When Is Chemotherapy Used
Systemic chemo can be used :
- Before surgery to try to shrink a tumor so that it’s easier to remove and to help lower the chance the cancer will come back. Giving chemo before surgery is called neoadjuvant therapy.
- After surgery . This is called adjuvant therapy. The goal of adjuvant therapy is to kill any cancer cells that may remain after other treatments. This can lower the chance that the cancer will come back later.
- In people getting radiation therapy, to help the radiation work better.
- As the main treatment for bladder cancers that have spread to distant parts of the body.
Prognostic Factors For Os And Css
In the univariate Cox proportional hazards analysis , performance status was found to be significantly associated with both OS and CSS , and sex was shown to be significantly associated with OS . Next, the variables that demonstrated P-values < 0.1 in the univariate analyses were included in the multivariate analysis. As a result, performance status was confirmed to be significantly associated with OS and CSS , and sex was found to be significantly associated with OS . None of the examined clinical variables, including age, performance status, histology, pathological stage, the number of tumors, the maximum tumor size, hydronephrosis, CIS and concurrent chemotherapy, differed significantly between males and females. Only histology was found to be associated with PFS in the univariate analyses , but this was not confirmed in the multivariate analysis .
Table 2
Turbt Radiation And Chemotherapy
Other patients may have another type of procedure called a transurethral resection of bladder tumor , in which the bladder tumor are removed from the bladder lining. The surgeon may use a procedure called fulguration to try to eliminate cancer cells that remain after the tumor is removed. Another treatment option for some patients is external radiation therapy with or without chemotherapy treatment. Some patients may choose to take part in a clinical trial to investigate a new type of treatment for bladder cancer.
Recommended Reading: Where Is The Bladder Located
Symptoms In Men And Women
Bladder cancer symptoms in men and women are the same. Men are more likely to get bladder cancer, but they are also more likely to have it diagnosed earlier, according to Moffitt Cancer Center.
Women are more likely to mistake bladder cancer symptoms for urinary tract infections or menstruation.
Rarely, bladder cancer may also be misdiagnosed as interstitial cystitis in women. IC is a painful, inflammatory bladder condition that affects more women than men.
In one study, doctors found bladder cancer in about one percent out of 600 patients referred to them for IC treatment, according to an article in Urology Times.
Future Directions And Research Priorities
Elderly adults with bladder cancer are faced with difficult choices with regard to the optimum management of their condition. Health-care providers need to consider the unique needs of older patients with bladder cancer. When facing any potentially catastrophic illness, issues related to functional independence and quality of life must be considered, as these factors may assume an importance equal to or even greater than that of survival. Many studies fail to include clinical outcome measures that are truly meaningful for older adults therefore, these studies are not able to appreciate the tremendous variability between individuals as they age. As the earlier discussion indicates, aging represents a very large risk factor for the development of bladder cancer, and may also increase the likelihood of muscle-invasive disease. Nevertheless, based on the available evidence, comorbidity, functional status and frailty may represent far better predictors of undesirable outcomes than chronological age alone. With these considerations in mind, future studies of elderly patients will need to incorporate these other dimensions of health status, as is normally done in the context of a geriatric assessment. Clinical domains that should be assessed include function, objective measures of physical performance, comorbidity, nutrition, social support, cognition and depression.
Recommended Reading: Can You Have Intercourse While Having A Bladder Infection
Low Grade And High Grade Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer starts in the lining of the bladder in about 90 percent of people diagnosed with this cancer. Bladder cancer is called low grade or high grade.
- Low-grade bladder cancer means the cancer has not invaded the muscles around the bladder . People rarely die from this type of bladder cancer, it often recurs after treatment.
- High-grade bladder cancer also often recurs and has a higher chance of spreading to other parts of the body. Almost all deaths from bladder cancer result this type so it is treated more aggressively.
Bladder Cancer Stages And Survival Rates
Cancer survival rates are also categorized according to the stage of the cancer when it was diagnosed. The stage of cancer generally refers to how far it has progressed, and whether it has spread to other parts of the body. For bladder cancer, the 5-year survival rate for people with:2,3
- Bladder cancer in situ is around 96 percent
- Localized bladder cancer is around 70 percent
- Bladder cancer that has spread to the regional lymph nodes is 35 percent
- Distant or metastasized bladder cancer is 5 percent
If you would like to learn more about bladder cancer statistics, consider speaking with someone on your health care team. They will be able to explain more about how these statistics apply to your cancer. Tell us about your experience in the comments below, or with the community.
