Classification Of Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs are classified into 6 categories. The first category is an uncomplicated infection this is when the urinary tract is normal, both structurally and physiologically, and there is no associated disorder that impairs the host defense mechanisms. The second category is an complicated infection this is when infection occurs within an abnormal urinary tract, such as when there is ureteric obstruction, renal calculi, or vesicoureteric reflux. The third category, an isolated infection, is when it is the first episode of UTI, or the episodes are 6 months apart. Isolated infections affect 2540% of young females. The fourth category, an unresolved infection, is when therapy fails because of bacterial resistance or due to infection by two different bacteria with equally limited susceptibilities. The fifth category, reinfection, occurs where there has been no growth after a treated infection, but then the same organism regrows two weeks after therapy, or when a different microorganism grows during any period of time., This accounts for 95% of RUTIs in women. Bacterial persistence happens when therapy is impaired by the accumulation of bacteria in a location that cannot be reached by antibiotics, such as infected stones, urethral diverticula and infected paraurethral glands. The sixth category, relapse, is when the same microorganism causes a UTI within two weeks of therapy however, it is usually difficult to distinguish a reinfection from a relapse.
What Conditions Are Related To Recurrent Utis
Recurrent UTIs sometimes happen along with other conditions, such as:
- vesicoureteral reflux , which is found in 30%50% of kids diagnosed with a UTI. In this congenital condition, pee flows backward from the bladder to the ureters. Ureters are thin, tube-like structures that carry pee from the kidney to the bladder. Sometimes the pee backs up to the kidneys. If it’s infected with bacteria, it can lead to pyelonephritis.
- hydronephrosis, which is an enlargement of one or both kidneys due to backup or blockage of urine flow. It’s usually caused by severe VUR or a blocked ureter. Some kids with hydronephrosis might need to take daily low doses of antibiotics to prevent UTIs until the condition producing hydronephrosis gets better or is fixed through surgery.
But not all cases of recurrent UTIs can be traced back to these body structure-related problems. For example, dysfunctional voiding when a child doesn’t relax the muscles properly while peeing is a common cause of UTIs. Not peeing often enough also can also increase a child’s risk for recurrent infections. Both dysfunctional voiding and infrequent urination can be associated with constipation.
Rarely, unrelated conditions that harm the body’s natural defenses, such as diseases of the immune system, also can lead to recurrent UTIs. Use of a nonsterile urinary catheter can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract and also cause an infection.
Home Remedies For Bladder Infection Symptoms
Drinking plenty of water can help clear the infection and may help relieve your symptoms sooner. Some people find that taking cranberry extract also helps relieve their symptoms. However, research on this is inconclusive.
Some research suggests that consuming cranberry juice, extract, or pills can help prevent bladder infections. However, these are not treatments for a bladder infection if you already have one. It is also important to drink at least eight glasses of water each day to help keep your bladder healthy and prevent infection.
If you are currently treating a bladder infection, drinking plenty of water can help flush out bacteria and clear the infection.
Recommended Reading: Bladder Infection And Back Pain
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection In Pregnancy
UTI is the most frequent medical complication of pregnancy. The risk factors of preterm delivery, low infant birth weight and abortions are most commonly associated with symptomatic and asymptomatic bacteriuria during pregnancy. In pregnancy, factors that contribute to UTI risk are ureteric and renal pelvis dilation increased urinary pH decreased muscle tone of the ureters, and glycosuria, which promotes bacterial growth. Treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy reduces the risk of pyelonephritis. As RUTIs are common in pregnancy, they need prophylactic treatment if they occur. Screening for bacteriuria is recommended in all pregnant women at their first prenatal visit and then in the third trimester., They should subsequently be treated with antibiotics such as nitrofurantoin, sulfisoxazole or cephalexin.,, Antibiotic prophylaxis for RUTI in pregnant women is effective using continuous or post-coital regimens. The causative organisms of UTI in pregnancy are similar to those found in non-pregnant patients, with E. coli accounting for 8090% of infections., Urinary group B streptococcal infections in pregnant women need to be treated and followed by intrapartum prophylaxis.
