Risk Factors For Bladder Cancer
There are some things that can make you more likely to develop bladder cancer. These are called risk factors and they include:
- smoking chemicals in cigarettes can cause bladder cancer, so if you smoke, your risk is up to 3 times that of a non-smoker
- age most people with bladder cancer are over 60 years of age
- being male men are around 3 times more likely than women to develop bladder cancer
- chemicals being in contact with certain chemicals for a long period of time, like aromatic amines, benzene products and aniline dyes, which have been linked to bladder cancer
- chronic infections frequent infections of the bladder over a long period of time
- previous cancer treatments some types of radiation therapy around the pelvis, and the chemotherapy drug cyclophosphamide
- family history a first degree relative with bladder cancer increases risk up to nearly 2 times higher than the general population.
Having these risk factors doesnt mean you will develop bladder cancer. Often there is no clear reason for getting bladder cancer. If you are worried about your risk factors, ask your doctor for advice.
Why Are Men More Likely To Get Bladder Cancer Than Women
Men are more likely to develop bladder cancer than women are. Exposure to certain chemicals. Your kidneys play a key role in filtering harmful chemicals from your bloodstream and moving them into your bladder. Because of this, its thought that being around certain chemicals may increase the risk of bladder cancer.
Bladder Cancer Treatment: Surgery
Transurethral Resection
Early-stage cancers are most commonly treated by transurethral surgery. An instrument with a small wire loop is inserted through the urethra and into the bladder. The loop removes a tumor by cutting or burning it with electrical current, allowing it to be extracted from the bladder.
Partial and Radical Cystectomy
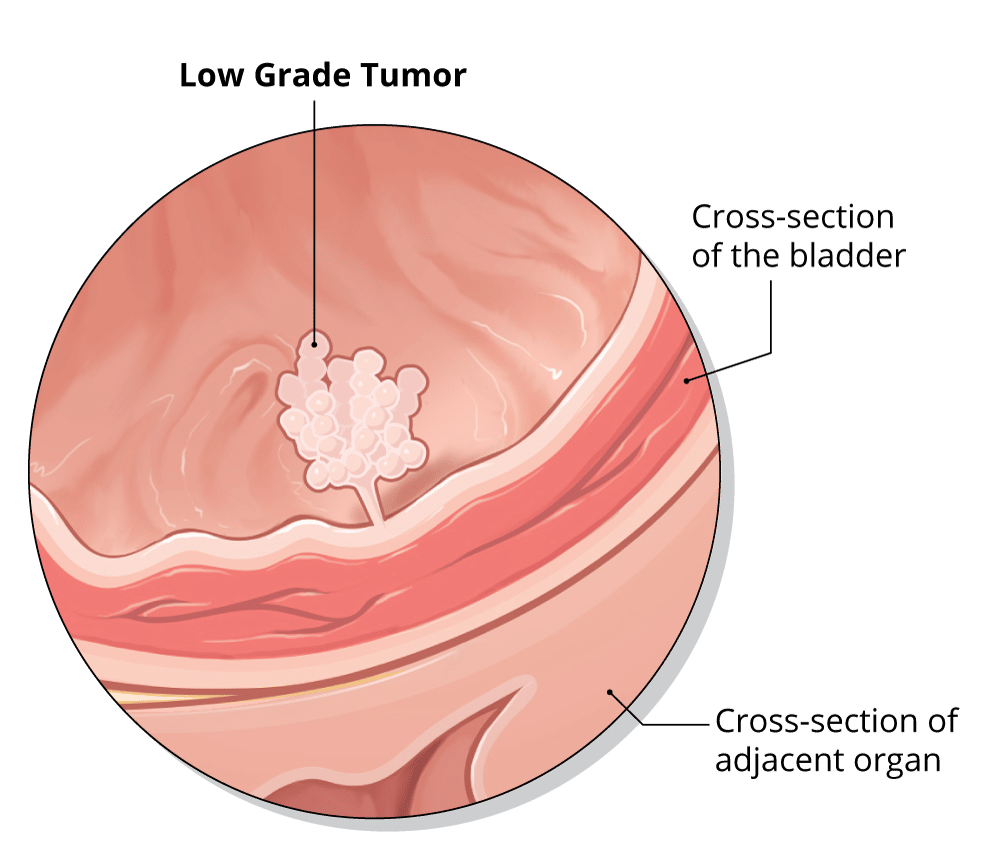
Partial cystectomy includes the removal of part of the bladder. This operation is usually for low-grade tumors that have invaded the bladder wall but are limited to a small area of the bladder. In a radical cystectomy, the entire bladder is removed, as well as its surrounding lymph nodes and other areas that contain cancerous cells. If the cancer has metastasized outside of the bladder and into neighboring tissue, other organs may also be removed such as the uterus and ovaries in women and the prostate in men.
