A New Toilet Or An Alternative
If you have real difficulties getting to the toilet, it may be possible to get a grant to build a new one, perhaps downstairs. An occupational therapist can advise you on this.
Not all homes are suitable for building new toilets, so a commode might be needed. A commode is a moveable toilet that doesnt use running water. It looks like a chair, with a container underneath that can be removed and cleaned after someone has used it. They can be very discreet.
Management Of Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction
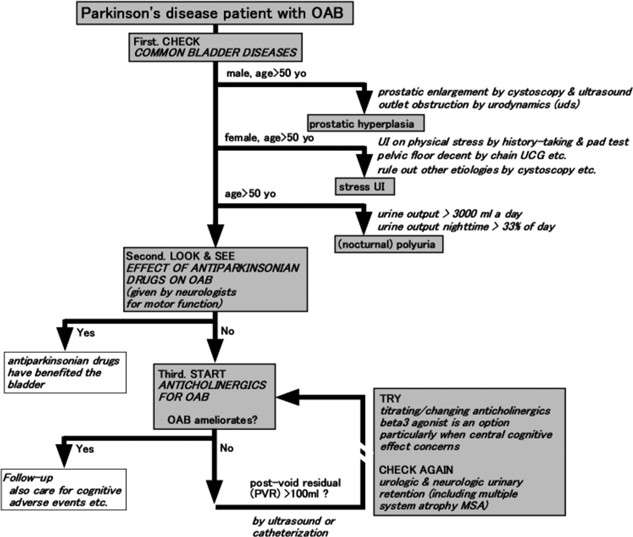
Despite the high prevalence of LUT symptoms and impact on quality of life, treatment options are currently limited and are often poorly tolerated or ineffective in PD. Most treatment options are derived from guidance around general management of LUT symptoms in neurological patients. Comprehensive history taking is a sound starting point, as this provides insight into whether patients have storage dysfunction or voiding dysfunction, or both. Patients often have other medical comorbidities and the medications prescribed for these may contribute to LUTS, for example, diuretics used for managing hypertension increase urinary urgency and frequency. A review of concomitant medications provides an opportunity to review a patients anticholinergic burden, and adding an antimuscarinic medication may increase the risk for falls, cognitive impairment and all-cause mortality . Physical examination involves examining the abdomen, flank and pelvic and genital organs, and when appropriate, evaluating urogenital sensations, sacral cord-mediated reflexes and anal sphincter tone and contractions. Digital rectal examination in a male patient allows evaluation of the size and consistency of the prostate gland.
Botulinum A Toxin As Second Line Treatment For Refractory Detrusor Over Activity And Over Active Bladder Symptoms
To date when urinary incontinence persists and patients become severely disabled a long-term indwelling catheter remains the only option for avoiding urinary incontinence. Botulinum A toxin has been successfully introduced for the treatment of intractable detrusor overactivity and it is now widely used for a number of neurological conditions characterized by muscle hyperactivity . Intravesical injections of BoNT/A provide satisfactory long-term results, and are now considered as second line-therapy in neurogenic patients who do not respond to standard anticholinergics.The use of botulinum neurotoxins in the lower urinary tract was pioneered as early as 20 yr ago with injections into the urethral sphincter reducing bladder-voiding pressures, urethral pressures, and post void residual urine.
BoNT/A consists of a light chain attached to a heavy chain via a disulfide bond with an associated zinc atom. It is synthesised as a single-chain polypeptide with a molecular weight of 150 kDa, which is then cleft into its active dichain polypeptide form. The heavy chain allows for binding to the neuron and internalisation of the toxin, whereas the light chain actively cleaves SNAP25 on the protein complex that is responsible for docking and releasing vesicles containing neurotransmitters .
Recommended Reading: Does Bactrim Treat Bladder Infection
What Examinations May I Need To Have
Your GP or specialist will probably ask a series of questions to find out what the problem is. These may include:
- When did the trouble start?
- How often does it happen?
- Can you feel when your bladder or bowel is full?
- Are you having difficulty emptying your bladder or bowel?
- How often are you using the toilet?
Parkinson’s symptoms, such as slowness of movement and rigid muscles, affect the muscles in the bowel wall. This can make it harder to push stools out of the body. You may be asked to keep a chart for several days of how often you use the toilet and how much you drink.
