Nursing Care Plan For Urinary Retention 1
Nursing Diagnosis: Urinary Retention related to mechanical blockage due to enlarged prostate, secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia , as evidenced by dribbling of urine, incontinence, frequent urination and hesitation, incomplete bladder emptying, and presence of residual urine
Desired Outcomes:
- The patient demonstrates no perceptible bladder distention and is able to urinate sufficiently.
- The patient will demonstrate improved urinary elimination, as evidenced by fewer than 50 mL postvoid residuals , absence of overflow, and dribbling of urine.
Nursing Care Plan for Urinary Retention 2
Nursing Diagnosis: Urinary Retention related to lack of motor control, secondary to Guillain Barre syndrome , as evidenced by ascending paralysis and bladder dysfunction
Desired Outcome: The patient will demonstrate regular patterns of urine elimination.
Nursing Care Plan for Urinary Retention 3
Nursing Diagnosis: Urinary Retention related to mechanical trauma, secondary to Hysterectomy or TAHBSO, as evidenced by urine production that is little, frequent, and/or non-existent, bladder distention, overflow incontinence, and feeling of bladder fullness.
Desired Outcome: The patient will empty his/her bladder on a regular and thorough basis.
Nursing Care Plan for Urinary Retention 4
Desired Outcomes:
- The patient will be able to empty his/her bladders to their satisfaction.
- The postvoid residuals of the patient will be within typical ranges.
Nursing Care Plan for Urinary Retention 5
The Advantages And Precautions Of Bladder Scanning
The main benefits of bladder scanning compared with urethral catheterisation are outlined in Box 2. However, while there are many advantages, the use of a bladder scanner may not be appropriate in all situations, including if:
- The patient is morbidly obese
- There is severe abdominal scarring
- Abdominal staples or tension sutures are in situ
- There is an infected abdominal wound present.
The manufacturers recommendations should be checked for use in pregnant women and studies indicate that bladder scanning in children aged < 36 months is unreliable and should be used with caution . Bladder volumes were underestimated and Wyneski et al stated that significant volumes in neonates were undetected in some scanning machines.
Caution should also be taken for women in the early postpartum period – Lukasse et al indicated that when certain brands of scanners are compared, sometimes they give varying results.
Caution should be taken as this could hinder identification of the true anatomical detail of the bladder. In general, the use of bladder scanners does not result in any complications but one study did report potential adverse effects including skin irritation and allergic reaction to gel and padding. However, bladder scanners themselves are deemed very safe and no epidemiological studies have shown human risks .
Box 2. Benefits and advantages of bladder scanning compared with catheterisation
- No risk of urinary tract infection related to the procedure
- Non-invasive
How Is Urinary Retention Treated
Treatment for urinary retention can depend on whether you have the acute form or the chronic form, as well as the cause of the condition. For the acute form, a catheter is put into the urethra to drain the bladder.
Treatment of the chronic form or the acute form that becomes chronicwill depend on the cause.
Medications for enlarged prostate: For men with an enlarged prostate, certain drugs may be used to try and open it up or shrink it. These include alpha-blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors . Also, procedures or surgery to open up the prostate may be tried.
Procedures for enlarged prostate: Many procedures are available when this problem is due to an enlarged prostate. Office-based treatments can be done with just local anesthetic only. These include water vapor therapy and prostatic urethral lift .
There are also several surgeries done under general anesthesia which are available. These include shaving down the inside of the prostate and opening up the prostate with a laser . A laser can also be used to carve out the entire enlarged portion of the prostate through the urethra , or this part of the prostate can be removed through the belly . All of these procedures can be effective in opening up the blockage.
Treatment for nerve issues: If the retention is due to a nerve-related issue, you may need to use a catheter on yourself at home.
