Genetics And Family History
If you have family members who have bladder cancer, you have a higher risk of developing it yourself. This could also be that family members share exposure to the same chemicals that cause cancer or they share the same changes in certain genes , making it harder for their bodies to break specific toxins down, increasing their risk of bladder cancer.
Possible Causes Of Bladder Cancer: Chemical Exposure
Exposure to certain chemicals on the job can increase risk of bladder cancer. Occupations that may involve exposure to cancer-causing chemicals include metal workers, hairdressers, and mechanics. Organic chemicals called aromatic amines are especially associated with bladder cancer and are used in the dye industry. Those working with dyes, metal workers, or in the manufacturing of leather, textiles, rubber, or paint should be sure to follow recommended safety protocols. Smoking increases the risk even more for these workers.
Bladder Cancer Treatment: Surgery
Transurethral Resection
Early-stage cancers are most commonly treated by transurethral surgery. An instrument with a small wire loop is inserted through the urethra and into the bladder. The loop removes a tumor by cutting or burning it with electrical current, allowing it to be extracted from the bladder.
Partial and Radical Cystectomy
Partial cystectomy includes the removal of part of the bladder. This operation is usually for low-grade tumors that have invaded the bladder wall but are limited to a small area of the bladder. In a radical cystectomy, the entire bladder is removed, as well as its surrounding lymph nodes and other areas that contain cancerous cells. If the cancer has metastasized outside of the bladder and into neighboring tissue, other organs may also be removed such as the uterus and ovaries in women and the prostate in men.
Don’t Miss: Can Overactive Bladder Cause Pain
Certain Factors Affect Prognosis And Treatment Options
The prognosis depends on the following:
- The stage of the cancer . Bladder cancer in the early stages can often be cured.
- The type of bladder cancer cells and how they look under a microscope.
- Whether there is carcinoma in situ in other parts of the bladder.
- The patients age and general health.
If the cancer is superficial, prognosis also depends on the following:
- How many tumors there are.
- The size of the tumors.
- Whether the tumor has recurred after treatment.
Treatment options depend on the stage of bladder cancer.
Bladder Cancer Clinical Trials
What about Clinical Trials?
You may hear about clinical trials for your bladder cancer. Clinical trials are research studies that test if a new treatment or procedure is safe and effective.
Through clinical trials, doctors find new ways to improve treatments and the quality of life for people with disease. Trials are available for all stages of cancer. The results of a clinical trial can make a major difference to patients and their families. Please visit our clinical trials research webpage to learn more.
You May Like: Where Is The Bladder Located
How Is Bladder Cancer Diagnosed
Several different diagnostic tests and procedures may be used to detect bladder cancer, often in combination. They are selected based on a patients symptoms and risk factors and may include:
- Urinalysis: a quick test used to detect blood and other substances in urine.
- Urine cytology: urine is examined microscopically to see if cancer cells are present.
- Genomic urine tests: non-invasive molecular tests, such as Cxbladder, which measure gene expression to detect or rule out bladder cancer.
- Cystoscopy: a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera is inserted into the bladder through the urethra. If an abnormal area is seen, a small sample of tissue is usually collected for laboratory examination.
- Imaging: several types of imaging test can be used to visualize the inside of the body, such as ultrasound, CT scan, MRI scan, and x-ray.
Facts And Stats On Bladder Cancer
-
Men have a higher incidence of bladder cancer than women.
-
Older adults are particularly affected as the risk for bladder cancer increases with age. Nine out of ten people diagnosed are over the age of 55. The average age is 73.
-
Bladder cancer has the highest recurrence rate of any form of cancer.
-
Due to the incidence and recurrence, prevention, early detection and prompt treatment are imperative.
Also Check: How Do Doctors Test For Bladder Infection
Treatment Of Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage IV bladder cancer that has not spread to other parts of the body may include the following:
- Urinary diversion or cystectomy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
Treatment of stage IV bladder cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, such as the lung, bone, or liver, may include the following:
- External radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Urinary diversion or cystectomy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- A clinical trial of new anticancer drugs.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
What Are The Risk Factors For Bladder Cancer
Some factors increase the risk of bladder cancer:
- Cigarette smoking is the biggest risk factor it more than doubles the risk. Pipe and cigar smoking and exposure to second-hand smoking may also increase one’s risk.
