Medical History And Physical Exam
Your doctor will want to get your medical history to learn more about your symptoms. The doctor might also ask about possible risk factors and your family history.
A physical exam can provide information about possible signs of bladder cancer and other health problems. The doctor might do a digital rectal exam , during which a gloved, lubricated finger is put into your rectum. If you are a woman, the doctor might do a pelvic exam as well. During these exams, the doctor can sometimes feel a bladder tumor, determine its size, and feel if and how far it has spread.
If the doctor finds things that aren’t normal, you may to have lab tests done and you might be referred to a urologist for further tests and treatment.
Removal Of The Tumour
Most superficial bladder tumours are removed by a specialist with the aid of a cystoscope . This is called transurethral resection , as the tumour is removed via a cystoscope which is passed up the water pipe . It does not involve an operation to cut into the bladder. Thin instruments can be passed down a side channel of the cystoscope to remove the tumour.
How Is Recurrence Tested
After your treatment for bladder cancer has ended, your healthcare providers will monitor you regularly during check-ups for signs and symptoms that your cancer may have recurred.1,2 This might involve tests such as physical examinations, urine tests, blood tests, and/or imaging tests.
Active surveillance is a type of follow-up that involves monitoring a patients condition with specialized tests for signs that the patients condition is getting worse. Usually, treatment is not needed unless the results of the test show that the condition has changed.
It is very important to continue visiting your healthcare provider regularly as scheduled for check-ups, especially if you are receiving active surveillance. Treatment for bladder cancer recurrence tends to be more effective when the recurrence is detected as early as possible.
Read Also: What Were Your Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
Cystoscopy: The Gold Standard
Although radiological tests provide important information about the kidneys and the ureters, cystoscopy is the best method of evaluating the bladder and the urethra and diagnosing and monitoring bladder cancer. The cystoscope, a long thin camera, is inserted through the urethra into the bladder.
Today, using flexible cystoscopes, most of these diagnostic procedures are performed in a urologists clinic with little or no discomfort. During the cystoscopy, the urologist will look through the cystoscope and make a note of anything in the bladder that may be abnormal. If a tumor or other abnormality is identified, the urologist will likely schedule you for a cystoscopy under anesthesia with bladder biopsy or transurethral resection of bladder tumor .
Some urologists may have the ability to perform small bladder biopsies in the office. The tissue sample, or biopsy, is then sent to the pathologist for examination . A sample of the urine from the bladder is sent for analysis of the cells to determine if the urine contains any cancer cells. The biopsy specimen and the urine sample will help the urologist make recommendations about your future care.
Click here to read our Get the Facts | Cystoscopy , filled with advice from patients who have experienced it.
Bladder Cancer Is More Common In Men Than Women
In the United States, bladder cancer occurs more often in men than in women, and more often in White individuals than in Black individuals. Rates of bladder cancer have stayed about the same since the 1970s, although more recently , bladder cancer rates have been decreasing slightly each year. Deaths from bladder cancer decreased in all races and sexes between 1975 and 2017.
Read Also: Where Is The Bladder Located
What Are The Treatment Options For Muscle
Treatment options that may be considered include surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy. The treatment advised for each case depends on various factors such as the stage of the cancer , and your general health.
You should have a full discussion with a specialist who knows your case. He or she will be able to give the pros and cons, the likely success rate, the possible side-effects and other details about the possible treatment options for your type of cancer.
You should also discuss with your specialist the aims of treatment. For example:
- Treatment may aim to cure the cancer. Some bladder muscle-invasive cancers can be cured, particularly if they are treated in the early stages of the disease.
- Treatment may aim to control the cancer. If a cure is not realistic, with treatment it is often possible to limit the growth or spread of the cancer so that it progresses less rapidly. This may keep you free of symptoms for some time.
- Treatment may aim to ease symptoms. If a cure is not possible, treatments may be used to reduce the size of a cancer, which may ease symptoms such as pain. If a cancer is advanced then you may require treatments such as painkillers or other treatments to help keep you free of pain or other symptoms.