Don’t Miss: Drugs That Cause Bladder Cancer
When Do You Know If You Have Bladder Cancer
Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside of the bladder. Regional: The cancer has spread from the bladder to nearby structures or lymph nodes. Distant: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as the lungs, liver or bones. Based on people diagnosed with bladder cancer between 2010 and 2016.
Hypofractionated Radiotherapy In Locally Advanced Bladder Cancer: An Individual Patient Data Meta
- Division of Cancer Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester, UKDepartment of Clinical Oncology, The Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester, UK
- Division of Cancer Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester, UKDepartment of Clinical Oncology, The Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester, UK
- Division of Cancer Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester, UKDepartment of Medical Physics and Engineering, The Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester, UK
- Radiotherapy and Imaging Division, The Institute of Cancer Research, London, UKUniversity Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust, Birmingham, UK
- Radiotherapy and Imaging Division, The Institute of Cancer Research, London, UKRoyal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK
- Division of Cancer Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester, UKDepartment of Clinical Oncology, The Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester, UKMount Vernon Cancer Centre, Northwood, UK
- Joint senior authors
Don’t Miss: Overactive Bladder And Back Pain
Bladder Cancer In Men
Bladder cancer affects about 70,000 Americans each year, according to ASTRO. It is four times more common in men than in women and two times more common in whites than African-Americans. Cure rates for advanced invasive bladder cancer are generally poor, with less than 40% of patients living more than five years after diagnosis.
In the U.S., the most common treatment for invasive bladder cancer is complete removal of the bladder, which means the patient has to wear a bag to collect urine for life, James says.
“We’ve shown that the addition of a small amount of chemotherapy to radiation gives you very good control of the bladder even in the very elderly, 80-plus patient who often can’t tolerate surgery. This may shift the balance from surgery to chemoradiation as the primary treatment for many patients with invasive bladder cancer,” James says.
Devlin tells WebMD that in the U.S., patients who are not fit for surgery or don’t want it are increasingly being offered a combination of chemo and radiation.
“This is a well-designed study confirming a trend across oncology showing combination therapies are often better than single therapies,” he says.
This study was presented at a medical conference. The findings should be considered preliminary as they have not yet undergone the “peer review” process, in which outside experts scrutinize the data prior to publication in a medical journal.
Show Sources
Phillip Devlin, MD, chief, brachytherapy, Harvard Medical School, Boston.
Understanding The Statistics: Cancer Survival
It is important to remember that all cancer survival numbers are based on averages across huge numbers of people. These numbers cannot predict what will happen in your individual case.
Survival rates will not tell you how long you will live after you have been diagnosed with bladder cancer. But, these numbers can give you an idea of how likely your treatment will be successful. Also, survival rates take into account your age at diagnosis but not whether you have other health conditions too.
Read Also: Can Overactive Bladder Start Suddenly
Side Effects Of Treatment
During treatment, there was an increase in serious side effects such as an extreme drop in the number of infection-fighting white blood cells in the group receiving chemotherapy: 36% vs. 28% in the group getting radiation alone, James says. But the difference was so small, it could have been due to chance, he says.
Nearly all patients in both groups — 80% to 90% of those who got radiation alone and 85% to 95% of those who also got chemo — reported some side effects such as nausea or fatigue.
After treatment, the rate of side effects was the same in both groups. “Seventy percent of patients reported no side effects at all after three months,” he says.