- Prior radiation exposure is the next most common risk factor .
- Certain chemotherapy drugs also increase the risk of bladder cancer.
- Environmental exposures increase the risk of bladder cancer. People who work with chemicals, such as aromatic amines are at risk. Extensive exposure to rubber, leather, some textiles, paint, and hairdressing supplies, typically related to occupational exposure, also appears to increase the risk.
- Infection with a parasite known as Schistosoma haematobium, which is more common in developing countries and the Middle East.
- People who have frequent infections of the bladder, bladder stones, or other diseases of the urinary tract, or who have chronic need for a catheter in the bladder, may be at higher risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
- Patients with a previous bladder cancer are at increased risk to form new or recurrent bladder tumors.
Other risk factors include diets high in fried meats and animal fats, and older age. In addition, men have a three-fold higher risk than women.
You May Like: Icd 10 Code For Neurogenic Bladder
Living With Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer symptoms and treatments can be overwhelming. No matter where you are on your treatment journey, youâll need to meet with your healthcare provider for regular checkups and tests. Talking to your healthcare team about the next steps and what to expect can provide a road map during this time.
If Youve Been Diagnosed With Bladder Cancer Seek Out A Team Of Experts
Most people require a combination of therapies to treat bladder cancer successfully. The best plan is different for each person, says Dr. Donat. This customized treatment approach requires the expertise of multiple specialists.
At MSK, most people with bladder cancer meet with a urologic surgeon and medical oncologist as well as a radiation oncologist when needed. This close collaboration helps ensure that MSK patients receive the best care possible. The benefit of MSK is that we bring world-class expertise in each type of treatment to bear for every individual we care for, and we are on the forefront of developing new treatments, says Dr. Donat.
Its also important to know that expert bladder cancer care means not only lifesaving treatments but preserving your quality of life and, if possible, your bladder. We want all of our patients female and male to feel their best after bladder cancer surgery, says Dr. Donat. As surgeons, we do that through a variety of techniques, including minimally invasive approaches and other specialized techniques to preserve or reconstruct the bladder and to maintain sexual function.
Read Also: Bladder Cancer Metastasis To Liver Prognosis
Symptoms In Men And Women
Bladder cancer symptoms in men and women are the same. Men are more likely to get bladder cancer, but they are also more likely to have it diagnosed earlier, according to Moffitt Cancer Center.
Women are more likely to mistake bladder cancer symptoms for urinary tract infections or menstruation.
Rarely, bladder cancer may also be misdiagnosed as interstitial cystitis in women. IC is a painful, inflammatory bladder condition that affects more women than men.
In one study, doctors found bladder cancer in about one percent out of 600 patients referred to them for IC treatment, according to an article in Urology Times.
Is Bladder Cancer Treatable
Many types of therapy are used to treat bladder cancer. In general, the treatment pathway chosen depends on the type and stage of bladder cancer present and a patients overall health and individual preferences. Common treatment options include:
- Surgery: to remove tumor cells and surrounding tissue. The type of surgery used depends on factors such as the size and progression of the tumor.
- Chemotherapy: which refers to the use of drugs to destroy cancer cells. Chemotherapy may be local or systemic .
- Immunotherapy: which uses naturally occurring or man-made substances to improve or bolster the bodys immune system function. Like with chemotherapy, immunotherapy may be delivered locally or systemically.
- Radiation therapy: which uses x-rays or other high-energy waves or particles to kill cancer cells.
You May Like: Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Survival
Possible Causes Of Bladder Cancer: Smoking
Smoking is the greatest known risk factor for bladder cancer smokers are four times more likely to get bladder cancer than nonsmokers. Harmful chemicals from cigarette smoke enter the bloodstream in the lungs and are ultimately filtered by the kidneys into the urine. This leads to a concentration of harmful chemicals inside the bladder. Experts believe that smoking causes about half of all bladder cancers in men and women.
