Should I Make Any Lifestyle Changes Including In My Diet Or Physical Activity
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight by eating a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and staying physically active, can help your overall health. These lifestyle changes can also have a positive effect for men with bone metastases, Tagawa says. Both diet and exercise, he says, are things that are under a mans direct control.
A healthy lifestyle can help you better manage side effects from treatment as well. Try setting small but realistic goals for yourself when it comes to eating a healthy diet and getting plenty of exercise.
While no single food is likely to have a benefit for prostate cancer, smart food choices may help you feel better day to day. Start by cutting out foods high in sugar, saturated fat, and added flavorings and preservatives.
If youre not sure which healthy foods to choose, ask your doctor for a referral to a dietitian. This specialist can help you develop a meal plan that includes foods that offer the best chance of slowing the cancers growth and keeping you as healthy as possible.
As an oncologist, Tagawa says he concentrates on treating the cancer itself, but hes aware that many of the men he sees with advanced prostate cancer are older and more likely than younger men to have health problems that can benefit from diet and exercise.
And if youre on hormone therapy, talk to your doctor about investing in some weights or elastic resistance bands to support your bone strength too.
There Are Different Types Of Urethral Cancer That Begin In Cells That Line The Urethra
These cancers are named for the types of cells that become malignant :
- Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common type of urethral cancer. It forms in the thin, flat cells in the part of the urethra near the bladder in women, and in the lining of the urethra in the penis in men.
- Transitional cell carcinoma forms in the area near the urethral opening in women, and in the part of the urethra that goes through the prostate gland in men.
- Adenocarcinoma forms in the glands that are around the urethra in both men and women.
Urethral cancer can metastasize quickly to tissues around the urethra and is often found in nearby lymph nodes by the time it is diagnosed.
Treatment For Bladder Cancer
Treatment for bladder cancer depends on how quickly the cancer is growing. Treatment is different for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer and muscle-invasive bladder cancer. You might feel confused or unsure about your treatment options and decisions. Its okay to ask your treatment team to explain the information to you more than once. Its often okay to take some time to think about your decisions.
Don’t Miss: Causes Of Weak Bladder Control
What Kind Of Treatment Will I Need
There are many ways to treat bladder cancer. You might want to get a second opinion about the best treatment plan for you.
Bladder cancer is most often treated with:
- Surgery
- Chemo
- Immunotherapy
Sometimes more than one type is used. The treatment plan thats best for you depends on:
- The stage and grade of the cancer
- Whether the cancer has spread into the bladder wall
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Other health problems you have
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
Tests To Determine Stage And Grade
Bladder cancer is classified by stage and grade. The stage is determined by the cancer growth in the bladder wall and how far it has spread to nearby tissues and other organs, such as the lungs, the liver, or the bones. The grade of bladder cancer is determined by how the cancer cells look in comparison with normal bladder cells.
Your doctor finds out the stage and grade of your bladder cancer by gathering information from several tests, including:
- Biopsies from the cystoscopy.
- An intravenous pyelogram or CT urogram to look for a mass near the kidneys, ureters, or bladder.
- Ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging . These help find out if the cancer has spread to lymph nodes, the lungs, the liver, or other abdominal organs.
- CT scan. This finds out if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
- Chest X-ray. This finds out if the cancer has spread to the lungs.
- Bone scan. This finds out if the cancer has spread to the bones.
Knowing the stage and grade of your cancer is important in choosing the right treatments.
Also Check: Difference Uti And Bladder Infection
How Long Will You Live If You Have Bladder Cancer
The survival rate depends on the stage of cancer at diagnosis and other health issues.
Overall, 70 to 90 percent of people with localized bladder cancer will live for at least five years or more. The physician calculates this with the help of survival rates. Survival rates indicate the percentage of people who live with a certain type of cancer for a specific time. The physician often uses an overall five-year survival rate. Factors that may affect survival rate include
Table. Five-year survival rates of different stages of bladder cancer
| Bladder cancer SEER stages | Five-year relative survival rate |
|---|---|
| In situ alone | 96 |
| All SEER stages combined | 77 |
The surveillance, epidemiology, and end results stages are taken from the SEER database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute. SEER database groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages.
- Localized: There is no indication that cancer has spread outside the bladder.
- Regional: Cancer has invaded the nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: Cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, such as the lungs, liver, or bones.
Thus, bladder cancer, if detected in the early stage is treatable and has higher survival rates. However, if the cancer is detected in the advanced stages, treatment becomes difficult and the survival rate is low.
Causes Of Bladder Cancer
There are certain things that can affect the chances of developing bladder cancer. These are called risk factors.
The main risk factor is age. Bladder cancer is more common in people over the age of 60. It is rare in people under the age of 40. Another risk factor is smoking. Smoking may cause about 4 in 10 bladder cancers.
Recommended Reading: What Should I Do If I Have A Bladder Infection
How Are Samples Collected
Requirements for urine sampling vary depending on the test/s being performed. Often the timing of collection is random, as dictated by the logistics of a doctor consult or access to a laboratory service. However, depending on the purpose of the test, certain urine voids of the day may be preferred. Collection of urine from all voids over a defined time period or sample collection at specific times after eating may also be necessary.