You May Like: Natural Supplements For Bladder Health
Symptoms Of Urinary Retention
There are a few telltale signs that urinary retention may complicate a lifestyle, or be an indicator of declining health. The largest symptom is an inability to completely empty the bladder. The other large symptom is an inability to urinate. Common symptoms include frequent urination, abdominal discomfort, and pressure, a lessened urge to urinate, trouble detecting the need to urinate, frequently needing to urinate, weak dribble or stream of urine, and waking up to urinate a few times each night.
Simple Ultrasound Measure Can Diagnose Postoperative Urinary Retention
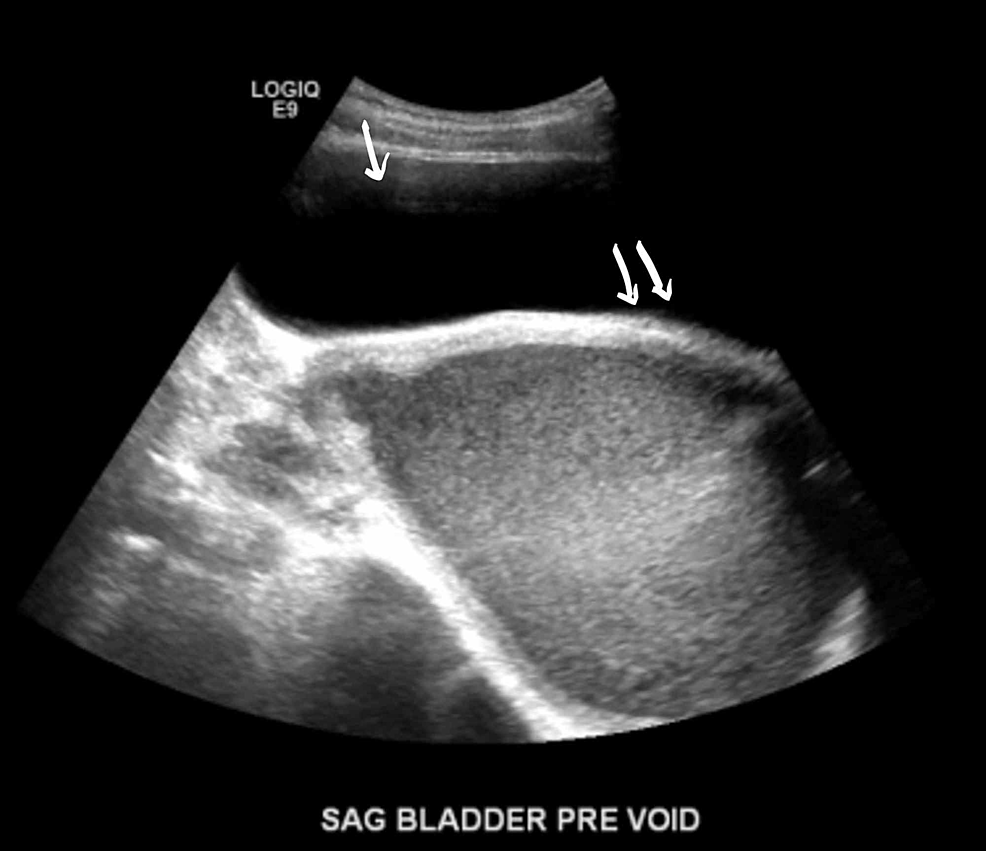
Test Provides Quick, Inexpensive Alternative for Assessing Common Complication, Reports Anesthesia & Analgesia
Newswise February 5, 2015 In patients who don’t resume normal urination after surgery, a simple ultrasound test can accurately diagnose the common problem of postoperative urinary retention , reports a study in Anesthesia & Analgesia.
Using ultrasound to measure bladder diameter provides a quick and inexpensive test for POUR, according to the new research by Dr Aurélien Daurat and colleagues of Lapeyronie University Hospital, Montpelier, France. The researchers believe their simplified approach may obviate the need for costly automated devices for measuring bladder volume.
