What Causes Overactive Bladder
An overactive bladder can be caused by several things, or even a combination of causes. Some possible causes can include:
- Weak pelvic muscles: Pregnancy and childbirth can cause your pelvic muscles to stretch and weaken. This can cause the bladder to sag out of its normal position. All of these factors can cause leakage.
- Nerve damage: Sometimes signals are sent to the brain and bladder to empty at the wrong time. Trauma and diseases can cause this to happen. These can include:
- Pelvic or back surgery.
- Stroke.
Often, there may be no specific explanation for why this is occurring.
Section : Research Needs And Future Directions
Figure 4: OAB Patient Groups
Epidemiology. Studies assessing how OAB develops and its natural history and progression are required. The timing and circumstances around which OAB develops and associated risk factors are not yet well-understood. While not specifically targeting epidemiology of OAB, there are large community-based studies that assess prevalence of lower urinary tract symptoms and urinary incontinence.280, 281 By longitudinally studying these community cohorts, these investigators have developed a new hypothesis that lower urinary tract symptoms are likely related to other systemic diseases/conditions.282, 283 Continuation of these types of studies could lead to potential preventive interventions for OAB symptoms and/or utilization of treatments that target the associated systemic conditions rather than the bladder. Epidemiologic studies provide a better cross sectional estimation of the overall population impact of OAB-type symptoms.284
Clinical studies should use validated standardized measures to report subjective outcomes. Objective outcomes should include frequency, nocturia, urgency, incontinence episode frequency and reporting of the variance for each of these measures. Furthermore, the Guideline Panel’s meta-analytic efforts were hampered by lack of consistent reporting of variance information for baseline and post-treatment measurements.
Uti And Other Symptoms
Urinary incontinence is a common sign of a UTI. Other symptoms typically occur along with the frequent urge to urinate. Someone with a UTI may also experience a burning sensation during urination or notice blood in their urine. Urine may also have a strong odor or a dark color.
Men with UTIs may experience rectal pain, while women with UTIs may have back or pelvic pain.
If you have any of these symptoms, you should be evaluated by a doctor. If youre diagnosed with a UTI, your doctor will prescribe a course of antibiotics.
Recommended Reading: Best Homeopathic Medicine For Overactive Bladder
Oab: What To Drink And When
First, make water your preferred beverage. Added ingredients in sodas and energy drinks, and caffeine in coffee, may aggravate an overactive bladder.
Staying hydrated is important to overall health. But for people with OAB, choosing how much and when to drink is essential. The old saying about drinking eight 8-ounce glasses of water a day? A healthy adult may not need that much. The American Urogynecologic Society suggests drinking water when you’re thirsty.
Here are six tips for managing your fluid intake:
- Spread out fluid intake throughout the day, sipping water between meals.
- Unless exercising, don’t carry a large water bottle with you.
- Fill your cup or glass half-way or use a smaller cup.
- Sip, don’t gulp.
- If you’re drinking enough water, your urine should be light yellow or almost colorless.
- Remember that you also get fluids in other foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and soups.
See your doctor if you have pain or burning with urination, or if your urine is cloudy, dark, or smells strong.
Oab: Drinks That May Increase The Urge To Go
One of the biggest OAB culprits iscaffeine, which can make you urinate more. Studies show that reducing caffeine intake to below 100 milligrams per day — the amount in one cup of drip coffee — may help reduce urge incontinence symptoms.
Cut down or cut out these problem beverages:
- Caffeinated drinks such as coffee, colas, energy drinks, and teas
- Acidic fruit juices, especially orange, grapefruit, and tomato
- Carbonated beverages, sodas, or seltzers
- Drinks with artificial sweeteners, such as aspartame and saccharin, which may irritate the bladder
If you can’t imagine starting your day without a morning cup of coffee, try to lower the amount of caffeine you take in. Make a cup that’s half decaf and half regular. You may want to wean yourself gradually to avoid caffeine withdrawal headaches.
For fruit juice, try switching to something with less acid, such as apple or pear juice, and dilute it with water.
You May Like: Why Does My Bladder Feel Full After I Pee
What Are The Specific Symptoms Of Overactive Bladder
Overactive bladder represents a collection of symptoms that can include:
- Urinary urgency: This is a failure to be able to postpone the need to urinate. When you feel you need to urinate, you have a limited amount of time to get to a bathroom.
