What To Expect After Botox Injection In Bladder
If youve ever gone for a jog and felt a trickle down below, or coughed and caught yourself leaking urine, you arent alone. The involuntary loss of urine is called urinary incontinence and more than 25 million Americans experience it Read More
If youve ever gone for a jog and felt a trickle down below, or coughed and caught yourself leaking urine, you arent alone. The involuntary loss of urine is called urinary incontinence and more than 25 million Americans experience it every day. Urinary incontinence can be caused by several factors from a urinary tract infection to overactive bladder to pregnancy and childbirth. The good news is urinary incontinence is a treatable medical condition, with one of the most effective treatments being Botox.
When most people think of Botox, they usually think of injections to the face to minimize wrinkles. However, Botox bladder injections are a routine treatment for urinary incontinence.
Here is a guide to what you should know about Botox injections in the bladder.
Should You Use Botox Or Oxytrol Patch Otc For Bladder Problems We Say Maybe Not
If you suffer from overactive bladder you now have two new options: Botox injections , and an over-the-counter version of the Oxytrol patch, which used to require a prescription. The Food and Drug Administration approved both recently. But our medical advisors recommend caution before trying either medication.
“The decision to move Oxytrol patch from prescription to OTC status may have been premature,” says Marvin M. Lipman, M.D., Consumer Reports’ Chief Medical Adviser. “The symptoms of overactive bladder, which include incontinence and a frequent need to urinate, overlap with those of bladder infections, other forms of incontinence, and even bladder cancer. Those conditions might go untreated if you mistakenly think your symptoms are due to overactive bladder. So see your physician, initially, for proper diagnosis.”
In addition, Oxytrol is only moderately effective for relieving overactive bladder symptoms–like all drugs in its class–and it can cause dry mouth and constipation. The patch form, which will be available OTC probably starting next fall, can cause skin reactions at the site of application in about a quarter of patients–in 11 percent of people the reactions are so severe, they stop using the patch.
If those drugs don’t work or you can’t take them, you could consider Botox. But make sure you understand the risks and benefits of the shots. For details, read our Botox precautions. And see our advice on off-label prescribing.
Risks & Potential Adverse Events Of Botox Therapy
Botox was placed as a Step 5 option for treatment because of the mixed results but also the risk of profound side effects. Some patients were unable to urinate voluntarily after the procedure and needed to self catheterize for several months before the effect wore off. Newer research studies determined that a lower dose of botox dramatically reduced this risk and was the motivation for its reclassification as a Step Four treatment option in 2014.
BOTOX, however, still carries risk and is not an appropriate treatment for those who are unable to self-catheterize. Other adverse events could include painful urination , straining and bladder retention. Botox has also been linked to far more serious side effects, including fatalities.
Patient Tip: If you are considering the use of Botox, please carefully review the AUA Treatment Guidelines first and make sure that you have tried EVERY therapy in Step One through Step Three first.
You May Like: What To Drink To Help Bladder Infection
Botox Eases Incontinence But Comes With Risks
You are free to share this article under the Attribution 4.0 International license.
When women suffer from bladder incontinence, the urge to urinate can come on suddenly and sometimes uncontrollably, leading to leaks.
Patients looking for relief can initially opt for first- and second-line therapies such as drinking fewer liquids or caffeinated beverages, pelvic floor muscle training, and medication.
If those treatments dont offer relief, more invasive options are available, including nerve stimulation called sacral neuromodulation , or a bladder injection of botulinum toxin, sold as Botox.
Researchers conducted a head-to-head comparison of the two and discovered that Botox provides more daily relief for womenbut also might be associated with more adverse events.
An injection of botulinum toxin in the bladder muscle works to address urgency urinary incontinence by relaxing the overactive bladder muscles that cause the condition. A sacral neuromodulation implant does the same thing by sending electrical pulses to nerves in the spine.
Demand for female urologists outpaces supply
Published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, the study involved 381 women from nine US medical centers who recorded at least six urgency incontinent episodes over three consecutive days and had not improved with other treatments.
Toxin in Botox can travel through nerves
Do You Need Anesthesia For Bladder Botox Injections

Botox bladder injections are performed as an outpatient procedure. You do not need general anesthesia for Botox injections in the bladder, but your doctor will administer a local anesthetic to temporarily numb your bladder so you will not feel the injections, similar to how a dentist numbs your mouth before filling a cavity. The local anesthetic generally wears off within one hour of completing the injections. Because Botox bladder injections do not require general anesthesia, you can drive yourself to and from your treatment.