Urine samples are usually obtained by spontaneous voiding, using the clean-catch, midstream urine collection method. This involves voiding the first portion of urine into the toilet, collecting the midstream portion into a clean container, then voiding the remaining portion into the toilet. This method greatly reduces the risk of contaminants entering the sample. Less commonly, an invasive method of urine collection, such as placement of a urinary catheter, may be required.
Learn about Cxbladder’s easy-to-use in-home sampling system
Transurethral Resection Of A Bladder Tumour
If abnormalities are found in your bladder during a cystoscopy, you should be offered an operation known as TURBT. This is so any abnormal areas of tissue can be removed and tested for cancer .
TURBT is carried out under general anaesthesia.
Sometimes, a sample of the muscle wall of your bladder is also taken to check whether the cancer has spread. This may be a separate operation within 6 weeks of the first biopsy.
You should also be offered a dose of chemotherapy after the operation. This may help to prevent the bladder cancer returning, if the removed cells are found to be cancerous.
See treating bladder cancer for more information about the TURBT procedure.
You May Like: Can A Ct Urogram Detect Bladder Cancer
Urethral Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Urethra
The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside the body. In women, the urethra is about 1½ inches long and is just above the vagina. In men, the urethra is about 8 inches long, and goes through the prostategland and the penis to the outside of the body. In men, the urethra also carries semen.
Urethral cancer is a rare cancer that occurs more often in men than in women.
Tests To Find Bladder Cancer
To find bladder cancer, doctors may run tests to see whether there are certain substancessuch as bloodin the urine. Tests may include:
- Urinalysis
- Urine cytology
- Urine culture
For patients who have symptoms or have had bladder cancer in the past, newer tests that look for tumor markers in urine may include:
- UroVysion
- BTA tests
- ImmunoCyt
- NMP22 BladderChek®
Researchers dont know yet whether these tests are reliable enough to be used for screening, but they may help find some bladder cancers.
Most doctors recommend a cystoscopy to find bladder cancer, and its often performed without anesthesia. During this procedure, the doctor inserts a long, thin tube with a camera into the urethra to see the inside of the bladder for growths and collect a tissue sample . The tissue is studied in a lab to search for cancer and obtain more information. During a cystoscopy, doctors may also perform a fluorescence cystoscopy, or blue light cystoscopy, inserting a light-activated drug into the bladder and seeing whether any cancer cells glow when they shine a blue light through the tube.
Doctors may also order imaging tests to see whether the cancer has spread. The most common imaging tests include:
Magnetic resonance imaging uses magnets and radio waves to take pictures of the inside of the body. Before the test, a contrast medium is administered orally or by injection to help make the scan clearer.
Ultrasound uses sound waves to take pictures of the inside of the body.
Don’t Miss: Can Overactive Bladder Start Suddenly
What Are The Treatments For This Type Of Tumor
The treatments for prostatic carcinoma are aimed at reducing the tumors size and the tendency for metastasis. Surgery may be considered as a palliative measure, though removal of the entire prostate or tumor is not typically successful without damage to the urethra. In pets with significant obstruction of the urethra, a surgical stent may be placed to allow for urination.
Treatments less invasive than surgery, such as radiation therapy, may be pursued. Targeted radiation therapy to the region of the prostate and affected lymph nodes or bone may be possible. Palliative radiation therapy may provide short-term relief for urinary obstruction.
The use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories such as piroxicam or carprofen, however, have been shown to be beneficial in the treatment of prostate cancer.
The role of chemotherapy is not well understood. The use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories , such as piroxicam or carprofen, have been shown to be beneficial in the treatment of prostate cancer. Bisphosphonates may also be helpful. These drugs are typically recommended with metastasis to the pelvic bone or lumbar vertebrae. They may reduce the active breakdown of the bone and reduce pain.
Read Also: Bladder And Prostate Cancer Together
Bladder Cancer That Comes Back
After initial treatment for bladder cancer, it is important to receive follow-up care, because bladder cancer often comes back . Your doctor will set up a regular schedule of checkups and tests.
Bladder cancer may recur in the bladder, or it may spread to other parts of the body. Recurrent bladder cancer may be treated with surgery or chemotherapy to slow cancer growth and relieve symptoms.
Participation in a clinical trial may be recommended if you have been diagnosed with recurrent bladder cancer.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Ingredients In Azo Bladder Control
Next Steps After Urine Lab Tests
Depending on the results of the patients physical examination and urine laboratory tests, healthcare providers may need to carry out further testing to help make a diagnosis.1,2 The tests can also be used in patients who have already been diagnosed with bladder cancer to help gather more information about the cancer and develop the patients treatment plan.
