Get Rid Of Your Uti For Good
Chronic bladder infections are more than annoying. Theyre painful and can eventually result in more dangerous conditions, like a kidney infection, if allowed to spread.
Learning whats causing your UTIs is the first step to finally getting rid of them for good. Whether its improper hygiene, your birth control, or an underlying condition, there are treatment options for you.
If youre experiencing the symptoms of a bladder infection, make an appointment with us today.
What Can You Do If You Keep Getting Utis
If you keep getting UTIs, you must talk to your doctor. After talking with you, your doctor will either recommend treatments for recurring urinary infections or send you to a special doctor called a urologist. A urologist focuses on diseases and problems of the entire urinary system, so he may be able to better pinpoint what is causing your infections and how to treat and prevent them.In addition to the tips mentioned above, you can also take some other simple steps to help prevent UTIs, such as:
- Drink plenty of water.
How Are Recurrent Utis Treated
Treatment for recurrent UTIs depends on what’s causing them. Sometimes the answer is as simple as teaching a child to empty their bladder as soon as they have the urge to go.
If a condition like VUR is causing the infections, the solution is a bit more complicated. Kids with VUR must be watched closely, because it can lead to kidney infection and kidney damage. Most kids outgrow the condition. Some might need surgery to correct the reflux.
Some kids with VUR benefit from daily treatment with a small amount of antibiotics, which can also make surgery unnecessary. Kids with VUR should see a pediatric urologist, who can decide if antibiotic treatment is the best option.
In some cases, surgery is needed to correct VUR. The most common procedure is ureteral reimplantation, in which one or both of the ureters are repositioned to correct the backflow of urine from the bladder. This procedure requires only a small incision and, in some children, can be done using robotic-assisted laparoscopy. When surgery is necessary, the success rate is high, but not everyone is a good candidate for it.
Kids may be candidates for ureteral reimplantation if they:
- have an intolerance to antibiotics
- get recurrent infections while on antibiotic treatment
- have severe, or “high-grade,” reflux
- are older kids and teens with reflux
Don’t Miss: How To Prevent Bladder Infections In The Elderly
When To Call A Healthcare Provider
Urinary tract infections require treatment with antibiotics. Even if a UTI is relatively mild, your healthcare provider will likely recommend a one- to three-day course of antibiotics.
If a UTI is causing dyspareunia, it is typically due to frequent or recurrent UTIs that require more extensive treatment. In some cases, a daily, low-dose antibiotic may be prescribed for six months or longer. In postmenopausal women, estrogen replacement therapy may be advised.
If a kidney infection develops, you need to seek prompt medical attention. If left untreated, pyelonephritis can lead to kidney failure and .
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- Do I need any tests, such as urinalysis?
- What is the likely cause of my urinary tract infection ?
- Do I need medicine? How should I take it?
- What are the possible side effects of the medicine?
- When should I expect relief from my symptoms?
- What symptoms would indicate that my infection is getting worse? What should I do if I experience these symptoms?
- I get UTIs a lot. What can I do to prevent them?
- Do I need preventive antibiotics? If so, should I be concerned about antibiotic resistance?
- My child gets UTIs a lot. Could an anatomical problem be causing his or her UTIs?
Don’t Miss: What Can You Do For A Bladder Infection
How Are Chronic Utis Treated
If you have recurrent or chronic UTIs, your doctor may send you to a urologist who specializes in diseases of the urinary system. According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, some of the ways that recurrent UTIs are evaluated and treated include:
- Testing The doctor will want to take a urine sample to test for bacteria and white blood cells. It may be necessary to do special X-ray studies to see if there is an obstruction or stones in the urinary tract. A urologist may look into your bladder by passing a special scope through the opening into your bladder. This exam is called cystoscopy.
- Antibiotics for Treatment Normally, UTIs responds very well to antibiotics, and you may only need to take medication for a few days. For recurrent UTIs, antibiotics may be needed for 10 days or more.
- Surgery In some cases of prostate disease, stones, or other obstruction of the urinary system, surgery may be done to restore normal flow of urine and help clear up infections.
- Antibiotics for Prevention Some strategies to prevent recurrent UTIs with antibiotics include taking low-dose antibiotics for six months or taking antibiotics after sexual intercourse.
- Frequent Urine Testing Women who have recurrent UTIs may benefit from testing their urine frequently with a dipstick that warns of any bacteria in the urine.
What Can You Do To Prevent Recurrent Utis
If you are suffering from recurrent UTIs, you must get in touch with your primary care physician or a urologist. After carefully evaluating your condition, he/she will design an appropriate course of treatment.
