Weight Loss And Gallstones
As mentioned above, an unfortunate side effect of rapid weight loss is the formation of gallstones.
Due to the prevalence of gallstones, surgeons generally put their patients on a 6-month course of preventative medication.
If there is a history of gallstones before gastric bypass surgery, the surgeon may suggest gallbladder removal before surgery.
Bariatric Surgery And Kidney
Despite the many positive metabolic outcomes, RYGB is also associated with higher risk of kidney stones and bone disease after surgery. Three years after surgery, new kidney stone incidence is 8% , and this continues to rise to 14% 10 years after surgery. In comparison, the rate for kidney stones in controls with obesity is 5% and 7% at 3 and 10 years, respectively . Similarly, the multivariate hazards ratio of developing a kidney stone is 2.3 for patients who have had RYGB compared with controls with obesity . In contrast, restrictive procedures, including SG, have not been associated with risk of kidney stones or fracture . Given that SG has increased in popularity only in the past few years, most studies of restrictive procedures and kidney stones have primarily included patients with adjustable gastric bands . One study that examined incidence rates in 85 patients with an SG found that only 1% of patients with an SG developed a stone after a mean of just over 2 years of follow-up . A recent, retrospective review found that 8% of patients who underwent RYGB surgery compared with 4% of patients with an SG developed a kidney stone postoperatively, with a mean follow-up of nearly 3 years . However, additional studies of patients who have undergone an SG with longer follow-up time are needed to better characterize the overall stone risk associated with SG.
Assessment Missing At Random Assumption
The UIQ was completed for 74.9% of the potential assessments across time. More than 64.8% of the missing UIQs were because no self-assessment forms were completed for an assessment. Another 29.2% were because participants stopped completing the self-assessment packet before reaching the UIQ. These missing data could not be attributed to incontinence status. However, for those missing incontinence status at 2 or 3 years, the prevalence of incontinence at other time points was greater and remained significant after controlling for factors that were independently related to the completeness of incontinence follow-up data . Therefore, a sensitivity analysis was performed using imputed data.
When missing incontinence status was followed by known incontinence status, the missing status was imputed from a logistic regression model containing variables related to the completeness of follow-up data or to the prevalence of incontinence. To impute missing incontinence status that was not followed by known incontinence status, a pattern mixture model that did not assume missing at random was used. Finally, multiple imputation was used to combine the results from 30 imputed data sets. The modeled values from the sensitivity analysis are reported in .
You May Like: Where Do You Feel Bladder Pain
What Happens When You Have Low Blood Sugar Often
It is extremely important to maintain normal blood sugar levels. If these health problems continue happening in the long-term, your body may no longer be able to provide signs and symptoms of altered blood sugar levels. This can lead to severe, life-threatening reactions.
You might have some unexpected symptoms of hypoglycemia that seem unrelated to your diet. This includes finding it difficult to sleep at night, slurred speech, clumsiness, bladder problems, and persistent infections.
These can be signs of a more serious problem. It is always recommended to consult with your healthcare provider about health concerns you might have.
Gastric bypass may resolve diabetes. If symptoms only improve, it is important to remember your glucose monitor and healthful maintenance of your blood sugar levels. Medications may be adjusted or even stopped. Even if bariatric surgery does not resolve type 2 diabetes, the improvements can still significantly change your life. Bariatric surgery and diabetes can be managed.
Bariatric Surgery Increases Urinary Levels Of Mir 200a And Mir 200b
Urinary levels of miR 200a and miR 200b were also measured. Both are expressed in the kidney and change in their expression is associated with diabetic nephropathy . MiR 200a urine levels increased 2.5-fold at 26 months and 3.4-fold at 12 years following surgery , although neither increase achieved statistical significance. MiR 200b levels increased 5.8-fold at 26 months and strikingly 28.6-fold at 12 years post-operatively . All but one patient demonstrated a post-operative increase of urinary miR 200a and all patients demonstrated an increase in urinary miR 200b relative to their individual pre-operative level. Significant correlations were observed between both miR 200a and miR 200b and days following bariatric surgery . There were also significant correlations between urinary levels of miR 192 and both miR 200a and miR 200b .