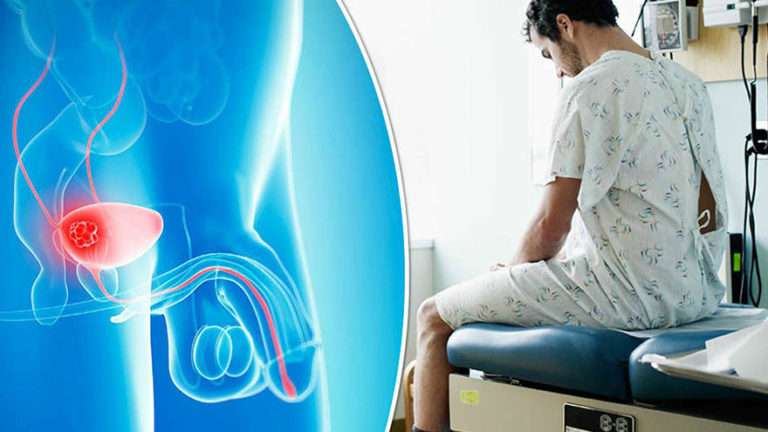
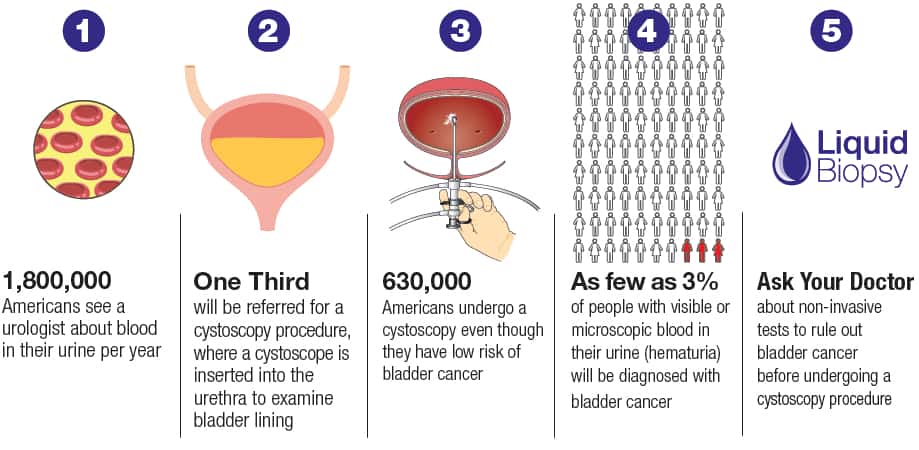
Urinalysis Testing For Blood In Urine
Urinalysis can be used to test a patients urine sample for the presence of blood in the urine.1-3 The medical term for the symptom of blood in the urine is hematuria. Many patients diagnosed with bladder cancer have the symptom of blood in the urine that is easily visible, but in some patients the amount of blood is so small that it is not visible to the naked eye. Urinalysis can detect very small amounts of blood in the urine, which can sometimes help to diagnose bladder cancer at an earlier stage, if bladder cancer is present. Urinalysis can also be used to check the levels of other substances, such as sugar, protein, and white blood cells, in a patients urine.
Read Also: What Causes Overactive Bladder In Women
What Are The Stages Of Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer can be either early stage or invasive .
The stages range from TA to IV . In the earliest stages , the cancer is confined to the lining of the bladder or in the connective tissue just below the lining, but has not invaded into the main muscle wall of the bladder.
Stages II to IV denote invasive cancer:
- In Stage II, cancer has spread to the muscle wall of the bladder.
- In Stage III, the cancer has spread to the fatty tissue outside the bladder muscle.
- In Stage IV, the cancer has metastasized from the bladder to the lymph nodes or to other organs or bones.
A more sophisticated and preferred staging system is known as TNM, which stands for tumor, node involvement and metastases. In this system:
- Invasive bladder tumors can range from T2 all the way to T4 .
- Lymph node involvement ranges from N0 to N3 .
- M0 means that there is no metastasis outside of the pelvis. M1 means that it has metastasized outside of the pelvis.