Recommended Reading: How To Do Kegel Exercises For Overactive Bladder
Don’t Miss: Can Chronic Utis Cause Bladder Cancer
Surgical Removal Of Bladder Tumors
The main option is to perform surgery to remove the cancerous bladder tumors along the bladder wall of your cat. Surgical removal is used on a case-by-case basis, so its hard to say if your cat will need to go under anesthesia and endure surgery. The decision to surgically remove the cancer is less likely to be made for elderly cats and incredibly young kittens alike because the operation is risky for cats at both ends of the age spectrum.
You May Like: How To Control My Bladder
Smoking Can Affect The Risk Of Bladder Cancer
Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesnt mean that you will not get cancer. Talk to your doctor if you think you may be at risk for bladder cancer.
Risk factors for bladder cancer include the following:
- Past treatment with radiation therapy to the pelvis or with certain anticancer drugs, such as cyclophosphamide or ifosfamide.
- Taking Aristolochia fangchi, a Chinese herb.
- Drinking water from a well that has high levels of arsenic.
- Drinking water that has been treated with chlorine.
- Having a history of bladder infections, including bladder infections caused by Schistosoma haematobium.
- Using urinarycatheters for a long time.
Older age is a risk factor for most cancers. The chance of getting cancer increases as you get older.
Don’t Miss: How To Find Out If You Have Bladder Cancer
Arsenic In Drinking Water
Drinking water containing arsenic is associated with a greater risk of bladder cancer. However, this is not a large concern in the U.S. Where you live, as well as if you drink well water, or public system water will determine your risk. Most public water systems meet standards for low arsenic content.
Understanding The Statistics: Cancer Survival
It is important to remember that all cancer survival numbers are based on averages across huge numbers of people. These numbers cannot predict what will happen in your individual case.
Survival rates will not tell you how long you will live after you have been diagnosed with bladder cancer. But, these numbers can give you an idea of how likely your treatment will be successful. Also, survival rates take into account your age at diagnosis but not whether you have other health conditions too.
You May Like: Can A Prolapsed Bladder Cause Uti
How Does Recurrence Of Bladder Cancer Affect Survival Rate
Recurrent bladder cancer is cancer that has returned after initial treatment. Recurrence rates for bladder cancer depend on the stage of the original tumor, with 5-year recurrence rates of approximately 65% in patients with non-invasive or in situ tumors and 73% in patients with slightly more advanced disease at first diagnosis.16
Many patients with non-invasive bladder cancer have recurrences that are typically not life threatening however, the prognosis is generally worse if the disease has spread into deeper layers of the bladder wall or beyond to the lymph nodes or other organs.
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- What treatment do you think is best for me?
- Whats the goal of this treatment? Do you think it could cure the cancer?
- Will treatment include surgery? If so, who will do the surgery?
- What will the surgery be like?
- How will I pee after surgery?
- Will I have other types of treatment, too?
- Whats the goal of these treatments?
- What side effects could I have from these treatments?
- Is there a clinical trial that might be right for me?
- What about treatments like special vitamins or diets that friends tell me about? How will I know if they are safe?
- What should I do to be ready for treatment?
- Is there anything I can do to help the treatment work better?
- Whats the next step?
Recommended Reading: Pure Cranberry Juice For Bladder Infection
How Does Bladder Cancer Spread
Bladder cancer usually begins in the cells of the bladder lining. In some cases, it may spread into surrounding bladder muscle. If the cancer penetrates this muscle, it can spread to other parts of the body, usually through the lymphatic system.
If bladder cancer spreads to other parts of the body, such as other organs, it’s known as metastatic bladder cancer.
New And Experimental Treatments
Several new treatments may prove useful in treating bladder cancer. Photodynamic therapy, used in early stage cancers, uses a laser light to activate a chemical that kills cancer cells. Some gene therapies use lab-created viruses to fight cancer. And targeted therapies aim to control the growth of cancer cells. You may be eligible to participate in a clinical trial of these or other cutting-edge treatments.