Also, there are a lot of ways through which you can minimize your chances of getting UTIs. For this,
- Drink plenty of water It will help you get flush out all the bacteria through urine.
- Do not hold your pee If you feel the urge to urinate, find a bathroom and go.
- Maintain good sexual hygiene Do not indulge in unhealthy sexual activities. Also, urinate shortly after sex.
- Always use clean washrooms Make sure the washroom that you are using is clean and fresh.
- Use dermatologically tested products Always use sprays, deodorants and powders that are medically approved. And avoid using sprays close to your genitals.
- Keep your genitals clean Always wipe yourself from front to back after urinating.
- Wear cotton underwear Always prefer cotton panties to help keep your urethra dry.
You May Like: Prostate And Bladder Cancer Survival Rate
What Causes Urinary Tract Infection
The vast majority of urinary tract infections are caused by the bacteria Escherichia coli , which is usually found in the digestive system. However, other pathogens may cause a UTI. These include:
- Klebsiella pneumonia
- Enterococcus faecalis
- Staphylococcus saprophyticus
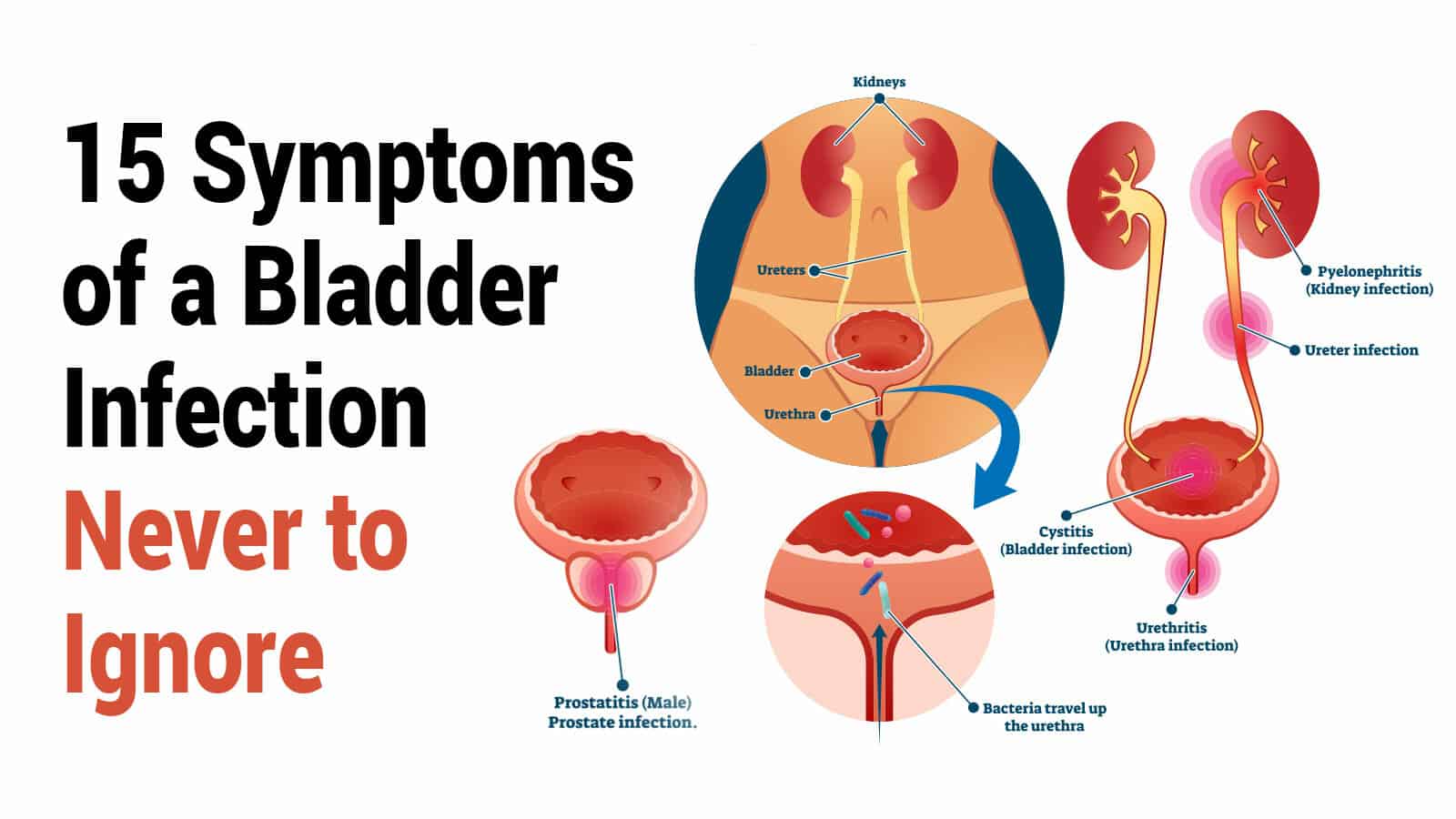
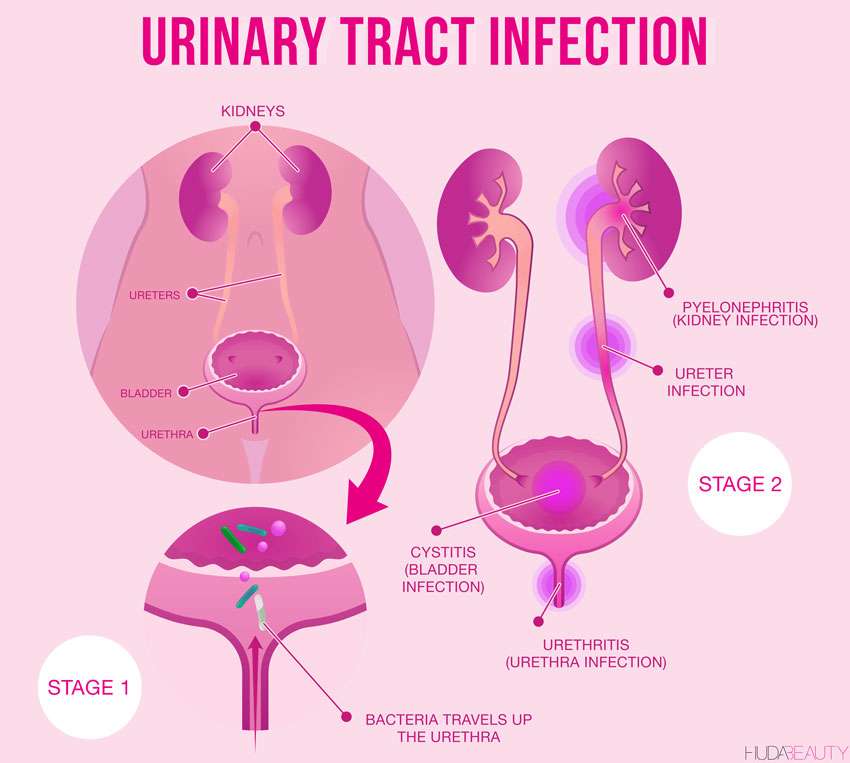
The bacteria may infect any part of the urinary tract bladder, urethra or kidneys. Depending on where the infection occurs, the UTIs are often known as:
- Cystitis infection of the bladder
- Urethritis infection of the urethra
- Pyelonephritis infection of the kidneys
The infection in urethra and bladder is usually not very serious and clears up with treatment. Similarly, ureters very rarely get infected. However, if a UTI reaches the kidneys, it may lead to kidney infections and a person may have to go to the hospital for treatment.
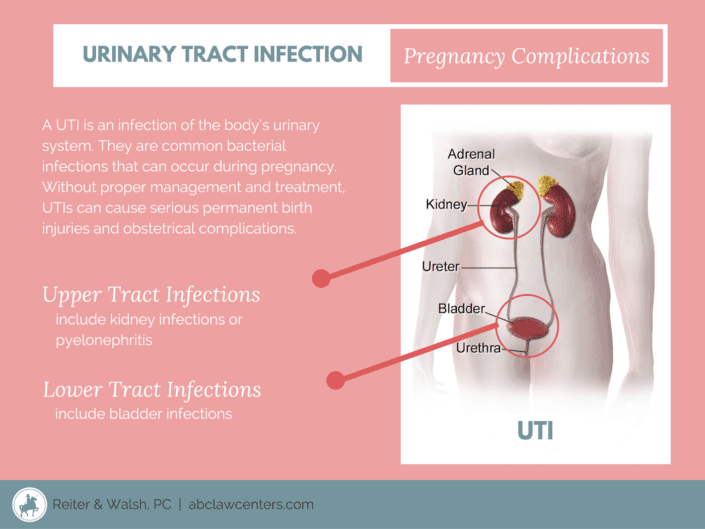
What Are Chronic Urinary Tract Infections
A chronic urinary tract infection is a repeated or prolonged bacterial infection of the bladder or urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body.
While urinary tract infections are common, some women suffer from repeated or recurrent infections .
