Urine Lab Tests To Rule Out Bladder Cancer
If the healthcare provider thinks that bladder cancer may be the cause of the symptoms, the patient may be asked to provide a urine sample for analysis in the laboratory. Several types of urine lab tests may be used to help make a diagnosis of bladder cancer, including:
- Urinalysis testing
- Urine tests for tumor markers
Diagnosis Of Bladder Cancer
Diagnosis is the process of finding out the cause of a health problem. Diagnosing bladder cancer usually begins with a visit to your family doctor. Your doctor will ask you about any symptoms you have and may do a physical exam. Based on this information, your doctor may refer you to a specialist or order tests to check for bladder cancer or other health problems.
The process of diagnosis may seem long and frustrating. Its normal to worry, but try to remember that other health conditions can cause similar symptoms as bladder cancer. Its important for the healthcare team to rule out other reasons for a health problem before making a diagnosis of bladder cancer.
The following tests are usually used to rule out or diagnose bladder cancer. Many of the same tests used to diagnose cancer are used to find out how far the cancer has spread . Your doctor may also order other tests to check your general health and to help plan your treatment.
Medical History And Physical Exam
Your doctor will want to get your medical history to learn more about your symptoms. The doctor might also ask about possible risk factors and your family history.
A physical exam can provide information about possible signs of bladder cancer and other health problems. The doctor might do a digital rectal exam , during which a gloved, lubricated finger is put into your rectum. If you are a woman, the doctor might do a pelvic exam as well. During these exams, the doctor can sometimes feel a bladder tumor, determine its size, and feel if and how far it has spread.
If the doctor finds things that aren’t normal, you may to have lab tests done and you might be referred to a urologist for further tests and treatment.
Don’t Miss: Overactive Bladder At Night Time Only
Biopsies To Look For Cancer Spread
If imaging tests suggest the cancer might have spread outside of the bladder, a biopsy might be needed to be sure.
In some cases, biopsy samples of suspicious areas are taken during surgery to remove the bladder cancer.
Another way to get a biopsy sample is to use a long, thin, hollow needle to take a small piece of tissue from the abnormal area. This is known as a needle biopsy, and by using it the doctor can take samples without surgery. Sometimes a CT scan or ultrasound is used to help guide the biopsy needle into the changed area.
Assessing The Extent And Spread
If initial tests confirm that the cancer is a superficial tumour then no further tests may be necessary. Superficial bladder tumours have a low risk of spread to other parts of the body.
However, if you have a muscle-invasive tumour, further tests may be advised to assess if the cancer has spread. For example, a CT scan, a magnetic resonance imaging scan or other tests. This assessment is called staging of the cancer. The aim of staging is to find out:
- How much the tumour in the bladder has grown, and whether it has grown to the edge or through the outer part of the bladder wall.
- Whether the cancer has spread to local lymph nodes.
- Whether the cancer has spread to other areas of the body .
By finding out the stage of the cancer, it helps doctors to advise on the best treatment options. It also gives a reasonable indication of outlook . See the separate leaflet called Stages of Cancer for more details.
Recommended Reading: Best Way To Treat Bladder Infection
What Is The Outlook
- Superficial bladder tumours. There is a good chance of a cure with treatment. Also, routine checks every few months following treatment will often detect returning tumours early and treatment can be repeated as necessary.
- Muscle-invasive bladder tumours. A cure is less likely than with a superficial tumour. As a rule, the earlier the stage of the tumour, the better the chance of a cure with the treatments listed above. However, even if it is not cured, treatment can often slow down the progression of the cancer.
The treatment of cancer is a developing area of medicine. New treatments continue to be developed and the information above about outlook is very general. The specialist who knows your case can give more accurate information about your particular outlook , and how well your type and stage of cancer is likely to respond to treatment.
Screening For Bladder Cancer
Early-stage bladder cancer often shows no symptoms, or symptoms that are similar to those of benign conditions such as bladder stones, an enlarged prostate, or urinary tract infection. For this reason it is important to be examined regularly by a physician. If symptoms do appear they should be evaluated promptly so that bladder cancer can be detected in its earliest, most treatable stages.