Figure 4. Urinary expression of miR 200 following bariatric surgery. miR-200a, n = 9 miR-200b, n = 8. Data represents mean fold change ± SEM relative to mean preoperative expression. **p< 0.01 vs. preoperative expression by paired t-test. Each patient is represented by a unique symbol. Timecourse of miR 200a and miR 200b expression following surgery. Data represented as fold change relative to individual preoperative expression.
Recommended Reading: Unable To Control Bowels And Bladder
Why The Procedure Is Performed
Weight-loss surgery may be an option if you are very obese and have not been able to lose weight through diet and exercise.
Doctors often use the body mass index and health conditions such as type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure to determine which people are most likely to benefit from weight-loss surgery.
Gastric bypass surgery is not a quick fix for obesity. It will greatly change your lifestyle. After this surgery, you must eat healthy foods, control portion sizes of what you eat, and exercise. If you do not follow these measures, you may have complications from the surgery and poor weight loss.
Be sure to discuss the benefits and risks with your surgeon.
This procedure may be recommended if you have:
- A BMI of 40 or more. Someone with a BMI of 40 or more is at least 100 pounds over their recommended weight. A normal BMI is between 18.5 and 25.
- A BMI of 35 or more and a serious medical condition that might improve with weight loss. Some of these conditions are obstructive sleep apnea, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.
Gastric Bypass Surgery Can Lead To Dental Problems
For many, gastric bypass surgery is the only realistic means of overcoming obesity and the myriad associated health issues. In my practice, more and more patients are opting for gastric bypass surgery, often with dramatic results. One 18 month follow-up study found a 57% recovery from diabetes, an 84 % cure from cholesterol problems, and a 47% cure from high blood pressure. These are all really good reasons to support the recommendations for surgery. Since the results from having gastric bypass surgery can be obtained from diet and lifestyle modifications, candidates must demonstrate that they have tried more conventional methods first, have a BMI of 40 or above, or have a BMI of 35 with other health related issues like diabetes.
Unfortunately, I often see uncontrolled tooth decay and tooth loss post-operatively. The reasons have not been widely investigated. There are a few logical explanations as to why this is happening.
