How Common Is Urinary Incontinence In Men
Urinary incontinence occurs in 11 to 34 percent of older men. Two to 11 percent of older men report daily urinary incontinence 2). Although more women than men develop urinary incontinence, the chances of a man developing urinary incontinence increase with age because he is more likely to develop prostate problems as he ages. Men are also less likely to speak with a health care professional about urinary incontinence, so urinary incontinence in men is probably far more common than statistics show. Having a discussion with a health care professional about urinary incontinence is the first step to fixing this treatable problem.
How Does The Urinary System Work
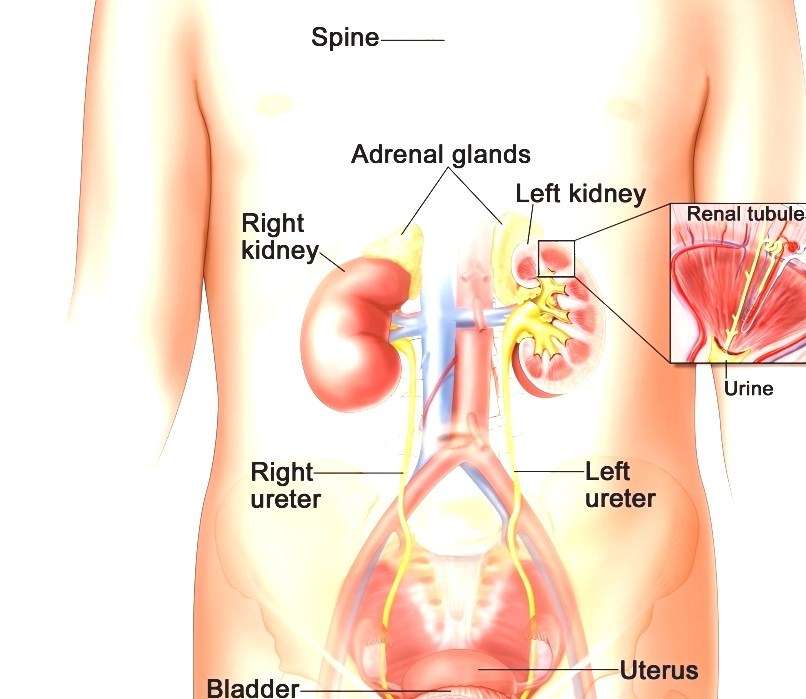
The urinary system’s function is to filter blood and create urine as a waste by-product. The organs of the urinary system include the kidneys, renal pelvis, ureters, bladder and urethra.
The body takes nutrients from food and converts them to energy. After the body has taken the food components that it needs, waste products are left behind in the bowel and in the blood.
The kidney and urinary systems help the body to eliminate liquid waste called urea, and to keep chemicals, such as potassium and sodium, and water in balance. Urea is produced when foods containing protein, such as meat, poultry, and certain vegetables, are broken down in the body. Urea is carried in the bloodstream to the kidneys, where it is removed along with water and other wastes in the form of urine.
Other important functions of the kidneys include blood pressure regulation and the production of erythropoietin, which controls red blood cell production in the bone marrow. Kidneys also regulate the acid-base balance and conserve fluids.
Layers Of The Bladder
Your bladder is made up of layers.
The first layer is on the inside of your bladder and is called transitional epithelium. It is a special type of lining that stretches as the bladder fills up. It stops the urine being absorbed back into your body.
The second layer is a thin layer of connective tissue called the lamina propria.
The third layer is muscle tissue called the muscularis propria.
The fourth layer is fatty connective tissue. It separates the bladder from other body organs, such as the prostate and kidneys.
You May Like: Can Anxiety Cause Bladder Leakage
How Can You Keep Your Urinary Tract Healthy
You can help keep your urinary tract healthy by following some basic tips.
Drink enough fluids, especially water. If youre healthy, try to drink six to eight 8-ounce glasses of fluid each day. You may need to drink more if you have kidney stones or bladder stones. At least half of your fluid intake should be water. You might need to drink less water if you have certain conditions, such as kidney failure or heart disease. Ask your health care professional how much fluid is healthy for you.
Keep your bowels regular. Regular bowel movements are important to your bladder health. You can promote both bowel health and bladder health by
- making healthy food choices. You can keep your urinary tract healthy by sticking to an eating plan that includes lean proteins, whole grains, fiber-rich breads, nuts, colorful berries, fruits, and vegetables to promote regular bowel movements.
- living a healthy lifestyle. Get regular physical activity, limit your alcohol intake, cut down on caffeinated food and drinks, and dont smoke.