Doctors may conduct some screening tests during an examination. During a urine cytology the doctor examines urine under a microscope to look for any cancerous or precancerous cells. During another test called a cystoscopy urologists place a cystocope, a flexible instrument consisting of a steerable slender tube with a camera or lens and a light, into the bladder through the urethra. They check the bladder and urethra for signs of cancer, remove any suspicious tissue, and check it under a microscope.
Read Also: Best Over The Counter Bladder Control Medication
What Causes Bladder Cancer
A cancerous tumour starts from one abnormal cell. The exact reason why a cell becomes cancerous is unclear. It is thought that something damages or alters certain genes in the cell. This makes the cell abnormal and multiply out of control. See the separate leaflet called Causes of Cancer for more details.
In many cases, the reason why a bladder cancer develops is not known. However, there are factors which are known to alter the risk of bladder cancer developing. These include:
Abdominal Ct Scan And The Detection Of Bladder Cancer
CT scan is able to detect large bladder irregularities, but not always small lesions, says Dana Rice, MD, a board certified urologist and creator of the UTI Tracker mobile app, which helps patients catalog daily urinary tract symptoms, medication and behavioral patterns, and offers personalized tips for UTI prevention.
Also, because the bladder is not a solid organ it is very easy to mistake a bladder fold for an abnormal finding and vice versa, continues Dr. Rice.
For instance, a CT scan may list or read a filling defect which means contrast dye does not fill the bladder evenly.
In this situation the defect may be from many causes, i.e., blood clot, prostate tissues, ureterocele , bladder tumor and more.
Other times, the CT scan can appear completely normal and there may be small tumors not seen or carcinoma in situ . For these reasons, cystoscopy to examine the bladder is the gold standard diagnostic test.
Read Also: What Is Bladder Sling Surgery
Diagnosis Of Bladder Papilloma
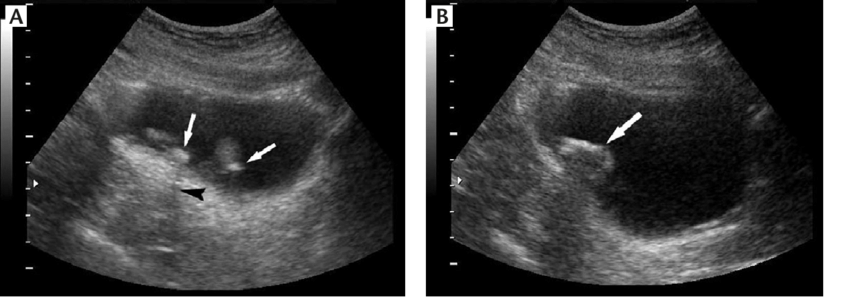
Diagnosis is based on clinical signs. In some cases, papilloma can be detected by conducting an ultrasound examination of the bladder. But the main method to clarify the diagnosis is cystoscopy with puncture biopsy of the tumor. Diagnosis of papilloma in bladder is carried out in two directions: laboratory tests and examinations. The doctor may recommend the following examinations:
- Urine tests. This includes microhematuria, a small amount of blood in the urine that cannot be seen with the naked eye.
- Endoscopic examination, in which a thin tube with a microscopic optical camera is inserted into the urethra. The doctor examines the state of the walls of the organ and can reveal even the smallest papillomas. The method is considered the most appropriate for detecting papilloma bladder cancer.
- Ultrasound can also help detect growths on the walls of the bladder. But with this method, only formations more than 1 cm in diameter are noticeable.
- An accurate and painless study that helps to identify papillomatosis in its early stages, starting with growths of 1 mm. The disadvantages of tomography are the high cost of diagnosis and the inability to determine the nature of the pathology.
- Histology . It may be performed during cystoscopy or already during surgery to remove papilloma. Histology is important for choosing the right treatment and subsequent rehabilitation.
