C679 Malignant Neoplasm Of Bladder Unspecified
NEC Not elsewhere classifiableThis abbreviation in the Tabular List represents other specified. When a specific code is not available for a condition, the Tabular List includes an NEC entry under a code to identify the code as the other specified code.
NOS Not otherwise specifiedThis abbreviation is the equivalent of unspecified.
This note further define, or give examples of, the content of the code or category.
List of terms is included under some codes. These terms are the conditions for which that code is to be used.The terms may be synonyms of the code title, or, in the case of other specified codes, the terms are a list of the various conditions assigned to that code.The inclusion terms are not necessarily exhaustive. Additional terms found only in the may also be assigned to a code.
Certain conditions have both an underlying etiology and multiple body system manifestations due to the underlying etiology.For such conditions, the ICD-10-CM has a coding convention that requires the underlying condition be sequenced first, if applicable, followed by the manifestation.Wherever such a combination exists, there is a use additional code note at the etiology code, and a code first note at the manifestation code.These instructional notes indicate the proper sequencing order of the codes, etiology followed by manifestation.
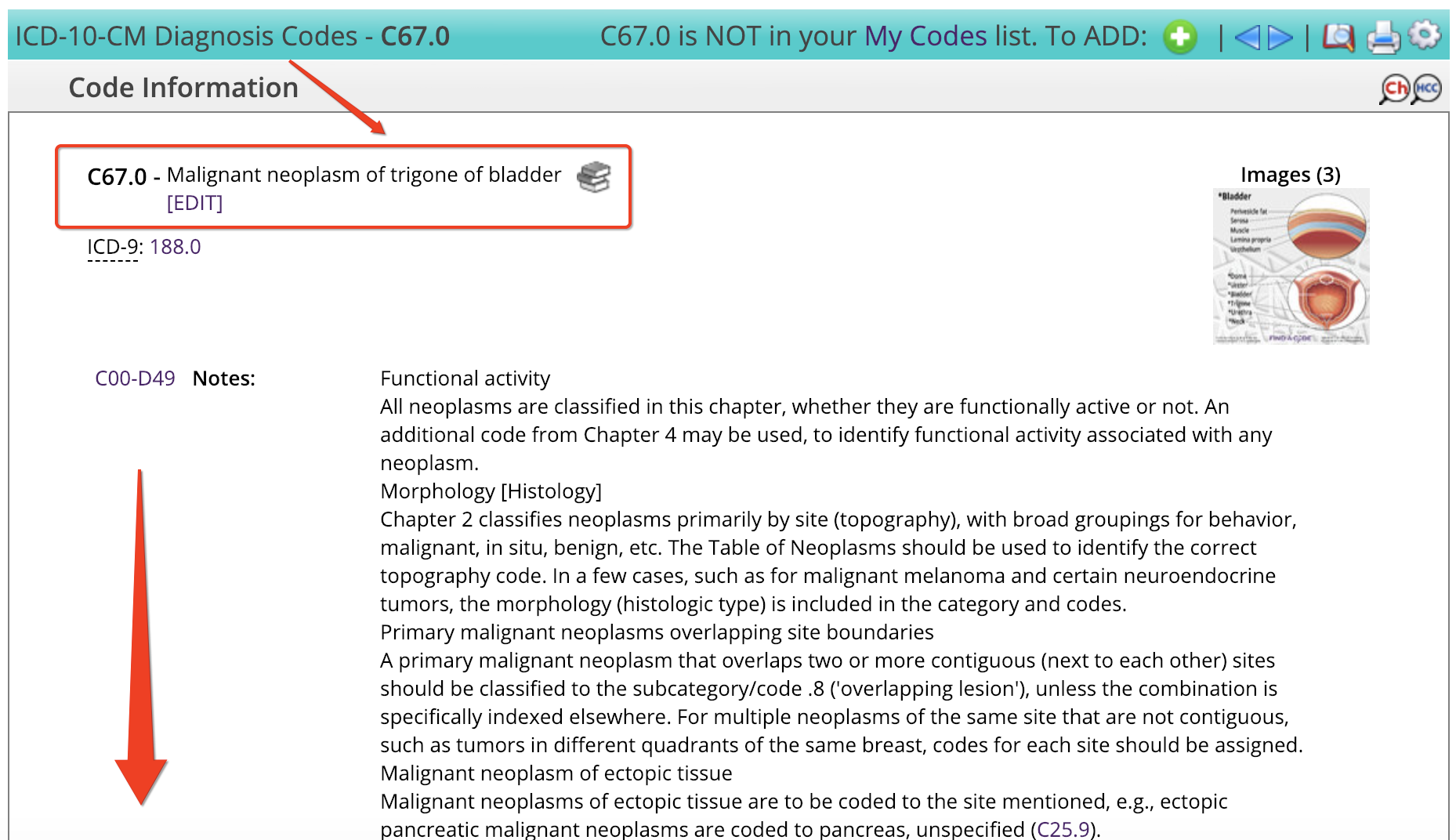
Malignant Neoplasm Of Trigone Of Bladder
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- C67.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C67.0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of C67.0 – other international versions of ICD-10 C67.0 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
What Is Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer starts when cells that make up the urinary bladder start to grow out of control. As more cancer cells develop, they can form a tumor and, with time, spread to other parts of the body.