Go whenever you need to. Often, people will hold their urine because its not a good time to go to the bathroom. However, holding in your urine for too long can weaken your bladder muscles and make it harder for your bladder to empty completely. Urine left in your bladder can allow bacteria to grow and makes you more likely to develop a urinary tract infection .
Submucosa Or Lamina Propria
The submucosa or lamina propriaconsists of loose connective tissue where stroma cells, blood vessels and thin smooth muscle bundles called muscularis mucosae are located and provide nutrients and support to the overlying urothelium and gives the urothelium an undulating or corrugated appearance when the organ is empty. The superficial layer of smooth muscle is not to be confused with the true muscular layer of the bladder called the muscularis propria or detrusor muscle. The subepithelial connective tissue is scant in the area of the trigone where the mucosa is always smooth due to its close attachment to the muscle of the wall .
Don’t Miss: How Can I Relax My Bladder Naturally
Anatomy Of The Ureter
The ureter is 2530cm long and approximately 5mm thick.
There are three physiologic bottlenecks where kidney stones are most likely to get impacted:
Transition from the renal pelvis into the ureter.
Sharp bend by the common/external iliac artery.
Passage into the urinary bladder .
Location
The ureter runs caudal on top of the psoas major, passes across the bifurcation of the common iliac artery or the external iliac artery as it enters the lesser pelvis, and then descends further caudally along the lateral wall of the pelvis near the peritoneum.
Fig. 15.8
Continued Path in the Male Body
Roughly at the level of the ischiadic spine, it changes its course medially and anteriorly in the direction of the urinary bladder. Slightly above the seminal vesicle, it reaches the posterior lateral wall of the bladder, where it is crossed by the vas deferens. Here, the vas deferens lies closer to the peritoneum than the ureter. Continuing on, the ureter crosses the bladder diagonally from posterolat-eral to anteromedial.
Continued Path in the Female Body
Topographic Relationships
-
inferior mesenteric artery or left colic artery
-
root of the mesentery
What Are The Types Of Urinary Incontinence In Men
The types of urinary incontinence in men include:
- Urgency incontinence
- Transient incontinence
Urgency Incontinence
Urgency incontinence happens when a man urinates involuntarily after he has a strong desire, or urgency, to urinate. Involuntary bladder contractions are a common cause of urgency incontinence. Abnormal nerve signals might cause these bladder contractions.
Triggers for men with urgency incontinence include drinking a small amount of water, touching water, hearing running water, or being in a cold environmenteven if for just a short whilesuch as reaching into the freezer at the grocery store. Anxiety or certain liquids, medications, or medical conditions can make urgency incontinence worse.
The following conditions can damage the spinal cord, brain, bladder nerves, or sphincter nerves, or can cause involuntary bladder contractions leading to urgency incontinence:
Urgency incontinence is a key sign of overactive bladder. Overactive bladder occurs when abnormal nerves send signals to the bladder at the wrong time, causing its muscles to squeeze without enough warning time to get to the toilet.
Stress Incontinence
Stress incontinence results from movements that put pressure on the bladder and cause urine leakage, such as coughing, sneezing, laughing, or physical activity. In men, stress incontinence may also occur:
- after prostate surgery
- after neurologic injury to the brain or spinal cord
- after trauma, such as injury to the urinary tract
- during older age
Don’t Miss: New Treatments For Neurogenic Bladder
S Of The Urinary Bladder
The apex of the bladder points forward towards the pubic symphysis, while the base lies posteriorly, against the rectum in males or vagina in females. The neck of the bladder is the inferior aspect where the bladder walls narrow and converge towards the urethra like a funnel. This directs urine into the urethra.
The body of the bladder is the largest part lying between the apex, fundus and neck of the bladder. The trigone of the bladder is a triangle region on the posterior wall. The two ureteric orifices and internal urethral orifice mark the three points of the trigone. It has a slight elevation known as the uvula of the bladder.
The parts of the detrusor muscle towards the neck of the bladder form the internal urethral sphincter. Some fibers run around the neck for better bladder control. This sphincter closes during ejaculation to prevent backward flow of semen into the bladder in men. The internal urethral sphincter is under involuntary control. The external urethral sphincter which is under voluntary control is formed by the urogenital diaphragm.
- Vesical venous plexus > > internal iliac veins or into the internal vertebral venous plexus
- Males vesical plexus communicates with the prostatic plexus
- Females vesical plexus communicates with the vaginal/uterovaginal plexus
Other Ways Of Describing Bladder Cancer
In addition to its cell type, bladder cancer may be described as noninvasive, non-muscle-invasive, or muscle-invasive.
