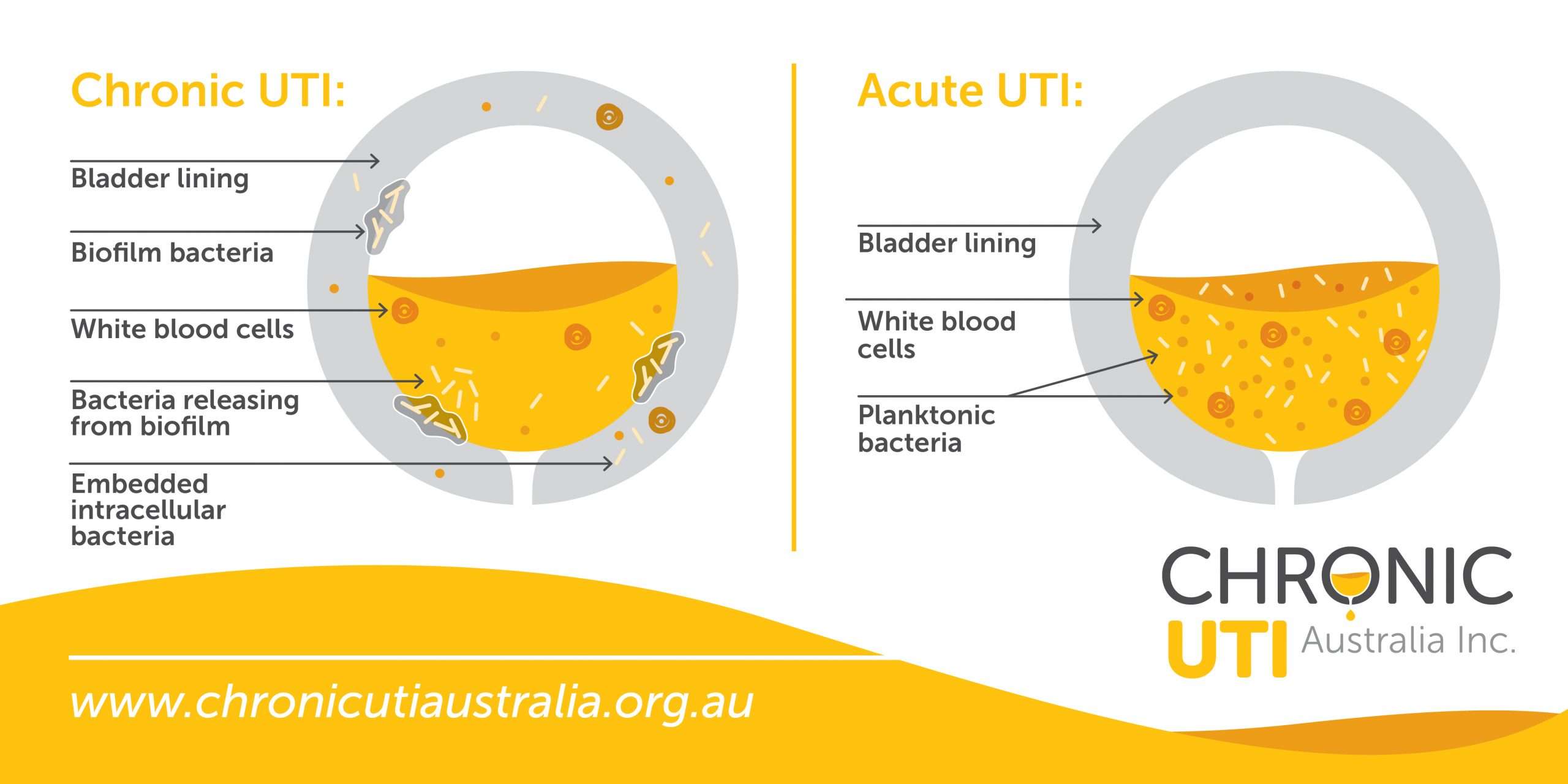
Embedded Or Biofilm Infection
When bacteria first enter the urinary tract, they are free-floating . However, under the right circumstances, these bacteria can stick to the bladder lining, and form a networked community, shielded by a protective slimy material. This slimy material protects the bacteria from antibiotics, as well as shielding it from the bodys natural defences. This is known as biofilm and can allow bacteria to survive for long periods. Once such a biofilm develops, whenever you get a UTI, instead of recovering completely, your body can be left with an embedded infection adherent to bladder wall, that is difficult to treat.
