Keeping Health Insurance And Copies Of Your Medical Records
Even after treatment, its very important to keep health insurance. Tests and doctor visits cost a lot, and even though no one wants to think of their cancer coming back, this could happen.
At some point after your cancer treatment, you might find yourself seeing a new doctor who doesnt know about your medical history. Its important to keep copies of your medical records to give your new doctor the details of your diagnosis and treatment. Learn more in Keeping Copies of Important Medical Records.
Emotional And Spiritual Changes
Everyone will feel different emotions when they are dying. A lot depends on:
- the type of person they are
- their age
- how much support they have
- their religious and spiritual beliefs
- the experiences they have had in life
Someone dying in their 20s is likely to feel very differently from someone who is 80. And someone leaving behind young children will have different worries from someone whose children are grown up and able to take care of themselves.
As death gets closer they might begin to let go and seem more at peace with things. Others might become very anxious, fearful or angry. Some people could appear to withdraw, even from the people they love and care about. But this doesnt mean that they dont care anymore.
These events are all very normal and are a natural part of dying.
Remission And The Chance Of Recurrence
A remission is when cancer cannot be detected in the body and there are no symptoms. This may also be called having no evidence of disease or NED.
A remission may be temporary or permanent. This uncertainty causes many people to worry that the cancer will come back. While many remissions are permanent, it is important to talk with your doctor about the possibility of the cancer returning. Understanding your risk of recurrence and the treatment options may help you feel more prepared if the cancer does return. Learn more about coping with the fear of recurrence.
If the cancer returns after the original treatment, it is called recurrent cancer. It may come back in the same place , nearby , or in another place .
When this occurs, a new cycle of testing will begin again to learn as much as possible about the recurrence. After this testing is done, you and your doctor will talk about the treatment options.
People with recurrent cancer often experience emotions such as disbelief or fear. You are encouraged to talk with the health care team about these feelings and ask about support services to help you cope. Learn more about dealing with cancer recurrence.
Recommended Reading: Natural Remedies For Cystitis Bladder Infection
Other Immunotherapies For Bladder Cancer
Researchers are testing other potential immunotherapy drugs to see how well they work on their own and combined with other treatments.
Theyâre also testing combinations of immunotherapies. Early results showed that nivolumab combined with another drug, ipilimumab, worked in 26% to 38% of people who took them.
Studies are also looking at atezolizumab in combination with another checkpoint inhibitor called MTIG7192A.
