Other Causes Of Bladder Spasms
Some medications may cause bladder spasms as a side effect. Medications that commonly cause bladder spasms include:
- A chemotherapy drug called valrubicin
- Medicines called diuretics, such as furosemide or hydrochlorothiazide, which help the body remove excess water
What you eat or drink can sometimes bother a fragile bladder and cause it to go into a spasm. This is especially true in patients who have a condition called interstitial cystitis.
Spicy, acidic, or citrusy foods and the chemicals in certain preservatives and food additives may irritate the lining of the bladder in some people. Such products may include:
- Alcohol
- Tomatoes
How Should I Take Phenazopyridine
Use exactly as directed on the label, or as prescribed by your doctor. Do not use in larger or smaller amounts or for longer than recommended.
Take phenazopyridine after meals.
Drink plenty of liquids while you are taking phenazopyridine.
Phenazopyridine will most likely darken the color of your urine to an orange or red color. This is a normal effect and is not harmful. Darkened urine may also cause stains to your underwear that may be permanent.
Phenazopyridine can also permanently stain soft contact lenses, and you should not wear them while taking this medicine.
Do not use phenazopyridine for longer than 2 days unless your doctor has told you to.
This medication can cause unusual results with urine tests. Tell any doctor who treats you that you are using phenazopyridine.
Store at room temperature away from moisture and heat.
Living With Overactive Bladder
Living with overactive bladder will depend on how serious your problem is and how well your treatment works. In either case, living with the condition may require better planning. You may have to plan when you consume liquids and how close you are to a bathroom. You also may consider wearing disposable undergarments that protect your clothing from leaking urine.
Read Also: What Vitamins Are Good For Bladder Health
Types Of Treatments For Bladder Spasms
Treatment of bladder spasms largely depends on the underlying cause. However, below are four common treatment options that conventional and integrative doctors consider when treating bladder spasms:
- Lifestyle changes
- Medications
- Injection
How do I stop bladder spasms? You can stop bladder spasms by diagnosing and treating their root cause. Common bladder spasm treatments include antispasmodic medication, Kegels, dietary changes, bladder training, and general stress relief.
Beta Agonists For Bladder Problems
This class of medication, mirabegron , works by relaxing the bladder muscle during the storage phase, thus increasing the capacity of bladder to hold more urine. They can be used for the treatment of overactive bladder . Mirabegron is the first drug in this category.
- How beta-agonist drugs work: They work by relaxing the bladder muscles and reducing bladder overactivity.
- Who should not use this medication: Individuals with the following conditions should not use mirabegron or a similar class of drugs:
- Allergy to this drug
- Advanced kidney disease
You May Like: Loss Of Bladder Control While Coughing
What Is Bladder Spasm
Normally, urine is filled in the bladder over a period time which is variable from some minutes to a few hours depending on the amount of fluid intake and once filled the individual gets the urge to go to the restroom. In people with bladder spasms, a sensation of the need to urinate comes suddenly and severely. Spasm is defined as a sudden and involuntary contraction of muscles. Bladder spasm which is also known by the name of detrusor contraction develops when there is sudden involuntary contraction of the bladder causing a sudden urge to urinate. At times, bladder spasm forces urine to come out of the bladder leading to leakage. This medical condition is termed as overactive bladder or urge incontinence. Sufferers of these spasms describe the symptoms as cramping like pain with burning sensation.
Common causes of bladder spasms include urinary tract infections, interstitial cystitis and catheter use.
Anticholinergic Drugs For Oab
The largest class of drugs used to treat OAB is anticholinergic drugs. They work by blocking a chemical in your body called acetylcholine. This chemical sends a message to your bladder to contract. By blocking this chemical, these drugs reduce the contractions that cause you to release urine. In studies that compared the drugs, all anticholinergics worked in treating OAB.
Anticholinergics are sold under different brand names. Some are also available as generic drugs. These medications include:
- oxybutynin
- solifenacin
- fesoterodine
All of these drugs except for Oxytrol come as either tablets or capsules that you take by mouth. Oxytrol is available as a skin patch.