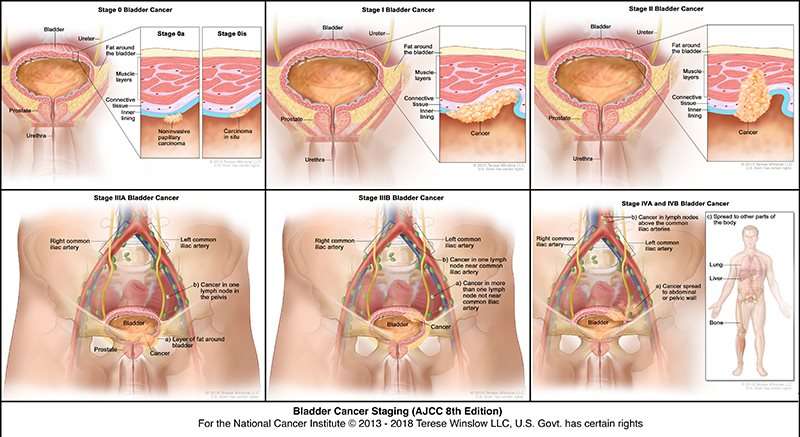
What Are The Stages Of Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer can be either early stage or invasive .
The stages range from TA to IV . In the earliest stages , the cancer is confined to the lining of the bladder or in the connective tissue just below the lining, but has not invaded into the main muscle wall of the bladder.
Stages II to IV denote invasive cancer:
- In Stage II, cancer has spread to the muscle wall of the bladder.
- In Stage III, the cancer has spread to the fatty tissue outside the bladder muscle.
- In Stage IV, the cancer has metastasized from the bladder to the lymph nodes or to other organs or bones.
A more sophisticated and preferred staging system is known as TNM, which stands for tumor, node involvement and metastases. In this system:
- Invasive bladder tumors can range from T2 all the way to T4 .
- Lymph node involvement ranges from N0 to N3 .
- M0 means that there is no metastasis outside of the pelvis. M1 means that it has metastasized outside of the pelvis.
Also Check: What Antibiotic Do You Take For A Bladder Infection
What Is Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
Muscle invasive bladder cancer is a cancer that spreads into the detrusor muscle of the bladder. The detrusor muscle is the thick muscle deep in the bladder wall. This cancer is more likely to spread to other parts of the body.
In the U.S., bladder cancer is the third most common cancer in men. Each year, there are more than 83,000 new cases diagnosed in men and women. About 25% of bladder cancers are MIBC. Bladder cancer is more common as a person grows older. It is found most often in the age group of 75-84. Caucasians are more likely to get bladder cancer than any other ethnicity. But there are more African-Americans who do not survive the disease.
What is Cancer?
Cancer is when your body cells grow out of control. When this happens, the body cannot work the way it should. Most cancers form a lump called a tumor or a growth. Some cancers grow and spread fast. Others grow more slowly. Not all lumps are cancers. Cancerous lumps are sometimes called malignant tumors.
What is Bladder Cancer?
When cells of the bladder grow abnormally, they can become bladder cancer. A person with bladder cancer will have one or more tumors in his/her bladder.
How Does Bladder Cancer Develop and Spread?
The bladder wall has many layers, made up of different types of cells. Most bladder cancers start in the urothelium or transitional epithelium. This is the inside lining of the bladder. Transitional cell carcinoma is cancer that forms in the cells of the urothelium.
Can A Urine Test Detect Bladder Cancer
Several types of urine test have an important role in the overall process of diagnosing bladder cancer. Among these tests, urine cytology and urine tumor marker tests are used to detect the presence or absence of bladder cancer. Urine cytology has been used to assist bladder cancer diagnosis for over 75 years and has well-established strengths and limitations which are discussed in more detail below. Molecular tumor marker tests such as Cxbladder have been more recently developed, and provide high diagnostic accuracy in both detection and rule-out.
Notably, no single test is best able to detect bladder cancer, and usually different types of tests are used in combination. For example, the Cxbladder genomic urine test in combination with ultrasound or computed tomography imaging has been shown to identify the presence or absence of bladder cancer with high accuracy in patients with hematuria. The specific diagnostic tests selected depend on several factors, including a patients symptoms and their risk for bladder cancer.
Also Check: What Causes Bladder Control Problems
What Are The Treatment Options For Bladder Cancer
There are four types of treatment for patients with bladder cancer. These include:
- Surgery
Sometimes, combinations of these treatments will be used.
Surgical options
Surgery is a common treatment option for bladder cancer. The type of surgery chosen will depend on the stage of the cancer.
- Transurethral resection of the bladder is used most often for early stage disease . It is done under general or spinal anesthesia. In this procedure, a special telescope called a resectoscope is inserted through the urethra into the bladder. The tumor is then trimmed away with the resectoscope, using a wire loop, and the raw surface of the bladder is then fulgurated .
- Partial cystectomy is the removal of a section of the bladder. At times, it is used for a single tumor that invades the bladder wall in only one region of the bladder. This type of surgery retains most of the bladder. Chemotherapy or radiation therapy is often used in combination. Only a minority of patients will qualify for this bladder-sparing procedure.
- Radical cystectomy is complete removal of the bladder. It is used for more extensive cancers and those that have spread beyond the bladder .
This surgery is often done using a robot, which removes the bladder and any other surrounding organs. In men, this is the prostate and seminal vesicles. In women, the ovaries, uterus and a portion of the vagina may be removed along with the bladder.
Chemotherapy
- Methotrexate
Intravesical therapy
Radiation therapy