In addition to biofilms attached to the bladder wall, bacteria can also invade bladder cells and then rapidly replicate within the cells to form intracellular bacterial communities with enhanced resistance to antibiotics. However, within hours of IBC development, the progeny of successfully invasive bacteria emerge from the bladder cells, again in a free-floating state, ready to invade neighbouring cells to start the cycle anew. This form of invasion and intracellular replication affords a survival advantage for the bacteria to persist within the bladder as it sheds it lining.
Only in the last 10-15 years have biofilms and intracellular bacterial communities been recognised as a contributor to chronic bladder infection. Fortunately, research is now throwing further light on these mechanism and potential treatments to combat them.
Uti In Men: Its Not You And Its Not Me Its Just Complicated
Statistically, every 4th woman will experience a UTI in her lifetime. In yet another shocking turn of events, men have it easy in the UTI arena as well! UTIs in men are rarer. Mens urethra is on average eight inches long so ladies, when your next date says that: its 8 inches long technically hes not lying. According to Dr. Turek, size does indeed mattermales urethra is eight inches longer than their female counterparts and therefore serves as a great first line of defense from harmful bacteria.
Furthermore, for men, unlike women, it takes much more than exposure to E. coli during intercourse to develop a UTI. Basically, a lot of things need to go wrong in order for bacteria to ascend to the bladder.
Every case of UTI in men is considered complicated. This means UTI in men need to be thoroughly evaluated, and not just treated with an antibiotic. While its not always clear why some women get a UTI, in men you could normally find the reason during an evaluation, says Dr. Turek. Dr. Turek urges men to avoid home remedies and seek a physicians help if one believes hes experiencing symptoms of a UTI.
Physicians would normally collect a urine sample and check lower and upper urinary tract in search for any of the following:
- Stones or tumors that obstruct normal urine flow
- Malformations or birth defects
- Prostate enlargement
When Should I Call The Doctor
As soon as you think that your child has a UTI, call your doctor. The doctor may recommend another urine test after treatment to be sure that the infection has cleared.
If your child has from recurrent UTIs, consult a pediatric urologist, who can do a thorough evaluation and order tests for urinary system abnormalities. In the meantime, follow your doctor’s instructions for treating a UTI.
Don’t Miss: Can You Have Intercourse While Having A Bladder Infection
Causes Of Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs are usually caused by bacteria from poo entering the urinary tract.
The bacteria enter through the tube that carries pee out of the body .
Women have a shorter urethra than men. This means bacteria are more likely to reach the bladder or kidneys and cause an infection.
Things that increase the risk of bacteria getting into the bladder include:
- having sex
-
do not use scented soap
-
do not hold your pee in if you feel the urge to go
-
do not rush when going for a pee try to fully empty your bladder
-
do not wear tight, synthetic underwear, such as nylon
-
do not drink lots of alcoholic drinks, as they may irritate your bladder
-
do not have lots of sugary food or drinks, as they may encourage bacteria to grow
-
do not use condoms or diaphragms with spermicidal lube on them try non-spermicidal lube or a different type of contraception
How Urinary Tract Infections Are Treated In Men
Whether an infection affects a man or a woman, the treatment is the same: a round of antibiotics to kill the bacteria and get rid of UTI symptoms. For an uncomplicated infection, a woman typically needs to take an antibiotic for one to three days. For men, a longer course of at least seven days of antibiotics is required, says Trost.
Also Check: What Causes Overactive Bladder In Women
Can I Prevent Recurrent Utis
There are steps you can take to help reduce UTIs. The most basic is to drink plenty of fluids. This encourages frequent urination and helps flush out bacteria.