21) Carol & Mike Werner / Visuals Unlimited / Corbis
American Urological Association: Bladder Cancer.
American Urological Association Foundation: Hematuria.
Journal of the American Medical Association: Association Between Smoking and Risk of Bladder Cancer Among Men and Women.
Occupational & Environmental Medicine: Bladder cancer among hairdressers: a meta-analysis.
British Journal of Cancer: Occupation and bladder cancer: a cohort study in Sweden.
National Cancer Institute: Staging,Bladder Cancer Treatment,Drugs Approved for Bladder Cancer,SEER Stat Fact Sheets: Bladder.
NIH Research Matters: Smoking and Bladder Cancer.
ScienceDaily: Cigarette Smoking Implicated in Half of Bladder Cancers in Women Bladder Cancer Risk from Smoking Is Higher Than Previously Estimated, Study Confirms.
Stanford Cancer Institute: Information About Bladder Cancer.
World Health Organization: Tobacco Free Initiative Cancer.
You May Like: Small Cell Carcinoma Bladder Cancer
There Are Different Types Of Treatment For Patients With Bladder Cancer
Different types of treatment are available for patients with bladder cancer. Some treatments are standard , and some are being tested in clinical trials. A treatment clinical trial is a research study meant to help improve current treatments or obtain information on new treatments for patients with cancer. When clinical trials show that a new treatment is better than the standard treatment, the new treatment may become the standard treatment. Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
Patients Can Enter Clinical Trials Before During Or After Starting Their Cancer Treatment
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCIs clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Don’t Miss: How To Control My Bladder
Sexuality And Bladder Cancer
Having bladder cancer and treatment can change the way you feel about yourself, other people, relationships and sex. These changes can be very upsetting and hard to talk about. Doctors and nurses are very understanding and can give you support. You can ask for a referral to a counsellor or therapist who specialises in body image, sex and relationships.
Recommended Reading: Natural Remedies To Cure Bladder Infection
Cancer That Has Spread To The Bladder
Sometimes cancer that has started elsewhere in the body can spread to the bladder. This can happen with prostate, rectum, ovary, cervix and womb cancer for example.
Cancers that have spread from somewhere else in the body are called secondary cancers. The cancer cells are the same type as the first cancer. So is the treatment.
If you have cancer that has spread to the bladder, you need to go to the section about your primary cancer.
-
Cancer and Its Management J Tobias and D HochhauserWiley Blackwell, 2015
-
A M Kamat and othersThe Lancet, 2016. Volume 388, Pages 276 -2810
-
AJCC Cancer Staging Manuel American Joint Committee on CancerSpringer, 2017
-
Bladder cancer: diagnosis and management of bladder cancerNational Institute of Health and Clinical Excellence, 2015
Read Also: How To Prevent Overactive Bladder
Side Effects Of Treatment For Bladder Cancer
All cancer treatments can have side effects. Your treatment team will discuss these with you before you start treatment. Talk to your doctor or nurse about any side effects you are experiencing. Some side effects can be upsetting and difficult, but there is help if you need it.
or email to speak with a caring cancer nurse for support.
Read Also: Bristol Myers Squibb Bladder Cancer
Papillary Or Flat Tumors
Papillary tumors grow out from the inner lining toward the hollow center of the bladder, in slim finger-shaped growths. These are often non-invasive, because they grow outward from the bladder lining rather than inward deeper into the bladder walls. One type of slow growing, non-invasive papillary bladder cancer is called papillary urothelial neoplasm of low malignant potential .
Flat bladder tumors do not grow into the hollow part of bladder, but grows in a flat shape instead. If a flat tumor has not grown outside of the urothelium layer of cells, then it is non-invasive. If it has grown deeper into the bladder wall, then it is called invasive.
Also Check: A Catheter Is Kept In The Bladder By
Transurethral Resection Of A Bladder Tumour
If abnormalities are found in your bladder during a cystoscopy, you should be offered an operation known as TURBT. This is so any abnormal areas of tissue can be removed and tested for cancer .
TURBT is carried out under general anaesthetic.
Sometimes, a sample of the muscle wall of your bladder is also taken to check whether the cancer has spread, but this may be a separate operation within 6 weeks of the first biopsy.