The most common side effects of anticholinergic drugs include:
- dry mouth
- blurry vision
- constipation
Seniors have the greatest risk of side effects from these drugs. These medications may also cause drowsiness and an increased risk of falls in seniors. Oxybutynin may cause more side effects than the other drugs in this class. However, taking oxybutynin in its extended-release form may reduce some of the side effects. Anticholinergics may also worsen dementia symptoms and should be used with caution in people with this disease.
Also Check: Homeopathic Medicine For Bladder Weakness
What Does A Bladder Spasm Feel Like
One of the most common bladder spasm symptoms is feeling an urgent need to urinate. As a result, the bladder spasms might cause urine leakage, otherwise known as urinary incontinence. If a urinary tract infection is causing bladder spasms, you might also notice the following bladder spasm symptoms:
- A burning sensation during urination
- Failure to fully empty the bladder
- Urine that has a cloudy, red, or pink appearance
- Strong smelling urine
- Pain in the pelvic area
- uncontrollable bladder contractions
On the other hand, if your bladder spasms are a result of an overactive bladder, you can also experience the following bladder spasm symptoms:
- Leakage of urine before you get to the toilet
- Frequent passing of urine, sometimes up to eight times per day
- Waking up once or twice during the night to urinate
Trying Over The Counter Treatment For Urinary Relief
My daughters encouraged me to try AZO and I am one happy customer. I take the Urinary Pain Relief and within 20 minutes I notice that the spasms are barely noticeable and my urgency to go subsides. One thing you must be aware of – AZO will turn your urine bright red or orange. This is normal. Be vigilant in cleaning your toilet while using AZO because it can stain the porcelain. It is quite a scary experience to look and see all red, even when you are expecting it, but believe me, it is totally normal.
You May Like: Botox Procedure For Overactive Bladder
Interstitial Cystitis/painful Bladder Syndrome
LINDA M. FRENCH, MD, University of Toledo College of Medicine, Toledo, Ohio
NEELAM BHAMBORE, MD, University of CaliforniaDavis Medical Group, Sacramento, California
Am Fam Physician. 2011 May 15 83:1175-1181.
Patient information: A handout on interstitial cystitis is available at .
Interstitial cystitis is a chronic condition characterized by painful symptoms including dysuria, pelvic pain, and dyspareunia. Urinary urgency and frequency are also typical. Interstitial cystitis mainly affects women. Expert opinion in the United States and Europe is that it should be considered with painful bladder as one syndrome, interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. According to the National Institutes of HealthNational Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases , an estimated 1.2 million women and 82,000 men in the United States have interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome.1
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Multimodal therapy that includes pentosan polysulfate sodium , a tricyclic antidepressant, and an antihistamine is proposed to relieve symptoms of interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome via complementary pathophysiologic mechanisms.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
What Behavioral Changes Can I Make To Help With Overactive Bladder
There are many techniques and changes to your typical behavior that you can try to help with an overactive bladder. These can include:
Keeping a log: During a typical day, write down your fluid intake, the number of times you urinate, the number of accidents and when they occur. Make a note about what happened when the accident happened, like when you:
- Cough.
- Laugh.
- Were unable to reach the bathroom in time.
Monitoring your diet: Eliminate or decrease foods or beverages that may worsen your bladder symptoms. These could include:
- Tea.
- Spicy and acidic foods and drinks.
- Foods and drinks that contain artificial sweeteners.
Maintaining bowel regularity: Constipation can place added pressure on the bladder and have a negative effect on your bladder function. By keeping healthy bowel habits, you may be able to avoid constipation and help to lessen bladder symptoms. The following are some suggestions for maintaining bowel regularity:
- Increase your fiber intake by eating foods like beans, pasta, oatmeal, bran cereal, whole wheat bread, and fresh fruit and vegetables.
- Every morning, take 2 tablespoons of this mixture: 1 cup apple sauce, 1 cup unprocessed wheat bran, and ¾ cup prune juice.
- Exercise regularly to maintain regular bowel movements.
Maintaining a healthy weight: Being overweight can add pressure on your bladder, which may contribute to bladder control problems. If you are overweight, weight loss can reduce the pressure on your bladder.
Read Also: Best Foods To Eat For Bladder Infection
Palliation Of Bladder Spasms
Background: Bladder spasms induced by involuntary bladder contractions are a distressing symptom affecting 7-27% of men and 9-43% of women . Seriously ill patients may develop bladder spasms as a complication from genitourinary malignancies, indwelling catheters, or other medical issues. For some, these contractions may be imperceptible and only appreciated on urodynamic testing for others, they can be incapacitating and associated with urinary incontinence.
