Uti And Other Symptoms
Urinary incontinence is a common sign of a UTI. Other symptoms typically occur along with the frequent urge to urinate. Someone with a UTI may also experience a burning sensation during urination or notice blood in their urine. Urine may also have a strong odor or a dark color.
Men with UTIs may experience rectal pain, while women with UTIs may have back or pelvic pain.
If you have any of these symptoms, you should be evaluated by a doctor. If youre diagnosed with a UTI, your doctor will prescribe a course of antibiotics.
What Conditions Cause Overactive Bladder
Many medical conditions can cause an overactive bladder. They include the following:
- infections, including UTIs
- lose weight
- stop smoking
- practice pelvic exercises like Kegels
Caffeine: Remember that caffeine is found in many foodsnot just coffee. Sodas, teas, chocolate, and even energy drinks can all have caffeine. Why should you avoid caffeine? Caffeine can cause the muscles in your bladder to contract. This can make you feel like you have to pee more often.
Weight Loss: You dont have to lose a lot of weight to improve incontinence symptoms. Losing just five to 10 percent of your body weight can cut the number of bathroom accidents down by half.
Obesity can affect how the muscles and nerves inside your genital tract work. So obesity can also cause urinary problems.
Pelvic Exercises & Kegels: If arent noticing much improvement after doing Kegels at home, a physical therapist can teach you how to do Kegels properly .
What If Diet & Exercise Dont Work
If home treatments dont work, it may be a good idea to see a urogynecologist. Urogynecologists are doctors who specialize in treating conditions that affect the bladder and other organs in your pelvis, including your vagina, cervix, and uterus.
A urogynecologist can recommend other treatments like physical therapy or devices you can put inside your vagina .
Don’t Miss: Overactive Bladder At Night Time Only
Types Of Urinary Incontinence
Stress incontinence
Stress urinary incontinence is the most common type of urinary incontinence. This is not caused by emotional stress but by strain on the bladder like jumping, bending, lifting, exercise, and even coughing or sneezing. Being overweight can also strain the bladder. If you have weak pelvic floor muscles, this strain can cause urine to leak. It can be a small amount of urine or just a few drops.
Stress incontinence is more likely to occur in women.
Overflow incontinence
Overflow incontinence occurs when the body makes more urine than the bladder can hold. This may also occur if the bladder is full and cant empty, which causes it to leak. The bladder muscle may not squeeze as it should or something might be blocking the flow. Overflow incontinence causes frequent urinating in small amounts and constant dribbling.
This type is more common in men and is often associated with prostate surgery or prostate problems.
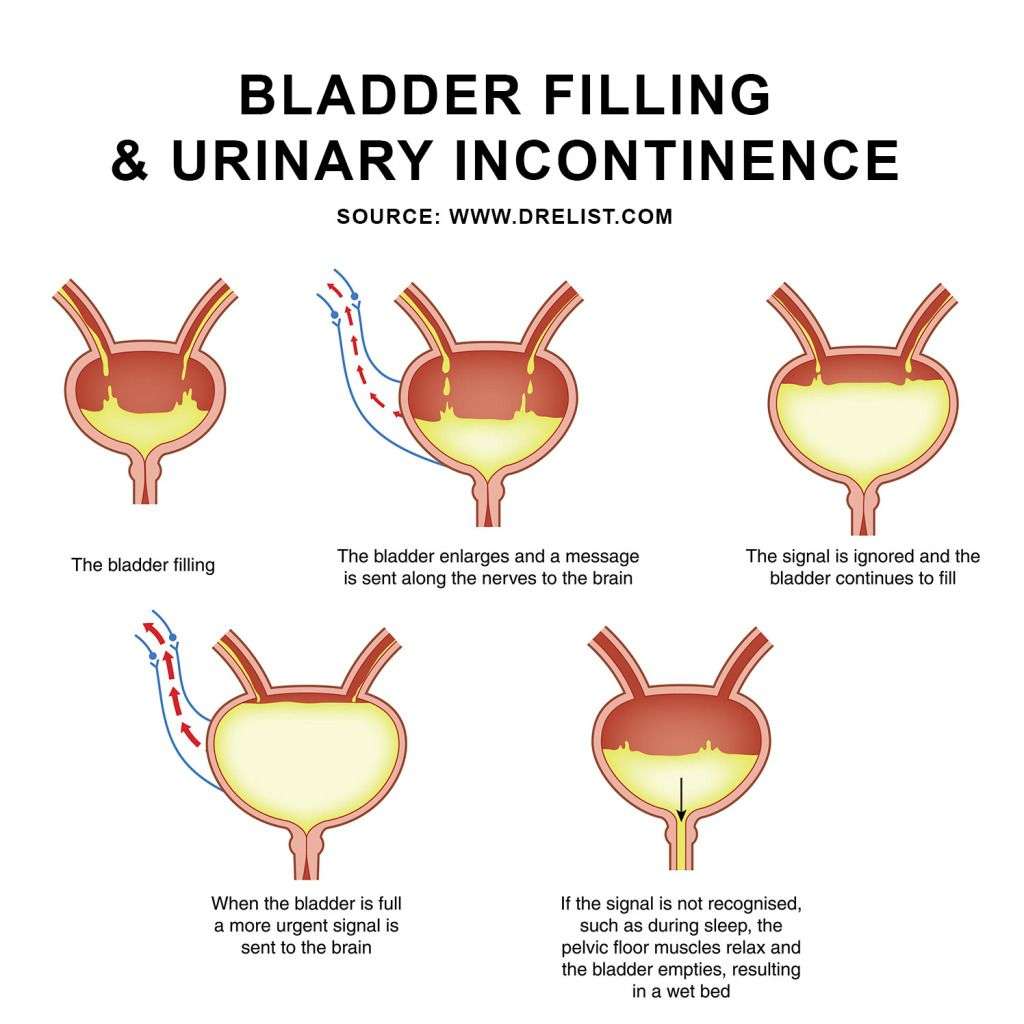