Tips To Prevent Recurrent Uti
If you suffer from recurrent UTI, you should seriously consider changing some habits and incorporating probiotics into your diet. Check out the following tips to stay away from UTI.
1. Drink lots of water
Developing a habit of drinking 6-8 glasses of water every day keeps you away from many problems. UTI is one of them. An optimum amount of water helps filter out toxins and harmful bacteria from your urinary tract. All the while keeping your kidneys and vagina healthy and hydrated.
2. Dont hold in your pee!
Peeing when the urge arises helps you get rid of toxins efficiently. If you hold it in for too long, the bacteria in the urine can attach to the inner lining of your bladder and start an infection. This infection will spread to other parts of the urinary system and cause a UTI .
3. Drink cranberry juice
Cranberry juice offers great hydration that helps with your urinary infections. Although theres little research to back up the fact that they have antibacterial properties, they sure do provide benefits that prevent urinary infection. Its important to mention that this hydration comes at the cost of high sugar intake. So, keep a regular check on how much sugar youre getting if youre including cranberry juice in your diet.
4. Take Vitamin C
The immune system is the firewall of your body! Vitamin C boosts the immune system. Not only will it prevent urinary infections, but it will also keep you away from other diseases .
5. Include probiotics in your diet
Read Also: How To Treat Overactive Bladder
What Causes Urinary Tract Infection
The vast majority of urinary tract infections are caused by the bacteria Escherichia coli , which is usually found in the digestive system. However, other pathogens may cause a UTI. These include:
- Klebsiella pneumonia
- Enterococcus faecalis
- Staphylococcus saprophyticus
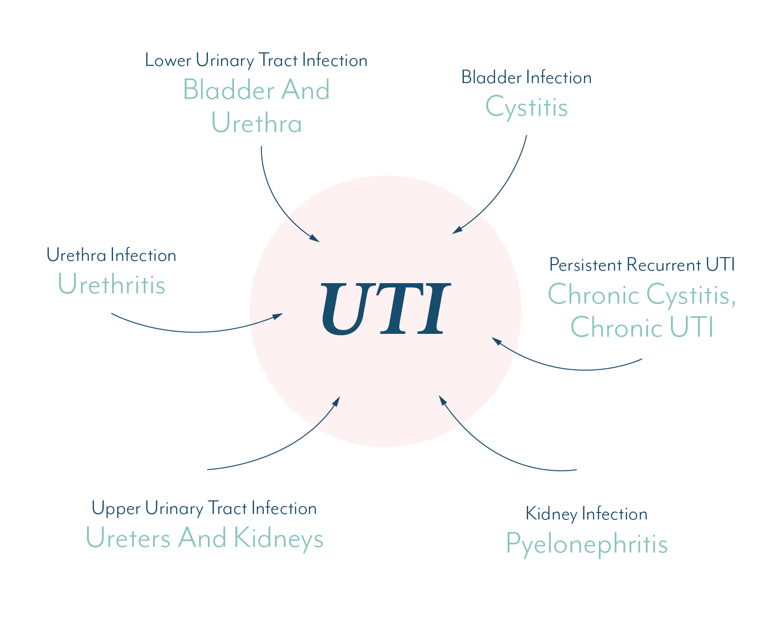
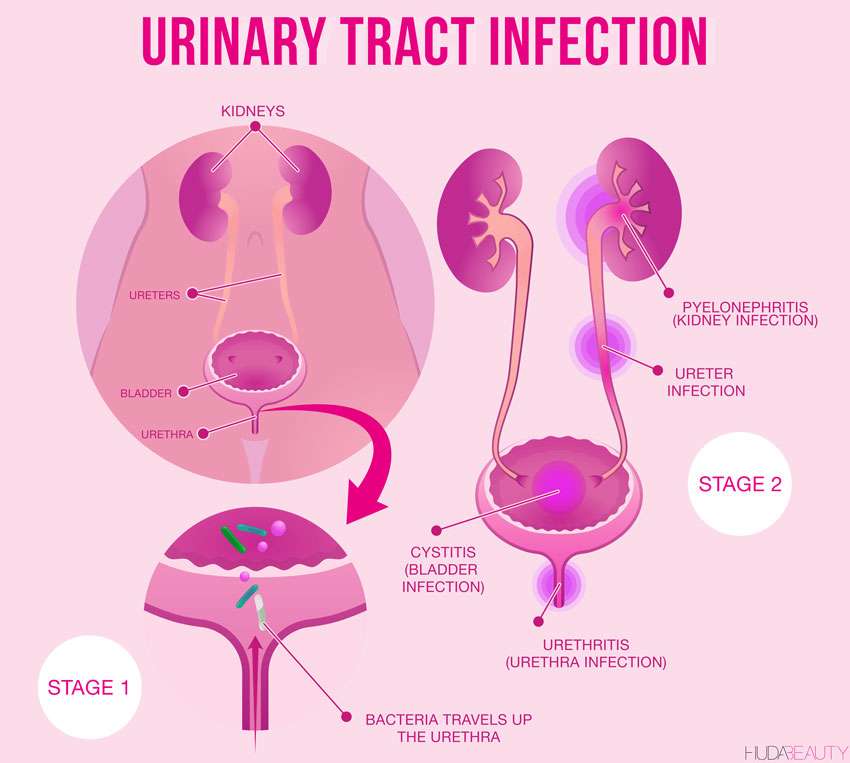
The bacteria may infect any part of the urinary tract bladder, urethra or kidneys. Depending on where the infection occurs, the UTIs are often known as:
- Cystitis infection of the bladder
- Urethritis infection of the urethra
- Pyelonephritis infection of the kidneys