Contact Cxbladder To Learn More About Our Suite Of Non
So, can women get bladder cancer? The answer is yes, and youll want to catch it as early as possible. If you’ve been experiencing any of the symptoms above or suspect you may have bladder cancer, contact Cxbladder to learn more about our suite of non-invasive urine tests. Cxbladder urine-based lab tests detect and diagnose bladder cancer quickly and accurately so you can begin treatment early.
Recommended Reading: How To Know If You Have Bladder Problems
Bladder Cancer Treatment: Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is given in some cases before surgery to shrink bladder cancer tumors. It can also be used after surgery to destroy any remaining tumor cells. Chemotherapy may be given intravenously or administered directly into the bladder . Intravesical chemotherapy is effective in decreasing the recurrence rate of superficial bladder cancers on a short-term basis, but not effective against bladder cancer that has already invaded the muscular walls. Systemic or intravenous chemotherapy is required when the cancer has deeply penetrated the bladder, lymph nodes, or other organs.
Chemotherapy Side Effects
Side effects vary from patient to patient. Common side effects of systemic chemotherapy include the following:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sores on the inside of the mouth or in the digestive tract
- Feeling tired or lacking energy
- Increased susceptibility to infection
What Is Chemotherapy For Bladder Cancer
Patients who are diagnosed with metastatic bladder cancer are usually treated with chemotherapy. Chemotherapy may also be used in cases of “locally advanced” bladder cancer in an attempt to decrease the chances of the cancer coming back after radical cystectomy. This is “adjuvant chemotherapy.” Another strategy entails administering “neoadjuvant chemotherapy” by giving these medications before radical cystectomy in an attempt to improve the results of surgery and decrease the size of the tumor before the operation.
Chemotherapy has the potential to control metastatic bladder cancer and increase the chances of cure when used in a neoadjuvant or adjuvant setting along with surgery. However, chemotherapy has its own set of side effects that some individuals find intolerable.
The time-honored chemotherapy regimen for bladder cancer is the MVAC. It is a combination of four medications given in cyclical form.
- C: Cisplatin
Oncologists currently prescribe MVAC in a “dose dense” fashion. This means the patient takes the drugs more frequently than was previously done in the accepted treatment schedule, as well as taking growth factors to help the blood counts to recover faster from the effects of the chemotherapy drugs. The older schedule for MVAC therapy is no longer recommended according to the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
Some patients with heart disease may not be in a condition to receive Adriamycin and may receive CMV instead
- Paclitaxel
- Docetaxel
Recommended Reading: Ways To Stop Bladder Leakage
What Is The Treatment For Superficial Bladder Cancer
Superficial bladder cancer is a cancer that has not invaded the muscle wall of the bladder and is confined to the inner lining of the bladder. This cancer is also termed non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. The T stage is Ta, T1, or Tis . After the initial TURBT or biopsy in case of CIS, the subsequent treatment in these cases may involve observation with regular follow-up with cystoscopy examinations of the bladder, instillation of medications in the bladder, or in certain cases, surgical removal of the bladder .
Small low-grade, superficial bladder cancers may not require aggressive management after the initial TURBT and may be simply followed up by doing repeated cystoscopy examinations at regular intervals . Some physicians will use fulguration to treat biopsy areas or other small areas that may contain bladder cancer cells.
It is very important to note that 30%-40% of these tumors tend to recur and these recurrences may not be associated with any symptoms. Hence, it is imperative to stick to a regular follow-up protocol to ensure that the disease does not go out of control. A single dose of a chemotherapy medication put inside the bladder immediately after a TURBT can decrease the chances of recurrence within the first two years after surgery.