Treating Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
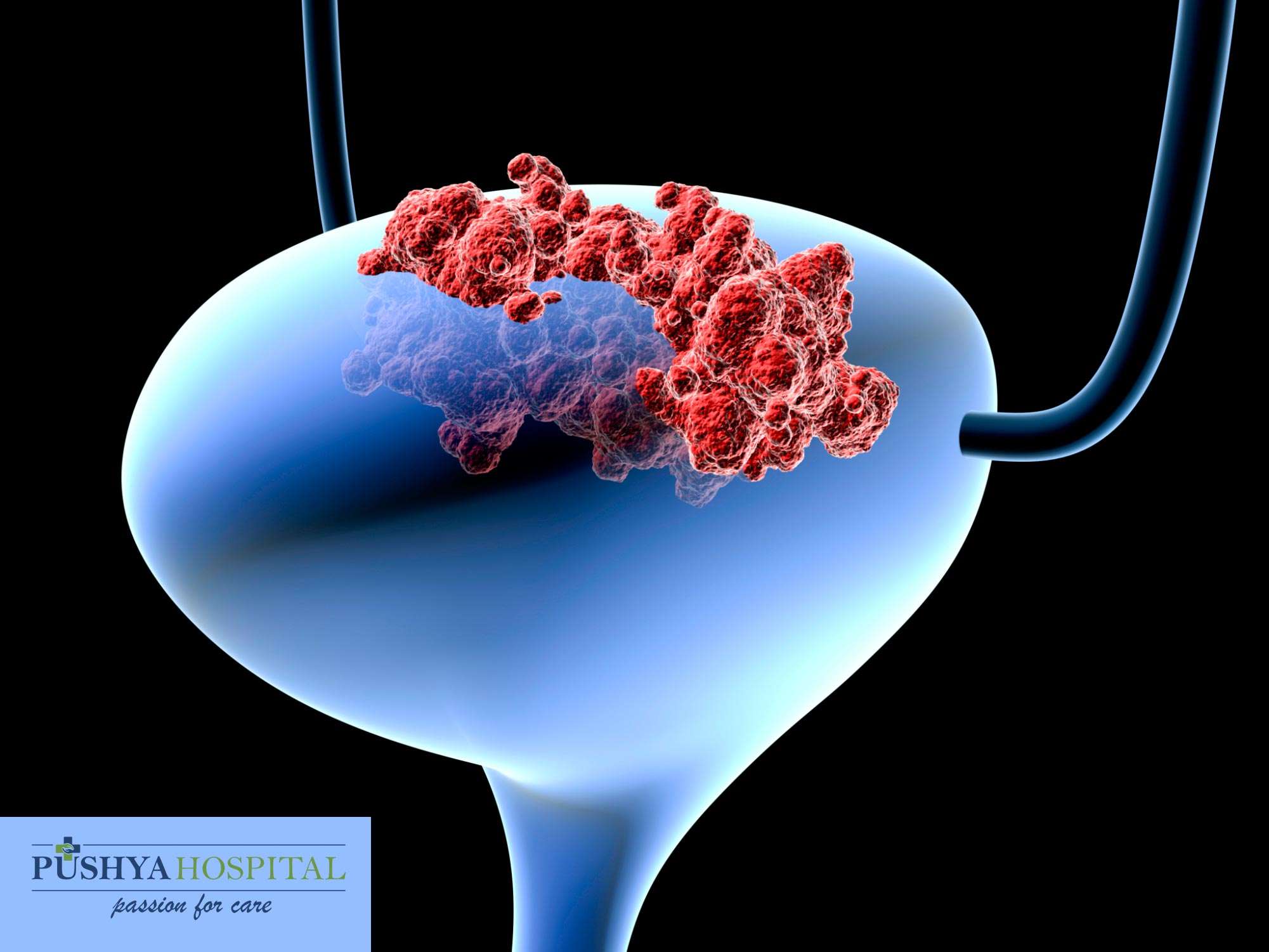
These cancers have reached the pelvic or abdominal wall , may have spread to nearby lymph nodes , and/or have spread to distant parts of the body . Stage IV cancers are very hard to get rid of completely.
Chemotherapy is usually the first treatment if the cancer has not spread to distant parts of the body . The tumor is then rechecked. If it appears to be gone, chemo with or without radiation or cystectomy are options. If there are still signs of cancer in the bladder, chemo with or without radiation, changing to another kind of chemo, trying an immunotherapy drug, or cystectomy may be recommended.
Chemo is typically the first treatment when bladder cancer has spread to distant parts of the body . After this treatment the cancer is rechecked. If it looks like it’s gone, a boost of radiation to the bladder may be given or cystectomy might be done. If there are still signs of cancer, options might include chemo, radiation, both at the same time, or immunotherapy.
In most cases surgery cant remove all of the cancer, so treatment is usually aimed at slowing the cancers growth and spread to help people live longer and feel better. If surgery is a treatment option, it’s important to understand the goal of the operation whether it’s to try to cure the cancer, to help a person live longer, or to help prevent or relieve symptoms from the cancer.
Because treatment is unlikely to cure these cancers, many experts recommend taking part in a clinical trial.
Also Check: Chronic Bladder Infection In Men
How You Might Feel
You are likely to feel some very strong emotions during the time your relative or friend is dying. You might feel that you want to try and change what is happening. Often all you can do is give them a lot of support and comfort during this difficult time.
You might need support and help yourself, when someone close to you is dying. It could help to speak to:
- the doctor or nurses on the ward
- a religious leader
- a counsellor
- close friends and relatives
Try not to worry that you are going to do something wrong. Just being with your loved one and letting them know you love and care for them is the most important thing.
-
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence , 7 December 2016
-
On Death and Dying
Local Bladder Cancer Metastasis
When bladder cancer spreads, it first invades the bladder wall, which is made up of four distinct layers. It can take some time for cancer to penetrate all of these layers, but once it has, it can then spread into the surrounding fatty tissues and lymph nodes. Once bladder cancer has reached the lymph nodes, it can travel to distant parts of the body through the lymphatic system. Separately, it can also continue to grow into surrounding areas such as the abdominal wall .
Read Also: Can You Have Intercourse While Having A Bladder Infection
Surgery For Bladder Cancer
Surgery is done for most bladder cancers. The type you have depends on the stage of the cancer.