Differential Diagnosis: Common etiologies of bladder spasms include a urinary tract infection , ingestion of chemical irritants like diet soda or caffeine, constipation, obstruction of the bladder outflow tract , disinhibition from interruption of upper motor neurons, or irritation of the detrusor muscle from a tumor, catheter, or intramural stone . Medications can also lead to spasms either by bladder irritation or disruption of the detrusor muscle or bladder outlet . See Fast Fact #287.
Clinical Evaluation of Bladder Spasms:
Interventional Procedures:
References
Bladder Spasms And Foley Catheter Usage Understanding And Prevention

A foley catheter is very commonly used medical device used to treat all manners of incontinence. Unfortunately, for some users, bladder spasms from the use of a foley catheter may also be quite common. By its very nature, an indwelling catheter is invasive and has the potential to trigger a wide range of side effects, but keeping bladders spasms in check is still possible.
Don’t Miss: My Bladder Always Feels Full
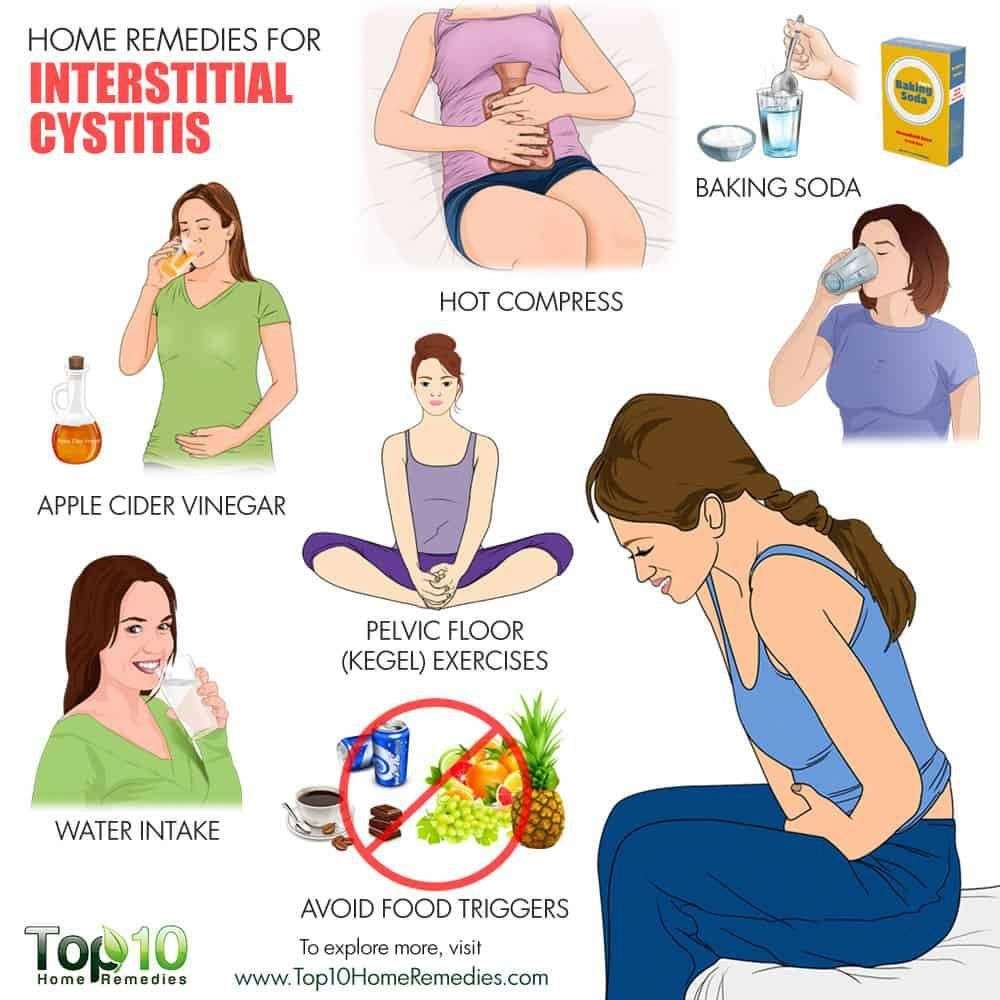
How To Stop Bladder Spasms Naturally: 12 Home Remedies
- Certain medications, such as bethanechol and furosemide
- Bladder stones
- Parkinsons disease
What you eat or drink can occasionally irritate a fragile bladder and cause it to become a spasm. This is especially true in patients who have a condition called interstitial cystitis.