Women suffering from chronic urinary tract infections may have:
- Two or more infections in a 6-month period and/or three or more infections in a 12-month period
- Symptoms that don’t disappear within 24 to 48 hours after treatment begins
- A urinary tract infection that lasts longer than two weeks
Chronic urinary tract infections can be a painful and frustrating disorder, but effective treatment is available.
You May Like: Bladder Problems After Gastric Bypass
How Are Urinary Abnormalities Diagnosed
It’s important for a doctor to rule out any underlying problems in the urinary system when a child gets UTIs repeatedly. Kids with recurrent infections should see a pediatric urologist to see what is causing the infections.
Some problems can be found before birth. Hydronephrosis that develops before birth can be seen in an ultrasound as early as 16 weeks. In rare cases, doctors may consider neonatal surgery if hydronephrosis affects both kidneys and is a risk to the fetus. Most of the time, though, doctors wait until after birth to treat the condition, because almost half of all cases seen prenatally disappear by the time a baby is born.
Doctors will closely watch the blood pressure of a newborn thought to have hydronephrosis or another urinary system abnormality, because some kidney problems can cause high blood pressure. Another ultrasound may be done to get a closer look at the bladder and kidneys. If the condition appears to be affecting both kidneys, doctors usually will order blood tests to check kidney function.
Utis And Sexually Transmitted Diseases
A number of sexually transmitted infections are known to cause UTIs, including trichomoniasis and chlamydia. Oftentimes a person will assume that the UTI is bacterial in nature and fail to identify the underlying STI.
It is, therefore, vital to consider your risk of STIs when any infection of the genitals or urinary tract is involved. This is especially true if you have multiple sex partners or have gotten a UTI after having sex with a new partner.
Current pediatric guidelines recommend that doctors take a comprehensive sexual history of any adolescent with urinary tract complaints and routinely test them for STIs.
Sexually active men under the age of 35 who don’t use condoms can experience a condition called epididymitis. It is an infection of the epididymis, the coiled tube to the back of the testicles, that can be caused either by bacteria or an STI, most often gonorrhea or chlamydia. Treatment varies based on the cause and severity.
Safer sex practices, which include the consistent use of condoms, are always the best plan for reducing the risk of these and other STIs.
Don’t Miss: How Long Should A Bladder Infection Last
Check If It’s A Urinary Tract Infection
Symptoms of a UTI may include:
- pain or a burning sensation when peeing
- needing to pee more often than usual during the night
- pee that looks cloudy
- needing to pee suddenly or more urgently than usual
- needing to pee more often than usual
- lower tummy pain or pain in your back, just under the ribs
- a high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a very low temperature below 36C
Remedies For Chronic Bladder Infections
Fortunately, there are some actions you and your doctors can take to get rid of chronic bladder infections once and for all.
Antibiotics: Antibiotics can be prescribed to kill the bacteria causing your UTIs and prevent new bacteria from entering.
Drinking Water: Drinking more water can help you pee more often to flush out any bad bacteria in your urinary tract.
Unsweetened Cranberry Juice: Adding unsweetened cranberry juice to your diet has been proven to help prevent and treat bladder infections.
Good Hygiene: Prevent bacteria from causing infections by wiping properly, urinating as soon as you need to, peeing all the way, and washing your genitals every day with the appropriate soaps.
Surgery: Surgery can be used to remove medical conditions such as kidney stones that contribute to chronic bladder infections.
Also Check: What Happens When A Bladder Infection Goes Untreated
Causative Factors And Pathogenesis
Escherichia coli is the predominant uropathogen isolated in acute community-acquired uncomplicated UTIs, followed by Staphylococcus saprophyticus . Enterococcus, Klebsiella, Enterobacter,and Proteus species are less common causes.7
In recurrent uncomplicated UTIs, reinfection occurs when the initially infecting bacteria persist in the fecal flora after elimination from the urinary tract, subsequently recolonizing the introitus and bladder.1 A number of host factors appear to predispose otherwise healthy young women to recurrent UTIs. These include local pH and cervicovaginal antibody changes in the vagina greater adherence of uropathogenic bacteria to the uroepithelium and possibly pelvic anatomic differences, such as shorter urethra-to-anus distance.
Diabetes mellitus, neurologic conditions, chronic institutional residence, and chronic indwelling urinary catheterization are important predisposing factors for complicated UTIs. In affected patients, organisms that are typically less virulent may cause marked illness, although E. coli infection remains the most common organism in nearly all patient groups. Klebsiella and group B streptococcus infections are relatively more common in patients with diabetes, and Pseudomonas infections are relatively more common in patients with chronic catheterization. Proteus mirabilis i s a c ommon u ropathogen i n p atients with indwelling catheters, spinal cord injuries, or structural abnormalities of the urinary tract.7
How Many Is Too Many Utis
Three or more UTIs in one year indicates a recurrent infection, according to the ACOG.