The bladder is a hollow organ in the lower pelvis. It has flexible, muscular walls that can stretch to hold urine and squeeze to send it out of the body. The bladder’s main job is to store urine. Urine is liquid waste made by the 2 kidneys and then carried to the bladder through 2 tubes called ureters. When you urinate, the muscles in the bladder contract, and urine is forced out of the bladder through a tube called the urethra.
Don’t Miss: Is Bladder Cancer Slow Growing
Drg Mapping Rules For C670
Diagnostic codes are the first step in the DRG mapping process.
The patient’s primary diagnostic code is the most important. Assuming the patient’s primary diagnostic code is C67.0, look in the list below to see which MDC’s “Assignment of Diagnosis Codes” is first. That is the MDC that the patient will be grouped into.
From there, check the subsections of the MDC listed. The patient will be mapped into the first subsection for which the treatment performed on the patient meet the listed requirements of that subsection.
DRG grouping rules are adjusted each year, so make sure to check the rules for the fiscal year of the patient’s discharge date.
Start And Spread Of Bladder Cancer
The wall of the bladder has many several layers. Each layer is made up of different kinds of cells .
Most bladder cancers start in the innermost lining of the bladder, which is called the urothelium or transitional epithelium. As the cancer grows into or through the other layers in the bladder wall, it has a higher stage, becomes more advanced, and can be harder to treat.
Over time, the cancer might grow outside the bladder and into nearby structures. It might spread to nearby lymph nodes, or to other parts of the body.
Also Check: Botox Injection For Bladder Incontinence
Papillary Vs Flat Cancer
Bladder cancers are also divided into 2 subtypes, papillary and flat, based on how they grow .
- Papillary carcinomas grow in slender, finger-like projections from the inner surface of the bladder toward the hollow center. Papillary tumors often grow toward the center of the bladder without growing into the deeper bladder layers. These tumors are called non-invasive papillary cancers. Very low-grade , non-invasive papillary cancer is sometimes called papillary urothelial neoplasm of low-malignant potential and tends to have a very good outcome.
- Flat carcinomas do not grow toward the hollow part of the bladder at all. If a flat tumor is only in the inner layer of bladder cells, it’s known as a non-invasive flat carcinoma or a flat carcinoma in situ .
If either a papillary or flat tumor grows into deeper layers of the bladder, it’s called an invasive urothelial carcinoma.
The Icd Code C67 Is Used To Code Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is any of several types of cancer arising from the epithelial lining of the urinary bladder. Rarely the bladder is involved by non-epithelial cancers, such as lymphoma or sarcoma, but these are not ordinarily included in the colloquial term “bladder cancer.” It is a disease in which abnormal cells multiply without control in the bladder.
| Specialty: |
- DRG Group #656-661 – Kidney and ureter procedures for neoplasm with MCC.
- DRG Group #656-661 – Kidney and ureter procedures for neoplasm with CC.
- DRG Group #656-661 – Kidney and ureter procedures for neoplasm without CC or MCC.
- DRG Group #656-661 – Kidney and ureter procedures for non-neoplasm with MCC.
- DRG Group #656-661 – Kidney and ureter procedures for non-neoplasm with CC.
- DRG Group #656-661 – Kidney and ureter procedures for non-neoplasm without CC or MCC.
- DRG Group #686-688 – Kidney and urinary tract neoplasms with MCC.
- DRG Group #686-688 – Kidney and urinary tract neoplasms with CC.
- DRG Group #686-688 – Kidney and urinary tract neoplasms without CC or MCC.
Recommended Reading: Can A Ct Urogram Detect Bladder Cancer
Medications Used For The Treatment Of Bladder Cancer And Associated Icd
This detailed article of codes related to bladder cancer is intended to assist practice managers and other healthcare providers and payers to ensure the proper use of coding and billing information associated with the treatment of patients with bladder cancer.
The following sections include:
- Associated ICD-10-CM codes used for the classification of bladder cancer
- Drugs that have been approved by the FDA for the treatment of bladder cancer
- Drugs that are Compendia-listed for off-label use for bladder cancer based on clinical studies that suggest beneficial use in some cases. Please note: If a check mark appears in the FDA column, it will NOT appear in the Compendia off-label use column
- Corresponding HCPCS/CPT® codes and code descriptions
- Possible CPT® administration codes for the drugs
Malignant Neoplasm Of Bladder Unspecified
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- C67.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C67.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of C67.9 – other international versions of ICD-10 C67.9 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
You May Like: Can Bladder Cancer Be Detected By Blood Test
Malignant Neoplasm Of Trigone Of Bladder C670
The ICD10 code for the diagnosis “Malignant neoplasm of trigone of bladder” is “C67.0”. C67.0 is a VALID/BILLABLE ICD10 code, i.e it is valid for submission for HIPAA-covered transactions.
- C67.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM C67.0 became effective on October 1, 2018.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of C67.0 – other international versions of ICD-10 C67.0 may differ.