What Are The Stages Of Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer can be either early stage or invasive .
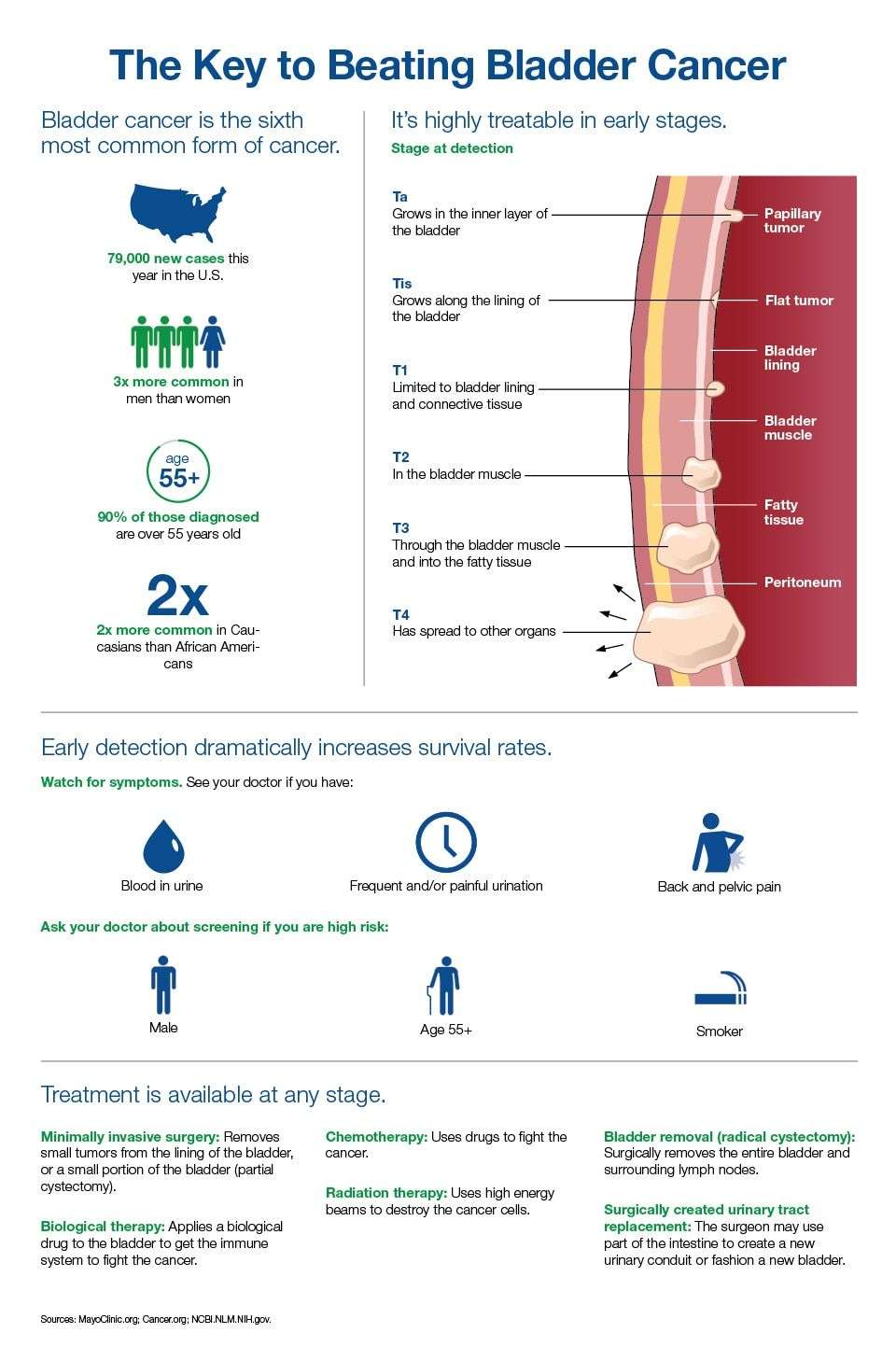
The stages range from TA to IV . In the earliest stages , the cancer is confined to the lining of the bladder or in the connective tissue just below the lining, but has not invaded into the main muscle wall of the bladder.
Stages II to IV denote invasive cancer:
- In Stage II, cancer has spread to the muscle wall of the bladder.
- In Stage III, the cancer has spread to the fatty tissue outside the bladder muscle.
- In Stage IV, the cancer has metastasized from the bladder to the lymph nodes or to other organs or bones.
A more sophisticated and preferred staging system is known as TNM, which stands for tumor, node involvement and metastases. In this system:
- Invasive bladder tumors can range from T2 all the way to T4 .
- Lymph node involvement ranges from N0 to N3 .