You should also be offered a dose of chemotherapy after the operation. This may help to prevent the bladder cancer returning if the removed cells are found to be cancerous.
See treating bladder cancer for more information about the TURBT procedure
What Are The Risks Of Bladder Cancer
No single factor is directly connected to bladder cancer, but factors that can increase the risk include:
- Age: Bladder cancer typically affects people age 55 and older.
- Smoking: Carcinogens from tobacco smoke come in contact with the lining of the bladder. Smokers are three times as likely as non-smokers to get bladder cancer.
- Family history: There is evidence that bladder cancer may have a genetic component.
- Industrial chemicals: Chemicals known as aromatic amines are often used in the dye industry. Workers who have daily exposure to them, such as painters, machinists and hairdressers, may be at a higher risk for bladder cancer.
- Drinking contaminated water: This includes water that has been treated with chlorine or drinking water with a naturally high level of arsenic, which occurs in many rural communities in the United States,.
- Taking certain herb: Supplements such as Aristolochia fangchi, a Chinese herb, sometimes used for weight loss has been linked to higher rates of bladder cancer.
Read Also: Kidney Bladder Or Prostate Cancer Symptoms
Is A Mass In The Bladder Always Cancer
If youve been told that you have a mass in your bladder, you need to have it evaluated by experts uniquely qualified to determine whether or not it is cancer.
While there are several types of benign masses that can grow in the bladder, these are uncommon and account for fewer than 1% of bladder masses,â says Khurshid Guru, MD, Chair of Roswell Parks Department of Urology.
What Happens When A Dog Gets Bladder Cancer
In the early stages of urinary bladder cancer, there are usually no serious signs and symptoms. As the disease progresses, it starts to show signs identical to those of a urinary tract infection. The signs include frequent urination, painful urination, bloody urine, producing larger volumes of urine, and more accidents in the house.
Symptoms will improve with anti-bacterial treatment but will soon reemerge. In the event of a bladder infection whose signs persist after treatment, you should seek medical advice and ask your vet to test for bladder cancer.
If treatment for bladder cancer doesnt start in time, it will start to spread to other organs outside the urinary system like the lungs, regional lymph nodes, bones, and others. Over 20% of bladder tumors are caught after metastasis which further worsens the prognosis.
Also Check: Is Bladder Cancer Fast Growing
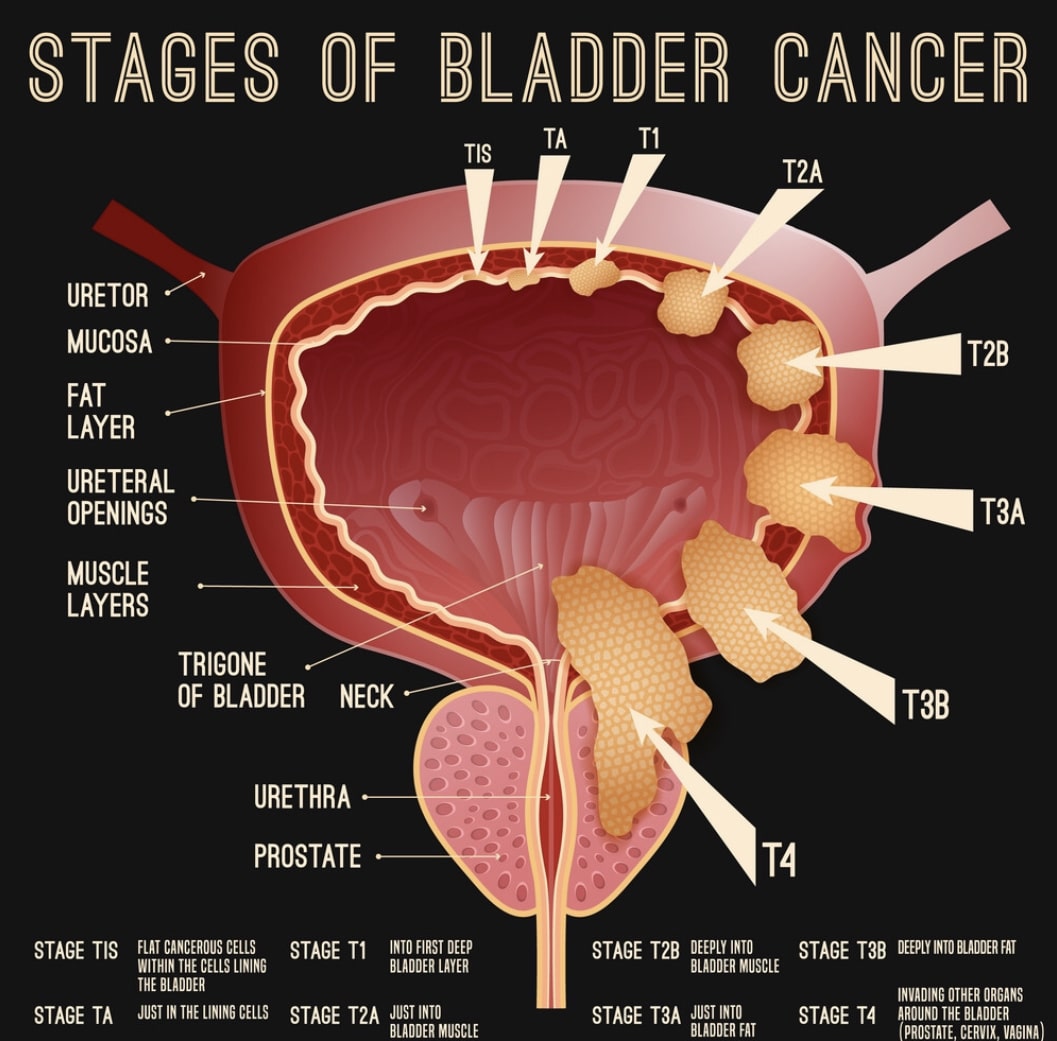
Treating Stage I Bladder Cancer
Stage I bladder cancers have grown into the connective tissue layer of the bladder wall , but have not reached the muscle layer.
Transurethral resection with fulguration is usually the first treatment for these cancers. But its done to help determine the extent of the cancer rather than to try to cure it. If no other treatment is given, many people will later get a new bladder cancer, which often will be more advanced. This is more likely to happen if the first cancer is high-grade .