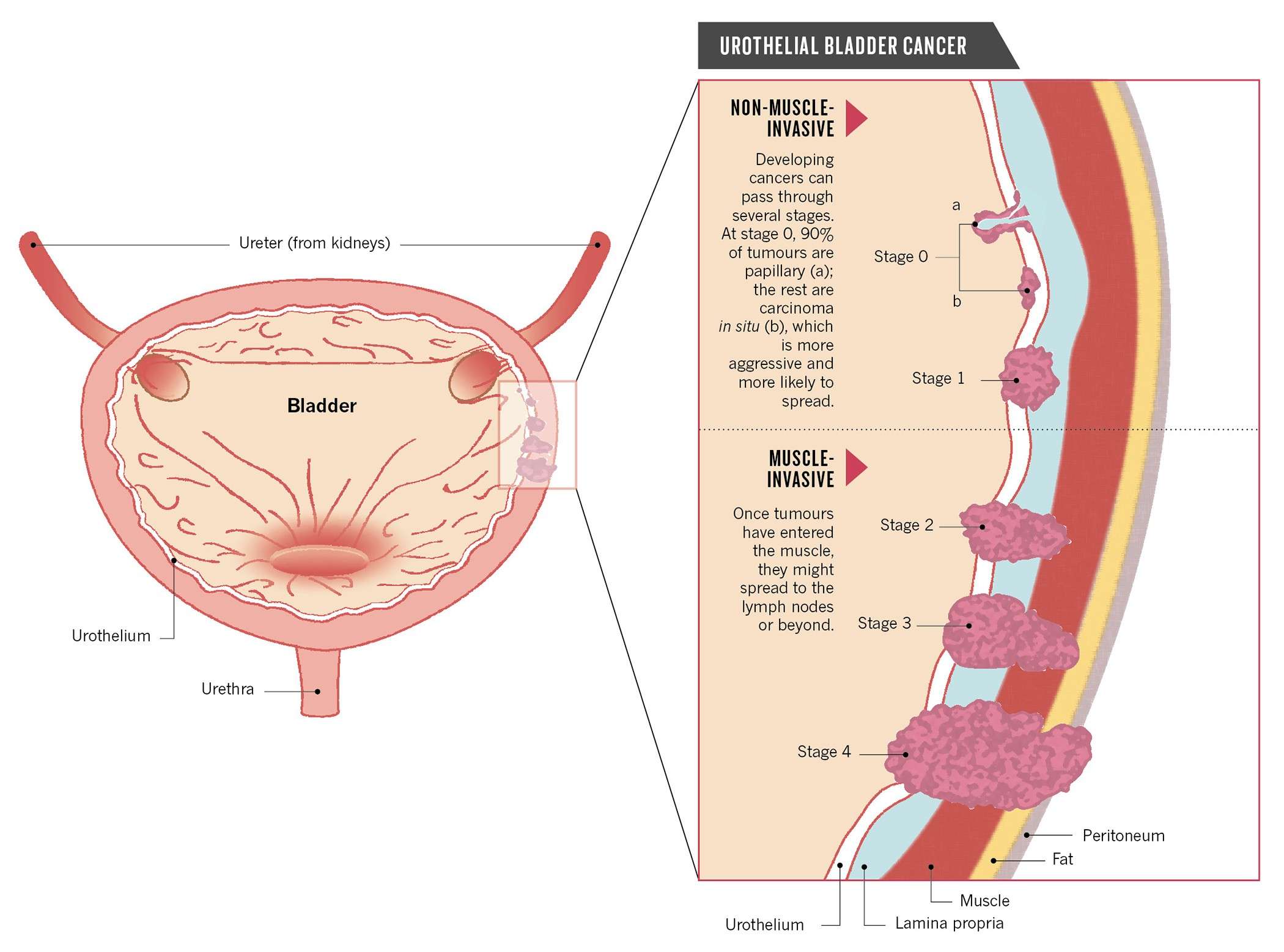
What Are The Stages Of Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer can be either early stage or invasive .
The stages range from TA to IV . In the earliest stages , the cancer is confined to the lining of the bladder or in the connective tissue just below the lining, but has not invaded into the main muscle wall of the bladder.
Stages II to IV denote invasive cancer:
- In Stage II, cancer has spread to the muscle wall of the bladder.
- In Stage III, the cancer has spread to the fatty tissue outside the bladder muscle.
- In Stage IV, the cancer has metastasized from the bladder to the lymph nodes or to other organs or bones.
A more sophisticated and preferred staging system is known as TNM, which stands for tumor, node involvement and metastases. In this system:
- Invasive bladder tumors can range from T2 all the way to T4 .
- Lymph node involvement ranges from N0 to N3 .
- M0 means that there is no metastasis outside of the pelvis. M1 means that it has metastasized outside of the pelvis.