Quick Ultrasound Measure of Bladder DiameterDr Daurat and coauthors evaluated their simplified approach to ultrasound bladder measurement in 100 patients who were considered at risk of POUR because they were unable to void after orthopedic surgery. Postoperative urinary retention is a common side effect after surgery and general anesthesia. If the bladder isn’t emptied, POUR can prolong the patient’s hospital stay and lead to potentially serious complications.
In the recovery room, all patients underwent a single ultrasound measurement of bladder diameter in the transverse dimension . These measures were obtained by nurses using a pocket-sized portable ultrasound device.
Don’t Miss: Medication To Treat Bladder Infection
Bladder Scanners And Urinary Problems
A bladder scanner is used primarily as a diagnostic aid to identify incomplete emptying, urinary retention and determine bladder volume in adults and children with urinary problems .
Urinary problems could result from:
- Neurological conditions, such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinsons disease, cerebrovascular accident, spinal injuries, spina bifida, diabetes
- Urethral obstruction due to various reasons including benign prostatic hypertrophy, urethral strictures, prostate cancer, tumours, prolapse, urethral calculi, foreign bodies, faecal impaction
- Trauma, surgery or surgical manipulation of the bladder nerves
- Anaesthetic agents such as spinal agents
- Medication such as anticholinergics, antihypertensives, antispasmodics, antihistamines
- Recreational/illicit drugs.
Bladder emptying can also be affected by:
- A lack of privacy
- Requests to void on command
- Voiding with a partially or overfilled bladder
- Pain .
The clinical indications for using a bladder scanner are highlighted in Box 1.
Bladder scans are non-invasive. Portable scanners usually comprise a base unit with display screen and a scanner head . The scanner emits ultrasound waves, which pulse through the body. The intensity of the returning echo of the sound waves and the time taken to receive a signal is measured to give either a two- or three-dimensional image of the bladder . The returning echo appears as a cross-section of the bladder on the screen and automatically calculates bladder and PVR measurements .
Post Void Residual Urine
Post-void residual urine is defined as the amount of urine left in the bladder at the end of micturition. It can be measured by catheterization or non-invasively by ultrasonography. PVR varies in a given individual, hence multiple measurements are often necessary. There is no evidence-based maximum volume that is considered normal.23 The Agency for Health Care Policy and Research guidelines state that, in general, a PVR less than 50 ml is adequate bladder empting and a PVR more than 200 ml is inadequate emptying.24
Charles Carter, … Robert Holleman, in, 2012
You May Like: Tissue Salts For Overactive Bladder
Signs And Symptoms Of Urinary Retention
- Bladder distention
- 2 hours of decreased or non-existent urination
- Frequent urination
- The feeling of bladder fullness and urgency
- Presence of residual urine
- Inability to empty the bladder
- Discomfort in the abdomen
A variety of factors can cause urinary retention. Primarily, these may include:
- Urinary incontinence
- Presence of swelling or edema
- Disruption in the urinary and nervous system communication due to nerve problems.
- Medications that are taken for other existing ailments
- Surgery-related complications and side effects of the prescribed post-operative medications.
Other causes:
- Antihistamines
- Muscle relaxant drugs
- Drugs for hormones
Urinary Retention Nursing Care Plans Diagnosis And Interventions
Urinary Retention NCLEX Review and Nursing Care Plans
Urinary retention, also referred to as ischuria, can be defined as a medical condition in which the bladder does not drain completely after urination. Individuals who are sedentary, immobile, or strictly confined to bed rest may suffer from urinary retention and incontinence.
Additionally, people who have medical disorders such as BPH, hysterectomy, disk surgery, or those taking medications may also be at risk of developing urinary retention and bladder distention since these medications may interfere with the nerve signals necessary to relax the sphincters.
Untreated urinary retention can lead to bladder injury and renal failure hence, it is critical to address urinary retention as soon as possible to avoid further complications.