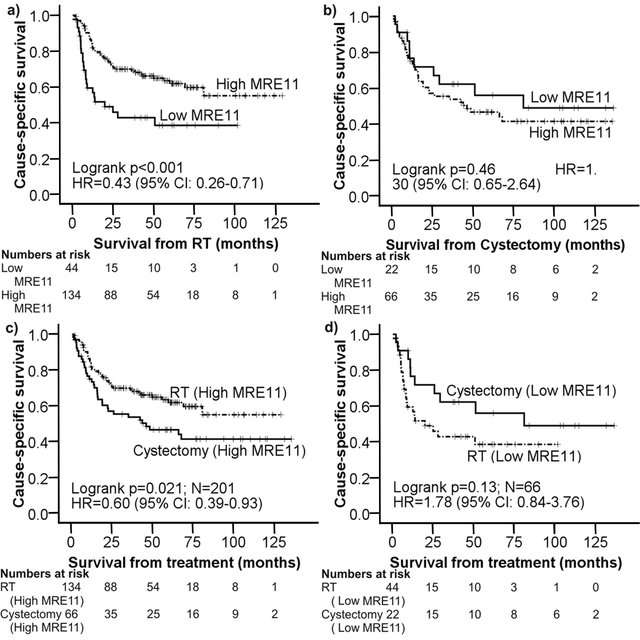
Dna Repair Gene Alteration
MIBCs are characterized by a complex genomic landscape, such as high mutation burden, frequent copy number alteration, and chromosomal translocations . These genomic instabilities are caused in part by alterations in the DNA repair pathway, which could also affect patients sensitivity to CRT-based treatments . Therefore, factors or genes involved in the DNA repair pathway have been investigated as potential biomarkers to predict outcomes in MIBC patients.
Ionizing radiation causes DNA double-strand breaks and consequently induces cell death. Double-strand break is detected by meiotic recombination 11 -RAD50-NBS1 complex which activate the DNA double-strand break repair pathway . Additionally, platinum agents produce DNA intrastrand adducts, which could be repaired by the nucleotide excision repair pathway, a highly conserved DNA repair mechanism. Excision repair cross-complementing group 1 is one of the key players in the nucleotide excision repair pathway .
MRE11
Nucleotide excision repair pathway genes
Recommended Reading: Doterra Oils For Bladder Infection
Molecular Biomarkers In Bladder Preservation Therapy
Clinicopathological factors play an important role in predicting better therapeutic outcomes post CRT-based BPT. However, these clinicopathological factors are insufficient to predict CRT response and outcomes after bladder preservation. Therefore, molecular biomarkers that can predict precise therapeutic outcomes are strongly warranted. Recent understanding of the molecular and genomic characteristics of bladder cancer has led to the identification of different molecular biomarkers of MIBC. In this chapter, we will discuss the possible prognostic or predictive biomarkers of BPT in MIBC patients.
Radiation Therapy For Bladder Cancer
Radiation therapy, also known as radiotherapy, uses a controlled dose of radiation to kill or damage cancer cells. The radiation is usually in the form of x-ray beams.
On its own, radiation therapy can help to control bladder cancer. In this case, you may have a single session, or up to 20 sessions given Monday to Friday over four weeks. This approach may be recommended if you are too unwell for other treatments or if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Radiation therapy can sometimes be combined with other treatments in trimodal therapy, with the aim of curing the cancer.
You will meet with the radiation oncology team to plan your treatment. During a radiation therapy session, you will lie on an examination table, and a machine will direct the radiation towards your bladder. The treatment is painless and cant be seen or felt.
You May Like: I Feel A Lot Of Pressure On My Bladder
When Do You Need An Urinary Catheter For Prostate Cancer
If your prostate is enlarged or you have had treatment for your prostate cancer you may need a urinary catheter. The catheter is used when you cannot urinate by yourself or when your bladder or urethra need time to heal. This may happen for a number of reasons, such as:
The outlook for people with stage 0a bladder cancer is very good. These cancers can be cured with treatment. During long-term follow-up care, more superficial cancers are often found in the bladder or in other parts of the urinary system.
Combination Of Immunotherapy And Bladder Preservation Therapy
The combination of immune checkpoint inhibitors with CRT-based BPT could be a promising approach in achieving a synergistic anti-tumor activity between radiation and immunotherapy . Evidence from other types of malignancies support such a combinatorial strategy. For instance, the PACIFIC trial, which evaluated patients with non-small-cell lung cancer treated with definitive CRT and subsequently randomized to receive checkpoint inhibitors durvalumab or placebo, reported significant improvement in survival outcomes in the durvalumab group .