Can Bladder Cancer Be Picked Up On Ultrasound
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Also Check: What Is Prescribed For Bladder Infection
How Bladder Cancer Is Diagnosed
If you or a loved one is being evaluated for bladder cancer, it can be a stressful and overwhelming time. But by learning as much as you can about the condition, including the tests performed to diagnose it, you are already taking an active role in your care.
Also, try to stay as organized as possible, be inquisitive about selecting your bladder cancer team, and attend appointments and tests with a partner or trusted loved one.
Verywell
How To Diagnose Bladder Papilloma And How To Treat It Right
Papilloma is a change in the epithelium of the skin or mucous membrane, in which tumors of different shapes are formed from tissue. Most often, the disease manifests itself on the body or in the genital area, but theoretically it can affect any part of the skin or mucous membrane. One of the most dangerous manifestations of papillomatosis are tumors on the internal organs, the bladder is one of them.
All papillomas are viral in nature. They develop under the influence of human papillomavirus. Almost 100 strains of HPV are known to medicine, many of which affect more than 80% of people around the globe. In fact, it
is difficult to find an adult in whose blood there would not be a single type of this virus. However, the prevalence of this infection does not mean the prevalence of the disease itself, which is called papillomatosis. In healthy people, carriage is most often observed, in which the immune system suppresses the reproduction of infectious agents and prevents the development of neoplasms. Find out how to detect the bladder papilloma and what to do with such a diagnosis.
Also Check: Over The Counter Bladder Control Meds
Bladder Cancer Risk Factors And Warning Signs
Although the cause of bladder cancer is unknown, it is linked to tobacco use and exposure to certain chemicals.
- Smoking and Bladder Cancer: Smoking is responsible for approximately 47 percent of bladder cancer deaths among men and 37 percent among women, according to the American Cancer Society.
- Workplace Exposure and Bladder Cancer: Workers in the rubber, chemical, leather, textile, metal, and printing industries exposed to substances such as aniline dye and aromatic amines may have increased risk for bladder cancer. Other at-risk occupations include hairdressers, machinists, painters, and truck drivers.
What To Expect When Having A Ct Scan
A CT scan is a painless procedure that is typically performed on an outpatient basis, taking about 1030 minutes to complete.
The patient may be told not to eat or drink before the test, and a laxative or enema may be used to clear the bowels so the images are clearer. Some CT scans may be performed using special contrast dyes, which may be swallowed as a liquid, delivered intravenously, or administered with an enema. These contrast agents can help improve the quality of the CT image.
For the test, the individual lies on a flat table that slides through the middle of the scanner. Buzzing and clicking noises may be heard within the scanner. During the test, the patient may have to stay still for several minutes or to briefly hold his/her breath.
Recommended Reading: Can Candida Cause Bladder Infection
Possible Side Effects Of A Ct Scan
Sensitivity or allergic reaction to the contrast dye can occur in some patients, which may manifest as rash, nausea, wheezing, shortness of breath, or itching or swelling of the face. Symptoms are usually mild and clear on their own. Uncommon but more severe manifestations are low blood pressure and breathing difficulties.
Of additional note, while the amount of radiation used in CT scans can vary in clinical practice, CT scans deliver considerably more radiation than a typical x-ray. Therefore CT scans can carry risks associated with increased radiation exposure, such as radiation-induced future cancer.
What Are The Treatment Options For Muscle
Treatment options that may be considered include surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy. The treatment advised for each case depends on various factors such as the stage of the cancer , and your general health.
You should have a full discussion with a specialist who knows your case. He or she will be able to give the pros and cons, the likely success rate, the possible side-effects and other details about the possible treatment options for your type of cancer.
You should also discuss with your specialist the aims of treatment. For example:
- Treatment may aim to cure the cancer. Some bladder muscle-invasive cancers can be cured, particularly if they are treated in the early stages of the disease.
- Treatment may aim to control the cancer. If a cure is not realistic, with treatment it is often possible to limit the growth or spread of the cancer so that it progresses less rapidly. This may keep you free of symptoms for some time.
- Treatment may aim to ease symptoms. If a cure is not possible, treatments may be used to reduce the size of a cancer, which may ease symptoms such as pain. If a cancer is advanced then you may require treatments such as painkillers or other treatments to help keep you free of pain or other symptoms.
