When To See Your Doctor
Itâs time to get things checked out if:
- You have to go to the bathroom a lot more than usual, and often canât hold in your urine until you get to the toilet
- You leak when you sneeze, cough, or even stand up
- You leak at random times, even if you didnât cough or sneeze
- You feel like your bladder still has urine in it, even after you go
- Your stream of urine is weak
- You have to strain when you urinate
- It hurts to urinate
- You feel pressure in your lower abdomen
Show Sources
Treatments For Male Urinary Incontinence
There are a number of treatment approaches for urinary incontinence to improve bladder control for men, depending on how severe it is and its underlying cause. A combination of treatments might be necessary. There are several categories of medications to treat overactive bladder and relax the bladder muscles and medications for men with incontinence caused by an enlarged prostate. Neuromodulation techniques include percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation, Botox injections in the bladder, and Interstim implantation. When indicated, surgical procedures are available to help alleviate incontinence issues.
Why Incontinence Pads Help
Lots of men balk at the idea of using pads or disposable undergarments. But not only do they stop leaks, they can protect skin from irritation and block odor. Best of all, they can help you regain confidence. You may be surprised at the number of product options. Unlike the big, bulky “adult diapers” you might imagine, today’s incontinence pads and undergarments are designed to be comfortable and unnoticeable.
Also Check: Why Do I Get Recurring Bladder Infections
Why Is It So Difficult To Talk About Bladder Control
Millions of men and women suffer from loss of bladder control. Bladder incontinence is twice as common in women because pregnancy, childbirth and menopause can affect pelvic muscle strength and damage nerves that control the bladder.
Many people feel embarrassed or ashamed to talk about their bladder control problems, yet many effective treatments are available. Your doctor may not ask about urinary function during an exam, so you should speak up if you are struggling with bladder control issues.
What The Caregiver Can Do

- Encourage or help the patient with appropriate skin care after using the bathroom. Use warm water and pat the area dry.
- Help the patient keep a diary that records specific foods or drinks that may affect how frequently the patient goes to the bathroom.
- Help the patient maintain a bladder or bowel plan.
- Encourage the patient to go to the bathroom at consistent time frames during the day, like after a meal.
- Encourage regular daily exercise, as permitted by the health care team.
Also Check: Why Is My Bladder Not Emptying
What Are The Causes Of Loss Of Bladder Control
Short-term loss of bladder control may come from urinary tract infections, vaginal infections, constipation, and some medications. However, if your loss of bladder control lasts longer than a week, tell your doctor.
Long-term loss of bladder control may be caused by:
- Weak muscles in the bladder
- Overactive bladder muscles
- Damage to nerves in the bladder
- Blockage from an enlarged prostate
Other Causes Of Bladder Control Problems
Surgery or radiation treatments for prostate cancer can lead to temporary or permanent bladder control problems.
Damaged nerves may send signals to the bladder at the wrong time or send no signals at all, leading to bladder control problems. Spinal cord injuries and conditions such as Alzheimers disease, Parkinsons disease, multiple sclerosis, diabetes and stroke may cause nerve problems as well.
Lifestyle choices like prescription medications, obesity, limited mobility, constipation, and sensitivities to foods and beverages may also cause or exacerbate bladder control issues.
Recommended Reading: How Can I Stop My Bladder From Leaking
Keeping A Bathroom Journal
You may be asked to keep a bathroom journal before or after your appointment. In your journal, youll log all your bathroom trips and bladder leakage or issues. It can also be helpful to record what you eat and drink in your bladder journal. This record will help your doctor get a more accurate idea of your symptoms and how often they occur. Keeping a journal can also determine what triggers your need to pee or any accidents.
Expert Review And References
- Urinary incontinence. American Society of Clinical Oncology . Cancer.Net. Alexandria, VA.: American Society of Clinical Oncology 2013.
- Landier W, Smith S. Late effects of cancer treatment. Yarbro, CH, Wujcki D, & Holmes Gobel B. . Cancer Nursing: Principles and Practice. 7th ed. Sudbury, MA: Jones and Bartlett 2011: 71: pp. 1756-1779.
- Shenot PJ. Urinary incontinence in adults. Beers, M. H., & Berkow, R., . Merck Manual for Healthcare Professionals. Rahway, NJ: Merck Research Laboratories 2012.
- Vorvick LJ. Urinary incontinence. PubMed Health. U.S. National Library of Medicine 2011.