- M0 means that there is no metastasis outside of the pelvis. M1 means that it has metastasized outside of the pelvis.
Smoking Can Affect The Risk Of Bladder Cancer
Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesn’t mean that you will not get cancer. Talk to your doctor if you think you may be at risk for bladder cancer.
Risk factors for bladder cancer include the following:
- Using tobacco, especially smoking cigarettes.
- Having a family history of bladder cancer.
- Having certain changes in the genes that are linked to bladder cancer.
- Being exposed to paints, dyes, metals, or petroleum products in the workplace.
- Past treatment with radiation therapy to the pelvis or with certain anticancer drugs, such as cyclophosphamide or ifosfamide.
- Taking Aristolochia fangchi, a Chinese herb.
- Drinking water from a well that has high levels of arsenic.
- Drinking water that has been treated with chlorine.
- Having a history of bladder infections, including bladder infections caused by Schistosoma haematobium.
- Using urinarycatheters for a long time.
Older age is a risk factor for most cancers. The chance of getting cancer increases as you get older.
Bladder Cancer Clinical Trials
What about Clinical Trials?
You may hear about clinical trials for your bladder cancer. Clinical trials are research studies that test if a new treatment or procedure is safe and effective.
Through clinical trials, doctors find new ways to improve treatments and the quality of life for people with disease. Trials are available for all stages of cancer. The results of a clinical trial can make a major difference to patients and their families. Please visit our clinical trials research webpage to learn more.
Read Also: How To Fight A Bladder Infection Without Antibiotics
Treatment Of Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage IV bladder cancer that has not spread to other parts of the body may include the following:
- Urinary diversion or cystectomy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
Treatment of stage IV bladder cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, such as the lung, bone, or liver, may include the following:
- External radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Urinary diversion or cystectomy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- A clinical trial of new anticancer drugs.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Early Signs Of Bladder Cancer In Women
Knowing the signs and symptoms can help you get diagnosed sooner, which may improve your prognosis. Here are five warning signs to watch for:
Also Check: What Causes Weak Bladder In Females
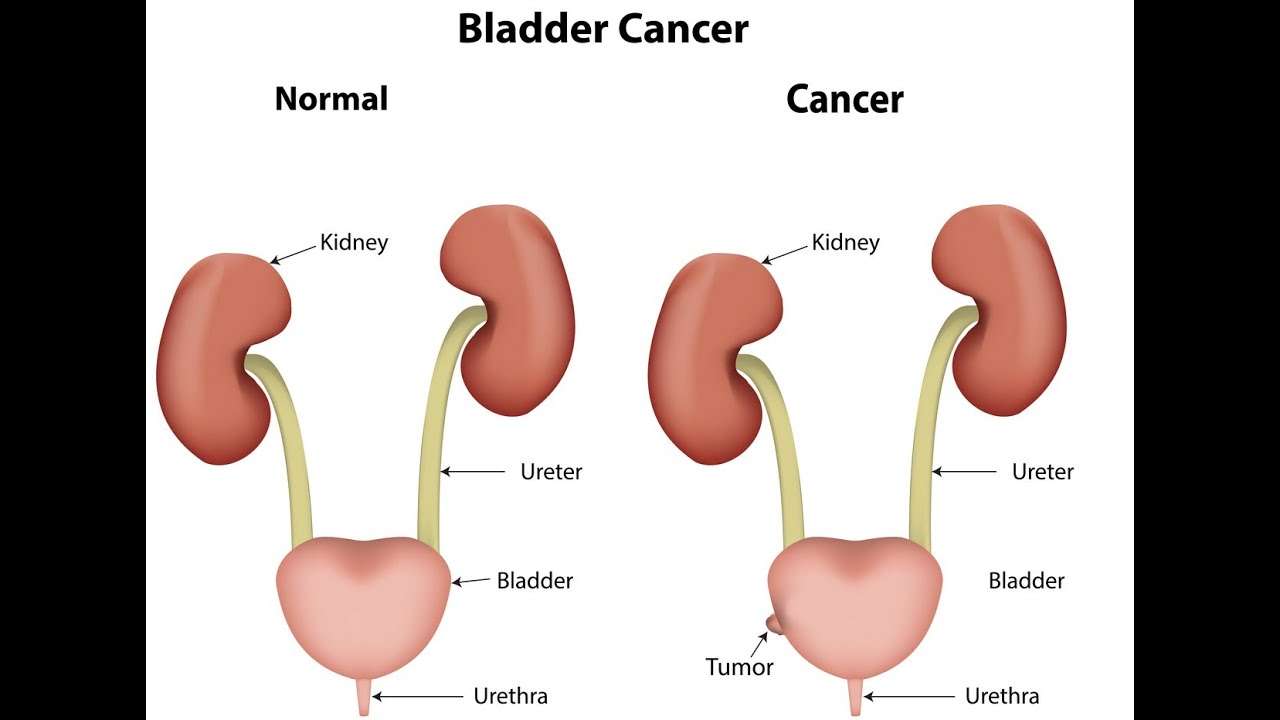
Bladder Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Bladder
The bladder is a hollow organ in the lower part of the abdomen. It is shaped like a small balloon and has a muscular wall that allows it to get larger or smaller to store urine made by the kidneys. There are two kidneys, one on each side of the backbone, above the waist. Tiny tubules in the kidneys filter and clean the blood. They take out waste products and make urine. The urine passes from each kidney through a long tube called a ureter into the bladder. The bladder holds the urine until it passes through the urethra and leaves the body.