Don’t Miss: Best Over The Counter Medication For Bladder Infection
Botox And The Bladder
In the bladder and/or pelvis, Botox has been studied with tight pelvic floor muscles , incontinence and IC/BPS. In the bladder, it is injected into the bladder wall in multiple sites during a hydrodistention procedure. Research studies have shown modest success. One study reported efficacy of 69% . Two studies reported high initial efficacy rates of 74% and 86% at three months. Another showed that frequency improved significantly at 3.5 months. Effectiveness diminished over time, however, and at one year symptoms were indistinguishable from baseline values. One study reported a low efficacy rate at 3 months with only 20% of patients exhibiting improvement.
Botulinum Toxin: Mechanism Of Action Types And Fda Status
Botulinum toxin is a neurotoxin produced by Clostridium botulinum, which inhibits calcium-mediated release of acetylcholine from presynaptic, cholinergic nerve terminals resulting in neuromuscular blockade , . This blockade leads to temporary loss or reduction in muscle contraction and muscle atrophy at affected sites , . Furthermore, BoTA exerts inhibitory effects on stimulatory neurotransmitters, neuropeptides, and their receptors, which affect sensory nerve fibers and improves the sensation of urgency .
Although 7 antigenic subtypes of botulinum toxin exist , only A and B are commercially available and approved by the FDA for therapeutic use -. Specifically, they can be injected into the detrusor muscle, external urethral sphincter, or both depending on the indication. Of the two, botulinum type A is most commonly used given its increased potency and longer duration of action , . Dykstra et al described the first use of BoTA for a urologic indication in 1988 in a small study of SCI patients with detrusor sphincter dyssynergia , which noted improvement in PVR and urethral pressure following external urethra sphincter injection of BoTA . Since this study, others have sought to describe the potential benefits of BoTA for other indications, including benign prostatic hyperplasia, nonneurogenic overactive bladder, chronic pelvic pain, and NDO , .
Read Also: How Many Radiation Treatments For Bladder Cancer
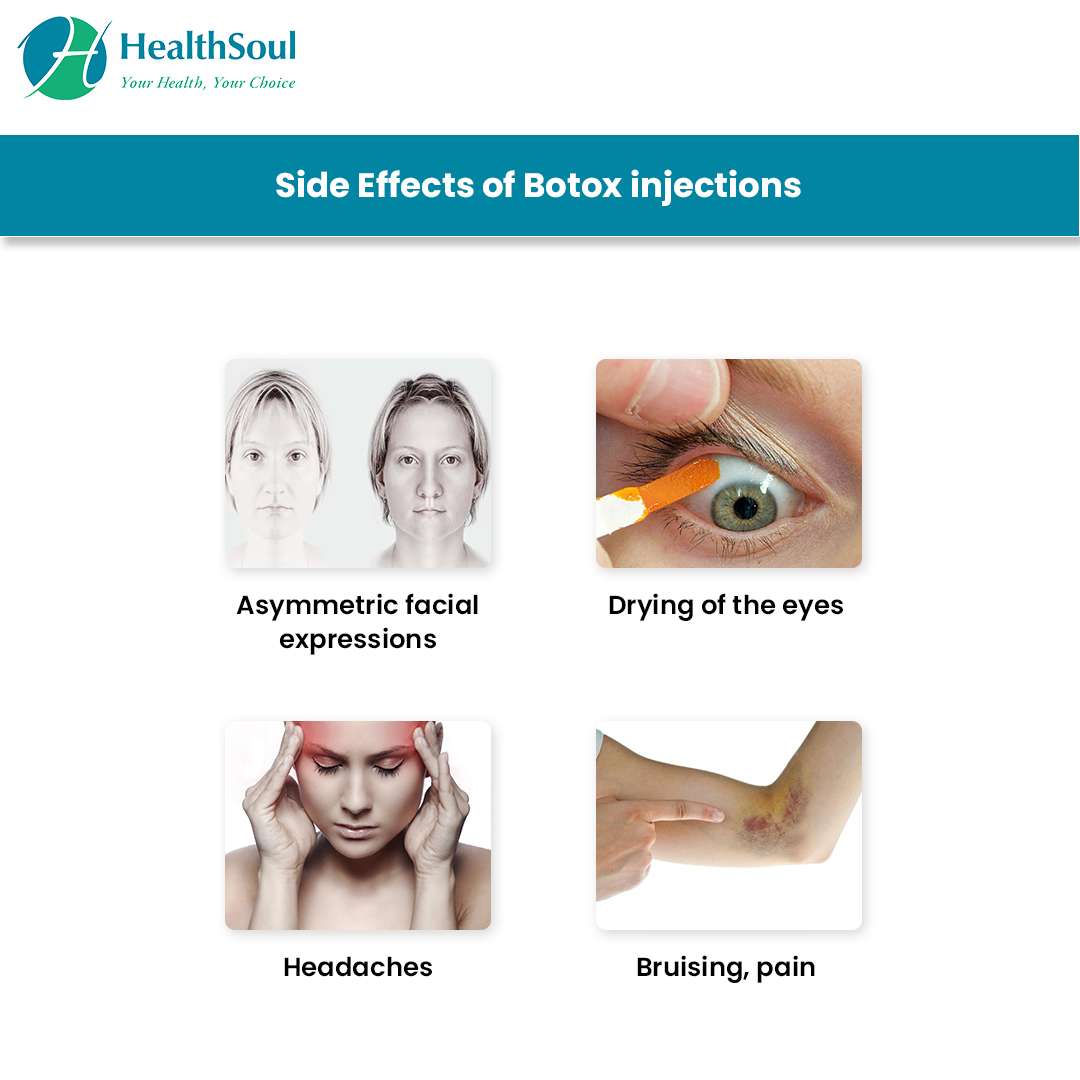
Bladder Botox: Side Effects
Some people experience mild pelvic or abdominal discomfort after receiving Botox in the bladder. This has been described as a sensation like period cramps. This discomfort typically doesnt last more than a couple days. Other potential side effects from Botox injections in the bladder include:
- Urinary tract infection
- Difficulty urinating
- Inability to empty your bladder
These side effects are not common and are temporary. If you are experiencing any issues with urination after Botox injections in the bladder you should contact your doctor.