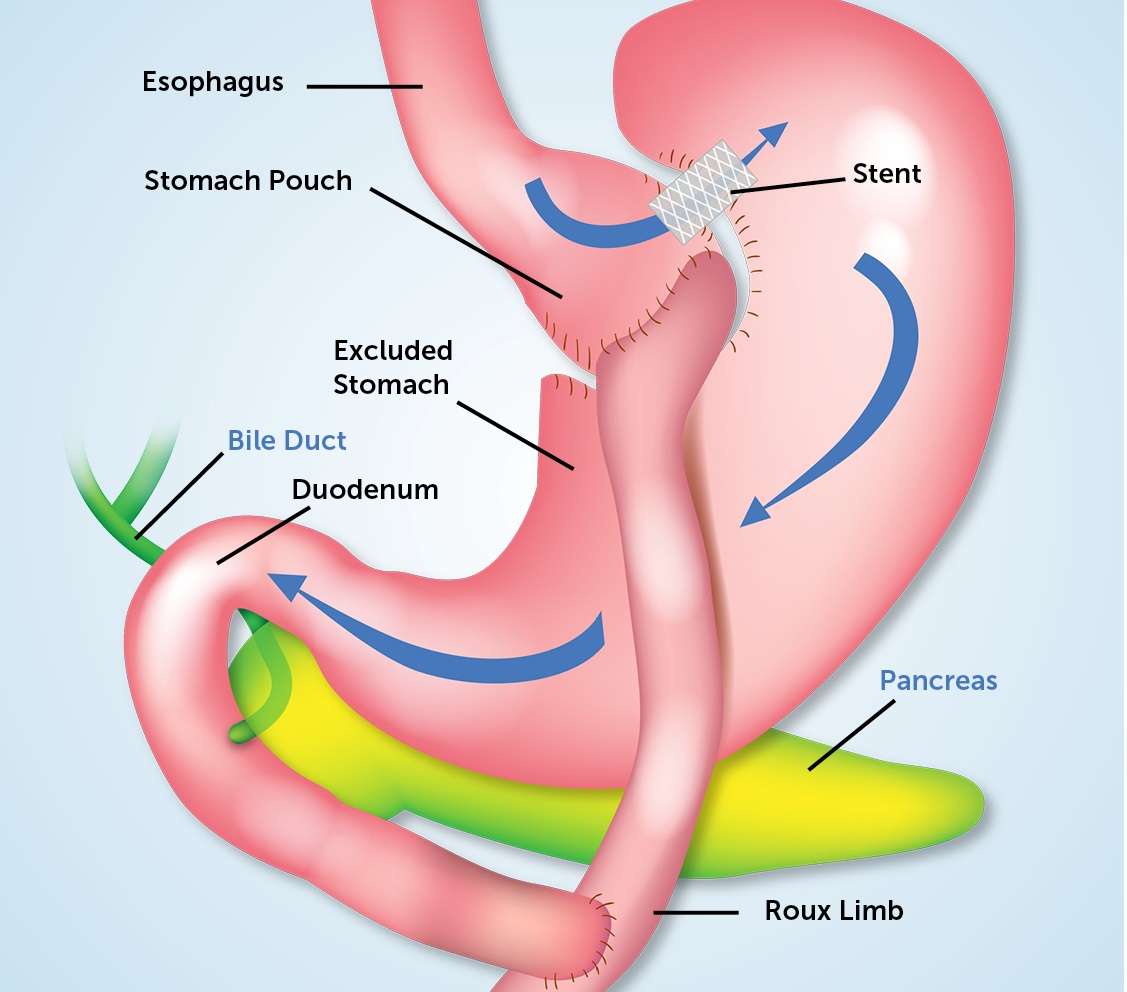
Now let me briefly describe what gastric bypass surgery is. The gold standard is known as Roux-en-Y surgery and involves separating the top of the stomach and connecting it to an area of the small intestines farther down, BYPASSING most of the stomach and some of the small intestines. The remaining unused part of the stomach is reattached to the small intestines to allow the digestive juices to continue to help digestion.
Recommended Reading: What Is Good For Bladder Health
Bariatric Surgery Modulates Urinary Levels Of Micrornas Involved In The Regulation Of Renal Function
- 1Department of Surgery and Cancer, Imperial College London, London, United Kingdom
- 2Dasman Diabetes Institute, Kuwait City, Kuwait
- 3Institute of Global Health Innovation, Imperial College London, London, United Kingdom
- 4Department of Academic Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism, Hull York Medical School, Kingston upon Hull, United Kingdom
- 5Weill Cornell Medical College Qatar, Qatar Foundation, Doha, Qatar
Background: Obesity and diabetes cause chronic kidney disease with a common pathophysiology that is characterized by the accumulation of collagen in the extracellular matrix. Recent evidence has implicated the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition as a key step in this pathology with regulation by microRNAs. Weight loss leads to improvements in renal function therefore, this study hypothesized that bariatric-surgery aided weight loss would lead to changes in urinary microRNAs involved in the regulation of renal function.
Materials and methods: Twenty-four bariatric patients undergoing Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy donated urine pre-operatively and at 26 months and 12 years post-operatively. Urine samples were also obtained from 10 healthy weight and 7 morbidly obese non-surgical controls. Expression levels of kidney microRNAs were assessed in urine and the function of microRNAs was assessed through the in vitro transfection of HK-2 cells, a kidney proximal tubule cell line.
How To Prevent Hypoglycemia In Bariatric Patients
After bariatric surgery, lifestyle change will promote desired weight loss and maintain health in the long-run. Your healthcare provider will be able to best direct you in how to handle your specific case of low blood sugar. Some changes that may prevent low blood sugar and other related complications are listed below.
