Actos And Bladder Cancer What Does Bladder Cancer Look Like
Actos was introduced to the U.S. busines in 1999, and is prescribed to treat diabetes mellitus form 2. Recently there have been pertains regarding the link between Actos and bladder cancer. For years, sales of the dose lagged behind those of a competitive diabetes medication called Avandia. This changed in 2007, when research studies been demonstrated that Avandia increased the risk of heart attacks. Actos soon reigned the market with sales in 2010 excess $ 4 billion. Because of a recent revealing by the FDA, nonetheless, the drugs make, Takeda Pharmaceuticals, is very likely to front the thousands of Actos lawsuit 2011 claims.
In June 2011, the FDA questioned a refuge forewarning about the narcotic, admonishing the public that using it for longer than a year could lead to the development of bladder cancer. Like other malignancies, it is feasible to fatal without therapy. Chemotherapy may be necessary if Actos and bladder cancer side effects are not spotcheck early. Below, well explain how the care wreaks, and describe the side effects caused by the drugs.
How Chemotherapy Kills Bladder Cancer Cells
Normally, cadres divide at a relatively uniform speed. Cancer cells, on the other hand, split quickly and erratically. This is the way they spread beyond the original site of the tumor. As they partition, they procreate other diseased cells that also subdivide speedily, letting the disease to proliferate out of control.
Common Side Effects Of Chemotherapy
Endoscopic Teflon Or Deflux Gel Treatment For Vesico
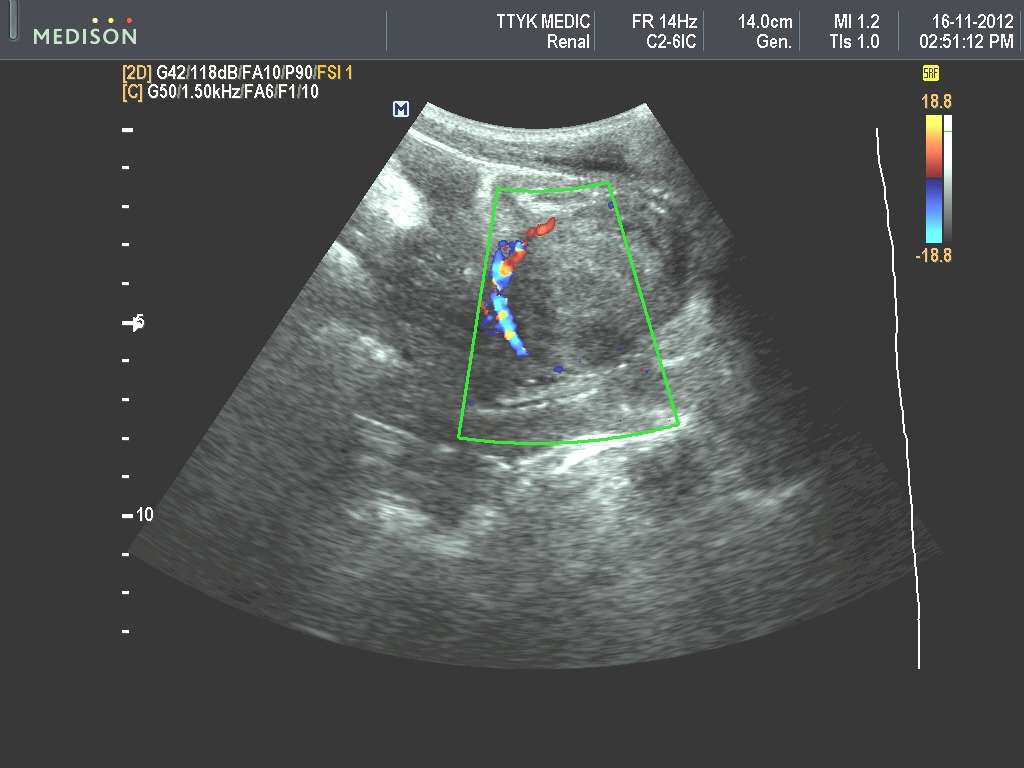
This patient shows an echogenic mound in the left vesico-ureteric junction. The Color Doppler image shows a ureteric jet emerging from this region suggesting that the left distal ureteric orificeis patent. This patient had a history of vesico-ureteric reflux. This was corrected by a Teflon gel injected in the submucosal part of the left VUJ viathe endoscopic route. There are 5 grades of vescio-ureteral reflux. Grade-1: the VUR reaches below the renal pelvis. Grade-2: VUR reaches up to the renal pelvis without causing dilation of thepelvis. Grade-3: There is mild to moderate dilation of the renal pelvis and ureter. Grade-4: Moderate dilation of renal pelvis, ureter and calyces is present. Grade-5: Gross dilation of pelvicalyceswith tortuous and dilated ureter. Endoscopic deflux or Teflon gel injection is used for correcting of VU reflux from grade-2 to grade-5. the gel causes a small mound to form in the submucosal part ofthe distal ureteral orifice resulting in a kind of valve formation preventing the reflux of urine up the ureter. Teflon is now being replaced by Deflux gel as the preferred material for thisprocedure. Ultrasound images of endoscopic Teflon gel injection are courtesy of Dr. ravi Kadasne, MD, UAE.