Spicy, acidic, or citrusy foods and also the chemicals in certain preservatives and food additives may irritate the lining of the bladder in certain individuals. Such products may include:
- Chocolate
When to consult a doctor.
Consult the doctor if you have :
- Leakage of urine
- Pain while urinating
- Pain in the lower abdominal area
Here are the best home remedies and self-care tips for treating urinary incontinence and bladder spasm.
Helpful During Bcg Treatments
This stuff is amazing! Also, it doesn’t dry me out like Oxybutynin. In my case, my spasms get worse the day of BCG and the day after, so that is when I use my Oxybutynin, but the rest of the time I use AZO. It helps me so much more.
My experience with AZO has strictly been used during my BCG treatments, but AZO can help tremendously if you are getting a Urinary Tract Infection and can help with the pain. AZO is NOT a replacement for antibiotics to rid yourself of the infection. It is just another tool we can keep in our arsenal while we fight this beast we call cancer.
Recommended Reading: Botox In Bladder For Incontinence
Exercises To Train The Pelvic Floor
The pelvic floor needs a workout in the form of physical therapy that can strengthen the bladder and help you hold the urine. Bladder retraining starts with Kegel exercises.
It can be a little difficult at first to manage the urge urinary incontinence and bladder symptoms. Still, with regular practice and muscle tightening, the pressure to the bladder can subside. Talk to your doctor for specific instructions on how to manage stress incontinence.
Oxybutynin May Cause Side Effects Tell Your Doctor If Any Of These Symptoms Are Severe Or Do Not Go Away:
- dry mouth
- dry eyes, nose, or skin
- stomach pain
- change in ability to taste food
- headache
- difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep
- nervousness
- frequent, urgent, or painful urination
- fast, irregular, or pounding heartbeat
If you experience a serious side effect, you or your doctor may send a report to the Food and Drug Administration’s MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting program online or by phone .
Oxybutynin may cause other side effects. Call your doctor if you have any unusual problems while you are taking this medication.
You May Like: Does Bladder Infection Cause Incontinence
How Should This Medicine Be Used
Oxybutynin comes as a tablet, a syrup, and an extended-release tablet to take by mouth. The tablets and syrup are usually taken two to four times a day. The extended-release tablet is usually taken once a day with or without food. Take oxybutynin at around the same time every day. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take oxybutynin exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Swallow the extended-release tablets whole with plenty of water or other liquid. Do not split, chew, or crush the extended-release tablets. Tell your doctor if you or your child cannot swallow tablets.
Use a dose-measuring spoon or cup to measure the correct amount of liquid for each dose, not a household spoon.
Your doctor may start you on a low dose of oxybutynin and gradually increase your dose, not more than once every week.
Oxybutynin may control your symptoms but will not cure your condition. Continue to take oxybutynin even if you feel well. Do not stop taking oxybutynin without talking to your doctor.
You may notice some improvement in your symptoms within the first 2 weeks of your treatment. However, it may take 68 weeks to experience the full benefit of oxybutynin. Talk to your doctor if your symptoms do not improve at all within 8 weeks.
What Are The Possible Side Effects Of Phenazopyridine
Get emergency medical help if you have any of these signs of an allergic reaction: hives difficult breathing swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Stop using phenazopyridine and call your doctor at once if you have:
- little or no urinating
- confusion, loss of appetite, pain in your side or lower back
- fever, pale or yellowed skin, stomach pain, nausea and vomiting or
- blue or purple appearance of your skin.
Common side effects may include:
- headache
- dizziness or
- upset stomach.