Also known as urge or urgency incontinence, this condition causes the bladder muscles to contract and signal a need to urinate even if the bladder is empty. It causes an overwhelming urge to urinate immediately and may cause accidents if you dont make it to the restroom in time.
Urgency incontinence can be caused by physical problems like damage to the spine, brain, or the nerves between the spine and the bladder. It can also be caused by a bladder infection.
Functional incontinence
How Is Overactive Bladder Diagnosed
A physician starts by first checking for infection, asking about a person’s urinary habits , and performing a physical exam to look for abnormalities in the abdomen or genitals. After that, a neurological exam can determine if nerve or sensory problems are impacting bladder function.
If results of these exams are inconclusive, additional diagnostics include:
- Measuring post-void residual urine: To determine how much urine remains in the bladder following urination, an ultrasound visualizes the bladder as a catheter is used to remove post-void residual urine. The urine volume is measured significant amounts can cause symptoms of overactive bladder.
- Measuring urine flow rate: This test will require the patient to urinate in an uroflowmeter, which provides a graph of the patient’s urine flow rate.
- Cystometry: Cystometry gauges the pressure inside of the bladder. One catheter fills the bladder with warm water while a pressure sensor is inserted in the vagina or rectum to measure the rigidity of the bladder muscle and assess its ability to hold in and push out fluid.
You May Like: What Were Your Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
Living With Bowel Or Bladder Incontinence
There is no single, right way to cope with bladder or bowel incontinence. The challenge is to find what is best for your situation, so you can get the help you need and return to a normal daily life. Talk with your health care team if you notice a change in bowel or bladder habits, and about the best ways to manage incontinence, if it is a problem. You might find it helpful to talk with other people who are dealing with incontinence, too. Ask a member of your cancer care team about support groups in your area.
Here are some things you can do that may help make incontinence less of a problem:
- Empty your bladder every 3 to 4 hours while awake, to avoid accidents.
- Empty your bladder before bedtime or before strenuous activity.
- Limit drinks with caffeine, or and avoid alcohol and citrus juices, which can irritate the bladder and make you have to go more often.
- Avoid hygiene products that may irritate you Women should avoid feminine spray or over-the-counter vaginal suppositories.
- Because belly fat can push on the bladder, avoiding weight gain or losing needed weight sometimes helps improve bladder control.
- Avoid tobacco use which can cause coughing and bladder irritation due to harmful substances in tobacco products.
- Talk to your doctor about all medicines, vitamins, herbs, and supplements youre taking. Some may affect urine control.