Liver/ Spleen Involvement In Schistosomiasis
his patient is a known case of Bilharziasis and ultrasound showed hepatosplenomegaly with increased echogenicity of the periportal regions of the portal veins suggesting periportal fibrosis.Fibrosis of the periportal regions of the liver is a known complication of hepatic involvement in schistosomiasis. Ultrasound images are courtesy of Ravi Kadasne, MD, UAE.
Read Also: Antibiotics Given For Bladder Infection
Bilharziasis Of The Urinary Bladder
This patient presented with lower urinary symptoms, dysuria and hematuria. Sonography of the pelvis showed thickening of the wall of the urinary bladder with extensive calcification. Theseultrasound images suggest a diagnosis of schistosomiasis or bilharziasis of the wall of the urinary bladder. Bilharziasis is a parasitic infestation which primarily involves the urinary bladder,though the liver and spleen may also be affected. The disease is caused by contact with water infested with the parasite- schistosoma and is endemic in parts of Africa . Both aboveimages are courtesy of Ravi Kadasne, MD, UAE.
If You Have Liver Disease
Certain diseases can make you more likely to get liver cancer, including:
- Long-term hepatitis B or C — viruses that attack and damage your liver
- Cirrhosis — liver damage that can make scar tissue replace healthy tissue
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease — a buildup of fat in your liver
- Liver diseases youâre born with, like hereditary hemochromatosis
4
Read Also: What Should I Do If I Have A Bladder Infection
Detecting Bladder Cancer With Ct Scans
A CT scan uses x-rays to obtain cross-sectional images of the body. Compared to a general x-ray test, which directs a broad x-ray beam from a single angle, the CT scan uses a number of thin beams to produce a series of images from different angles. These images are then digitally reconstructed to create a single image representing a slice of a particular region in the body.
A CT scan of the kidneys, ureters and bladder is referred to as a CT urogram.
Screening For Bladder Cancer
Early-stage bladder cancer often shows no symptoms, or symptoms that are similar to those of benign conditions such as bladder stones, an enlarged prostate, or urinary tract infection. For this reason it is important to be examined regularly by a physician. If symptoms do appear they should be evaluated promptly so that bladder cancer can be detected in its earliest, most treatable stages.
Doctors may conduct some screening tests during an examination. During a urine cytology the doctor examines urine under a microscope to look for any cancerous or precancerous cells. During another test called a cystoscopy urologists place a cystocope, a flexible instrument consisting of a steerable slender tube with a camera or lens and a light, into the bladder through the urethra. They check the bladder and urethra for signs of cancer, remove any suspicious tissue, and check it under a microscope.
Also Check: What Is The Best Medication For Bladder Infection
Can An Ultrasound Tell If An Ovarian Cyst Is Cancerous
Vaginal ultrasound can help to show whether any cysts on your ovaries contain cancer or not. If a cyst has any solid areas it is more likely to be cancer. Sometimes, in women who are past their menopause, the ovaries do not show up on an ultrasound. This means that the ovaries are small and not likely to be cancerous.