Don’t Miss: How Long Can You Live With Aggressive Bladder Cancer
What Is An Ultrasound
An ultrasound scan is a medical test that uses high-frequency sound waves to create live images from the inside the body. Also called a sonogram or sonography, ultrasounds let doctors see the bodys soft tissues, which X-rays cant do.
Doctors order ultrasounds for many reasons, such as to look for the causes of pain, swelling, and infection. Ultrasound scans are safe and painless.
The Clinical Importance Of Bladder Scanners In Urinary Retention
Urinary retention is a disorder in which a person cannot fully empty their bladder. Someone who has urinary retention may be able to urinate, but not completely able to empty their bladder. This condition needs immediate medical attention and can be considered a symptom of a life-threatening condition. Bladder scanners are helpful tools in which medical professionals can evaluate the health of their patient, and help prevent unnecessary procedures. Before portable bladder scanners, physicians and clinicians had to resort to catheterization which was not always needed. Now with the frequent use of bladder scanners, nurses can help better determine the need for catheterization and cystoscopies. Keep reading to learn more about the importance of releasing patients with empty bladders.
You May Like: Why Do I Get Bladder Infection After Intercourse
Clinical Indicators For A Bladder Scan
For the clinician, these are:
- Part of a continence assessment
- To confirm urinary retention
- To identify incomplete bladder emptying
- To assess post void residual urine volume
- In a trial without catheter , to prevent bladder distension
- To assess bladder volume if indwelling catheter not draining
- To determine bladder volume in a client with decreased urine output.
For the patient/client, these are:
- In a bladder retraining program, it determines the need to void based on bladder volume and not time
- To assess effectiveness of mechanical bladder emptying
- To identify level of bladder sensation related to bladder volume
- To identify if adverse side effects of urinary retention are present such as with medications, e.g. anticholinergics