Depression Anxiety Attention Deficit Disorder And Oab
It is probably too simplistic to view OAB with urge UI as just a myogenic or afferent disorder. Certain individuals seem predisposed to OAB. Circumstantial evidence suggests individuals with depression, anxiety, and attention deficit disorder may experience symptoms of OAB more often than the general population. Wolfe and colleagues suggested that depression, anxiety, feeding disturbances, pain, irritable bowel syndrome, fibromyalgia, and changes in voiding are associated with disturbances in brain circuits using specific neurotransmitters, in particular serotonin . Fibromyalgia and irritable bowel syndrome are conditions seen more often in patients with IC than the general population, and these conditions are associated with OAB and possibly with depression, which provides a potential link with 5-HT metabolism. Perhaps the strongest evidence for diminished 5-HT function in depressed patients is the remarkable efficacy of selective serotonin uptake inhibitors in this group of patients. In addition, neuropharmacologic evidence indicates that some forms of depression are associated with abnormalities in the promoter for the serotonin transporter gene.,
Also Check: Men’s Overactive Bladder Treatment
Managing Bladder Or Urinary Incontinence
Sometimes urinary incontinence can last a short time, depending on what’s causing it. But sometimes incontinence can be long-term and uncomfortable, making some everyday activities difficult to manage.
Your health care team will ask you questions to determine the type of bladder incontinence you might have. Then, you might need tests to verify the type and learn the cause of it which will help them know the best way to manage it.
- Pelvic floor muscle strengthening may be recommended. A physical therapist that specializes in pelvic floor muscle exercises can help. This might help muscle strength and bladder control get better by doing exercises that tighten and relax muscles that control the flow of urine.
- Bladder training canhelp manage how often you need to urinate throughout the day, by assigning certain time intervals to empty your bladder.
Medications For Overactive Bladder
Medications that relax the bladder can be effective for alleviating symptoms of overactive bladder and reducing episodes of urge incontinence. These drugs include tolterodine , oxybutynin , an oxybutynin skin patch , trospium , solifenacin , darifenacin and now mirabegron . These medications are usually used in combination with other treatments.
Don’t Miss: Causes Of Weak Bladder Control
Molecular Basis For Plasticity Due To Ngf: Sodium Channel Isoforms
How could NGF produced by a target tissue, as in SCI, obstruction, and inflammation, and then retrogradely transported to the DRG lead to OAB? Recent data suggest that membrane conductance and thus excitability of DRG neurons are altered in models associated with increased access to NGF. This altered conductance is postulated to result from changes in the structure or combination of protein subunits of sodium and potassium channels in the cell membrane. A change in Na+ channel isoform appears sufficient to change the properties of afferents. NGF is known to lower the threshold for firing of bladder neurons and induce spontaneous and burst firing . The site of abnormal ectopic firing has been determined to be the DRG, and the firing appears to be due to changes in the isoforms for voltage-gated Na+ channels, which causes spontaneous ectopic discharges. Voltage-gated Na+ channels generate currents during the upstroke of the nerve action potential and are involved in the propagation of the nerve impulse.
TTX binds to and inactivates voltage-gated Na+ channels. Most voltage-gated Na+ channels exhibit rapid inactivation kinetics and sensitivity to nanomolar concentrations of TTX. These Na+ channels are termed TTX-sensitive . Small bladder sensory neurons in the L6-S1 DRG show two types of Na+ currents, a rapidly inactivating TTX-S sodium current and a slowly inactivating TTX-resistant INa.
What Is Urge Incontinence And How Is It Treated
There are many different types of urinary incontinence the loss of bladder control. One of the most common types is urge incontinence, which is characterized by a sudden, intense urge to urinate followed by an involuntary loss of urine. You may need to urinate often, including throughout the night.
Urinary incontinence is more common among women with approximately 17 percent of women and 3 to 11 percent of men experiencing urge incontinence at some point in their lives. Fortunately, there are many different treatment options for urge continence ranging from conservative to more invasive.
CONSERVATIVE TREATMENTS
Conservative ways to treat urinary incontinence include:
MEDICATIONS
There are two primary categories of medications used to treat urge incontinence. Your health care provider will help you determine which is right for you and your condition.
Medications include:
INTERVENTIONAL THERAPIES
If you have had little luck with other incontinence interventions, you may need to consider:
Read more helpful tips and lifestyle changes that can help you manage urinary retention and incontinence.