Recurrent urinary tract infections are treated with antibiotics. A week or two after you finish the antibiotic treatment, your doctor may perform a urine test to make sure the infection is cured.
Your doctor may also ask you about factors that increase the risk of a recurrent UTI, including:
- Young age at first UTI
Don’t Miss: Botox Procedure For Overactive Bladder
Chronic Urinary Tract Infections
Assuming that a man gets a UTI, theyre probably going to get another. Around 1 out of 5 ladies have a second urinary tract infection, and some have them over and over. As a rule, every infection is welcomed on by an alternate kind or strain of microorganisms. Yet, a few microbes can attack your bodys cells and increase, making a state of anti-infection safe microscopic organisms. They then, at that point, travel out of the cells and yet again attack your urinary tract.
Predisposing Factors For Recurrent Uti
Risk factors for recurrent UTIs in younger women include:
- Sexual intercourse
- Which makes it easier for bacteria to enter the urinary tract
Risk factors for recurrent UTIs in postmenopausal women include:
- Post menopausal changes in the vaginal tissues which make:
- Vaginal and urethral tissues thinner and more fragile
- Results in a change in the balance of the normal healthy bacteria in the vagina
Risk factors for recurrent UTIs in men include:
- Blockage in the urinary tract e.g.:
- Due to benign enlargement of the prostate gland
You May Like: Clamp Foley For Bladder Training
How To Prevent Urinary Tract Infections Re
Following a few hints can assist you with trying not to get another Urinary Tract Infections:
Void your bladder regularly when you want to pee dont rush, and be certain youve discharged your bladder totally.Clear off of front to back after you utilize the latrine.Drink loads of water.Avoid female cleanliness showers, scented douches, and scented shower items theyll just build aggravation.Scrub your genital region before sex.Pee after sex to flush out any microscopic organisms that might have entered your urethra.Assuming that you utilize a stomach, unlubricated condoms, or spermicidal jam for contraception, you might need to change to another strategy. Stomachs can build microscopic organisms development, while unlubricated condoms and spermicides can disturb your urinary tract. All can make UTI manifestations almost certain.Keep your genital region dry by wearing cotton clothing and baggy garments. Try not to wear tight pants and nylon clothing they can trap dampness, establishing the ideal climate for microbes development.
What Are The Causes Of Bladder Infections In Men
A bladder infection is also called a UTI or urinary tract infection. This infection occurs due to the retention of urine in the urethral tract which causes irritation and the formation of a narrow track. This blockage leads to an infection.
The cause of Bladder infection is the obstruction of the urinary tract, which can be caused due to various reasons like enlarged prostate gland, injury, or a stone in the kidney.
Some other causes of bladder infections include:
- Frequent sexual intercourse with same or new partners.
- Not urinating immediately after sexual intercourse.
- Chronic diabetes.
- Changes in the urinary system.
- Diagnosed with bladder or kidney infection within the past year.
The problems associated with bladder infection are irritation in the urethra, which leads to painful urination, frequent urge to urinate, nausea, and vomiting.
Don’t Miss: How Long To Take Antibiotics For Bladder Infection
When To Contact A Health Care Provider
Needing to relieve the bladder more often than usual for just a day may not be a major cause for concern. But if the urge to pee frequently persists for multiple days or is accompanied by other symptoms, it is likely time to seek medical care.
These are some of the symptoms to watch for when you have frequent urination. If any of these symptoms are present, contact your doctor to have the issue checked out and to determine the reasons for excessive urination.
- Back pain
How Is A Chronic Urinary Tract Infection Diagnosed
If you have a chronic UTI, you probably had a UTI in the past.
Performing lab tests on a sample of urine is the most common method doctors use to diagnose UTIs. A medical professional will examine the sample of urine under a microscope, looking for signs of bacteria.
In a urine culture test, a technician places a urine sample in a tube to encourage the growth of bacteria. After one to three days, theyll look at the bacteria to determine the best treatment.
If your doctor suspects kidney damage, they may order X-rays and kidney scans. These imaging devices take pictures of parts inside your body.
If you have recurring UTIs, your doctor may want to perform a cystoscopy. In this procedure, theyll use a cystoscope. Its a long, thin tube with a lens at the end used to look inside your urethra and bladder. Your doctor will look for any abnormalities or issues that could cause the UTI to keep coming back.
Also Check: How To Deal With A Bladder Infection At Home