Tumor DNA repair deficiency has been studied as a potential biomarker for immune checkpoint inhibitors , and among them, the most well established biomarker is the mismatch repair deficiency . Although the association between other DNA repair pathways and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors are less established, several recent studies reported an association between alteration in DNA repair genes and improved response to immune checkpoint inhibitors . These data suggest that combinatorial use of immune checkpoint inhibitors and CRT in treating patients with bladder cancer that resulted from alterations in DNA repair pathways, such as the mismatch, the DNA double-strand break, and the nucleotide excision repair pathways, could yield beneficial results.
Table 3
Recommended Reading: Is Amoxicillin Good For Bladder Infection
Systemic Therapy Prior To Cystectomy
Following a radical cystectomy, local recurrence of cancer is uncommon because the cancer and bladder are removed. Some patients however will still develop distant recurrences because undetected cancer cells called micrometastases spread to other locations in the body before the bladder was removed. Treatment with a systemic therapy such as chemotherapy or immunotherapy may reduce or eliminate these micrometastases reducing the risk of cancer recurrence and avoid cystectomy.
Neoadjuvant therapy refers to systemic therapy that is given before surgery. The rationale behind neoadjuvant therapy for bladder cancer is twofold. First, pre-operative treatment can shrink some bladder cancers and therefore, may allow more complete surgical removal of the cancer. Second, because systemic therapy kills undetectable cancer cells in the body, it may help prevent the spread of cancer when used initially rather than waiting for patient recovery following the surgical procedure.
A study published in the New England Journal of Medicine reported that patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer who received chemotherapy prior to cystectomy had better survival than patients treated with cystectomy alone.1
Chemo Plus Radiation Prevents Bladder Cancer Return
Study Shows Benefits of Adding Chemotherapy to Radiation Therapy
Nov. 2, 2010 — The addition of chemotherapy to radiation for the treatment of bladder cancer allowed more people to remain disease free than if they received radiation alone, British researchers report.
“By adding chemotherapy to radiation therapy, 82% of patients were free of invasive bladder cancer — the most worrisome form of the disease — two years after treatment,” Nicholas James, MD, professor of clinical oncology at the University of Birmingham, England, tells WebMD.
“This compared to 68% of those who received radiation alone.”
That corresponds to cutting the risk of an invasive recurrence by nearly half, James says.
“In the majority of cases, people were able to preserve normal urinary function,” he says. “For patients, that’s hugely important.”
The findings come a day after former basketball star Maurice Lucas died from bladder cancer.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Symptoms Of Advanced Bladder Cancer
Mechanistic Interactions Between Bladder Cancer And Aging
Several broad hypotheses have proposed potential mechanisms for the association between cancer and aging, whereby the biological processes of aging could influence the development and/or progression of cancer in older adults. The processes interact at multiple levels for example, tumor protein 53 a tumor suppressoris involved in both cancer and aging: alteration of the p53 gene is the most frequently encountered mutation in human cancers , and the efficiency of the response to p53 has been found to vary according to age. In a mouse study, Feng et al. reported that the efficiency of the p53 response was significantly reduced in older mice compared with their younger counterparts. The reduced response predominantly resulted from decreased transcriptional activity and p53-dependent apoptosis decreased stabilization of p53 after stress was found to be the major factor in this decline.