For the safety of our patients, staff and visitors, Mayo Clinic has strict masking policies in place. Anyone shown without a mask was either recorded prior to COVID-19 or recorded in a non-patient care area where social distancing and other safety protocols were followed.
Topics in this Post
Don’t Miss: What Is The Treatment For Low Grade Bladder Cancer
What Are The Symptoms Associated With Overactive Bladder
Symptoms of overactive bladder include:
- A frequent and sudden urge to urinate
- Involuntary loss of urine
- Increased urinary frequency during the daytime
- Increased urinary frequency at night
Although many patients may ignore symptoms associated with overactive bladder because they believe they are a normal part of aging, the condition typically has an underlying medical cause.
Treatment For Urge Incontinence
Treatments for urge incontinence vary between patients and are based on the underlying cause of the problem. These treatments may include:
- Improved diet and exercise as well as lifestyle change to reduce the strain on the bladder. This may include changing water consumption habits as well as avoiding diuretics such as alcohol and caffeinated drinks. Spicy and acidic foods can irritate the bladder, making spasms more likely
- Bladder retraining, involving bladder muscle exercises to improve urinary retention. This can improve urge incontinence if there are no other significant challenges
- Pelvic floor exercises such as kegels can assists with urge incontinence
- Medications can be used to treat urge incontinence or its underlying cause, however patients should be aware of side-effects
- Surgery can be used to treat urge incontinence or its root cause . Surgery does come with risks that should be discussed with a qualified medical professional
- In-office BPH therapy can effectively improve or eliminate urge incontinence in men suffering from excess prostatic tissue with excellent long-term results and few sexual side effects. Urologix offers both Cooled ThermoTherapy and Prostiva RF . As with any medical procedure, you should talk to a medical professional to learn about the benefits and risks
- Nerve stimulation
Read Also: Can Lower Back Pain Cause Bladder Problems
Mixed Incontinence In Women
There are several forms of incontinence. In urge incontinence also called overactive bladder the woman experiences loss of urine that is associated with a sudden, strong desire to urinate that can’t be postponed. In stress incontinence, increased pressure in the abdomen momentarily puts physical stress on the pelvis, resulting in urine loss. Activities such as coughing, sneezing, laughing, exercise, and even standing up can cause leakage in women with stress incontinence.
It’s common for women to experience symptoms of both urge and stress incontinence. This condition is called mixed incontinence.
Adult Pediatric Urology & Urogynecology
The attentive, compassionate physicians, providers, and staff at Adult Pediatric Urology & Urogynecology are committed to providing innovative, quality patient care in our state-of-the-art facility.
From screening and prevention to treatment and recovery, we will be there for you. Our team of dedicated physicians has been serving residents of Nebraska, Iowa, and South Dakota for more than 25 years.
Don’t Miss: New Drug For Overactive Bladder
Worried About Your Health
Find a range of women’s health pharmacy services, delivered by local providers at a time that suits you
Treatments include:
- Some general lifestyle measures which may help.
- Bladder retraining, which is a common treatment. This can work well in up to half of cases.
- Medication. This may be advised in addition to bladder retraining.
- Pelvic floor exercises. These may also be advised in some cases.
- Surgery. This is a last resort and rarely used to treat urge incontinence.
Morphologic Changes In The Detrusor
Regardless of the etiology, unstable detrusor develops common changes in the macroscopic structure of the bladder. Unstable human bladders frequently show patchy denervation of the muscle bundles. Some muscle fascicles may be completely denervated, while neighboring bundles appear normal. Other regions may show intermediate innervation. The areas of reduced innervation become infiltrated with connective tissue. After complete denervation, hypertrophy of the smooth muscle cells occurs. At an ultrastructural level, a common feature in unstable detrusor is the presence of protrusion junctions and ultra-close abutments between the myocytes. This picture is rare in the normal detrusor and may represent the morphologic correlate to increased electrical coupling in unstable bladders.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Ingredients In Azo Bladder Control
Symptoms Of Overactive Bladder
There are a variety of symptoms unique to an overactive bladder that can help you differentiate it from urinary incontinence. Below are some symptoms that might be indicative of OAB:
- Urgency: If you experience the sudden urge to urinate even if you just emptied your bladder
- Unintentional loss of urine: If you experience the unintentional loss of urine after feeling the urges that accompany an overactive bladder
- Frequent urination: If you urinate more than eight times per day and have any other symptoms in this list
- Urinating in the middle of the night: If you are frequently awakened by your need to urinate at night
What Behavioral Changes Can I Make To Help With Overactive Bladder
There are many techniques and changes to your typical behavior that you can try to help with an overactive bladder. These can include:
Keeping a log: During a typical day, write down your fluid intake, the number of times you urinate, the number of accidents and when they occur. Make a note about what happened when the accident happened, like when you:
- Cough.