There are three types of bladder cancer that begin in cells in the lining of the bladder. These cancers are named for the type of cells that become malignant :
- Transitional cell carcinoma: Cancer that begins in cells in the innermost tissue layer of the bladder. These cells are able to stretch when the bladder is full and shrink when it is emptied. Most bladder cancers begin in the transitional cells. Transitional cell carcinoma can be low-grade or high-grade:
- Low-grade transitional cell carcinoma often recurs after treatment, but rarely spreads into the muscle layer of the bladder or to other parts of the body.
- High-grade transitional cell carcinoma often recurs after treatment and often spreads into the muscle layer of the bladder, to other parts of the body, and to lymph nodes. Almost all deaths from bladder cancer are due to high-grade disease.
See the following PDQ summaries for more information:
What Are The Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
Many people with bladder cancer can have blood in their urine but no pain while urinating. There are a number of symptoms that might indicate bladder cancer like fatigue, weight loss, and bone tenderness, and these can indicate more advanced disease. You should pay particular attention to the following symptoms:
- an intravenous pyelogram
- X-rays
Your doctor can rate bladder cancer with a staging system that goes from stages 0 to 4 to identify how far the cancer has spread. The stages of bladder cancer mean the following:
- Stage 0 bladder cancer hasnt spread past the lining of the bladder.
- Stage 1 bladder cancer has spread past the lining of the bladder, but it hasnt reached the layer of muscle in the bladder.
- Stage 2 bladder cancer has spread to the layer of muscle in the bladder.
- Stage 3 bladder cancer has spread into the tissues that surround the bladder.
- Stage 4 bladder cancer has spread past the bladder to the neighboring areas of the body.
Your doctor will work with you to decide what treatment to provide based on the type and stage of your bladder cancer, your symptoms, and your overall health.
You May Like: Cysts On Bladder And Kidneys
There Are Three Ways That Cancer Spreads In The Body
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Facts About Bladder Cancer In Women
While bladder cancer typically hasnt been associated with women, it is important to understand the unique way that bladder cancer does affect women, and why its critical that bladder cancer isnt overlooked.
- Approximately 50% of cases are diagnosed while the cancer is still in the bladder. However, that percentage is lower in women, because symptoms are often overlooked.
- Women have a 1 in 89 chance of developing bladder cancer in their lifetime . However, bladder cancer in women is on the rise.
- Approximately 90% of bladder cancer cases are in individuals over 55 years old, so it is important to be extra vigilant of early signs of bladder cancer as you age.
- Bladder cancer has a high recurrence rate. If you have been diagnosed with bladder cancer, it is important to continue to receive regular exams in order to handle any potential recurrence.
Recommended Reading: What Can Help Overactive Bladder
Patients Can Enter Clinical Trials Before During Or After Starting Their Cancer Treatment
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCIs clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
What Are The Risk Factors For Bladder Cancer
Some factors increase the risk of bladder cancer:
- Cigarette smoking is the biggest risk factor it more than doubles the risk. Pipe and cigar smoking and exposure to second-hand smoking may also increase one’s risk.
- Prior radiation exposure is the next most common risk factor .
- Certain chemotherapy drugs also increase the risk of bladder cancer.
- Environmental exposures increase the risk of bladder cancer. People who work with chemicals, such as aromatic amines are at risk. Extensive exposure to rubber, leather, some textiles, paint, and hairdressing supplies, typically related to occupational exposure, also appears to increase the risk.
- Infection with a parasite known as Schistosoma haematobium, which is more common in developing countries and the Middle East.
- People who have frequent infections of the bladder, bladder stones, or other diseases of the urinary tract, or who have chronic need for a catheter in the bladder, may be at higher risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
- Patients with a previous bladder cancer are at increased risk to form new or recurrent bladder tumors.
Other risk factors include diets high in fried meats and animal fats, and older age. In addition, men have a three-fold higher risk than women.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Rid Of Overactive Bladder
What Is Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
Muscle invasive bladder cancer is a cancer that spreads into the detrusor muscle of the bladder. The detrusor muscle is the thick muscle deep in the bladder wall. This cancer is more likely to spread to other parts of the body.