For women, following good hygiene practices is especially important:
- After a bowel movement, wipe from front to back to reduce the chance of moving E. coli bacteria from the rectal area to the urethra.
- Pee immediately before and after sex.
- Dont douche or use feminine deodorants on your genitals.
- Wear cotton underwear.
For older adults, take care to deal with retention problems, which are especially an issue as you age.
I tell them to double-void urinate and then go back and urinate again, Dr. Vasavada says.
What about drinking cranberry juice to fight UTIs?
Thats one of the most commonly asked questions, Dr. Vasavada says. Theres conflicting data. Its not going to cure an infection, but it could help prevent one, so we dont discourage it.
What Are The Symptoms Of Bladder Infection In Men
While different individuals will not have the same signs, the following are the most common symptoms of bladder infection:
A sudden and frequent urge to urinate
Peeing little amounts of urine
Lower back pain or cramping in the lower abdomen
Burning sensation when urinating
Frequent urination during the night
Foul-smelling urine that may appear cloudy
Fever
Feeling tired
Blood in the urine this is a sign that your bladder walls are inflamed, in which case you should seek medical assistance urgently.
The following UTI symptoms are specific to men:
Discharge from the penis
Swollen scrotum
It is important to note that bladder infection in males is more likely to recur after the initial infection because bacteria may hide and multiply within the prostate gland.
Don’t Miss: Sodium Bicarbonate For Bladder Infection
Can Recurrent Utis Be A Sign Of Cancer
Both UTIs and bladder cancer can cause similar symptoms, such as a frequent need to urinate and even blood in the urine, according to the University of Rochester Medical Center.
According to the American Cancer Society, urinary tract infections, kidney and bladder stones, and other causes of chronic bladder irritation have been linked to bladder cancer. However, its not clear whether recurrent urinary or bladder infections can actually cause bladder cancer or whether they constitute a true risk factor for bladder cancer.
The biggest known risk factor for bladder cancer is smoking. The risk of bladder cancer also increases with age. Most people who get bladder cancer are over the age of 55.
If you think you may have chronic or recurrent UTIs, its best to get checked out by your doctor. Your provider can rule out other health issues, including bladder cancer, and get you the treatment you need to get rid of chronic UTIs.
What Is Interstitial Cystitis/bladder Pain Syndrome
Interstitial cystitis /bladder pain syndrome is a chronic bladder health issue. It is a feeling of pain and pressure in the bladder area. Along with this pain are lower urinary tract symptoms which have lasted for more than 6 weeks, without having an infection or other clear causes.
Symptoms range from mild to severe. For some patients the symptoms may come and go, and for others they don’t go away. IC/BPS is not an infection, but it may feel like a bladder infection. Women with IC/BPS may feel pain when having sex. The more severe cases of IC/BPS can affect your life and your loved ones. Some people with IC/BPS have other health issues such as irritable bowel syndrome, fibromyalgia, and other pain syndromes.
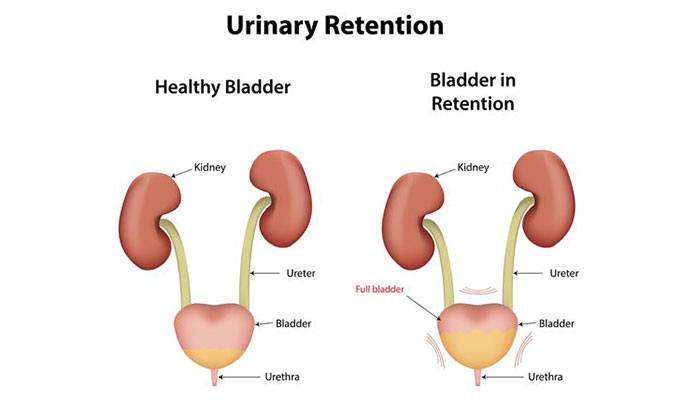
The bladder and kidneys are part of the urinary system, the organs in our bodies that make, store, and pass urine. You have 2 kidneys that make urine. Then urine is stored in the bladder. The muscles in the lower part of your abdomen hold your bladder in place.