Also Check: Losing Control Of Your Bladder
Preparing For Your Scan
Check your appointment letter for any instructions about how to prepare for your scan.
You usually need to drink about 1 litre of fluid an hour before the test, so that your bladder is comfortably full. Do not empty your bladder before the test. This is so your bladder can be seen clearly in the scan.
Take your medicines as normal unless your doctor tells you otherwise.
What Is Bladder Cancer And How Common Is It
Bladder cancer is a common cancer it is the seventh most common cancer in the UK. About 10,000 people develop bladder cancer in the UK each year. In most cases in the UK, the bladder cancer develops from the transitional cells which line the inside of the bladder. This type of cancer is called transitional cell bladder cancer. Other types of bladder cancer are rare in the UK.
The rest of this leaflet only deals with the common type of bladder cancer – transitional cell bladder cancer.
Transitional cell bladder cancer is divided into two groups:
- Superficial tumours. These occur in about 4 in 5 cases. These tumours are confined to the inner lining, or just below the inside lining, of the bladder. Sometimes the cells which form this type of cancer multiply to form little growths which stick out like warts from the inside lining of the bladder.
- Muscle-invasive tumours. These occur in about 1 in 5 cases. These tumours have spread to the muscle layer of the bladder or right through the wall of the bladder.
The treatment and outlook for each of these two groups are very different. Superficial tumours rarely spread and can usually be cured. However, if left untreated, in some cases they can develop into muscle-invasive tumours. Muscle-invasive tumours have a high chance of spreading to other parts of the body and treatment has less chance of being curative.
See the separate leaflet called Cancer for more information about cancer.
Read Also: Where Is The Bladder Located
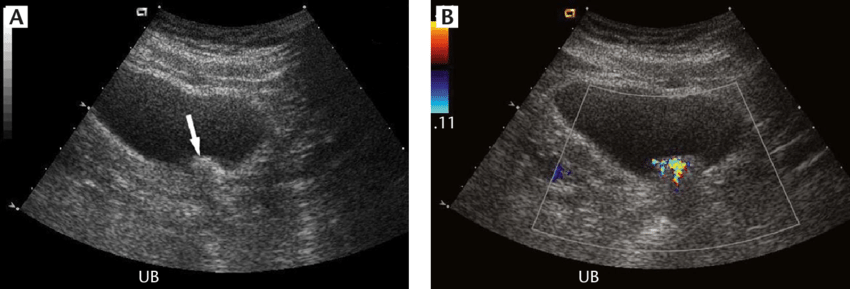
How Do Ultrasounds Help Detect And Monitor Bladder Cancer
An ultrasound of the urinary tract can help assess the size of a bladder tumor and whether a bladder cancer has spread. Ultrasound is able to differentiate between fluid-filled cysts and solid tumors, however, it cannot determine if a tumor is cancerous. Ultrasound can also be used to guide a biopsy needle to sample a suspected cancer.
Ultrasound scan showing a tumor on the back wall of the bladder.
Bladder Cancer Screening And Diagnosis
If doctors suspect that a patient has bladder cancer because of the presence of blood in the urine or an urgency to urinate, burning with urination, or unexplained increased frequency of urination, they may use several methods to confirm the diagnosis and determine the stage of the disease. Doctors at Columbia University Department of Urology at NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital use the latest laboratory testing and diagnostic technologies including:
Read Also: How Do Poise Bladder Supports Work
What To Expect With Bladder Ultrasounds
Ultrasounds are typically outpatient procedures and usually take 2030 minutes to complete.
Preparation is often not required ahead of an ultrasound, however, in some instances the patient will be asked to take a laxative, use an enema, or not to eat before the test. Some patients having an abdominal ultrasound may be required to drink a large amount of water so that the bladder is filled, which will improve the quality of the images.
During a bladder ultrasound, the individual is often lying down while the probe is passed over the skins surface. A lubricating gel is administered to the skin which helps the sound waves conduct.
Notably, ultrasound is a safe procedure with a low risk of side effects.