Don’t Miss: Where Is The Bladder Located
Obesity And Bariatric Surgery
Obesity and metabolic syndrome are well-established risk factors for kidney stones. Higher body mass index , larger body size, and weight gain are each strongly associated with higher risk of kidney stones in men and women . For example, compared with a BMI of 2122.9 kg/m2, the multivariate relative risk for developing kidney stones with a BMI of 30 kg/m2 is 2.09 in young women, 1.90 in older women, and 1.33 in men . Furthermore, diabetes mellitus and hypertension are both independently associated with higher risk of developing kidney stones.
Trend in more overall bariatric surgery procedures and more sleeve gastrectomies over time in the United States. DS, duodenal switch GB gastric band RYGB, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass SG, sleeve gastrectomy. Data from .
Gallbladder Removal / Surgery And Weight Loss
The gallbladder may be removed via an abdominal incision. Nowadays, it is more probable your physician will choose the laparoscopic surgical procedure. This process involves a couple of tiny incisions. Your hospital stay and complete recovery period will probably be substantially shorter following a laparoscopic operation.
You May Like: Can Lower Back Pain Cause Bladder Problems
Gastric Sleeve And Gallbladder Problems
Posted by Jet Medical Tourism® | Last updated Jul 24, 2018 | Gastric Sleeve Surgery
Gastric sleeve and gallbladder problems are related to one another in large part because of the link between gallstones, obesity, and rapid weight loss.
A common complication after gastric sleeve surgery is problems with the gallbladder, and most often this comes in the form of gallstones.
Even though gastric sleeve can be a life-altering and potentially life-saving bariatic surgery that can help you lead the life youve always wanted, there are health issues that can arise because of the operation.
When youre considering a bariatric procedure like the gastric sleeve, its important to be aware of these possible complications, so today were going to talk about gastric sleeve and gallbladder problems.
How A Gastric Bypass Affects What Foods To Avoid Or Eat With Caution

Post-operation, the diet is typically all-liquid for several weeks and then only soft or mashed foods until the post-surgical swelling in the digestive system heals. Thereafter, the small size of the gastric pouch and the reduced digestive capacity make it necessary to choose foods with some care. Potentially long term problematic foods include, seeds, popcorn, and some nuts. These foods food may be difficult to digest. Certain foods may expand in the gastric pouch and temporarily block your connection to the intestines or chronically cause pouch dilatation. Dried fruit may expand in the gastric pouch. Soft drinks with carbonation are not only bad for any diet but the gas expansion effect of carbonation can be a real pain in the stomach pouch. Breads are high in carbohydrates. The difference between white bread and cake is not always so different from a nutritional perspective. Bread may throw off your glycemic index and may also be prone to expand in the pouch. From this list, its obvious that the cautionary for foods include anything difficult to digest, foods that might block the gastric pouch exit, any food with sharp edges, and food or drink that has a tendency to expand in the stomach. Youll probably develop a personally relevant list of foods to avoid or eat differently in consultation with your doctor, a nutritionist and through experience.
Read Also: Turbt Treatment For Bladder Cancer
Gallbladder Problems After Gastric Bypass Surgery
Research has shown that at least 35% of bariatric patients develop gallstones during their weight loss journey. Rapid weight loss after gastric bypass surgery is associated with gallstone formation. How does this happen and can we prevent it?
This article aims to answer those questions. Here we will expand your knowledge on the causes of gallstones and possible preventive measures.
We also discuss the facts about gastric bypass surgery and why it may cause gallbladder problems.
The Causes Of Low Blood Sugar After Gastric Bypass Surgery
After a gastric bypass, also called Roux-en-Y bariatric surgery, there are quite a few alterations made to the digestive tract. The way your body digests food is also different. Low blood sugar or reactive hypoglycemia can develop for various reasons, including:
- Drinking alcohol
- Eating food or beverages high in simple carbohydrates or sugar
- Dumping syndrome
The changes of gastric bypass can cause excess insulin production. Eating certain foods can trigger the release of hormones to cause a rapid decline in glucose. Exercise can also have an effect on blood sugar levels.