Bladder Botox To Treat Incontinence
Health editor, BBC News online
Botox injections can now be offered as a treatment for urinary incontinence, says England’s NHS drugs watchdog.
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence says female patients should have free access to the drug, better known as an anti-wrinkle aid.
Some five million women in England and Wales have urinary incontinence, but many suffer in silence because they are too embarrassed to seek help.
Botox helps control the muscular bladder wall.
You May Like: What Are The Symptoms Of Advanced Bladder Cancer
How Choosing To Suffer From Incontinence Complicates Your Happiness
You didnât choose to have incontinence, but you can choose to put an end to it. Urge incontinence comes with uncertainty. You canât possibly know when it will strike, making you question, âwill I be able to make it to the bathroom on time?â Having this thought in the back of your mind takes up space that could be occupied by happier thoughts.
Happiness requires certainty and trust. You deserve to be certain that you can make it to the bathroom before leaking, and be able to trust your body to perform. Botox for male urge incontinence may be able to bring you the certainty you need and build trust between you and your body to make life easier and more enjoyable.
Major Insurance Providers Accepted
We accept most insurance policies for your convenience. Please contact your insurance carrier to verify your individual benefits and any copays or coinsurance that are part of your plan. Patients are responsible for notifying our office if a specific plan requires precertification, preauthorization, or a referral . Please call the phone number on the back of your insurance card to verify your provider network participation as insurance carriers change policies often.
Don’t Miss: How Can I Heal My Bladder Naturally
Who Is A Candidate For Botox Bladder Injections
This type of treatment is not for every patient. The procedure may be helpful for those who have bothersome OAB symptoms, such as urinary frequency , urgency and incontinence, and who have tried and failed with OAB medications. Botox bladder treatment may also be recommended for people who have medical conditions such as uncontrolled high blood pressure or glaucoma, or who have chronic constipation and therefore should not take OAB medications. The procedure is also approved for patients who have incontinence problems due to a neurologic condition, such as a spinal cord injury or multiple sclerosis .
What Are The Alternatives To Botox
There are a couple of alternatives to botox injection into the bladder.
Read Also: Drugs To Treat Bladder Infection
What Are Botox Bladder Treatment Risks And Side Effects
As with any medical procedure, there are some potential risks and temporary side effects. There is some risk of damage caused by passing the scope through the urethra to the bladder. There is also a risk of urinary tract infection and not being able to empty the bladder completely. Patients with difficulty emptying their bladders may need a catheter for urination for a short time period after the procedure. Patients may experience some pain or discomfort with urination for the first few days and there may be some blood in the urine. There is a very minor risk of blood clotting.
In clinical trials, only 6.5 percent of patients treated with Botox for incontinence needed to use a catheter after treatment.1
As with any Botox procedure, there is also a minor concern about the Botox spreading beyond the treated area and affecting other parts of the body. Your doctor will discuss the risks and benefits of Botox for incontinence and help you decide whether this is an appropriate treatment option for you.
How Often Will I Get Botox Injections
How often you receive Botox injections may vary. Youll need to track the symptoms of your bladder condition so that your doctor can determine how often you need the injections.
The minimum period between injections is 12 weeks, but in some cases, people feel the effects of Botox for longer periods. This means that they may need injections less often.
If you have questions about how often youll need to get Botox injections for your condition, talk with your doctor.
You May Like: Can Hernia Mesh Cause Bladder Problems
Botox Is Used For Several Bladder Conditions
When most people think of Botox, they think about wrinkles, preventing aging and, after treatment, a face that is oddly expressionless. Ironically, though, Botox has been used for the treatment several bladder conditions. Originally a Step 5 treatment option, in 2014 it was reduced to a Step 4 treatment option for IC/BPS in the AUA Treatment Guidelines.