Removing the tumor from the inside bladder is the most common surgery for early bladder cancer. This can be done during a cystoscopy. A a cystoscope with a looped wire on the end is used to remove the tumor.
When the cancer is more invasive, the cancer is removed along with part of the bladder or the entire bladder.
If only part of the bladder is removed, you’ll still be able to hold and release urine as normal, though in smaller amounts. If the entire bladder is removed, you’ll need another way to store and pass urine. Your doctor can explain the options for this.
Side effects of surgery
Any type of surgery can have some risks and side effects. For instance, removing the bladder not only changes how your body passes urine, but it can also cause sexual side effects. If you have these or any other problems, let your doctors know. There are ways to help deal with many side effects.
Stage 0 Bladder Cancer
Stage zero bladder cancers are called noninvasive papillary carcinoma and carcinoma in situ. Theyre precancerous lesions that could develop into more serious cancers if not treated.
These growths develop on the inner lining of the bladder. Noninvasive papillary carcinoma, also called stage 0a, forms long, thin growths into the empty space inside the bladder.
Carcinoma in situ, also called stage 0is bladder cancer, forms flatter growths that tend to be of a wilder grade. It is considered a more aggressive disease and is more likely to spread into the muscular walls of the bladder.
According to the National Cancer Institutes SEER database of cancer statistics, about half of bladder cancers are diagnosed at stage 0.
Recommended Reading: Bladder Problems After Gastric Bypass
Bladder Cancer Clinical Trials
What about Clinical Trials?
You may hear about clinical trials for your bladder cancer. Clinical trials are research studies that test if a new treatment or procedure is safe and effective.
Through clinical trials, doctors find new ways to improve treatments and the quality of life for people with disease. Trials are available for all stages of cancer. The results of a clinical trial can make a major difference to patients and their families. Please visit our clinical trials research webpage to learn more.
Certain Factors Affect Prognosis And Treatment Options
The prognosis depends on the following:
- The stage of the cancer . Bladder cancer in the early stages can often be cured.
- The type of bladder cancer cells and how they look under a microscope.
- Whether there is carcinoma in situ in other parts of the bladder.
- The patients age and general health.
If the cancer is superficial, prognosis also depends on the following:
- How many tumors there are.
- The size of the tumors.
- Whether the tumor has recurred after treatment.
Treatment options depend on the stage of bladder cancer.
You May Like: How To Prevent Bladder Infection After Intercourse
Where Does Metastatic Bladder Cancer Spread To
Bladder cancer spreads when cancerous cells reproduce and invade surrounding healthy tissues. This is known as metastasis. Usually, metastatic bladder cancer refers to cancer that has spread to distant organs, but metastasis can occur locally in the muscles and connective tissues that are directly adjacent to the bladder as well.
Removing The Whole Bladder
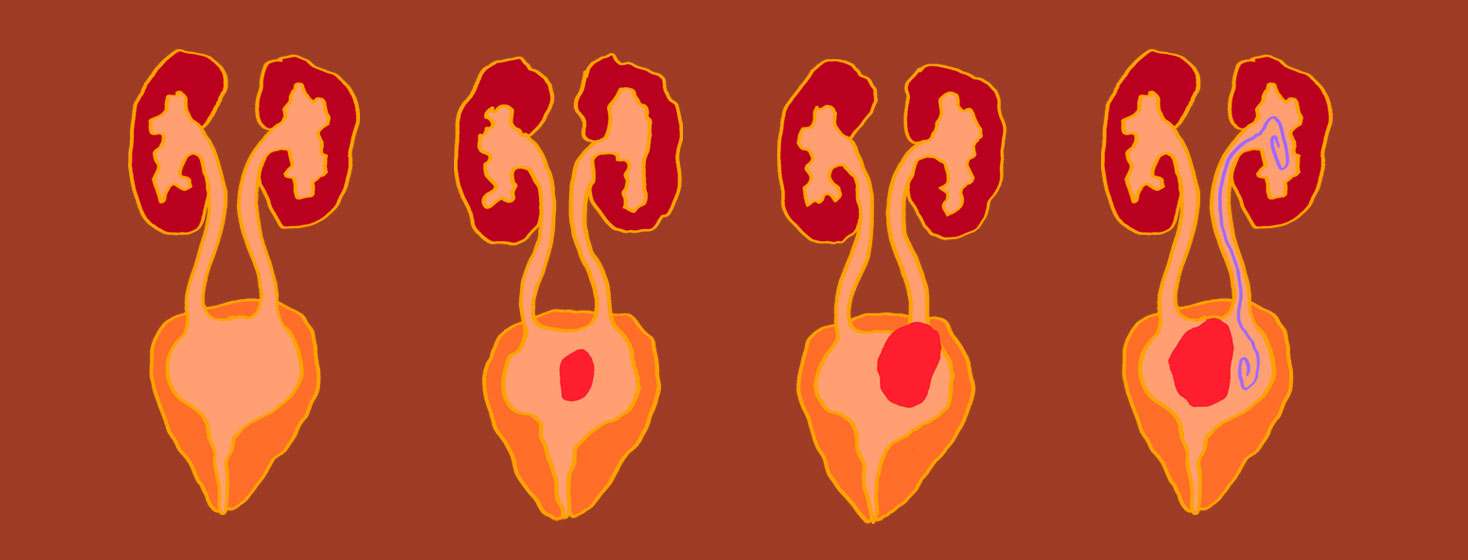
A radical cystectomy means taking out the whole bladder and the nearby lymph nodes.