You may also be asked for a urine sample to test for infection and they will normally carry out a physical examination.
Bladder or bowel problems can be complex in Parkinson’s, so sometimes specialist tests or X-rays may be needed. All of these can usually be done in an outpatient department or clinic.
Evaluating And Treating Urinary Issues In Parkinson’s Disease Multiple System Atrophy And The Other Atypical Parkinsonism Disorders
In this hour-long webinar, neuro-urologist Ekene Enemchukwu, MD focuses on urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, urinary retention, and other urinary issues in PD, MSA, and the atypical parkinsonism disorders. Following the presentation, moderator Candy Welch, Brain Support Networks MSA caregiver support group leader, asks Dr. Enemchukwu many questions submitted by webinar participants.
Read Also: What Can Help Overactive Bladder
Increased Risk Of Overactive Bladder In Patients With Idiopathic Parkinsons Disease: Insight From A Nationwide Population
-
Roles Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing original draft
Affiliation Department of Neurology, China Medical University Hospital, China Medical University School of Medicine, Taichung, Taiwan
-
Affiliation Department of Neurology, China Medical University Hospital, China Medical University School of Medicine, Taichung, Taiwan
- Cheng-Li Lin,
Roles Data curation, Formal analysis, Project administration
Affiliations College of Medicine, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan, Management Office for Health Data, China Medical University Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan
-
* E-mail:
Affiliations National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Health Research Institutes, Miaoli, Taiwan, Institute of Occupational Medicine and Industrial Hygiene, College of Public Health, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan, Ph.D. Program in Environmental and Occupational Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
Management Of Urinary Symptoms In Parkinsons Disease
Questionnaires including bother scores identify LUTS in PD with higher specificity than questionnaires without bother scores . When addressing bladder problems in patients with Parkinsonism in daily clinical work, systematic interview is needed. Addressing nocturia, urgency, frequency feeling of incomplete emptying and incontinence often provides the needed information for initiating treatment. It is important to address how these symptoms affect the daily life of the patients, as symptoms of overactive bladder may be particularly unpleasant in a patient with an akinetic rigid syndrome with postural instability.
Also Check: Antibiotic For Bladder Infection In Elderly
Management Of Sexual Dysfunction
Management of sexual dysfunction in patients with PD includes both behavioural and pharmacological options depending on the nature of the sexual dysfunction. Behavioural therapy may be used to treat SD, if considered as a learned maladaptive behaviour and may involve the use of psychodynamic psychotherapy and cognitive behavioural therapy . Pharmacological treatment of SD, on the other hand, requires either the reduction or elimination of drugs interfering with the sexual function or the introduction of drugs that improves sexual function . Ultimately, treatment options for SD may require multidisciplinary input from neurologists and psychologists for optimum results . Although phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors are standard treatment option for erectile dysfunction , intracavernosal alprostadil 1.2510 g injections can be used.
The management of hypersexuality as part of an impulse control disorder includes reduction/stopping of dopamine receptor agonist and practical therapeutic strategies including psychological therapies but not limited to counselling, psychotherapy, sex, couple and behavioural therapies . Hormonal treatment specifically testosterone has been tried in PD .
Papers Of Particular Interest Published Recently Have Been Highlighted As: Of Importance Of Major Importance
Don’t Miss: Can A Bladder Sling Be Removed
Sexual Dysfunction In Parkinsons Disease
People with PD may experience sexual dysfunction, including loss of desire, inability to orgasm, erectile dysfunction in men, decreased lubrication in women, or pain with intercourse in women. Some studies have found that sexual dysfunction may occur in 60-80% of men and women with PD. Older patients with PD have more sexual dysfunction than younger patients, although sexual dysfunction is also greater in older adults who do not have PD. In addition to age, conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and depression can factor into sexual dysfunction.3,4
There are several factors that can lead to sexual dysfunction in people with PD. In addition to the motor symptoms of PD, which may create practical barriers to engaging in sexual activity, non-motor symptoms like depression, anxiety, or sleep disturbances can also impact a persons sex drive. Many people with PD express dissatisfaction with their sexual life.3,5
Some people with PD who are treated with dopamine agonists develop impulse control disorders, like hypersexuality. Hypersexuality can lead to unusual or increased sexual behavior, which may have devastating effects on relationships. Changing medications or reducing the dose of medication can help, and people who experience any side effects such as impulse control disorders should bring it to the attention of their doctor.3
Prevalence Of Urinary Symptoms
Earlier studies suggested that the prevalence of urinary symptoms in patients with PDranges from 38% to 71% however in anumber of these studies the clinical distinction between PD and other parkinsonisms, including multiple-system atrophy was not addressed. Furthermore, some studies were based on patients presenting to urology clinics with urinary symptoms. . More recent studies in PD using validated questionnaires showed that the prevalence of urinary symptoms varied between27% to 39% and using a non validated questionnaire was greater than 40% . Additionally Araki and Kuno founda correlation between urinary disturbances and neurological disability andbetween severity of urinary disturbances and stages of the disease , suggesting a relationship between dopaminergic degeneration and voiding dysfunction .