- Frequency of urination: People who experience this symptom need to urinate very often. Typically its an increase in the number of times you urinate compared to what you previously experienced.
- Urge incontinence: In this case, there can be a leakage of urine when you get the urge to urinate.
- Nocturia: This symptom is characterized by the need to get up and urinate at least two times each night.
Medications For Overactive Bladder
Medications that relax the bladder can be effective for alleviating symptoms of overactive bladder and reducing episodes of urge incontinence. These drugs include tolterodine , oxybutynin , an oxybutynin skin patch , trospium , solifenacin , darifenacin and now mirabegron . These medications are usually used in combination with other treatments.
Recommended Reading: Botox For Bladder Control Reviews
Treatment For Different Types Of Urinary Incontinence
Lifestyle changes and treatments can help with symptoms. Your doctor can help you come up with a plan thatâs right for you.
For stress incontinence, treatments include:
Pads and Vaginal Inserts.
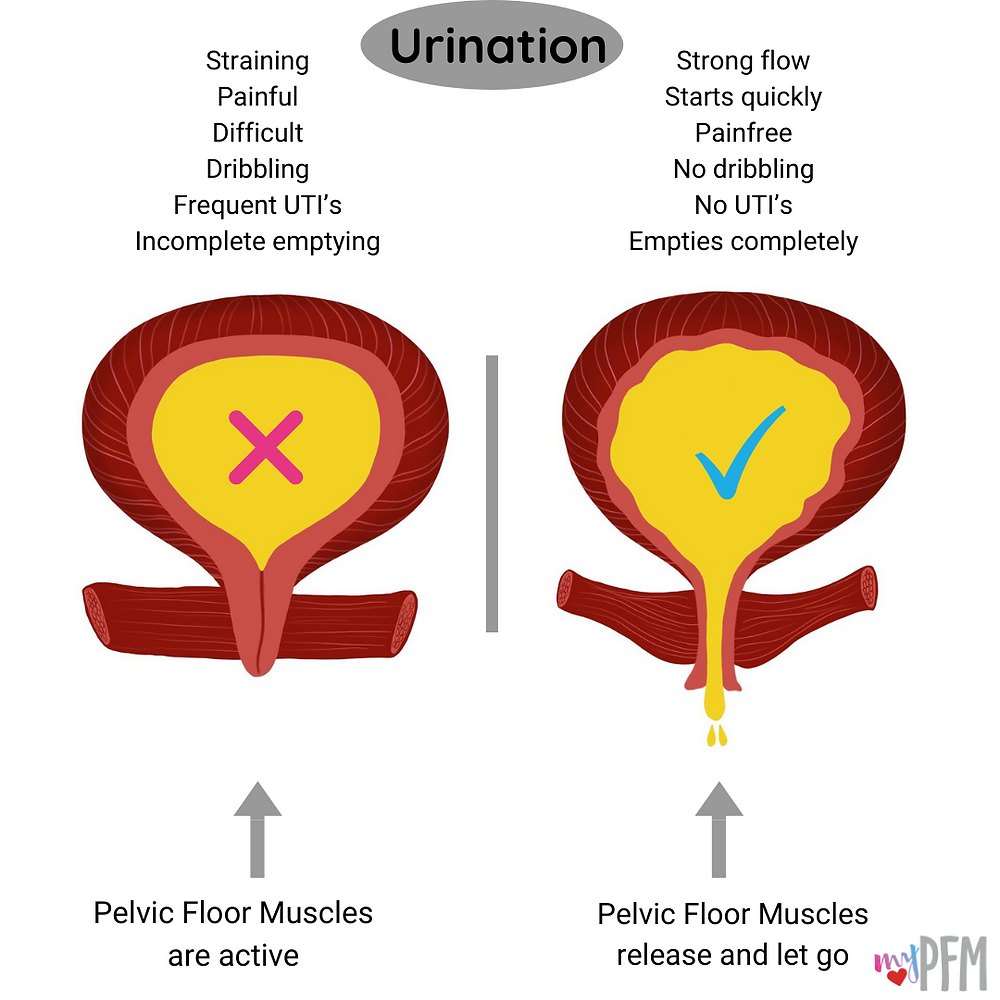
Pelvic floor exercises. If you’ve had a baby, chances are you’ve been told to do Kegel exercises. These help to strengthen the pelvic floor after childbirth. They also help prevent stress incontinence. Best of all, you can do Kegels anytime, anywhere.
