral nervous system involvement .
A long history of ill-defined symptoms, such as fatigability, mild gastrointestinal complaints, or thin body habitus can precede the onset of more overt symptoms. To further complicate diagnosis, the order in which symptoms appear is unpredictable, although in a review of 102 patients the first symptoms were gastrointestinal , ptosis/ophthalmoplegia , peripheral neuropathy , and myopathy . Onset is before 20 years of age in 60% of cases, while the earliest reported onset was at five months .
Prevalence is unknown. Parental consanguinity is common, as the disease is transmitted as an autosomal recessive condition.
Progressive gastrointestinal dysmotility, caused by enteric myopathy, occurs in virtually all affected individuals and is carachterized by gastric and small bowel hypomotility resulting in early satiety, nausea, dysphagia, gastroesophageal reflux, postprandial emesis, episodic abdominal pain and/or distention, and diarrhea. Despite severe GI dysfunction, serum concentrations of micronutrients and vitamins are usually normal.
Neurologic presentation includes ptosis, ophthalmoplegia or ophthalmoparesis, leukoencephalopathy and demyelinating PN.
Histologically, demyelination and remyelination are observed, along with loss of large myelinated fibers.
You May Like: Best Product For Bladder Leakage
What Causes Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is caused by high blood sugar levels sustained over a long period of time. Other factors can lead to nerve damage, such as:
- damage to the blood vessels caused by high cholesterol levels
- mechanical injury, such as injuries caused by carpal tunnel syndrome
- lifestyle factors, such as smoking or alcohol use
Low levels of vitamin B-12 can also lead to neuropathy. Metformin, a common medication used to manage diabetes, can decrease levels of vitamin B-12. You can ask your doctor for a simple blood test to identify any vitamin deficiencies.
Peripheral Neuropathy: Evaluation And Differential Diagnosis
GREGORY CASTELLI, PharmD, BCPS, BC-ADM, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center St. Margaret, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
KRISHNA M. DESAI, MD, Columbia University Medical Center, New York, New York
REBECCA E. CANTONE, MD, Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, Oregon
Am Fam Physician. 2020 Dec 15 102:732-739.
Peripheral neuropathy is one of the most common neurologic problems encountered by family physicians.1,2 Peripheral neuropathy can be classified clinically by the anatomic pattern of presenting symptoms and, if indicated, by results of electrodiagnostic studies for axonal and demyelinating disease.2,3 Peripheral nerves consist of motor, sensory, and autonomic nerve fibers. It is important to differentiate peripheral neuropathy from other disorders with similar presentations and to identify and address potential causes.
Don’t Miss: Anti Spasm Medication For Bladder