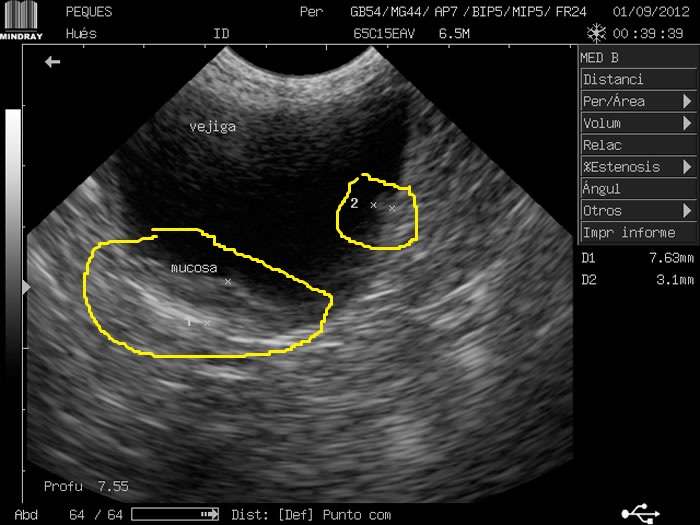
Urinary Bladder Wall Trabeculation In A Case Of Lower Urinary Tract Obstruction
Sonography of the urinary system was done on this elderly male patient having lower urinary tract symptoms. Ultrasound images show evidence of trabeculation of the urinary bladder. This is seen asfolds of hypertrophied bladder mucosa and bladder smooth muscle. There is also evidence of bilateral moderate hydronephrosis . The cause of Lower urinary tract obstruction appears tothe enlarged prostate with intravesical enlargement of the median lobe . The fourth image shows significant post-voiding residual urine in theurinary bladder .
Bladder trabeculation has been graded from 0 to 3 as:
grade 0- no trabeculation.
grade1- mild: area affected is less than 1/2 of the bladder and depth of trabeculation less than 5 mm.
grade2- moderate: area affected is greater than 1/2 of the bladder and depth of trabeculation is 5 to 10 mm.
grade 3- severe: area affected is greater than 1/2 of the bladder and depth of trabeculation is greater than 10 mm.
All images by Joe Antony, MD, using a Toshiba Nemio-XG ultrasound system.
Recommended Reading: Cranberry Juice For Bladder Health
Tests To Find Cancer In The Bladder
The main test to look for bladder cancer is a cystoscopy. This is an examination of the inner lining of the bladder with a cystoscope, a tube with a light and a camera on the end. Other tests can give your doctors more information about the bladder cancer. These may include an ultrasound before the cystoscopy, a biopsy taken during a cystoscopy, and a CT or MRI scan.
Learn more about:
Imaging Techniques To Detect Bladder Cancer
Imaging techniques, which include ultrasound, computed tomography scanning, magnetic resonance imaging and x-ray approaches, provide an important means of assessing the urinary tract, including the kidneys, and play an important role in the detection, diagnosis, and monitoring of bladder cancer.
Imaging is used in both an exploratory setting when another test suggests an anomaly, or to help confirm a diagnosis. The use of a specific imaging procedure linked to bladder cancer is dependent on a number of factors including other irregular test results, local access and availability, pre-existing medical conditions, the characteristics of a suspected tumor or unusual growth , and possible side effects of the procedure.
Irregularities in the upper urinary tract are often assessed with imaging given its accuracy in this setting and an inability to access the region via cystoscopy. In contrast, imaging techniques are less useful for diagnosing tumors in the lower urinary tract. Small and flattened bladder tumors may also be difficult to visualize with imaging.
Its important to note that imaging is generally used in combination with other bladder cancer diagnostic tests to reach a diagnosis. Cxbladder, a genomic urine test, for example, can be used with imaging to increase overall detection accuracy, and to rule out bladder cancer in low risk patients without the need for further invasive procedures.Learn more about Cxbladder
Also Check: Prostate Cancer Spread To Bladder Neck
Detecting Bladder Cancer With Ultrasound
An ultrasound uses high frequency sound waves to produce images of internal organs. Echoes, which are created as sound waves bounce off organs and tissues, produce computer images that provide information on the structure and movement of organs and the blood flow through vessels. An ultrasound does not use radiation or contrast dyes.
What Are The Limitations Of Pelvic Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasound waves are disrupted by air or gas. Therefore, ultrasound is not an ideal imaging technique for the air-filled bowel or organs obscured by the bowel. Ultrasound is not as useful for imaging air-filled lungs, but it may be used to detect fluid around or within the lungs. Similarly, ultrasound cannot penetrate bone, but may be used for imaging bone fractures or for infection surrounding a bone.
Large patients are more difficult to image by ultrasound because greater amounts of tissue weaken the sound waves as they pass deeper into the body and need to return to the transducer for analysis.
Don’t Miss: How To Train A Weak Bladder
How Should I Prepare
Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing. You may need to remove all clothing and jewelry in the area to be examined.
You may need to change into a gown for the procedure.
Ultrasound exams are very sensitive to motion, and an active or crying child can prolong the examination process. To ensure a smooth experience, it often helps to explain the procedure to the child prior to the exam. Bring books, small toys, music, or games to help distract the child and make the time pass quickly. The exam room may have a television. Feel free to ask for your child’s favorite channel.
How Do Ct Scans Help Detect And Monitor Bladder Cancer
A CT urogram can:
- Determine if urinary tract abnormalities are present or if there are enlarged lymph nodes that may contain cancer
- Assess the shape, size, and location of a tumor
- Help to determine the stage of disease
- Be used to guide a biopsy needle to take samples where a bladder cancer is suspected to have spread
Computed tomography scan of the bladder showing bladder cancer .
You May Like: Will Overactive Bladder Go Away
Calculus In Female Urethra
This female patient complained of dysuria for which she underwent routine sonography. This ultrasound image shows the cause of the dysuria- a calculus lodged in the female urethra. Though calculiare often seen in the male urethra due to its length, it is very unusual to sonographically image a calculus in the female urethra. Despite its small size, such a calculus can produce significantdysuria. This ultrasound image is courtesy of Dr. Ravi Kadasne, MD, UAE.
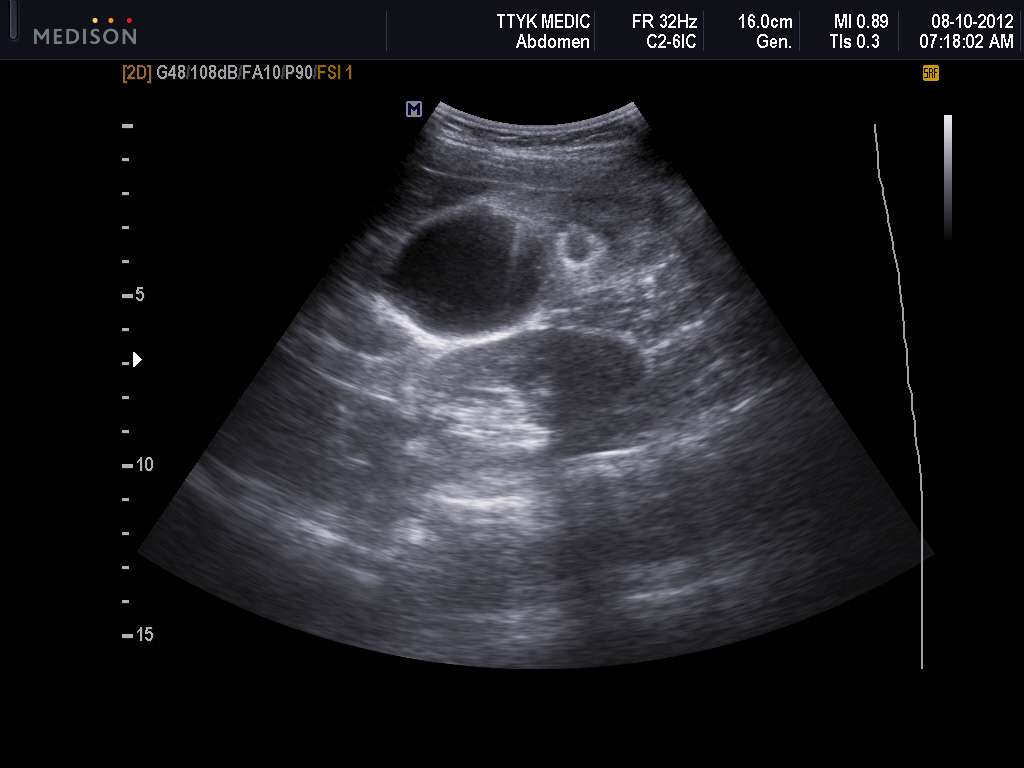
Ultrasound Images Of Urinary Bladder And Both Kidneys
Transabdominal ultrasound images show a polypoid mass in the bladder close to the bladder neck. Is this a bladder mass or an enlarged median lobe of the prostate? Faced with this dilemma wedecided to perform a transrectal ultrasound scan . The kidneys were almost normal but for a small calculus in left kidney.
Recommended Reading: Is Green Tea Good For Bladder Infection
Ureterocele Seen On Trus Imaging
The above ultrasound images show transrectal imaging of the urinary bladder with a small left ureterocele visible. The left ureter also appears mildly dilated . The ureterocele isseen partially distended and also seen in the collapsing stage as the pressure builds up within the sac with resultant evacuation of the urine into the bladder . The jet of urine is seen emanating from the ureterocele sac. All 4 ultrasound images taken via TRUS study using Toshiba Nemio-XG system.