How the Urinary System Works
Read Also: Can Anxiety Cause Bladder Leakage
Check If It’s A Urinary Tract Infection
Symptoms of a UTI may include:
- pain or a burning sensation when peeing
- needing to pee more often than usual during the night
- pee that looks cloudy
- needing to pee suddenly or more urgently than usual
- needing to pee more often than usual
- lower tummy pain or pain in your back, just under the ribs
- a high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a very low temperature below 36C
Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
If you are a healthy adult man or a woman who is not pregnant, a few days of antibiotic pills will usually cure your urinary tract infection. If you are pregnant, your doctor will prescribe a medicine that is safe for you and the baby. Usually, symptoms of the infection go away 1 to 2 days after you start taking the medicine. Its important that you follow your doctors instructions for taking the medicine, even if you start to feel better. Skipping pills could make the treatment less effective.
Your doctor may also suggest a medicine to numb your urinary tract and make you feel better while the antibiotic starts to work. The medicine makes your urine turn bright orange, so dont be alarmed by the color when you urinate.
Read Also: What Causes Weak Bladder In Females
What Are The Symptoms Of Bladder Infections In Men
Bladder infections are a common problem in men that is highly misunderstood. There are many varieties of bladder infections, and each one has a different cause and effect. The most common variety is due to acute bacterial infection which occurs when there is an imbalance of bacteria in the urinary tract. Once the balance of healthy bacteria is disturbed, it allows for the multiplication of the infection-causing bacteria. Below are some of the common symptoms of bladder infections:
- Frequent urination.
- Cloudy urine with a strong odor.
- Blood in the urine .
- Trouble urinating, especially if you have a problem with your prostate.
How Do I Talk To My Gp About Chronic Urinary Tract Infections
Unfortunately currently guidelines for GPs dont even mention chronic UTI. We know it can be difficult to explain all this and describe your symptoms in a short doctors appointment.
Write down all your symptoms as we outlined above and take them with you to your appointment.
Your doctor may well investigate if your UTIs are related to your prostate. But if these investigations come back negative ask your GP to consider chronic UTI.
No detail is too small when visiting the doctor about urinary problems. It may help to write down a list of symptoms, no matter how small, and take them with you to your appointment. For example an unusual smell, abnormal amounts of foam, or persistently darker urine than usual may seem unimportant to you, but to a doctor these can be the characteristic symptoms required to diagnose a given condition.
You May Like: Botox Dose For Overactive Bladder
How Are Chronic Utis Treated
If you have recurrent or chronic UTIs, your doctor may send you to a urologist who specializes in diseases of the urinary system. According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, some of the ways that recurrent UTIs are evaluated and treated include:
- Testing The doctor will want to take a urine sample to test for bacteria and white blood cells. It may be necessary to do special X-ray studies to see if there is an obstruction or stones in the urinary tract. A urologist may look into your bladder by passing a special scope through the opening into your bladder. This exam is called cystoscopy.
- Antibiotics for Treatment Normally, UTIs responds very well to antibiotics, and you may only need to take medication for a few days. For recurrent UTIs, antibiotics may be needed for 10 days or more.
- Surgery In some cases of prostate disease, stones, or other obstruction of the urinary system, surgery may be done to restore normal flow of urine and help clear up infections.
- Antibiotics for Prevention Some strategies to prevent recurrent UTIs with antibiotics include taking low-dose antibiotics for six months or taking antibiotics after sexual intercourse.
- Frequent Urine Testing Women who have recurrent UTIs may benefit from testing their urine frequently with a dipstick that warns of any bacteria in the urine.
Are Any Tests Needed
A urine sample can confirm the diagnosis and identify the germ causing the infection. Further tests are not usually necessary if you are otherwise well and have a one-off infection. However, your doctor may advise tests of your kidney, prostate gland, or bladder if an underlying problem is suspected.