The infection in urethra and bladder is usually not very serious and clears up with treatment. Similarly, ureters very rarely get infected. However, if a UTI reaches the kidneys, it may lead to kidney infections and a person may have to go to the hospital for treatment.
Treatment Of Recurrent Utis
Most UTIs go away with a short course of antibiotics. UTIs may be treated with antibiotics in addition to home remedies such as drinking large amounts of water, frequent urination and completely emptying the bladder, and taking cranberry supplements.
However, women with recurrent UTIs often require preventive antibiotics, depending on the frequency or triggers of their infections.
Women who regularly develop UTIs following sexual intercourse may benefit from a dose of antibiotics that is taken after sex. For women who have less than three UTIs per year, a physician may provide a prescription for antibiotics that can be filled whenever symptoms start to appear.
For women whose recurrent UTIs occur more than three times per year, another treatment option is to take a regular, low dose of antibiotics to help prevent infections.
Other women with recurrent UTIs that may benefit from preventive antibiotics include women who have spinal cord injuries or other complex conditions involving the nervous system, such as multiple sclerosis or diabetes.
Recurring urinary tract infections may be a side effect of a more serious condition. If you are concerned, take our âDo I need a Urogynecologist?â self-assessment.
If youâre struggling with a pelvic floor disorder, we want to help. Contact us today to learn about our services and treatment options.
Skip call wait times by requesting an appointment online.
Don’t Miss: How Long Is Bladder Surgery
How To Beat Recurrent Utis
A UTI, known in full as a urinary tract infection, is a common infection that affects the urinary tract, comprised of the kidneys, bladder, and urethra. UTIs are very common, especially among women, because their urinary tracts are more exposed. Bacteria like E.coli are usually the cause, but certain fungi can also result in an infection. A UTI is typically characterized by a frequent urge to urinate, cloudy or dark urine, a burning sensation when urinating, pelvic pain, and a strong urine odor. People with UTIs also report feeling constant discomfort.