-
Noninvasive. Noninvasive bladder cancer includes noninvasive papillary carcinoma and carcinoma in situ . Noninvasive papillary carcinoma is a growth found on a small section of tissue that is easily removed. This is called stage Ta. CIS is cancer that is found only on or near the surface of the bladder, which is called stage Tis. See Stages and Grades for more information.
-
Non-muscle-invasive. Non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer typically has only grown into the lamina propria and not into muscle, also called stage I. Non-muscle-invasive cancer may also be called superficial cancer, although this term is being used less often because it may incorrectly suggest that the cancer is not serious.
-
Muscle-invasive. Muscle-invasive bladder cancer has grown into the bladder’s wall muscle and sometimes into the fatty layers or surrounding tissues or organs outside the bladder.
It is important to note that non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer has the possibility of spreading into the bladder muscle or to other parts of the body. Additionally, all cell types of bladder cancer can spread beyond the bladder to other areas of the body through a process known as metastasis.
Don’t Miss: Over The Counter Bladder Medication
How Is Urinary Incontinence In Women Diagnosed
Women should let their health care provider, such as a family practice physician, a nurse, an internist, a gynecologist, urologist, or a urogynecologista gynecology doctor who has extra training in bladder problems and pelvic problems in womenknow they have urinary incontinence, even if they feel embarrassed. To diagnose urinary incontinence, a health care professional will take a medical history and conduct a physical exam. The health care professional may order diagnostic tests, such as a urinalysis.
Medical History
The health care professional will take a medical history and ask about symptoms, patterns of urination and urine leakage, bowel function, medications, history of childbirth, and past pelvic operations. To prepare for the visit with the health care professional, a woman may want to keep a bladder diary for several days beforehand. Information that a woman should record in a bladder diary includes:
- what and how much she drinks
- how many times she urinates and how much urine is released
- how often she has accidental leaks
- whether she feels a strong urge to go before leaking
- what she was doing when leaks occurred, for example, coughing or lifting
Physical Exam
The health care professional will also perform a limited physical exam to look for signs of medical conditions that may cause urinary incontinence. The health care professional may order further neurologic testing if necessary. The health care professional may also perform pelvic and rectal exams.
Where Is The Urinary Bladder Located In A Frog
Where Is The Urinary Bladder Located In A Frog?
Is urinary bladder present in frog? One of the unique features of all amphibians is the presence of a urinary bladder that develops as a ventral outpocketing of the cloaca and has no direct connection with the ureters.
What does the urinary bladder do in a frog? Urinary Bladder The organ that collects and stores urine until released. Fat Bodies Masses of fat in the body cavities of frogs. Needed for hibernating and mating. Spleen Organ in the frogs circulatory system that makes, stores, and destroys blood cells.
Is urinary bladder present in amphibians? A urinary bladder is present in fish as an expansible part of the urinary duct, in amphibians and bladder-possessing reptiles as a pocket in the cloaca. In mammals it is a greatly expandible muscular sac.
Also Check: Best Way To Treat Bladder Infection
Location Of Bladder In Children
Contrary to the general position in the pelvic region among human adults, the bladder has different location in children. That is, it has a bit higher place in abdominal cavity not only in infants, but also in young children. The same is the case even when it is empty and does not contain any traces of urinary excretions.
Bladder In Relation To Nearby Structures
In males, the seminal vesicles, ductus deferens, ureters, and rectum border the inferoposterior aspect of the bladder and prostate. Anterior to the bladder is the space of Retzius or retropubic space, which is composed of fibroadipose tissue and the prevesical fascia. The dome and posterior surface of the bladder are covered by parietal peritoneum, which reflects superiorly to the seminal vesicles and is continuous with the anterior rectal peritoneum.
In females, the posterior peritoneal reflection is continuous with the uterus and vagina and is referred to as the anterior cul-de-sac or vesicouterine pouch. The inferoposterior aspect of the bladder thus rests on the anterior vaginal wall, through which the urethra courses. As a result of positioning adjacent to the reproductive organs and behind the bony pubis, the bladder neck and urethra are at risk for both direct and hypoxic injury during childbirth. See the image below.
Recommended Reading: What Is Good For Bladder Health
Bladder Anatomy Location Parts And Pictures
Posted by Dr. Chris
The urinary bladder is a hollow muscular organ located in the lesser pelvis when empty. It serves as a reservoir for urine and can stretch considerably to store close to a maximum of 500 milliliters of urine. The average full bladder that is not overly distended contains about 350 milliliters of urine. It receives urine produced in the kidneys via the ureters and passes it out into the external environment through the urethra.
The Female Urethra Is Shorter Than The Male Urethra
Urine produced in the kidneys passes through the ureters, collects in the bladder, and is then excreted through the urethra. In females, the urethra is narrow and about 4 cm long, significantly shorter than in males. It extends from the bladder neck to the external urethral orifice in the vestibule of the vagina.