- As a standard investigation for at-risk groups when presenting with urinary problems
Why Are Bladder Ultrasounds Done
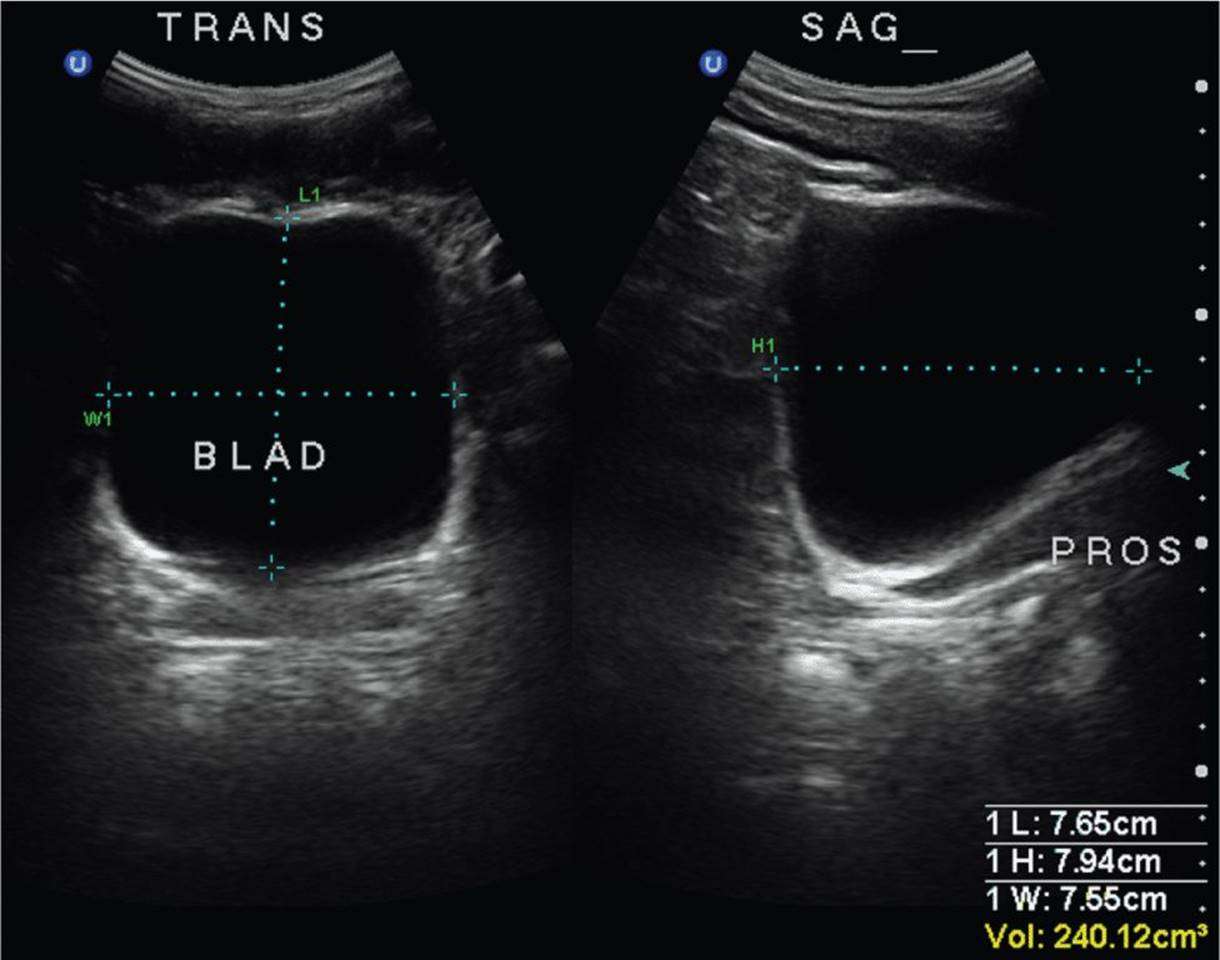
Doctors order bladder ultrasounds when there’s a concern about bladder problems, such as trouble with peeing or daytime wetting.
A bladder ultrasound can show how much urine the bladder holds when it’s full and whether someone completely empties the bladder when peeing. It can show if theres anything unusual about the bladder, such as its size, the thickness of the bladder walls, and if there are blockages or kidney stones. A bladder ultrasound is often done along with a kidney ultrasound.
The doctor may ask that your child drink lots of fluids before the exam so that their bladder is full. The first image is done while your childs bladder is full. Then, your child will be asked to pee before more images are recorded.
Also Check: Can A Bladder Infection Cause Dizziness
Complications Of Urinary Retention
Normally, urine is a sterile fluid and the normal flow of urine prevents bacteria from infecting the urinary tract. With urinary retention, the abnormal urine flow gives bacteria, at the opening of the urethra, a chance to infect the urinary tract. This is when you can get a urinary tract infection . Bladder or kidney damage can also occur. If the bladder becomes stretched too far for long periods of time, the muscles can become permanently damaged and lose their ability to contract. In some cases, the retention can also cause urine to flow backward into the kidneys. The backward flow can cause damage or even scar the kidney.
Postvoid Residual Volume :
After micturition, the length, width and height of the bladder are recorded in sagittal and horizontal planes . The postvoid residual volume is calculated using the formula:
Various factors ranging from 0.50.7 are found in the literature. Depending on the bladder shape, considerable inaccuracy is possible. Normally there is no residual urine. PVR volumes over 100ml are considered significant in adults. In children, a PVR volume exceeding 10% of the urinary bladder capacity is pathological . Please see the following table for the differential diagnosis of PVR.