Recommended Reading: Average Age Of Bladder Cancer
Increasing Your Fibre Intake
Eating the right amount of fibre and drinking enough fluids can help if you have constipation.
To get more fibre in your diet:
- choose a breakfast cereal containing wheat, wheat bran or oats, such as Weetabix, porridge or bran flakes.
- eat more vegetables, especially peas, beans and lentils.
- eat more fruit fresh, stewed, tinned or dried. High fibre fruits include prunes or oranges.
- drink plenty of fluids throughout the day to avoid dehydration. Lots of fluids are suitable, including water, fruit juice,
- milk, tea and squashes. Cut out caffeine to avoid overstimulation of your bladder.
If you find it difficult chewing high-fibre food, you can get some types which dissolve in water. You can also get drinks which are high in fibre.
Try to increase how much fibre you get gradually to avoid bloating or flatulence .
A dietitian can give you further advice. Ask your GP, specialist or Parkinsons nurse for a referral.
Helping Someone With Pd

While not everyone with PD will have related bladder issues, recent studies show that up to 40% of people will. Only about 15% of individuals will have severe Parkinson’s-related incontinence. Whether or not someone is dealing with severe incontinence, many steps can be taken to improve the quality of life for those with bladder issues.
Learning more about urinary incontinence and PD is the first step to helping someone struggling with both. With research, you can learn the current treatments for frequent urination and suggestions to improve incontinence and heighten the quality of life. Understanding the problem can help everyone, including you, so simply being an advocate is a great place to start.
You May Like: Where Is My Bladder Located Female
Urinary Dysfunction And Parkinsons
This one-page fact sheet explains that urinary dysfunction is one of several non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease that are the result of Parkinsons impairing proper function of the autonomic nervous system, especially in later stages of the disease process. Several types of urinary dysfunction and treatment options are outlined.
How Is Neurogenic Bladder Diagnosed
A doctor will do an exam and may order several tests of the nervous system and the bladder to diagnose neurogenic bladder: These include:
- Urodynamic studies: These bladder function tests measure how much urine the bladder can hold, the pressure within the bladder, how well urine flows, and how well the bladder empties when it is full. Special sensors may be placed on the skin near the urethra or rectum to see if the muscles and nerves in those parts of the body are working properly.
- Cystoscopy: The doctor may perform this procedure to examine the inside of the bladder and urethra with the use of a small telescope .