Even if the cancer is found to be low grade , a second TURBT is often recommended several weeks later. If the doctor then feels that all of the cancer has been removed, intravesical BCG or intravesical chemo is usually given. If all of the cancer wasnt removed, options are intravesical BCG or cystectomy .
If the cancer is high grade, if many tumors are present, or if the tumor is very large when its first found, radical cystectomy may be recommended.
For people who arent healthy enough for a cystectomy, radiation therapy might be an option, but the chances for cure are not as good.
Treatment For Bladder Cancer
Treatment for bladder cancer depends on how quickly the cancer is growing. Treatment is different for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer and muscle-invasive bladder cancer. You might feel confused or unsure about your treatment options and decisions. Its okay to ask your treatment team to explain the information to you more than once. Its often okay to take some time to think about your decisions.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Stop Bladder Leakage
Bladder Cancer Clinical Trials
What about Clinical Trials?
You may hear about clinical trials for your bladder cancer. Clinical trials are research studies that test if a new treatment or procedure is safe and effective.
Through clinical trials, doctors find new ways to improve treatments and the quality of life for people with disease. Trials are available for all stages of cancer. The results of a clinical trial can make a major difference to patients and their families. Please visit our clinical trials research webpage to learn more.
You May Like: How Do You Treat A Bladder Infection
In The World Of Bladder Tumors: Size Does Matter
Article type: Research Article
Authors: Loloi, Justina | Allen, Jordan L.a | Schilling, Amberb | Hollenbeak, Christopherc | Merrill, Suzanne B.a | Kaag, Matthew G.a | Raman, Jay D.a*
Affiliations: Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, Penn State Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, The Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine, Hershey, PA, USA | Division of Outcomes Research and Quality, Department of Surgery, The Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine, Hershey, PA, USA | Department of Health Policy and Administration, The Pennsylvania State University, State College, PA, USA
Correspondence: Correspondence to: Jay D. Raman, M.D., F.A.C.S., Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, Division of Urology, 500 University Drive, BMR Building c4830B, Hershey, PA 17033-0850, USA. Tel.: +1 717 531 6979 Fax: +1 717 531 4475 E-mail: .
Keywords: Bladder, TURBT, cancer, tumor, size, resection, complication, postoperative
DOI: 10.3233/BLC-200273
Journal: Bladder Cancer, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 195-200, 2020
Abstract
You May Like: Will Azo Help A Bladder Infection