Antibiotics commonly treat UTIs. However, many people have reported recurrent infections even after treatment. This is typically because the infection-causing bacteria are not eliminated completely. Women can experience recurrent infections four or more times a year. However, this does not mean it is impossible to beat recurrent infections. Below are some tips to help you prevent recurrent UTIs.
Drink plenty of water or unsweetened drinks
Increase your vitamin C intake
Some evidence shows that taking Vitamin C can help reduce recurrent UTIs. This is because vitamin C increases acidity in your urine, and this acidic environment in your urinary tract helps kill the bacteria that cause UTIs. You can increase your vitamin C intake by eating more fruits and vegetables, like oranges, grapefruit, kiwi, and red peppers. Taking vitamin C as a supplement can also help with UTI treatment.
Practice proper hygiene
What Can You Do To Prevent Recurrent Utis
If you are suffering from recurrent UTIs, you must get in touch with your primary care physician or a urologist. After carefully evaluating your condition, he/she will design an appropriate course of treatment.
Also, there are a lot of ways through which you can minimize your chances of getting UTIs. For this,
- Drink plenty of water It will help you get flush out all the bacteria through urine.
- Do not hold your pee If you feel the urge to urinate, find a bathroom and go.
- Maintain good sexual hygiene Do not indulge in unhealthy sexual activities. Also, urinate shortly after sex.
- Always use clean washrooms Make sure the washroom that you are using is clean and fresh.
- Use dermatologically tested products Always use sprays, deodorants and powders that are medically approved. And avoid using sprays close to your genitals.
- Keep your genitals clean Always wipe yourself from front to back after urinating.
- Wear cotton underwear Always prefer cotton panties to help keep your urethra dry.
Also Check: Will Overactive Bladder Go Away
Can Recurrent Utis Be A Sign Of Cancer
Both UTIs and bladder cancer can cause similar symptoms, such as a frequent need to urinate and even blood in the urine, according to the University of Rochester Medical Center.
According to the American Cancer Society, urinary tract infections, kidney and bladder stones, and other causes of chronic bladder irritation have been linked to bladder cancer. However, its not clear whether recurrent urinary or bladder infections can actually cause bladder cancer or whether they constitute a true risk factor for bladder cancer.
The biggest known risk factor for bladder cancer is smoking. The risk of bladder cancer also increases with age. Most people who get bladder cancer are over the age of 55.
If you think you may have chronic or recurrent UTIs, its best to get checked out by your doctor. Your provider can rule out other health issues, including bladder cancer, and get you the treatment you need to get rid of chronic UTIs.
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Utis
Symptoms of a UTI can include:
- pain when peeing
- changes in how often a child needs to pee
- changes in the look or smell of pee
- fever
- lower belly pain
- lower back pain or discomfort
UTIs also can cause kids to wet their pants or the bed, even if they haven’t had these problems before. Infants and very young children may only show nonspecific signs, such as fever, vomiting, or decreased appetite or activity.
Read Also: What Herbs Are Good For Bladder Control
Recurrent Utis At A Glance
- A urinary tract infection is a bacterial infection in the urethra, bladder, ureters, and/or kidneys.
- UTIs are considered recurrent if they occur two or more times in six months, or three or more times in a year.
- Common symptoms include a strong urge to urinate, and frequent urination in small amounts, often accompanied by a burning sensation.
- UTIs are predominately treated by primary care physicians or urologists treatment commonly includes preventive antibiotics, either taken continuously in low doses or as needed when UTI symptoms or triggers are presents.
- More severe UTIs may require hospital treatment, particularly in the case of an infection that travels to the kidneys.
How Do Probiotics Work In The Urinary Microbiome
Research has shown that Lactobacillus probiotic strain works in three different ways in your urinary system. One way is by producing lactic acid in the microbiome that helps fight and kill infection-causing bacteria and viral pathogens. Another way is the formation of protective epithelial colonies in the urinary tract lining that prevents any bacteria from settling and colonizing. The last way is by stimulating the immune response to kill any foreign microbe in the body .