Also Check: What Can Be Done For Overactive Bladder
Recommended Reading: Can A Hernia Affect Your Bladder
Urinary Incontinence In Older Adults
Urinary incontinence means a person leaks urine by accident. While it can happen to anyone, urinary incontinence, also known as overactive bladder, is more common in older people, especially women. Bladder control issues can be embarrassing and cause people to avoid their normal activities. But incontinence can often be stopped or controlled.
What happens in the body to cause bladder control problems? Located in the lower abdomen, the bladder is a hollow organ that is part of the urinary system, which also includes the kidneys, ureters, and urethra. During urination, muscles in the bladder tighten to move urine into the tube-shaped urethra. At the same time, the muscles around the urethra relax and let the urine pass out of the body. When the muscles in and around the bladder dont work the way they should, urine can leak, resulting in urinary incontinence.
Incontinence can happen for many reasons, including urinary tract infections, vaginal infection or irritation, or constipation. Some medications can cause bladder control problems that last a short time. When incontinence lasts longer, it may be due to:
- Weak bladder or pelvic floor muscles
- Overactive bladder muscles
- Damage to nerves that control the bladder from diseases such as multiple sclerosis, diabetes, or Parkinsons disease
- Diseases such as arthritis that may make it difficult to get to the bathroom in time
Most incontinence in men is related to the prostate gland. Male incontinence may be caused by:
Dementia And Changes To The Lower Urinary Tract
Dementia is an umbrella of neurodegenerative disorders which cause degeneration of the CNS. The Alzheimers Disease Association estimated that currently, there are 46.8 million people living with dementia worldwide and this number will double every 20 years to 74.7 million in 2030 and 131.5 million in 2050. Much of this increase will be in the developing world.
Central control of detrusor activities includes the frontal cortex, basal ganglia, Pontine Micturition Centre. The central control provides an inhibitory input on the detrusor to reduce contractions during the bladder filling phase. Dementia, particularly vascular dementia, normal pressure hydrocephalus, Frontotemporal lobe dementia, Alzheimers Disease present with features of detrusor over-activity where urgency is the main symptom. Among the elderly with Alzheimers disease, urge incontinence is the commonest presentation and UI is proportional to the dementia severity and impairment of ADLs .
Diffuse Lewy Body Dementia , Multisystem atrophy, Parkinsons Disease Dementia and AD have additional component of autonomic dysfunction, in addition to the central causes. The autonomic dysfunction presents with detrusor over-activity as the main type of UI. The synuclein deposition in PDD and DLBD is present in central nervous system and postganglionic sympathetic nerves .
Read Also: How Is Botox Administered For Overactive Bladder
How Do You Do Kegel Exercises
- The first step is to find the right muscles. Imagine that you are trying to stop yourself from passing gas. Squeeze the muscles you would use. If you sense a “pulling” feeling, those are the right muscles for pelvic exercises.
- Do not squeeze other muscles at the same time or hold your breath. Also, be careful not to tighten your stomach, leg, or buttock muscles. Squeezing the wrong muscles can put more pressure on your bladder control muscles. Squeeze just the pelvic muscles.
- Pull in the pelvic muscles and hold for a count of 3. Then relax for a count of 3. Repeat, but do not overdo it. Work up to 3 sets of 10 repeats. Start doing your pelvic muscle exercises lying down. This position is the easiest for doing Kegel exercises because the muscles then do not need to work against gravity. When your muscles get stronger, do your exercises sitting or standing. Working against gravity is like adding more weight.
- Be patient. Do not give up. It takes just 5 minutes, three times a day. Your bladder control may not improve for 3 to 6 weeks, although most people notice an improvement after a few weeks.
Medications For Urinary Incontinence
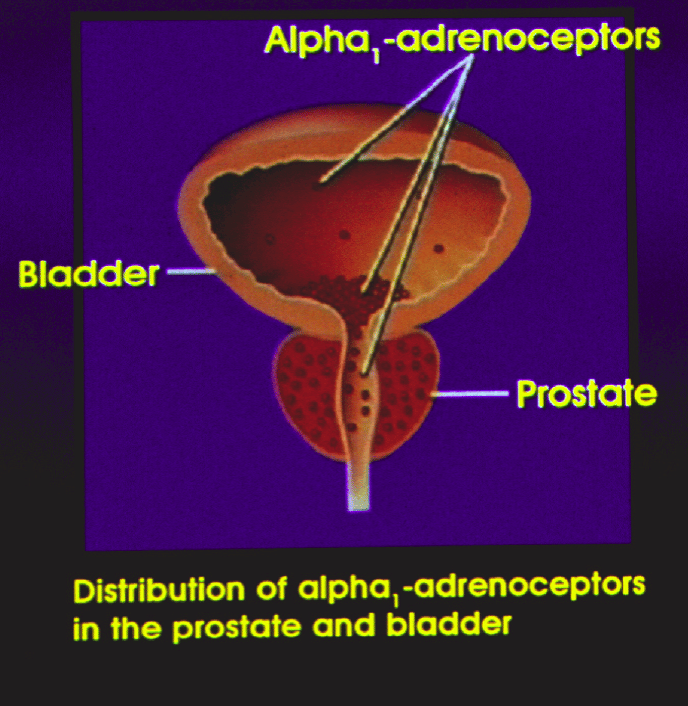
If medications are used, this is usually in combination with other techniques or exercises.