When you skip meals, there is an imbalance in food intake and insulin production. You may feel light-headed, tired, dizzy, or your mood may change.
Reactive hypoglycemia is a little different. It can happen after you have eaten. It may happen after youve eaten something high in sugar or refined carbohydrates.
Refined carbohydrates can include added sugars and refined grains that are stripped of nutrients. These are foods like pastries, candy, soft drinks, fruit juices, muffins, pasta, and hidden sugar in many condiments we use, such as tomato sauce and salad dressings. These types of foods and beverages may be called high glycemic index options because they spike blood sugar and lead to a drop.
This can also be an effect of dumping syndrome when high sugar food sources are consumed and enter the small intestine too quickly. An excessive amount of insulin is secreted, leading to low blood sugar as well.
Also Check: How Long Should A Bladder Infection Last
Symptoms Of Low Blood Sugar After Gastric Bypass Surgery
The symptoms can include:
- mood swings
- headache
Reactive hypoglycemia can happen within a few hours after a meal or snack. People can see symptoms of dumping syndrome anywhere from 10 minutes to 3 hours after eating.
If you feel you are having low blood sugar, you should check with a glucose monitor. If it is too low, you may need to treat it with 15 grams of a fast acting carbohydrate, or as directed by your healthcare provider.
This can be a very serious matter and bariatric patients should be cautious.
What Problems Can Occur After Gastric Bypass Surgery
There are numerous problems which can arise after gastric bypass surgery.
Staple line or anastomotic leak can occur after any stomach or bowel resectional surgery. If a section of the staple line or the joins dont heal properly, it can break down resulting in a hole in the stomach or bowel much like a ruptured ulcer with leakage of stomach/intestinal contents into the abdominal cavity. This can be a life-threatening complication if not recognised early and appropriately managed.
“There are many factors that affect the risk of a leak including the expertise of your surgeon and issues that impair the healing process including smoking, poorly controlled diabetes and immunosuppressive medications.” Mr Krishna Epari | Bariatric surgeon Perth
The intestinal bypass is a low pressure system which theoretically decreases the risk and can make them relatively easier to manage. However only the traditional Roux en Y bypass excludes bile refluxing and is thus much easier technically to manage a leak and the leak tends to be less hazardous though still serious. There is no single effective treatment for all leaks which may require a variety of endoscopic, surgical and radiological procedures to manage and may require prolonged hospitalisations, intensive care and repeat procedures. Prevention is always better than cure. In expert hands and with thorough assessment and preparation the risk of a leak should be under 1%. You should therefore choose your Surgeon wisely.
Don’t Miss: Not Being Able To Hold Bladder
Faq Obesity And Bariatric Surgery
What is morbid obesity?Morbid obesity is generally defined as a Body Mass Index of 40 or greater, which is roughly equal to 100 pounds or more over ideal body weight or those with a BMI greater than 35 who have two or more co-morbid conditions. The disease of morbid obesity interferes with basic physical functions such as breathing or walking. Long-term effects of morbid obesity include serious health consequences and shorter life expectancy. Back to Top
What causes morbid obesity?The causes of morbid obesity are multiple and complex. Genetic, environmental and social factors may play a role. Studies have demonstrated that, once the problem is established, efforts such as dieting and exercise programs have a limited ability to provide effective long-term relief. Back to Top
What is a co-morbid condition?It is the presence of one or more disorders or diseases in addition to a primary disorder or disease or, the presence of a disorder or disease that is caused by or otherwise related to another condition in the same patient. The primary disease of morbid obesity can lead to several co-morbid conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, sleep apnea and joint damage. Back to Top
How does bariatric surgery work?Bariatric surgery is the clinical term for several different procedures. The procedures use one or both of two approaches to help patients lose weight and improve or resolve co-morbid conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure.
Examples of restrictive procedures: