Treatments For Cystitis From A Gp
If you see a GP and they diagnose you with cystitis, you’ll usually be prescribed a course of antibiotics to treat the infection.
These should start to have an effect within a day or 2.
If you keep getting cystitis, a GP may give you an antibiotic prescription to take to a pharmacy whenever you develop symptoms, without needing to see a doctor first.
Your GP can also prescribe a low dose of antibiotics for you to take continuously over several months.
Favorite Organizations For Essential Uti Info
We love the patient-friendly foundation page of the American Urological Association website. Here, youll find lots of support and educational resources for those with urological issues. Our favorite part is that all your must-know info can come straight to your mailbox: UCF offers free subscriptions to its UrologyHealth Extra magazine.
This no-nonsense clearinghouse is run by the National Institutes of Health, and provides gobs of information on urinary tract infections from the National Library of Medicine. We especially like that you can easily find the latest published research on UTIs and that theres a quick link to current clinical trials for those who are interested.
The CDC is a trusted go-to source for the writers and editors of Everyday Health, thanks to their commitment to science-based research and reporting. What makes the CDC a particularly helpful resource for urinary tract infection information is the fact that their antibiotics and treatment guidelines for UTIs are always up-to-date.
Complications Of Urinary Tract Infections
Delayed treatment for UTIs can lead to complications. Most UTIs cause no lasting damage if they are treated quickly. But if left untreated, UTIs can lead to complications that include:
- Recurring infections
- Narrowing of the urethra in men
- A potentially life-threatening infection called sepsis, especially when kidneys are infected
Read Also: Drugs That Cause Bladder Cancer
Im Pregnant How Will A Uti Affect My Baby
If you have a UTI and it isnt treated, it may lead to a kidney infection. Kidney infections may cause early labor. Fortunately, asymptomatic bacteriuria and bladder infections are usually found and treated before the kidneys become infected. If your doctor treats a urinary tract infection early and properly, it wont hurt your baby.
Signs And Symptoms Of Cystitis
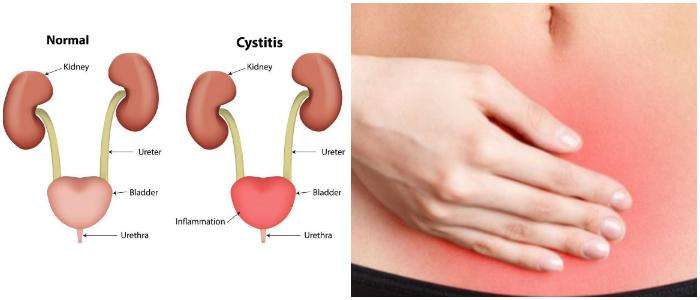
The main symptoms of cystitis include:
- pain, burning or stinging when you pee
- needing to pee more often and urgently than normal
- urine that’s dark, cloudy or strong smelling
- pain low down in your tummy
- feeling generally unwell, achy, sick and tired
Possible symptoms in young children include:
- pain in their tummy
- reduced appetite and vomiting
Recommended Reading: What Were Your Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
What Is The Prognosis For A Person With A Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections typically respond very well to treatment. A UTI can be uncomfortable before you start treatment, but once your healthcare provider identifies the type of bacteria and prescribes the right antibiotic medication, your symptoms should improve quickly. Its important to keep taking your medication for the entire amount of time your healthcare provider prescribed. If you have frequent UTIs or if your symptoms arent improving, your provider may test to see if its an antibiotic-resistant infection. These are more complicated infections to treat and may require intravenous antibiotics or alternative treatments.
Urine Infection Treatment: How Do You Know You Have A Bladder Infection
One of the most common infections is a bladder or urinary tract infection. Although they are very common, they are quite painful and lead to other issues unless treated properly.
A bladder infection is caused by bacteria that enter the body through the urethra and make their way to the bladder. When this bacteria fails to get flushed out during urination, it results in an infection.
Although they are more common in women, anyone can get one. Kidney issues and Sepsis can result from an untreated bladder infection, so its a good idea to know the warning signs.
Lets take a look at the most common symptoms and then some steps to effective urine infection treatment.
Recommended Reading: What Doctor To See For Bladder Infection
Causes Of Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs are usually caused by bacteria from poo entering the urinary tract.
The bacteria enter through the tube that carries pee out of the body .
Women have a shorter urethra than men. This means bacteria are more likely to reach the bladder or kidneys and cause an infection.
Things that increase the risk of bacteria getting into the bladder include:
- having sex
-
do not use scented soap
-
do not hold your pee in if you feel the urge to go
-
do not rush when going for a pee try to fully empty your bladder
-
do not wear tight, synthetic underwear, such as nylon
-
do not drink lots of alcoholic drinks, as they may irritate your bladder
-
do not have lots of sugary food or drinks, as they may encourage bacteria to grow
-
do not use condoms or diaphragms with spermicidal lube on them try non-spermicidal lube or a different type of contraception
Pain Or Burning When You Urinate
Finally, a very common early UTI symptom is pain and/or burning when you urinate. At the first signs of this, see a doctor at Coastal Urgent Care of Bossier right away.
This pain will only become more intense. It can also progress very quickly. A small pain today can often become excruciating by tomorrow.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Weak Bladder In Females
Eating Diet & Nutrition
Experts dont think eating, diet, and nutrition play a role in preventing or treating bladder infections. If you have any type of UTI, talk with a health care professional about how much to drink each day to help prevent or relieve your infection.
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and other components of the National Institutes of Health conduct and support research into many diseases and conditions.
Gall Bladder Infection Symptoms
The presenting symptoms of an infected gallbladder are the following:
- The pain felt may start at the back, in between the shoulder blades. The pain is sometimes restricted to the right shoulder. Abdomen is also described as tender and is greatly felt in the upper quadrant. The pain is more prominent when the person is coughing or when one moves. Sometimes slight movement can emit excruciating.
- Nausea and vomiting are sometimes in conjunction. Abdominal discomfort is usually experienced by a patient.
- Excessive burping is due to the infection causing gas formation.
- Indigestion and diarrhea are common manifestations of gallbladder infection.
- Fever is part of the inflammatory process making the person uncomfortable. The infectious process causes to have fever and may be accompanied by chills.
- Usually, the elderly people experience fatigue, abdominal discomfort such as vomiting and loss of appetite. Fever is not common to the age group.
- Jaundice is also expected. It is presented by yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eye.
- Alteration of the stool and urine color is a result of the lack of bile. Because of the infection, the person shall have a dark-colored urine while there stools are grayish in color.
Read Also: Essential Oils For Bladder And Kidney Health
How Is A Bladder Infection Diagnosed
Bladder infections are usually diagnosed with a urine test.
- Urinalysis, which checks for white blood cells in the urine that can be a sign of infection
- Urine culture, which uses a sample of urine to try and grow bacteria in a laboratory to identify the type of bacteria causing the UTI and determine which antibiotics would be effective against that bacteria
In people who have recurrent bladder infections, additional testing may be indicated to check for abnormalities in the kidneys, ureter, bladder, or urethra, or for kidney stones. Tests may include:
- Computed tomography scan
- Cystoscopy
How Do You Prevent A Bladder Infection
People who have recurrent bladder infections may be able to prevent them in some cases:
- Drink more fluids
- Urinate right after intercourse
- It is believed this will help flush out germs that can enter the bladder. There is no evidence this prevents bladder infections but it is not harmful.
Preventive antibiotics or antibiotics taken following intercourse, as recommended by your doctor
Cranberry juice, cranberry tablets, and a supplement called D-mannose have been promoted to help prevent frequent bladder infections but there are no studies that show these products are effective. However, use of these products probably is not harmful. Tell your doctor before taking any supplements.
Read Also: Reasons For Bladder Control Loss
How To Feel Better
If your healthcare professional prescribes you antibiotics:
- Take antibiotics exactly as your healthcare professional tells you.
- Do not share your antibiotics with others.
- Do not save antibiotics for later. Talk to your healthcare professional about safely discarding leftover antibiotics.
Drink plenty of water or other fluids. Your healthcare professional might also recommend medicine to help lessen the pain or discomfort. Talk with your healthcare professional if you have any questions about your antibiotics.
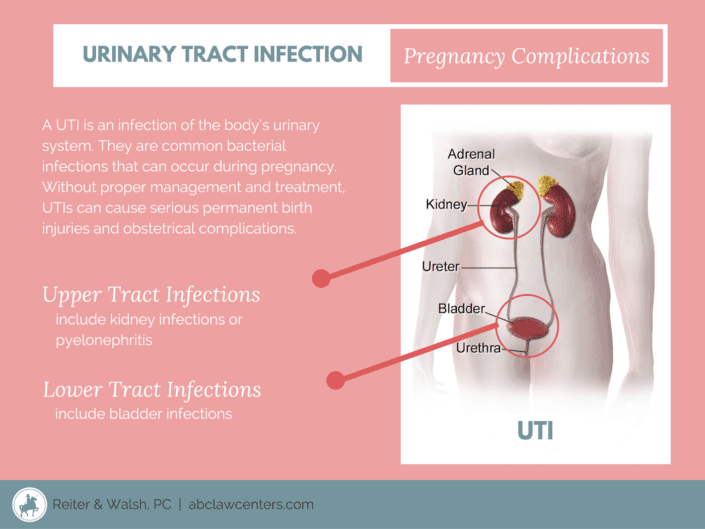
What Is The Urinary Tract
The urinary tract makes and stores urine, one of the body’s liquid waste products. The urinary tract includes the following parts:
- Kidneys: These small organs are located on back of your body, just above the hips. They are the filters of your body removing waste and water from your blood. This waste becomes urine.
- Ureters: The ureters are thin tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to your bladder.
- Bladder: A sac-like container, the bladder stores your urine before it leaves the body.
- Urethra: This tube carries the urine from your bladder to the outside of the body.
Also Check: How Do Doctors Test For Bladder Cancer
Top Five Causes Of Bladder Infections
Can I Become Immune To The Antibiotics Used To Treat A Uti
Your body can actually get used to the antibiotics typically used to treat a urinary tract infection . This happens in people who have very frequent infections. With each UTI and use of antibiotics to treat it, the infection adapts and becomes harder to fight. This is called an antibiotic-resistant infection. Because of this, your healthcare provider may suggest alternative treatments if you have frequent UTIs. These could include:
- Waiting: Your provider may suggest that you watch your symptoms and wait. During this time, you may be encouraged to drink plenty of fluids in an effort to flush out your system.
- Intravenous treatment: In some very complicated cases, where the UTI is resistant to antibiotics or the infection has moved to your kidneys, you may need to be treated in the hospital. The medicine will be given to you directly in your vein . Once youre home, you will be prescribed antibiotics for a period of time to fully get rid of the infection.
Also Check: What Causes A Cyst On Your Bladder
What Is A Bladder Infection
Cystitis is inflammation of the bladder. Most cystitis is from bacterial infections involving the bladder and less commonly may be due to other infectious diseases, including yeast infections, viral infections, or the result of other causes such as chemical irritants of the bladder, or for unknown reasons . Bladder infection is a type of urinary tract infection . Other forms of urinary tract infection include pyelonephritis , urethritis , and prostatitis . This review will specifically address infectious cystitis.
The urine in the bladder is normally free of bacteria . However, bacteria may be present in the bladder but not cause inflammation or symptoms of an infection.
- This is asymptomatic bacteriuria, not cystitis.
- Asymptomatic bacteriuria is bacteria in the urine that does not cause symptoms.
- It is important to differentiate asymptomatic bacteriuria from cystitis, to prevent overuse of antibiotics.
- Most people with asymptomatic bacteriuria do not require antibiotics.
- In fact, the guidelines for the Infectious Disease Society of America recommend only treating asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant women or immediately before urologic procedures.
What Are Other Possible Causes Of Painful Urination
A painful burning feeling when you urinate is often a sign of a urinary tract infection . However, painful urination can occur even if you dont have an infection. Certain drugs, like some used in cancer chemotherapy, may inflame the bladder. Something pressing against the bladder or a kidney stone stuck near the entrance to the bladder can also cause painful urination.
Painful urination can also be caused by vaginal infection or irritation. You might be sensitive to chemicals in products such as douches, vaginal lubricants, soaps, scented toilet paper, or contraceptive foams or sponges. If it hurts to urinate after youve used these products, youre probably sensitive to them.
Also Check: How To Treat An Irritated Bladder
Living With Urinary Tract Infections
If you have 3 or more urinary tract infections each year, your doctor may want you to begin a preventive antibiotic program. A small dose of an antibiotic taken every day helps to reduce the number of infections. If sexual intercourse seems to cause infections for you, your doctor many suggest taking the antibiotic after intercourse.
What Else Can You Do When Antibiotics Fail

When it comes to the best treatment for recurrent chronic UTIs there are two main camps.
Some physicians prefer a long-term antibiotic treatment protocol, frequently prescribing a variety of antibiotics over the course of several months .
Others advocate for the mindful use of antibiotics and focus on correcting underlying dysbiosis as the main reason for recurrent UTIs. In fact, we are still learning about the human microbiome and the effect bacteria have on our health and it seems less and less probable that antibiotics alone could solve chronic issues.
Moreover, antibiotics were developed when we thought that a healthy bladder is sterile which we now know is far from the truth.
What is the best approach to cure a chronic UTI? Here is a selection of posts that can help you to get up to speed:
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of A Bladder Infection Without Antibiotics
Which Antibiotic Gets Rid Of A Uti Fastest
The antibiotic you will be prescribed will depend on a few factors, such as how often you get UTIs, your medication allergies, and other medical conditions you have. No matter which one your provider chooses, though, know that they all work well.
-
is a first choice because it works very well and can treat a UTI in as little as 3 days when taken twice a day. Some providers might choose to have you take it a few days longer than that to be sure your infection is totally gone. Unfortunately, Bactrim is a sulfa drug, and many people are allergic to it.
-
is another first choice for UTIs, but it has to be taken a bit longer than Bactrim. You have to take Macrobid twice a day for a minimum of 5 days for UTIs, but many providers will have you take it for a week to be sure you are all better.
-
remains a fan favorite because it works in as little as 3 days and only has to be taken once a day. But it does carry some serious risks like tendon ruptures and heart problems. It also tends to cause bacterial resistance more often than the previously mentioned antibiotics.
Risk Factors That Make You More Likely To Get A Uti
UTIs are much more common in women than men, and they’re especially rare in young and middle-aged men. This is partly due to the female anatomy women have shorter urethras, making it easier for bacteria to enter the bladder.
Having sex more frequently, and with new partners, can increase a person’s risk of developing a UTI. A womans urethra is located next to both the vagina and anus, enabling bacteria to easily travel into the urinary tract during sexual intercourse.
Other factors that can increase the risk of a UTI include:
- Pregnancy
- Wearing thong underwear
Don’t Miss: What Is Aggressive Bladder Cancer
Follow Up After The Infection
It is routine to check another urine culture about two weeks after treatment to make sure the urine has cleared up.
If your child has recurrent bladder infections, you should check a urine culture every one or two months to monitor for infections. If your child goes for six months without an infection, you can space out these urine checks per your doctors advice.