Recent Improvements In The Sonographic Detection Of Ovarian Cancer
Related Searches
ovarian cancer images of bloated stomachcan ovarian cancer be missed on ultrasoundmy first symptoms of ovarian cancerhow to check for ovarian cancer at homeodd symptoms of ovarian cancerbenign vs malignant ovarian cyst ultrasounddifference between ovarian cyst and ovarian cancer
About publicaffairs
You May Like: Can Too Much Sugar Cause A Bladder Infection
How Is The Diagnosis Made
Ultrasound of a bladder showing diffuse disease along the bladder wall
Transitional cell carcinoma cells. Multinucleated neoplastic transitional epithelial cell . Athens Diagnostic Lab, University of Georgia.
TCC is one of the tumor types that can easily seed itself in other locations. For this reason, collecting urine through cystocentesis should not be done to avoid the risk of seeding the tumor cells in the abdomen or skin in the area. Surgery is usually not possible because of the location that these tumors typically occur. They tend to be found in the trigone area of the bladder, which is where the urethra exits the bladder and the ureters enter the bladder. In addition, these tumors often are multifocal within the bladder. In a series of 67 dogs with TCC that underwent surgery, complete tumor-free margins were only obtained in 2 dogs. Of the 2 dogs, one had a relapse in the bladder 8 months later and the other developed metastatic disease.
Why Did My Ultrasound Hurt
The probe will be inserted slowly and carefully, but you may still feel some discomfort as it moves. The probe will make contact with your cervix, which can feel uncomfortable for some women. You will feel some pressure as the probe is moved during the scan to take pictures from different angles.
Also Check: How To Fix Bladder Issues
Why You Have It
Pelvic ultrasound and vaginal ultrasound scans can show whether:
- your ovaries are the right size
- your ovaries look normal in texture
- there are any cysts in your ovaries
Vaginal ultrasound can help to show whether any cysts on your ovaries contain cancer or not. If a cyst has any solid areas it is more likely to be cancer.
Sometimes, in women who are past their menopause, the ovaries do not show up on an ultrasound. This means that the ovaries are small and not likely to be cancerous.
If you have a suspicious looking cyst, your specialist will recommend that you have surgery to remove it. The cyst will be looked at closely in the laboratory.
Risk of malignancy index
Doctors can use a tool called the risk of malignancy index to decide if an abnormality is more likely to be cancer or not. This index combines the results of the ultrasound, CA125 blood levels and menopausal status .
This gives doctors a final score. Women with a high score are referred to a specialist multidisciplinary team . They decide on which further tests and surgery may be necessary.
Your specialist may ask you to have a CT scan to show the ovaries more clearly. Sometimes though, it is not possible to diagnose ovarian cancer for certain without an operation.
If your specialist thinks it unlikely that you have cancer, but cannot completely rule it out, they may ask you to come back for a repeat ultrasound scan in 3 months time, to see if anything has changed.
Living With Bladder Cancer
Cancer is a life-changing experience. And although there’s no surefire way of preventing a recurrence, you can take steps to feel and stay healthy. Eating plenty of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and keeping to modest portions of lean meat is a great start. If you smoke, stop. Limit alcohol to one drink a day for women and up to two drinks a day for men. Daily exercise and regular checkups will also support your health and give you peace of mind.
Don’t Miss: Reasons For Lack Of Bladder Control
How Does Ultrasound Work
An ultrasound machine has 3 key parts: a control panel, a display screen, and a transducer, which usually looks a lot like a microphone or a computer mouse. The transducer sends out sound waves and picks up the echoes. The doctor or ultrasound technologist moves the transducer over the part of the body being studied. The computer inside the main part of the machine analyzes the signals and puts an image on the display screen.
The shape and intensity of the echoes depend on how dense the tissue is. For example, most of the sound waves pass right through a fluid-filled cyst and send back very few or faint echoes, which makes them look black on the display screen. But the waves will bounce off a solid tumor, creating a pattern of echoes that the computer will show as a lighter-colored image.
Risk Factor: Chemical Exposure
Research suggests that certain jobs may increase your risk for bladder cancer. Metal workers, mechanics, and hairdressers are among those who may be exposed to cancer-causing chemicals. If you work with dyes, or in the making of rubber, textiles, leather, or paints, be sure to follow safety procedures to reduce contact with dangerous chemicals. Smoking further increases risk from chemical exposure.
Anyone can get bladder cancer, but these factors put you at greater risk:
- Gender: Men are three times more likely to get bladder cancer.
- Age: Nine out of 10 cases occur over age 55.
- Race: Whites have twice the risk of African-Americans.
Other factors at play include a family history of bladder cancer, previous cancer treatment, certain birth defects of the bladder, and chronic bladder irritation.
Don’t Miss: Low Grade Bladder Cancer Recurrence