Causes of postvoid residual urine and urinary retention.
| DD urinary retention | |
| Diseases of the prostate | |
| Urethral strictures, urethral valves, female urethral cancer and male urethral cancer, foreign bodies, phimosis. | |
| Diseases of the urinary bladder | Neurogenic bladder disorders, drugs , pelvic surgery, diabetes mellitus. |
Don’t Miss: Why Do I Get Bladder Infections So Easily
Urinary Retention In Adults: Diagnosis And Initial Management
BRIAN A. SELIUS, DO, and RAJESH SUBEDI, MD, Northeastern Ohio Universities College of Medicine, St. Elizabeth Health Center, Youngstown, Ohio
Am Fam Physician. 2008 Mar 1 77:643-650.
Urinary retention is the inability to voluntarily urinate. Acute urinary retention is the sudden and often painful inability to void despite having a full bladder.1 Chronic urinary retention is painless retention associated with an increased volume of residual urine.2 Patients with urinary retention can present with complete lack of voiding, incomplete bladder emptying, or overflow incontinence. Complications include infection and renal failure.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
In men with benign prostatic hyperplasia, initiation of treatment with alpha blockers at the time of catheter insertion improves the success rate of trial of voiding without catheter.
A = consistent, good-quality patient-oriented evidence B = inconsistent or limited quality patient-oriented evidence C = consensus, disease-oriented evidence, usual practice, expert opinion, or case series. For information about the SORT evidence rating system, see page 579 or .
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
In men with benign prostatic hyperplasia, initiation of treatment with alpha blockers at the time of catheter insertion improves the success rate of trial of voiding without catheter.
Bladder Ultrasound Made Easy: Step
Primary Authors: Jade Deschamps, Vi Dinh Co-authors: Jessica Ahn, Satchel Genobaga, Annalise Lang,Victor Lee, Reed Krause, Devin Tooma, Seth White. Oversight, Review, and Final Edits by Vi Dinh .
One of the most important and underrecognized organs is the bladder. We assess it each day in our clinical practice using urine output, urinalysis, and physical exam. Even newer technology such as the Verathon BladderScan can significantly under or overestimate bladder volume from our experience.
Using Point of Care Ultrasound to evaluate the bladder is the easiest, quickest, and most accurate way to directly visualize the bladder at the bedside. Bladder ultrasound allows you to assess bladder volume, bladder obstruction, foley catheter placement/malfunctions, and other bladder pathology such as bladder stones, ureteral jets, and bladder masses.
In this post we will show you how to use Point of Care Bladder Ultrasound to:
Don’t Miss: I Keep Getting Bladder Infections
Transabdominal Ultrasonography Of The Prostate
The prostate is scanned through the filled bladder. After determining the length, width and height in two planes, the volume is calculated using the formula prostate volume = Length × Width × Height × 0.5. The transabdominal measurement method offers advantages in very large prostate glands due to the larger field of vision . In addition, transabdominal ultrasonography of the prostate easily identifies enlarged median lobes or prostatic cysts.
Measurement of prostate size with transabdominal sonography:
Measuring Post Void Residual Urine Volume
- A PVR of below 100ml is considered normal for any adult. This PVR may be higher in a frail older adult and cause no symptoms
- If the PVR is between 100-200ml give advice to promote more effective bladder emptying sit down with feet well supported, take time, lean forward, use double voiding. Arrange to repeat scan in 1-2 weeks.The bladder will function more effectively if the correct toilet posture and technique is followed
- If the PVR is over 200ml discuss the scan results and the individuals bladder diary information with a medical/specialist practitioner
- A PVR of 250ml is more significant if the voided volumes are low, 80-100ml than if they are higher 200-250ml because it may indicate an outflow obstruction and/or underactive bladder
- Urgent discussion is required for high post void residuals 500-1000+ ml
- If the bladder stretches to hold volumes over 1000ml the detrusor muscle is very likely to become permanently damaged, resulting in an atonic bladder.
Clinical Practice Point. Note the 1000ml is the volume voided + the residual volume. i.e. if the person voids 400ml and has a PVR of 740ml, their bladder is holding 1140ml.
Also Check: Drugs To Treat Bladder Infection