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Read Also: Does Bph Cause Overactive Bladder
Medical Therapy And Devices For Neurogenic Bladder
Besides behavioral therapy, there are medications and devices used to treat neurogenic bladder, including:
- Anticholinergic drugs: Several medications are available that may help people with frequent or urgent urination, or leakage due to neurogenic bladder. Anticholinergic drugs act by relaxing the muscles of the bladder, and decreasing the urgency or leakage due to overactivity or spasms of the bladder. The drugs have many side-effects, such as drowsiness, blurred vision, heart palpitations and facial redness. Patients may need to try several drugs before finding one that works well.
- Antispasmodic drugs: Antispadmodic medications also work by relaxing the muscles of the bladder. This can increase the capacity of the bladder and decrease the need to urinate frequently. These drugs have similar side effects to anticholinergic medications and may interfere with activities that require physical coordination and mental alertness, such as driving or operating heavy machinery.
- Antidepressant drugs: Certain antidepressant drugs can be used to treat bladder problems, although they are not approved by the Food and Drug Administration for these uses. The drugs work by relaxing the muscles of the bladder and can be used to treat frequent urination .
What Medications Can I Use For Overactive Bladder
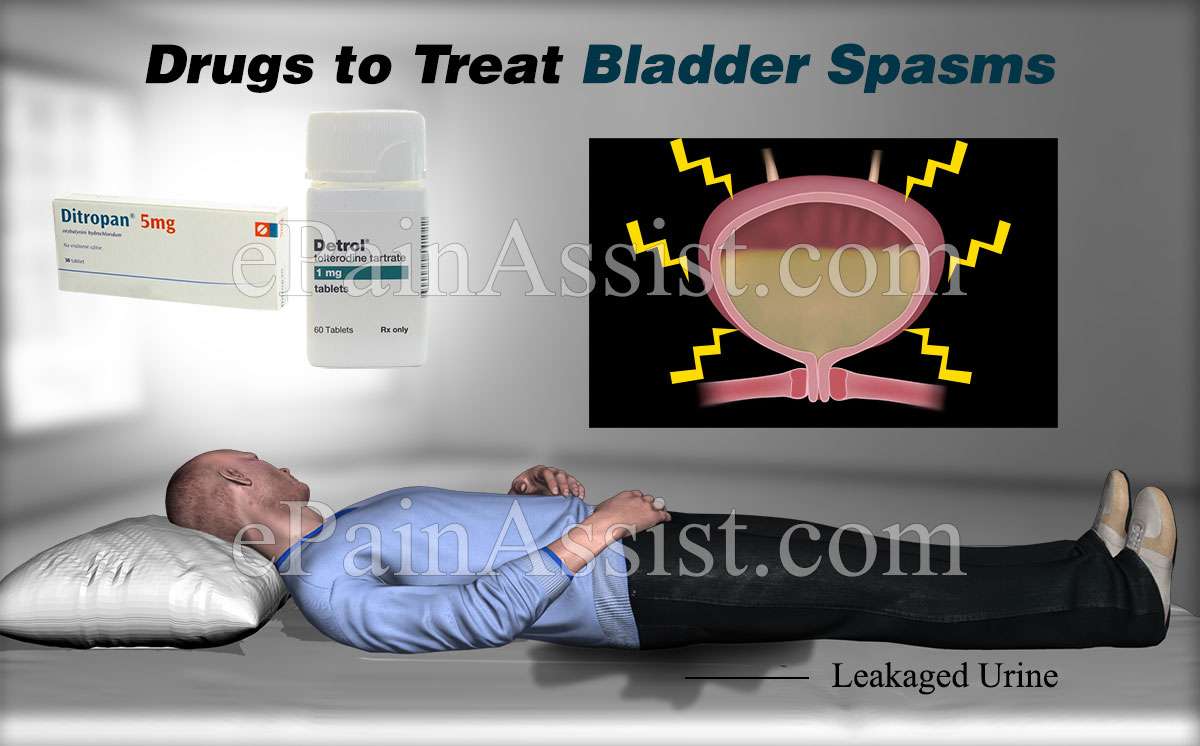
Your doctor may suggest trying behavioral techniques before having you use a medication to treat overactive bladder. However, medications can work very well to return normal function to the bladder. Ask your doctor about the risks and benefits of using the following commonly prescribed medications:
Anticholinergic medications
These medications control muscle spasms in the bladder:
- Oxybutynin , oxybutynin XL , oxybutynin TDDS .
- Tolterodine .
- Mirabegron .
Read Also: Low Grade Bladder Cancer Recurrence