- X-rays
Don’t Miss: What Antibiotic Do You Take For A Bladder Infection
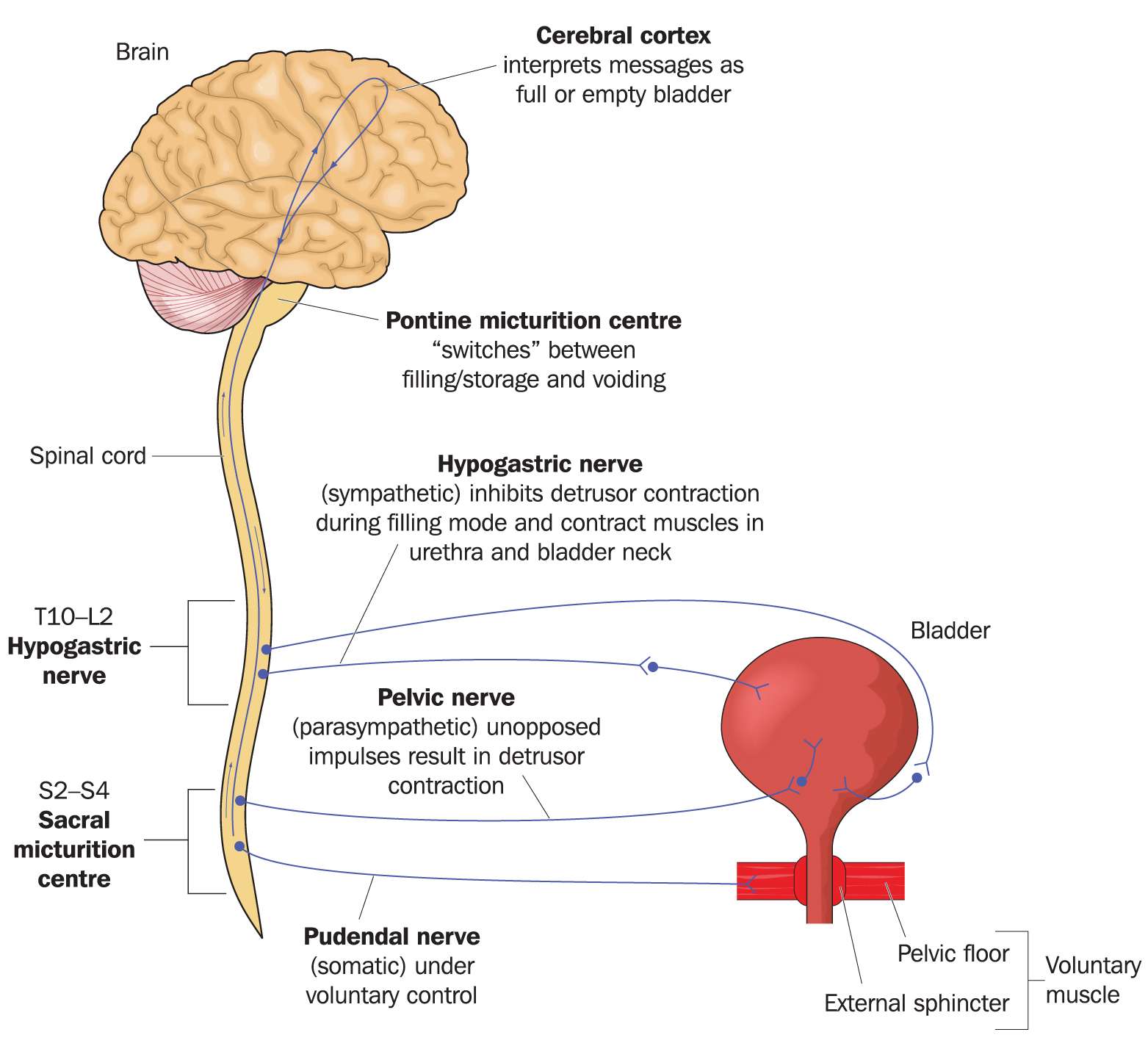
The Role Of Central Nervous System In The Control Of The Micturition Reflex
The normal micturition reflex in the adult is mediated by a spino-bulbo-spinal pathway, which passes through relay centers in the brain.Micturition occurs in response to afferent signals from the lower urinary tract, and the distension of the bladder wall is considered the primary stimulus .
During bladder filling, once threshold tension is achieved, afferent impulses, conveyed mainly by the pelvic nerve, reach the CNS. Afferent neurons send information to the periaqueductal gray, and relay with the pontine tegmentum, where two different regions involved in micturition control have been described acting independently . One is a dorsomedially located M-region, corresponding to Barringtons nucleus or the pontine micturition center . A more laterally located L-region may serve as a pontine urine storage center, and likely suppress bladder contraction by regulating the activity of the striated musculature of the bladder outlet during urine storage.Centers rostral to the pons control the beginning of micturition. The forebrain, therefore, even though not essential for the basic micturition reflex plays a role in determiningwhen and where micturition should take place . Recent positron emission tomography studies gave further information on the brain structures involved in urine storage and voiding .
Compliance With Ethical Standards
Amit Batla and Natalie Tayim each declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Mahreen Pakzad has been a speaker for Astellas.