Here’s how:
Note: You can learn how to do Kegels by stopping your urine, but donât do this routinely. Stopping the flow of urine can lead to an infection.
Biofeedback. A probe is inserted to monitor when your bladder muscles squeeze. When youâre able to recognize it as it’s happening, you can start to gain control of it. It’s often used in combination with Kegel exercises.
Pessary. For women, doctors may prescribe a device called a pessary that is inserted into the vagina. It repositions the urethra to help reduce leakage.
Injections and surgery. Shots to bulk up your urethral area may help. In more extreme cases, you may need surgery. One procedure pulls the urethra back up to a more normal position, relieving the pressure and leakage. Another surgery involves securing the urethra with a “sling,” a piece of material that holds up the urethra to prevent leakage.
Pads.
Getting Help For Overactive Bladder
The first step in treatment is to ask for help. It may feel funny talking to your doctor about something as private as urinary issues, but rest assured that your doctor is a professional and is here to help. Be prepared before your appointment by keeping a bladder diary for a few days. This will help your doctor see the extent of your problem, and may help him or her to see any triggers that may be causing your urinary urgency issues.
Be prepared to have a thorough discussion with your doctor about your overactive bladder symptoms, as well as any other symptoms you may be experiencing. You should also let you doctor know if you suffer from any other conditions, such as diabetes, and provide a list of medications youre currently taking, which may be contributing to your symptoms.
Making a list of questions beforehand is also a great idea to ensure that you dont forget anything during your appointment. You may want to ask your doctor about different treatment options that he thinks may be a good fit for you, or about any options youve read about that youre interested in trying. Make sure you find out about the potential side effects for any treatment your doctor proposes, as well as what you can expect in terms of a success rate.
Don’t Miss: Can You Have Intercourse While Having A Bladder Infection
What To Know About Incontinence And Overactive Bladder
-
How many suffer? According to the American Urological Association, about 33 million Americans have overactive bladder , with 40 percent of women and 30 percent of men dealing with OAB symptoms. That number may be even higher, because many people are too embarrassed to seek treatment.
-
Types of incontinence: Incontinence, or leaking urine when you feel the urge to urinate, is a type of overactive bladder. Stress urinary incontinence means you leak urine when you laugh or sneeze, or do physical activity like running. Some people may have both OAB and SUI.
-
How OAB affects you: OAB and incontinence can affect every area of your life, including sleep, social activities, work, relationships and your ability to exercise. We offer many treatments, both surgical and nonsurgical, that can make a big difference.
How Can Nerve Stimulation Help Overactive Bladder
There are several treatments that involve stimulating your nerves to help improve overactive bladder. Your nerves help communicate the message that your bladder needs to be emptied to your brain. By treating the nerves, your healthcare provider can improve your bladder control. Nerve stimulation is a reversible treatment that is considered when conservative treatments have not worked or have not been tolerated. Conservative treatments include behavioral therapies and medications.
There are several types of nerve stimulation treatments. These can include:
Don’t Miss: Why Does My Bladder Feel Full
Should I Drink Less Water Or Other Fluids If I Have Urinary Incontinence
No. Many people with urinary incontinence think they need to drink less to reduce how much urine leaks out. But you need fluids, especially water, for good health.
Women need 91 ounces of fluids a day from food and drinks.11 Getting enough fluids helps keep your kidneys and bladder healthy, prevents urinary tract infections, and prevents constipation, which may make urinary incontinence worse.