In men, the surgeon also removes the prostate gland and glands that store semen . This is because bladder cancer can come back in this area. In women, the surgeon usually removes the womb and fallopian tubes. Sometimes the surgeon removes your ovaries and part of your vagina. Your surgeon talks this through with you beforehand.
You may also have part of your bowel removed. This is so your surgeon can create another way for your body to collect and pass urine. It’s called a recto sigmoid pouch. Your surgeon will discuss this with you beforehand if you’re having this operation.
Recommended Reading: Bowel And Bladder Problems After Back Surgery
What Increases Your Chances Of Getting Bladder Cancer
Anything that increases your chances of getting a disease is called a risk factor. The main risk factors for bladder cancer include:
- Smoking. Cigarette smokers are much more likely than other people to get bladder cancer.
- Being older than 40, being male, or being white .
- Being exposed to cancer-causing chemicals, such as those used in the wood, rubber, and textile industries.
- What you eat. A diet high in fried meats and fats increases your risk for bladder cancer.
- Parasites. There is a parasite that causes schistosomiasis, which can increase your risk. This condition is sometimes found in developing countries and rarely occurs in North America.
Loss Of Bladder And Bowel Control
The dying person might lose control of their bladder and bowel. This happens because the muscles in these areas relax and dont work as they did. This can be distressing to see and you might worry that they may feel embarrassed. The nursing staff will do all they can to protect the bed and keep your relative or friend as clean and comfortable as possible.
If you are caring for the person at home, the district nurses and specialist nurses can arrange for you to have protective sheets or pads for the bed. They might also be able to arrange a laundry service for you, if necessary. As people become very close to death and are not eating or drinking, the amount of urine and stools they produce gets less and less.
Recommended Reading: Doterra Oils For Bladder Infection
Physical Emotional And Social Effects Of Cancer
Cancer and its treatment cause physical symptoms and side effects, as well as emotional, social, and financial effects. Managing all of these effects is called palliative care or supportive care. It is an important part of your care that is included along with treatments intended to slow, stop, or eliminate the cancer.
Palliative care focuses on improving how you feel feels during treatment by managing symptoms and supporting patients and their families with other, non-medical needs. Any person, regardless of age or type and stage of cancer, may receive this type of care. And it often works best when it is started right after an advanced cancer diagnosis. People who receive palliative care along with treatment for the cancer often have less severe symptoms, better quality of life, report that they are more satisfied with treatment, and they may live longer.
Palliative treatments vary widely and often include medication, nutritional changes, relaxation techniques, emotional and spiritual support, and other therapies. You may also receive palliative treatments similar to those meant to get rid of the cancer, such as chemotherapy, surgery, or radiation therapy.
Before treatment begins, talk with your doctor about the goals of each treatment in the treatment plan. You should also talk about the possible side effects of the specific treatment plan and palliative care options.
Symptoms In Men And Women
Bladder cancer symptoms in men and women are the same. Men are more likely to get bladder cancer, but they are also more likely to have it diagnosed earlier, according to Moffitt Cancer Center.
Women are more likely to mistake bladder cancer symptoms for urinary tract infections or menstruation.
Rarely, bladder cancer may also be misdiagnosed as interstitial cystitis in women. IC is a painful, inflammatory bladder condition that affects more women than men.