Jalesh N. Panicker has received royalties from Cambridge University Press, has been involved in trials supported by FirstKind Ltd, Allergan and Ipsen and has received speaker honoraria from Wellspect, Astellas and Allergan.
You May Like: Used Marine Fuel Bladder For Sale
Relationship Between Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction And Clinical Features In Chinese Parkinsons Disease Patients
Juan Feng
1Department of Neurology, Shengjing Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, No. 36 Sanhao Street, Shen Yang 110004, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
Parkinsons disease is the second most prevalent neurodegenerative disease and is caused by a loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. PD is characterized by the manifestation of motor symptoms such as bradykinesia, static tremor, and rigidity. In addition to motor symptoms, nonmotor symptoms such as hyposmia, sleep disorders, neuropsychiatric symptoms, and autonomic dysfunction become increasingly recognizable over time. These nonmotor symptoms accelerate disease progression and severely affect the patients quality of life. Lower urinary tract dysfunction is a common nonmotor symptom of PD and was recently reported to occur in 27%63.9% of PD patients during any stage of their disease . LUT dysfunction primarily presents with storage and voiding symptoms. A storage symptom can manifest as nighttime frequency, daytime frequency, urgency, or urge incontinence, while a voiding symptom can manifest as dysuria or a prolonged time of micturition. LUT dysfunction in PD patients manifests primarily with symptoms of storage difficulty, suggesting an overactive bladder .
2. Subjects and Methods
2.1. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Basic Information for the Recruited PD Patients
3.2. Comparison of Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of the PD-OAB and PD-NOAB Groups
| Factor |
4. Discussion
Bladder Problems Are A Common Non
When we asked people affected by Parkinsons what their research priorities were for improving everyday life, reducing urinary problems emerged in the top ten.
Bladder problems can have a significant impact on peoples quality of life.
Lets hear Pauls story
I was diagnosed with Parkinsons about two years ago, but I can now look back and see that Ive had symptoms for five years or so, and this includes problems with the waterworks. My problem is not an inability to go, but if I need to go, I need to go now.
It really affects me, my first thought when planning a trip is when am I going to be able to go to the toilet. My life is controlled by where my nearest toilet is. Its a very embarrassing situation to be in. My doctor has given me pills for an overactive bladder, which help a bit. But they dont make the problem go away. Although my other Parkinsons symptoms can be frustrating at times, if I could control my bladder problems it would be life changing for me.
It has taken me some time to accept that my condition is a disability and as such I can access disabled facilities. The Radar Key Scheme allows me to access over 10,000 disabled facilities across the UK and you dont need to have a blue badge to use one. The scheme has given me much more confidence. If like me you are struggling with bladder incontinence then you should consider getting yourself a Radar Key, it can be a lifesaver!
Paul, Patient and Public Involvement Volunteer
Ongoing research
Also Check: Vitamin D And Bladder Problems
Bowel Incontinence: Another Embarrassing Casualty Of Pd
Fecal Incontinence is where you lose control of your bowels. This blog post explains the primary cause of this in Parkinsons disease. Problems reaching the toilet in time because of mobility, abdominal bloating or cramping compound the problem. Dr. De León has included a check list of things to help minimize occurrences and embarrassment, even to the point of surgery, if necessary.
Changes In The Way You Think
Some people with Parkinsonâs have cognitive changes. That means you may have a harder time focusing, finishing tasks, forming thoughts, thinking of words, and remembering things. When these changes affect your day-to-day life, it becomes dementia.
How can I manage them?
- Exercise regularly, eat a healthy diet, and get enough sleep.
- Clear your home of clutter. Reducing things in the world around you may help with confusion.
- Create a regular routine. You may feel more comfortable with a structured day.
What are the treatments? These changes may be a medication side effect talk to your doctor.
You may need to see an occupational therapist, who can teach you ways to make daily life easier. A speech therapist can help with language issues. There are also some Alzheimerâs drugs that treat these cognitive symptoms.
Read Also: Can A Ct Urogram Detect Bladder Cancer
Parkinson’s Disease And The Bladder
In this 30-minute video lecture Dr. Donna Deng explains the cause of bladder dysfunction and quality of life consequences. Treatment options include behavioral modification, pharmacologic, nerve stimulation , Implantable Impulse Generator, and Botox injections. Last line of treatment for older men with Parkinsons should be prostate surgical procedures.