- Laugh.
- Were unable to reach the bathroom in time.
Monitoring your diet: Eliminate or decrease foods or beverages that may worsen your bladder symptoms. These could include:
- Tea.
- Spicy and acidic foods and drinks.
- Foods and drinks that contain artificial sweeteners.
Maintaining bowel regularity: Constipation can place added pressure on the bladder and have a negative effect on your bladder function. By keeping healthy bowel habits, you may be able to avoid constipation and help to lessen bladder symptoms. The following are some suggestions for maintaining bowel regularity:
- Increase your fiber intake by eating foods like beans, pasta, oatmeal, bran cereal, whole wheat bread, and fresh fruit and vegetables.
- Every morning, take 2 tablespoons of this mixture: 1 cup apple sauce, 1 cup unprocessed wheat bran, and ¾ cup prune juice.
- Exercise regularly to maintain regular bowel movements.
Maintaining a healthy weight: Being overweight can add pressure on your bladder, which may contribute to bladder control problems. If you are overweight, weight loss can reduce the pressure on your bladder.
Read Also: Can Overactive Bladder Start Suddenly
Overactive Bladder And Urge Urinary Incontinence
You may find yourself hurrying a lot to find a bathroom if you have an overactive bladder.
Overactive bladder is a condition in which the bladder can spasm and cause a sudden, intense and frequent urge to urinate. In some cases, these urges can lead to episodes of involuntary urine leakage, which is called urge urinary incontinence or UUI-wet. Overactive bladder contractions that send you running to the bathroom quite frequently, without any leakage is referred to as UUI-dry.
What Causes an Overactive Bladder?
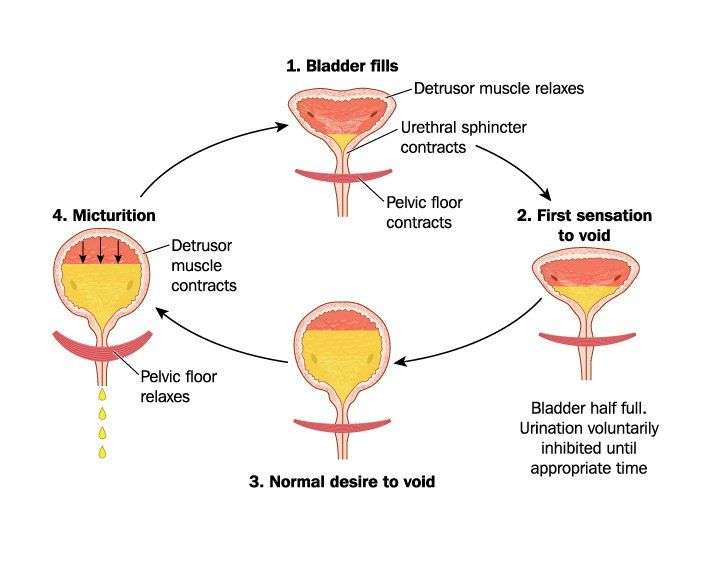
The bladder is a muscle, and like all muscles it is controlled by nerves. As the bladder fills, the nerves sense the fullness and send a signal to your brain telling you that you need to urinate. Usually, your body responds to this urge to urinate so that youll have enough time to get to the bathroom. When you are at the toilet, your brain will send the message to your bladder that it is now appropriate to urinate. The message sent to the bladder tells the detrusor muscle to contract and expel the urine. When you have OAB, the nerves alert you that you need to urinate, but your ability to inhibit this urge is compromised and then the bladder starts to spasm on its own and push the urine out.
Prevention
Treatment and Management
Medical Reviewer: Karen Sasso, MSN, RN, APN, CCCN
Karen Sasso, MSN, RN, AP