The Botox Treatment Procedure
Prior to the day of treatment, the patient will be given an antibiotic to reduce the chances of a urinary tract infection . Before treatment, a test will be completed to make sure the patient does not have a UTI. If they do have one, the treatment will be rescheduled.
At Urology Associates Botox is administered under general anesthesia or sedation in an ambulatory surgical center. The doctor performs a cystoscopy by inserting a cystoscope through the urethra, the opening where urine exits the body. Botox is given through the cystoscope by a series of quick injections into specific areas of the patients bladder muscle.It can take 24-72 hours before the Botox takes effect, but in rare cases it may take longer.
About 6 out of every 100 patients require a catheter after the treatment. If this is needed, the doctor will discuss the catheter process including cleaning prior to treatment. This is a smaller catheter than those found in hospitals and can be easily hidden.
Read Also: What Doctor To See For Bladder Infection
Approved Uses For Urogenital Disorders
Botulinum toxin is US Food and Drug Administration -indicated for multiple purposes, but with regard to urogenital and pelvic floor disorders , in 2020, it is only approved for treatment of overactive bladder with symptoms of urinary urge incontinence, urgency, and frequency in adults who have an inadequate response to or are intolerant of an anticholinergic medication, and treatment of urinary incontinence because of detrusor overactivity associated with a neurologic condition in adults who have an inadequate response to or are intolerant of an anticholinergic medication. Botox has been FDA approved for treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity since 2011 and for refractory overactive bladder symptoms since 2013, increasing the likelihood of insurance coverage, and thus the affordability of and access to this treatment for pelvic floor indications. Additionally, studies have shown Botox to be cost effective relative to nonselective anticholinergics, advocating for consideration as a first-line treatment for overactive bladder.
Clinical Applications of Botox in the Treatment of Urogenital and Pelvic Floor Disorders
What Are The Side Effects Of Botox When Injected In The Bladder For Treatment Of Bladder Control Problems
Large studies have shown that Botox, when injected in the urinary bladder for treatment of urinary symptoms including urinary urgency, frequent urination and for bladder control in patients with urinary incontinence, is a safe and effective treatment with few serious side effects.
While the warning label states that distant side effects of Botox are possible such as difficulty speaking/swallowing/breathing, they are apparently exceedingly rare when Botox is injected for treatment of OAB. No patients experienced distant side effects in randomized studies of Botox. In theory, the onabotulinumtoxinA can spread to other areas of the body but this would be an extremely rare occurrence following a relatively small dose of the medication which is given directly into the bladder.
Most common side effects from Botox administration in the bladder:
Don’t Miss: Where Is Your Bladder Woman
What Is Botox And How Does It Work In The Bladder
Botox is a drug made from a toxin called botulinum toxin. It works by paralyzing muscle. When injected in the face it paralyzes the muscles in the face to reduce wrinkles.
When the bladder contracts where we are not ready for it to contract, it can cause urinary urgency, frequency, nocturia, and urge urinary incontinence. By injecting botox into the bladder it paralyzes the bladder muscle and can reduce Overactive Bladder symptoms and urge urinary incontinence.
Treatment Strategies Before Availability Of Botulinum Toxin A

Classically, treatment strategies have aimed at symptomatic relief as well as reduction in clinical sequelae including urinary tract infection and renal deterioration from elevated bladder pressures and urine reflux , . Prior to U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval of intradetrusor BoTA injections for the treatment of NDO and DSD described below, treatment options included pharmacotherapies , assisted bladder drainage , neuromodulation, surgical intervention such as sphincterotomy, urinary diversion or bladder augmentation, or a combination approach.
Antimuscarinics
Intravesical AMs, most commonly oxybutynin, is also an option in which pills are crushed, diluted in water or saline, and then instilled into the bladder via a catheter -. Prospective studies in both children and adults have shown that this application is well tolerated, with significantly reduced side effects compared to oral therapy, and is efficacious, with significant improvements in maximum detrusor pressure, bladder capacity, and even continence , -.
Lastly, it is important to note that the use of AM agents, whether oral or intravesical, often require concomitant intermittent catheterization or other method of assisted bladder drainage.
Alpha-blockers
Assisted Bladder Drainage
Sacral Neuromodulation
Surgical Interventions
Also Check: Botox Procedure For Overactive Bladder
However You Should Not Get A Botox Treatment If You:
- Are allergic to botulinum toxin.
- Have a current bladder infection or you are unable to urinate .
Disclaimer
Every effort has been made to ensure that the information provided above is accurate, up-to-date and complete, but no guarantee is provided. The information is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, warnings, allergic reactions, or adverse effects. If you have questions about this treatment, check