Read Also: Unable To Control Bowels And Bladder
Blood Supply And Lymphatics
The superior and inferior vesicle arteries provide the blood supply to the bladder. These are indirect branches of the internal iliac arteries. The bladder also receives some of its blood supply from the obturator artery and the inferior gluteal artery. In some cases, the inferior vesicle artery may be a branch of the internal pudendal artery.
Blood is drained from the bladder via the vesical venous plexus that empties into the internal iliac vein. Lymphatics are drained via various lymph nodes associated with the veins in the area, with most of the drainage occurring via the external iliac lymph nodes.
Clinical Relevance: Spinal Cord Injuries And The Bladder
The bladder has important clinical considerations when it comes to spinal cord lesions. There are two different clinical syndromes, depending on where the damage has occurred.
Reflex Bladder Spinal Cord Transection Above T12
In this case, the afferent signals from the bladder wall are unable to reach the brain, and the patient will have no awareness of bladder filling. There is also no descending control over the external urethral sphincter, and it is constantly relaxed.
There is a functioning spinal reflex, where the parasympathetic system initiates detrusor contraction in response to bladder wall stretch. Thus, the bladder automatically empties as it fills known as the reflex bladder.
Flaccid Bladder Spinal Cord Transection Below T12
A spinal cord transection at this level will have damaged the parasympathetic outflow to the bladder. The detrusor muscle will be paralysed, unable to contract. The spinal reflex does not function.
In this scenario, the bladder will fill uncontrollably, becoming abnormally distended until overflow incontinence occurs.
Recommended Reading: Will Overactive Bladder Go Away
What Region Is The Urinary Bladder In
4.5/5Urinary Bladderurinary bladderurineread here
The bladder is a subperitoneal, hollow muscular organ that acts as a reservoir for urine. The bladder is located in the lesser pelvis when empty and extends into the abdominal cavity when full. In children, the bladder is located in the abdomen and does not completely descend into the pelvis until puberty.
Secondly, what makes up the urinary bladder? The urinary bladder, usually just called the bladder, is a major part of the body’s urinary system. It is a hollow organ that is made mostly out of muscle. The bladder’s job in the urinary system is to store the urine produced by your body until it is released from the body when you urinate.
One may also ask, is the urinary bladder in the abdominal cavity?
The abdominopelvic cavity is a body cavity that consists of the abdominal cavity and the pelvic cavity. It contains the stomach, liver, pancreas, spleen, gallbladder, kidneys, and most of the small and large intestines. It also contains the urinary bladder and internal reproductive organs.
Are the urinary bladder and gallbladder the same structure?
Answer and Explanation:No, the bladder and the gallbladder are different organs that happen to both have the word bladder in their names. The bladder is part of the excretory system and holds urine until it can be released from the body. The gallbladder stores bile, a digestive fluid, produced by the liver.
Muscularis Propria Or Detrusor Muscle
Muscularis propria or detrusor muscle consists of thick smooth muscle bundles that form the wall of the bladder. Anatomically, there three layers of smooth muscle, an external longitudinal layer, a middle circular layer and an inner longitudinal layer. For purposes of staging bladder cancer, the muscularis propria has been divided into a superficial half and a deep half.
Recommended Reading: Turbt Treatment For Bladder Cancer
How Is Urinary Incontinence In Men Treated
Treatment depends on the type of urinary incontinence.
Urgency Incontinence
As a first line of therapy for urgency incontinence, a health care professional may recommend the following techniques to treat a mans problem:
- behavioral and lifestyle changes
If those treatments are not successful, the following additional measures may help urgency incontinence:
- medications
- bulking agents
- surgery
A health care professional may recommend other treatments for men with urgency incontinence caused by Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia.
Behavioral and lifestyle changes. Men with urgency incontinence may be able to reduce leaks by making behavioral and lifestyle changes:
To Help Prevent Bladder Problems, Stop Smoking
People who smoke should stop. Quitting smoking at any age promotes bladder health and overall health. Smoking increases a persons chance of developing stress incontinence, as it increases coughing. Some people say smoking worsens their bladder irritation. Smoking causes most cases of bladder cancer. People who smoke for many years have a higher risk of bladder cancer than nonsmokers or those who smoke for a short time 3).
Medications. Health care professionals may prescribe medications that relax the bladder, decrease bladder spasms, or treat prostate enlargement to treat urgency incontinence in men.
Tricyclic antidepressants. Tricyclic antidepressants such as imipramine can calm nerve signals, decreasing spasms in bladder muscles.
Stress Incontinence
Functional Incontinence