In the U.S., bladder cancer is the third most common cancer in men. Each year, there are more than 83,000 new cases diagnosed in men and women. About 25% of bladder cancers are MIBC. Bladder cancer is more common as a person grows older. It is found most often in the age group of 75-84. Caucasians are more likely to get bladder cancer than any other ethnicity. But there are more African-Americans who do not survive the disease.
What is Cancer?
Cancer is when your body cells grow out of control. When this happens, the body cannot work the way it should. Most cancers form a lump called a tumor or a growth. Some cancers grow and spread fast. Others grow more slowly. Not all lumps are cancers. Cancerous lumps are sometimes called malignant tumors.
What is Bladder Cancer?
When cells of the bladder grow abnormally, they can become bladder cancer. A person with bladder cancer will have one or more tumors in his/her bladder.
How Does Bladder Cancer Develop and Spread?
The bladder wall has many layers, made up of different types of cells. Most bladder cancers start in the urothelium or transitional epithelium. This is the inside lining of the bladder. Transitional cell carcinoma is cancer that forms in the cells of the urothelium.
When To Make An Appointment With Your Urologist
Bladder cancer may be overlooked in women because its easy to chalk up symptoms to a stubborn UTI or normal vaginal spotting. Unfortunately, this means women are often diagnosed after the cancer has spread and become harder to treat. So if youre worried, dont just write off your symptoms. Call your doctor to determine if its a minor infection or something more serious. If it is bladder cancer, its easier to treat if you catch it early.
If you would like to talk to a urologist, you can see if we have a location near you or you can contact us to ask a question or make an appointment.
Don’t Miss: How Can I Heal My Bladder Naturally
Treatment Of Stages Ii And Iii Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
- Transurethral resection with fulguration.
- A clinical trial of a new treatment.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Risk Factors Of Bladder Cancer
By far, smoking is the biggest risk factor to be concerned about when it comes to bladder cancer. According to the National Institutes of Health, about 50% of women diagnosed with bladder cancer are smokers. Because the rate of occurrence is so much higher for smokers, if you notice any of the above symptoms and you smoke, let your doctor know as soon as possible.
Another major risk factor is previously having bladder cancer. Bladder cancer has a 50-80% recurrence rate, which is among the highest of any form of cancer. This is why it is imperative to continue to see your physician and be on the lookout for any symptoms of bladder cancer if youve had it before. When in doubt, get it checked out.
Age is another major factor. The average age of diagnosis in women is 73. Any woman over the age of 55 years old should keep an extra eye out for symptoms.
You May Like: Bladder Retraining For Urge Incontinence
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if bladder cancer spreads to the bone, the cancer cells in the bone are actually bladder cancer cells. The disease is metastatic bladder cancer, not bone cancer.
Treatment For Stage 2 And Stage 3
Treatment for stage 2 and stage 3 bladder cancer may include:
- removal of part of the bladder in addition to chemotherapy
- removal of the whole bladder, which is a radical cystectomy, followed by surgery to create a new way for urine to exit the body
- chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or immunotherapy that can be done to shrink the tumor before surgery, to treat the cancer when surgery isnt an option, to kill remaining cancer cells after surgery, or to prevent the cancer from recurring
Also Check: What Were Your Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
Five Types Of Standard Treatment Are Used:
Surgery
One of the following types of surgery may be done:
- Transurethral resection with fulguration: Surgery in which a cystoscope is inserted into the bladder through the urethra.A tool with a small wire loop on the end is then used to remove thecancer or to burn the tumor away with high-energy electricity. This is known as fulguration.
- Radical cystectomy: Surgery to remove the bladder and anylymph nodes and nearby organs that contain cancer. This surgery may bedone when the bladder cancer invades the muscle wall, or when superficialcancer involves a large part of the bladder. In men, the nearby organs that areremoved are the prostate and the seminal vesicles. In women, the uterus, theovaries, and part of the vagina are removed. Sometimes, when the cancer hasspread outside the bladder and cannot be completely removed, surgery to removeonly the bladder may be done to reduce urinarysymptoms caused by the cancer.When the bladder must be removed, the surgeon creates another way for urine toleave the body.
- Partial cystectomy: Surgery to remove part of thebladder. This surgery may be done for patients who have a low-grade tumor thathas invaded the wall of the bladder but is limited to one area of the bladder.Because only a part of the bladder is removed, patients are able to urinate normally afterrecovering from this surgery. This is also called segmental cystectomy.
- Urinary diversion: Surgery to make a new way forthe body to store and pass urine.
Radiation therapy
Chemotherapy