The Difference In Cancer Detection
Early detection saves lives and is a crucial factor when it comes to the treatment of bladder cancer. Cxbladder is a clinically proven cutting-edge genomic urine test that quickly and accurately detects or rules out bladder cancer in patients presenting with blood in the urine and those being monitored for recurrence.
If you’re worried about bladder cancer, a Cxbladder test can provide accurate results that will allow your Doctor to make informed decisions about your care. Ask your Doctor about Cxbladder today, or contact us for more information.
Recommended Reading: Harmony Urinary Tract And Bladder Support
How Do You Test For Bladder Cancer
There are a few ways for a physician to test for bladder cancer. Diagnosis usually begins when a patient seeks medical attention for unusual symptoms, which can include blood in the urine or frequently feeling the need to urinate even when the bladder is empty.
After evaluating symptoms, a physician may want to order a series of tests to gain a clearer picture of the patients condition. These tests often include:
- Urinalysis to observe the levels of protein, sugar and red and white blood cells in the urine, which can signal the possibility of cancer.
- Urine cytology to look for abnormal cells in the urine under a microscope.
- Imaging such as an ultrasound, X-ray, computed tomography scan or magnetic resonance imaging to view detailed images of the bladder.
- Cystoscopy to closely examine the bladder and remove a small piece of abnormal tissue for biopsy, if necessary, using a thin instrument with a lens. This minimally invasive procedure is known as transurethral resection of bladder tumor .
Two Tests May Be Used To Screen For Bladder Cancer In Patients Who Have Had Bladder Cancer In The Past:
Cystoscopy
Cystoscopy is a procedure to look inside the bladder and urethra to check for abnormal areas. A cystoscope is inserted through the urethra into the bladder. Tissue samples may be taken for biopsy.
Urine cytology
Urine cytology is a laboratory test in which a sample of urine is checked under a microscope for abnormal cells.
Recommended Reading: How To Fix Bladder Leakage After Pregnancy
Blood Test For Bladder Cancer
Get information on having blood tests. A blood test can help measure how well your kidneys are working.
Blood tests can:
- check your general health, including how well your liver and kidneys are working
- check numbers of blood cells
- help diagnose cancer and other conditions
Your blood sample gets sent to the laboratory. Specialist technicians and doctors look at your sample under a microscope.
They can see the different types of cells and can count the different blood cells. They can also test for different kinds of chemicals and proteins in the blood.
Can I Lower My Risk Of Cancer Returning
Unfortunately, researchers do not yet understand exactly what causes bladder cancer to recur in some people, but not in others.2 There are studies being carried out to try and find out if there are any vitamins, minerals, supplements, or medicines that might help to reduce the risk of recurrence. But as of now, there is no proof that any of these things have an effect on the chance that bladder cancer will recur.
Maintaining a healthy body and lifestyle is good for your overall health, however. Following a healthy diet, staying active, and avoiding unhealthy behaviors, such as smoking, is a good idea for everyone. If you find yourself worrying about bladder cancer recurrence, stress-relieving activities such as exercise or meditation might help to reduce your anxiety.
Recommended Reading: How Do Bladder Infections Happen
Diagnosis Of Bladder Cancer
Diagnosis is the process of finding out the cause of a health problem. Diagnosing bladder cancer usually begins with a visit to your family doctor. Your doctor will ask you about any symptoms you have and may do a physical exam. Based on this information, your doctor may refer you to a specialist or order tests to check for bladder cancer or other health problems.
The process of diagnosis may seem long and frustrating. Its normal to worry, but try to remember that other health conditions can cause similar symptoms as bladder cancer. Its important for the healthcare team to rule out other reasons for a health problem before making a diagnosis of bladder cancer.
The following tests are usually used to rule out or diagnose bladder cancer. Many of the same tests used to diagnose cancer are used to find out how far the cancer has spread . Your doctor may also order other tests to check your general health and to help plan your treatment.
It Matters Getting The Right Diagnosis
If you seek a second opinion at Roswell Park, our bladder cancer team will review your tests, scans and pathology. In about 10% of cases we review, the diagnosis is changed, impacting your treatment options and decisions.