Don’t Miss: Can Weak Bladder Muscles Be Fixed
What Is The Prognosis For Bladder Cancer
The most important factors that affect the prognosis of bladder cancer are the stage and grade of the tumor. The lower the stage and grade, the better the outlook. Other factors such as number, size, pattern of recurrence , response to initial treatment like BCG, coexistent carcinoma in situ, and certain genetic mutations also play a role. The table below is based on the National Cancer Institute’s database:
| Stage | |
|---|---|
| IV | 15% |
For low-risk superficial bladder cancer , the chances of recurrence are about 50% in five years after the initial diagnosis. This necessitates regular follow-up, even in these low-risk tumors. However, unlike the more aggressive variants of bladder cancer, the chances of progression are minimal. Typically, these tumors, even when they recur, do so in the same stage and grade as the original tumor and do not compromise the life expectancy of the patient.
High-risk superficial tumors are those that are high-grade, T1 tumors and are associated with extensive areas of carcinoma in situ. Multiple tumors, large tumors, and those that recur despite BCG treatment are also at an increased risk for recurrence and progression. These tumors have a recurrence rate in the range of 50%-70% at one and five years, respectively. They are also much likely to invade into the deeper layers. Doctors need to manage these tumors more aggressively since they have a potential to invade and spread to other parts of the body thereby shortening the life expectancy of the patient.
Five Types Of Standard Treatment Are Used:
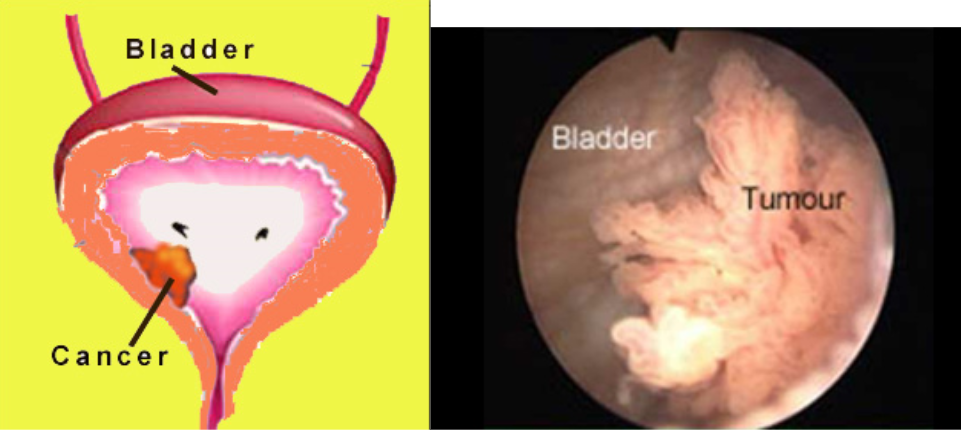
Surgery
One of the following types of surgery may be done:
- Transurethral resection with fulguration: Surgery in which a cystoscope is inserted into the bladder through the urethra.A tool with a small wire loop on the end is then used to remove thecancer or to burn the tumor away with high-energy electricity. This is known as fulguration.
- Radical cystectomy: Surgery to remove the bladder and anylymph nodes and nearby organs that contain cancer. This surgery may bedone when the bladder cancer invades the muscle wall, or when superficialcancer involves a large part of the bladder. In men, the nearby organs that areremoved are the prostate and the seminal vesicles. In women, the uterus, theovaries, and part of the vagina are removed. Sometimes, when the cancer hasspread outside the bladder and cannot be completely removed, surgery to removeonly the bladder may be done to reduce urinarysymptoms caused by the cancer.When the bladder must be removed, the surgeon creates another way for urine toleave the body.
- Partial cystectomy: Surgery to remove part of thebladder. This surgery may be done for patients who have a low-grade tumor thathas invaded the wall of the bladder but is limited to one area of the bladder.Because only a part of the bladder is removed, patients are able to urinate normally afterrecovering from this surgery. This is also called segmental cystectomy.
- Urinary diversion: Surgery to make a new way forthe body to store and pass urine.
Radiation therapy
Chemotherapy
Recommended Reading: What Helps With Bladder Infection Pain