In one study, doctors found bladder cancer in about one percent out of 600 patients referred to them for IC treatment, according to an article in Urology Times.
Don’t Miss: Bladder Control Problems At Night
What Are The Risk Factors For Bladder Cancer
Some factors increase the risk of bladder cancer:
- Cigarette smoking is the biggest risk factor it more than doubles the risk. Pipe and cigar smoking and exposure to second-hand smoking may also increase one’s risk.
- Prior radiation exposure is the next most common risk factor .
- Certain chemotherapy drugs also increase the risk of bladder cancer.
- Environmental exposures increase the risk of bladder cancer. People who work with chemicals, such as aromatic amines are at risk. Extensive exposure to rubber, leather, some textiles, paint, and hairdressing supplies, typically related to occupational exposure, also appears to increase the risk.
- Infection with a parasite known as Schistosoma haematobium, which is more common in developing countries and the Middle East.
- People who have frequent infections of the bladder, bladder stones, or other diseases of the urinary tract, or who have chronic need for a catheter in the bladder, may be at higher risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
- Patients with a previous bladder cancer are at increased risk to form new or recurrent bladder tumors.
Other risk factors include diets high in fried meats and animal fats, and older age. In addition, men have a three-fold higher risk than women.
How Does Transitional Cell Carcinoma Of The Bladder Spread
Transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder tends to remain superficial however, in 5% to 20% of cases, it progresses to muscle invasion and, more rarely, can metastasize. TCC of the bladder primarily spreads via regional lymphatics. The most common sites of distant metastases of TCC are the liver, lung, mediastinum and bone.
You May Like: Heavy Feeling In Bladder And Frequent Urination
Articles On Bladder Cancer Treatments
If you have bladder cancer, there are several available treatment options. Your doctor will help you decide which treatment is best for you. This will depend on a number of things, including your age, how much the cancer has spread , and any other health conditions you have.
Many people with bladder cancer need surgery. But in some cases, it canât remove all of the disease. So youâll need other treatments along with, or instead of, an operation. These could include chemotherapy, radiation, and immunotherapy.
Treating Stage Ii Bladder Cancer
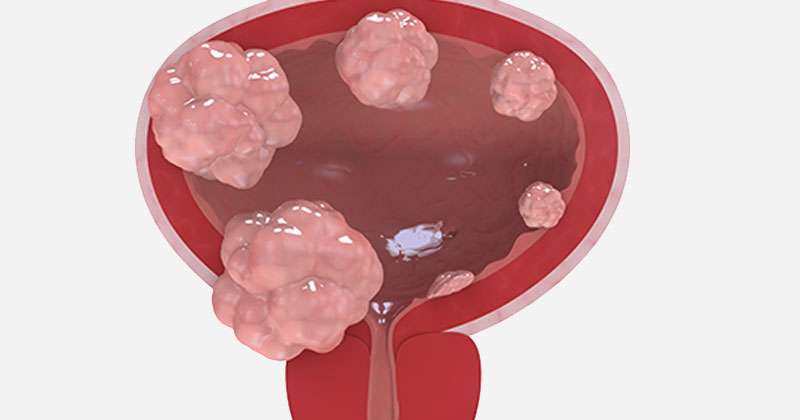
These cancers have invaded the muscle layer of the bladder wall , but no farther. Transurethral resection is typically the first treatment for these cancers, but it’s done to help determine the extent of the cancer rather than to try to cure it.
When the cancer has invaded the muscle, radical cystectomy is the standard treatment. Lymph nodes near the bladder are often removed as well. If cancer is in only one part of the bladder, a partial cystectomy may be done instead. But this is possible in only a small number of patients.
Radical cystectomy may be the only treatment for people who are not well enough to get chemo. But most doctors prefer to give chemo before surgery because it’s been shown to help patients live longer than surgery alone. When chemo is given first, surgery is delayed. This is not a problem if the chemo shrinks the bladder cancer, but it might be harmful if the tumor continues to grow during chemo.
If cancer is found in nearby lymph nodes, radiation may be needed after surgery. Another option is chemo, but only if it wasn’t given before surgery.
For people who have had surgery, but the features of the tumor show it is at high risk of coming back, the immunotherapy drug, nivolumab, might be offered. When given after surgery, nivolumab is given for up to one year.
For patients who cant have surgery because of other serious health problems, TURBT, radiation, chemotherapy, or some combination of these may be options.
Also Check: How Can I Heal My Bladder Naturally