After age 60, people are less likely to get enough water, putting them at risk for dehydration and conditions that make urinary incontinence worse.12
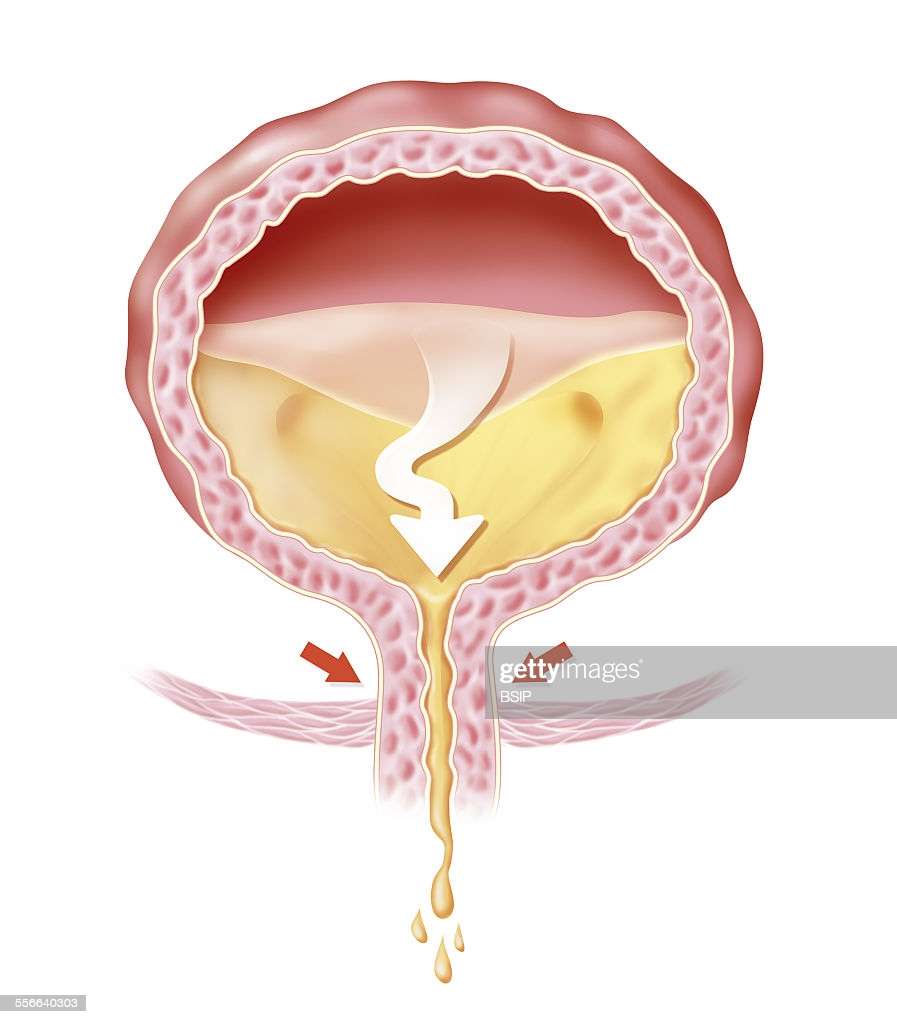
Medical And Surgical Treatments For Urge Incontinence
If behavioral modifications such as timed voiding and bladder training do not improve the symptoms of urge incontinence, your doctor may decide to try various medical or surgical treatments. These methods have the same goal — relief of the symptoms and inconvenience of urge incontinence.
Medical treatments for urge incontinence include:
- Medications: There are several medications that are used to treat urge incontinence. They include:
Trospium
Oxytrol for women is the only drug available over the counter.
Your health care provider may also recommend other medications that may help control bladder spasms. They include hyoscyamine or dicyclomine .
If behavioral treatments and medications do not help, other options for treatment include:
The drug Botox injected into the bladder muscle causes the bladder to relax, increasing its storage capacity and reducing episodes of leakage. It can be used in adults that do not respond to or cannot use other medications that treat overactive bladder.
Another drug treatment that may be helpful for some women is hormone therapy, which uses estrogen alone or in combination with progesterone. However, evidence of benefit for urge incontinence has been mixed. In addition, because of the possible risks of hormone therapy — including a potential increased risk of blood clots and breast cancer — you should discuss this therapy with your doctor.
- Electrical stimulation:
- Surgery
Surgical procedures for urge incontinence include:
Show Sources
You May Like: Cysts On Bladder And Kidneys
Causes Of Overactive Bladder
The causes of an overactive bladder begin with a lack of coordination in the urinary system. When your kidneys filter out minerals and nutrients from your blood, they produce waste in the form of urine. The urine then travels to your bladder, where it is stored until your brain sends the appropriate signals for your detrusor muscle to contract and your urinary sphincter to relax. This is how our bodies know when to urinate!