You should keep in mind that chronic UTI should only be treated by using properly prescribed medicines by your doctor. Dont start supplements without prior knowledge of your condition and expect relief from chronic infections. Probiotics are good for preventing recurrent UTI and keeping you safe in the long term.
Also Check: How To Do Bladder Training
Check If It’s A Urinary Tract Infection
Symptoms of a UTI may include:
- pain or a burning sensation when peeing
- needing to pee more often than usual during the night
- pee that looks cloudy
- needing to pee suddenly or more urgently than usual
- needing to pee more often than usual
- lower tummy pain or pain in your back, just under the ribs
- a high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a very low temperature below 36C
How Are Urinary Abnormalities Diagnosed
It’s important for a doctor to rule out any underlying problems in the urinary system when a child gets UTIs repeatedly. Kids with recurrent infections should see a pediatric urologist to see what is causing the infections.
Some problems can be found before birth. Hydronephrosis that develops before birth can be seen in an ultrasound as early as 16 weeks. In rare cases, doctors may consider neonatal surgery if hydronephrosis affects both kidneys and is a risk to the fetus. Most of the time, though, doctors wait until after birth to treat the condition, because almost half of all cases seen prenatally disappear by the time a baby is born.
Doctors will closely watch the blood pressure of a newborn thought to have hydronephrosis or another urinary system abnormality, because some kidney problems can cause high blood pressure. Another ultrasound may be done to get a closer look at the bladder and kidneys. If the condition appears to be affecting both kidneys, doctors usually will order blood tests to check kidney function.
Recommended Reading: Urinary Incontinence And Overactive Bladder
Causes Of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections
The most common recurrent urinary tract infection causes in women are
- The female urethra is shorter than a mans, which means that bacteria has a shorter distance it needs to travel in order to get to the bladder, multiply, and cause infection.
- The proximity of the female urethra and rectum can result in a bacteria exchange from the rectum to the urethra, particularly if the patient wipes back to front instead of front to back after defecating.
They can be prevented by:
- Staying hydrated aka drinking plenty of water, ideally a gallon per day, to flush out bacteria.
- Being cautious when using a diaphragm during sex. Diaphragms can push up against the urethra, which makes it harder to fully empty the bladder during urination. The urine that doesnt empty is more likely to grow bacteria.
- Avoiding spermicides, vaginal douches, and certain oral antibiotics. They can change the bacterial makeup of the vagina, which increases the risk of developing a chronic UTI.
Why Are Women More Commonly Affected By Utis
Women are more commonly affected by UTIs because of:
- The female anatomy
- The female urethra is short which allows easier entry of skin and surface bacteria into the bladder.
- The female urethra is close to the vagina and back passage that normally contain bacteria and makes it easier for bacteria to enter the urinary system.
Recommended Reading: Can Prostate Cancer Spread To The Bladder
Living With Urinary Tract Infections
If you have 3 or more urinary tract infections each year, your doctor may want you to begin a preventive antibiotic program. A small dose of an antibiotic taken every day helps to reduce the number of infections. If sexual intercourse seems to cause infections for you, your doctor many suggest taking the antibiotic after intercourse.
How Are Chronic Urinary Tract Infections Diagnosed
Prompt diagnosis is key to treating chronic urinary tract infections. Testing may be performed to help rule out other conditions. Diagnostic testing may include:
- Urinalysis. To look for the presence of bacteria and red or white blood cells
- Urine culture. To determine which bacteria are present and possibly test different antibiotics
- Imaging. To view the health of the urinary tract , including CT scan, ultrasound, and x-ray: a special dye is used in some cases to aid in imaging
- Cystoscopy. Use of a scope to view inside the bladder and urethra and check for abnormalities
Read Also: Stage 3 Bladder Cancer Life Expectancy