An underlying problem is more likely if the infection does not clear with an antibiotic medicine, or if you have:
- Symptoms that suggest a kidney is infected .
- Recurring urine infections. For example, two or more in a three-month period.
- Had problems with your kidney in the past, such as kidney stones or a damaged kidney.
- Symptoms that suggest an obstruction to the flow of urine.
- Blood-stained urine which persists after treatment with antibiotics.
Tests may include:
- An examination of your prostate gland by examination of your back passage .
- Tests to see how well your bladder is working, called urodynamic tests.
You May Like: New Treatments For Neurogenic Bladder
What Is A Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection occurs when bacteria invade the bladder or kidneys. The bacteria can often be found naturally in our bowels or on our skin, but they are harmless there. However, when they get into the urinary tract, they can cause an infection.
Women in general get more UTIs. This is mainly because the female urethra is shorter, which allows bacteria easier access into the bladder.
Typically a woman may have one UTI per year on average. But some women get them more often. If it occurs about four times a year, its considered a recurrent UTI. An estimated 2% to 10% of women get chronic UTIs, according to a review in the journal Climacteric.
UTIs tend to be more common in older men than younger men. This is likely because UTIs in men are often caused by not completely emptying the bladder. This is often due to an enlarged prostate, a condition common in older men.
UTIs are treated with antibiotics and go away quickly.
What Causes Chronic Uti
Bacteria can enter the urinary tract from the outside to cause a UTI to come back, or a recurrent infection can be caused by bacteria that remain in the urinary tract after a previous infection. Symptoms of recurrent UTI in men and women include the frequent urge to urinate, burning pain or pressure when passing urine, cloudy or discoloured urine, and chills and fever. Children with UTIs are more likely to have fever without the other symptoms. Common conditions that can lead to recurrent UTIs include:
-
Being in a nursing home or hospital
-
Diabetes
-
Having an infected or enlarged prostate
-
Being born with an abnormality of the urinary tract
Read Also: How Do Poise Bladder Supports Work
Chronic Urinary Tract Infection
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Heres our process.
What is a chronic urinary tract infection?
Chronic urinary tract infections are infections of the urinary tract that either dont respond to treatment or keep recurring. They may either continue to affect your urinary tract despite getting the right treatment, or they may recur after treatment.
Your urinary tract is the pathway that makes up your urinary system. It includes the following:
- Your kidneys filter your blood and generate body waste in the form of urine.
- Your ureters are tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Your bladder collects and stores urine.
- Your urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of your body.
A UTI can affect any part of your urinary system. When an infection only affects your bladder, its usually a minor illness that can be easily treated. However, if it spreads to your kidneys, you may suffer from serious health consequences, and may even need to be hospitalized.
Although UTIs can happen to anyone at any age, theyre more prevalent in women. In fact, the
Acute And Chronic Prostatitis
In the 1800s, prostatitis was thought to be secondary to excessive alcohol consumption or physical or sexual activity. It was often associated with gonorrhea and could be fatal or lead to abscess formation. By the 1920s, most cases were attributed to microorganisms, and antibiotics combined with prostate massage were standard therapy after World War II. Although the role of bacteria was questioned in the 1950s, it was reemphasized in 1968 when Meares and Stamey described their “4-glass test.”
Acute prostatitis is caused by an acute infection of the entire prostate gland, resulting in fever and localized pain. Microscopically, neutrophilic infiltrates, diffuse edema, and microabscesses may be seen, which may coalesce into larger collections.
Chronic prostatitis may be caused by inflammatory or noninflammatory diseases. This condition may arise via dysfunctional voiding, intraprostatic reflux, chronic exposure to microorganisms, autoimmune mechanisms, irritative urinary metabolites, and as a variant of neuropathic pain. Chronic bacterial prostatitis often produces few or no symptoms related to the prostate, but it is probably the most common cause of relapsing UTI in men.
Chronic prostatitis has been subdivided by the National Institutes of Health into the following categories:
Read Also: How Long Does Overactive Bladder Last