Overactive bladder occurs when the signaling process from the brain to the bladder gets mixed up. The signals tend to be urgent and intense, even when your bladder is not completely full. For instance, most people can hold up to 2 cups of urine in their bladder before they have to urinate. For people with overactive bladder, you may get an urge to urinate with the same intensity as if your bladder was full, but it may only be half or less than halfway full.
How Is Overactive Bladder Diagnosed
In most cases OAB can be diagnosed by history and physical exam and a urine analysis to rule out infection or blood in the urine. An abnormal urine analysis may prompt treatment or further testing . Sometime you doctor will check to see if your bladder is emptying well. This can be done with a small ultrasound or with a catheter). Many times, treatment can be recommended based on the information obtained from these simple things.
In some cases, a bladder diary may be recommended to help understand the severity of the condition. A bladder diary is a record kept by the patient that includes fluid intake, number or urinations, and the amount of urine with each urination.
In more complex cases further testing may be done to get a better understanding of the function and anatomy of the lower urinary tract. These tests may include:
Don’t Miss: What Should I Do If I Have A Bladder Infection
Overactive Bladder Vs Urinary Incontinence
Overactive Bladder
- Condition in which the bladder can no longer hold urine normally.
- Often feel a sudden urge to urinate or experience an accident.
- Defining symptom is urgency, or the inability to postpone urination.
- OAB is typically a chronic problem
- Often requires strengthening of pelvic floor muscles to get rid of symptoms like urinary incontinence.
- Symptoms including urinary incontinence are ongoing.
- Bladder muscle problems at the root of it.
- Can result from regularly consuming alcohol and caffeine in large quantities.
- Serious health conditions can lead to OAB including a stroke, diabetes, kidney disease, multiple sclerosis , or Parkinsons disease.
Urinary Incontinence
- Is when you lose control of your bladder.
- Isnt a condition its a symptom.
- Is a symptom of OAB.
- Can be caused by a loss or weakening of control over the urinary sphincter.
- Can be a sign of something simple like a singular occasion of too much fluid consumption, a temporary problem.
- Is a common symptom of a UTI along with a burning sensation during urination and/or blood in the urine.
Other Treatments To Try
In rare cases when all OAB treatment fails and overactive bladder is severe, doctors may recommend one of several types of surgery.
A procedure called bladder augmentation uses part of the bowel to increase bladder capacity. Or, urinary diversion, an alternate route for bladder drainage for severe, complicated OAB patients.
Sacral nerve stimulation. Another procedure implants a small device, similar to a pacemaker, under the skin. The device is connected to a wire, which sends small electrical pulses to nerves around the pelvic floor that control the bladder and muscles surrounding it. This helps build bladder control. Itâs often called a bladder pacemaker. The main limitation with this treatment is that it keeps you from having a spinal MRI.
Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation. The doctor places a needle on nerves near your ankle that affect bladder control. Youâll have one session a week for 12 weeks and then maintenance treatments as needed. This procedure is done in the office.
An overactive bladder doesnât have to get in the way of your daily life. With a little time, patience, and the right treatment, you can regain control — and peace of mind. Whatever treatment for overactive bladder you and your doctor decide upon, it’s important that you stick with it. If you do, chances are your condition will improve in time.
Show Sources
Read Also: How To Help A Weak Bladder Naturally
Depression Anxiety Attention Deficit Disorder And Oab
It is probably too simplistic to view OAB with urge UI as just a myogenic or afferent disorder. Certain individuals seem predisposed to OAB. Circumstantial evidence suggests individuals with depression, anxiety, and attention deficit disorder may experience symptoms of OAB more often than the general population. Wolfe and colleagues suggested that depression, anxiety, feeding disturbances, pain, irritable bowel syndrome, fibromyalgia, and changes in voiding are associated with disturbances in brain circuits using specific neurotransmitters, in particular serotonin . Fibromyalgia and irritable bowel syndrome are conditions seen more often in patients with IC than the general population, and these conditions are associated with OAB and possibly with depression, which provides a potential link with 5-HT metabolism. Perhaps the strongest evidence for diminished 5-HT function in depressed patients is the remarkable efficacy of selective serotonin uptake inhibitors in this group of patients. In addition, neuropharmacologic evidence indicates that some forms of depression are associated with abnormalities in the promoter for the serotonin transporter gene.,