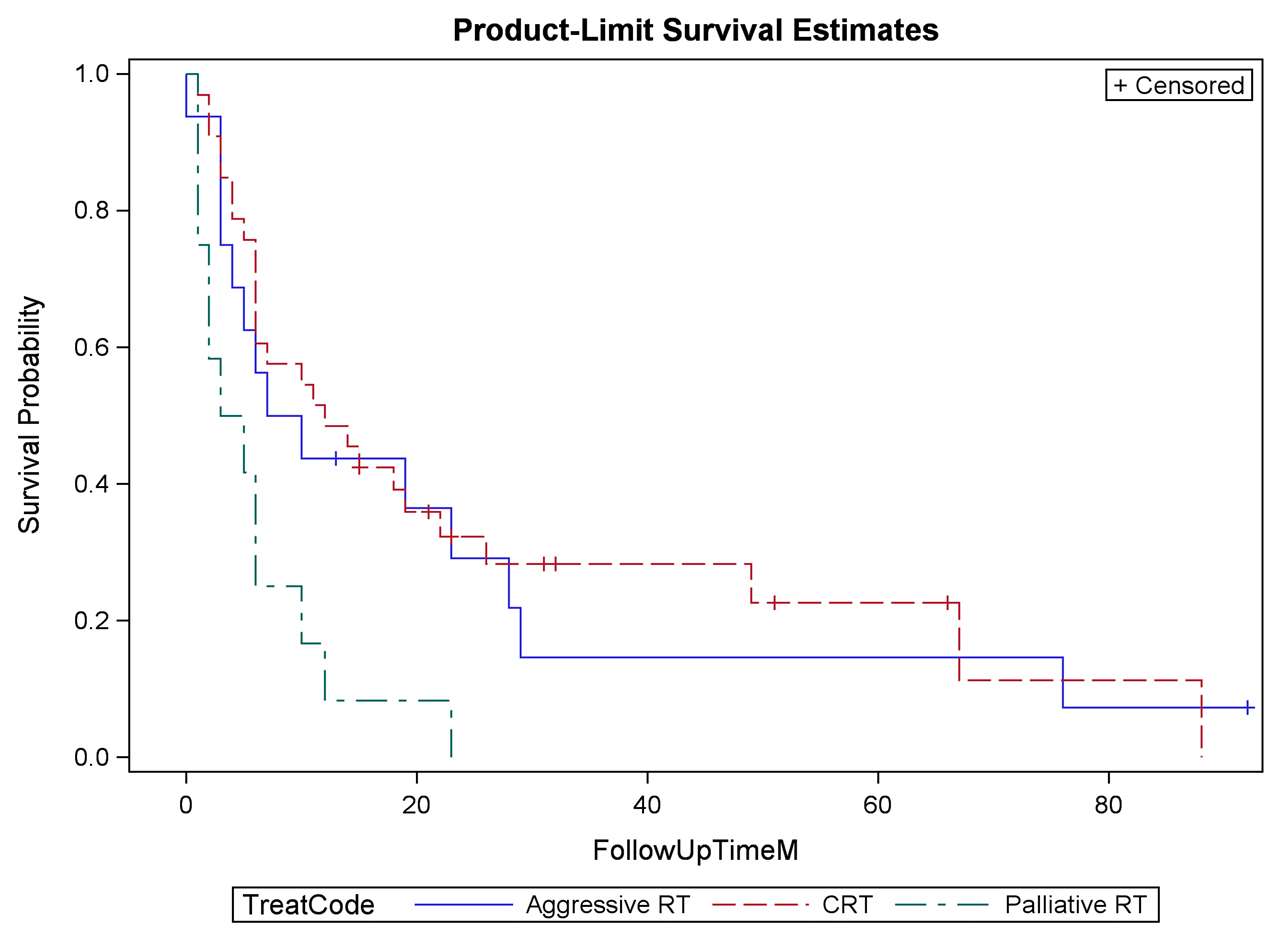
Neoadjuvant Or Adjuvant Chemotherapy Along With Trimodality Therapy
While the positive impact of neoadjuvant chemotherapy prior to RC on oncologic outcomes in MIBC patients is widely acknowledged , there has been no definitive evidence regarding its utility in BPT. In the single institutional large series , the Massachusetts General Hospital team analyzed MIBC patients who underwent TMT with or without neoadjuvant chemotherapy , and showed that there was no significant association between the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy and survival outcomes . In contrast, a separate study in 104 MIBC patients, who underwent neoadjuvant therapy with gemcitabine and cisplatin followed by CRT , showed favorable local cancer control and survival outcomes with complete response, five-year cancer-specific survival and five-year overall survival rates of 79%, 76%, and 68%, respectively . Most recently, Jiang et al. retrospectively analyzed 57 MIBC patients treated neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by CRT , and demonstrated encouraging outcomes and tolerability with overall survival rate of 74% and disease-specific survival of 88% at two years . Several phase 1-2 trials in MIBC patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy post CRT demonstrated five-year overall survival rate to be 5673% . Further studies are warranted to define the potential role of neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy in BPT.
Also Check: What Is The Treatment For Low Grade Bladder Cancer