Getting an accurate diagnosis of your bladder cancer including your cancers type, grade, shape, stage and whether its invasive or noninvasive is essential to determining your treatment options and the way forward. At Roswell Park, our team of urologists, pathologists and radiologists, are uniquely experienced and specialize in performing and interpreting the tests, scans and procedures necessary for an accurate bladder cancer diagnosis.
You May Like: Prostate Cancer Spread To Bladder Neck
Why You Might Have A Cystoscopy
You may have this test if you’re:
- passing blood when you wee
- having problems passing urine including being unable to empty your bladder properly , you’re unable to control when you need to wee or going more frequently than usual
This is the most important test for diagnosing cancer of the bladder. As well as examining the bladder your doctor can take samples of the bladder lining to check for cancer cells.
Other reasons you might have a cystoscopy is to check:
- whether your cancer has come back
- for spread from another type of cancer
Undergoing A Cystoscopy And Biopsy
Recommended Reading: Ways To Control Your Bladder
How Are Samples Collected
Requirements for urine sampling vary depending on the test/s being performed. Often the timing of collection is random, as dictated by the logistics of a doctor consult or access to a laboratory service. However, depending on the purpose of the test, certain urine voids of the day may be preferred. Collection of urine from all voids over a defined time period or sample collection at specific times after eating may also be necessary.
Urine samples are usually obtained by spontaneous voiding, using the clean-catch, midstream urine collection method. This involves voiding the first portion of urine into the toilet, collecting the midstream portion into a clean container, then voiding the remaining portion into the toilet. This method greatly reduces the risk of contaminants entering the sample. Less commonly, an invasive method of urine collection, such as placement of a urinary catheter, may be required.
Learn about Cxbladder’s easy-to-use in-home sampling system
What Are The Typical Results For Urine Test For Cancer
Cancer Cell Affecting Normal Cells
All the three results, visual, microscopy and biochemistry, are interpret to arrive at what might be an indication of cancer.
- If the urine sample was collect accurately, avoiding interference of certain foods, medications, and dietary supplements, red-colored urine is an indication that blood is present and represents a disease state that has caused damage to an organ of the urinary system. For example, Cancer of the bladder.
- In general, yellow-brown or greenish-brown urine may be a sign of bilirubin leaking from the liver into the urine. It may also be due to obstruction of the bile duct . This can give an indication of liver cancer or bile duct cancer.
- Blood test, together with different imaging tests can be use to diagnose blood cancers .
- In fact, cancer in the kidney, bladder, or ureter may shed cancer cells into the urine. This is referred to as renal transitional cell carcinoma , or renal urothelial carcinoma . It is a malignant tumor which originated from epithelial cells lining the urinary tract. Tumor marker tests indicate can be use to detect their presence and levels to provide information of urinary system cancer.
Also Check: How To Empty Your Bladder With A Uti
Screening For Bladder Cancer
Screening is the use of tests or exams to look for a disease in people who have no symptoms. At this time, no major professional organizations recommend routine screening of the general public for bladder cancer. This is because no screening test has been shown to lower the risk of dying from bladder cancer in people who are at average risk.
Some providers may recommend bladder cancer tests for people at very high risk, such as:
- People who hadbladder cancer before
- People who had certain birth defectsof the bladder
- People exposed to certain chemicals at work
Urine Test For Cancer
Urine test for cancer utilizes midstream urine sample to detect disease in body, which includes different types of infections. In this case, urinalysis is used to check if there is blood in the urine as an indication of infection or if certain types of drugs are present. The tests analyze urine by physical, microscopical and biochemical techniques. If a cancer diagnosis is being sought, the cells are collect from the urine by centrifugation and a special microscope is utilize to examine cells and plausible cancer activity they exhibit and this is refer to as urine cytology test.
For cancer detection, if the urinalysis tests reveal abnormal cells, additional tests are carry out to obtain more information in order to confirm that there has been the development of cancer. Urinalysis tests have been use as a convenient method of identifying bladder cancer at early stages but it is not solely use as a screening test however, other techniques are use to confirm a positive urine test result.
Also Check: What Is The Treatment For Low Grade Bladder Cancer