The following medications are prescribed to treat urinary incontinence:
- Anticholinergics calm overactive bladders and may help patients with urge incontinence.
- Topical estrogen may reinforce tissue in the urethra and vaginal areas and lessen some of the symptoms.
- Imipramine is a tricyclic antidepressant.
Also Check: Why Do You Bleed When You Have A Bladder Infection
Recovery Of Lack Of Bladder Control In Dogs
Prognosis for your dog varies based on the cause. If your dog has been prescribed medication, you will need to monitor him for side effects and return to the veterinarian in order to test blood and urine for overall health. Lifestyle changes may be required to help manage the condition, such as letting your dog outside to urinate more frequently, and/or only allowing your dog to lay down and fall asleep on surfaces that can be easily cleaned.
Living With Bowel Or Bladder Incontinence
There is no single, right way to cope with bladder or bowel incontinence. The challenge is to find what is best for your situation, so you can get the help you need and return to a normal daily life. Talk with your health care team if you notice a change in bowel or bladder habits, and about the best ways to manage incontinence, if it is a problem. You might find it helpful to talk with other people who are dealing with incontinence, too. Ask a member of your cancer care team about support groups in your area.
Here are some things you can do that may help make incontinence less of a problem:
- Empty your bladder every 3 to 4 hours while awake, to avoid accidents.
- Empty your bladder before bedtime or before strenuous activity.
- Limit drinks with caffeine, or and avoid alcohol and citrus juices, which can irritate the bladder and make you have to go more often.
- Avoid hygiene products that may irritate you Women should avoid feminine spray or over-the-counter vaginal suppositories.
- Because belly fat can push on the bladder, avoiding weight gain or losing needed weight sometimes helps improve bladder control.
- Avoid tobacco use which can cause coughing and bladder irritation due to harmful substances in tobacco products.
- Talk to your doctor about all medicines, vitamins, herbs, and supplements youre taking. Some may affect urine control.
You May Like: What Should I Take For A Bladder Infection
Male Urinary Incontinence Home Remedies
There are a number of home remedies and lifestyle adaptations that are known to assist with UI, as well as help to prevent it. They can either be tried on their own, such as for mild cases of UI, or combined with other medical treatments. However, a consultation with a urologist is recommended to evaluate each individual case. With expert medical assistance, these home remedies can be adopted in addition to receiving any other necessary treatments.
Burning Or Painful Urination
People with UTI often feel a burning sensation when they urinate. This symptom is one of the key signs that a person may have a urinary tract infection.
Burning urination or painful urination is medically known as dysuria. It can be caused by infectious and noninfectious conditions.
A urinary tract infection makes the lining of the bladder and urethra become red and irritated.
In addition to the burning sensation, there is also an itchy or stinging feeling as the urine comes out. The pain can be felt at the start of urination or after urination.
Pain is often felt in the urethra. These are the tubes that carry urine to the bladder. The pain can also extend to the area around the genitals.
4.7/5controlledBladderbladdermore on it
Pelvic parasympathetic nerves: arise at the sacral level of the spinal cord, excite the bladder, and relax the urethra. Lumbar sympathetic nerves: inhibit the bladder body and excite the bladder base and urethra. Pudendal nerves: excite the external urethral sphincter.
Likewise, can bulging disc cause bladder problems? If the herniated disk presses on nerves in the nearby spinal canal, this can cause variety of nerve-related symptoms, including pain, numbness and muscle weakness. In the most severe cases, a herniated disk can compress nerves that control the bowel and bladder, causing urinary incontinence and loss of bowel control.
In respect to this, what nerves control the bladder and bowels?
Can a pinched nerve cause urinary problems?
Don’t Miss: How Do They Test For Overactive Bladder
Related Conditions And Causes Of Urinary Incontinence
Fecal incontinence is light to moderate bowel leakage due to diarrhea, constipation, or muscle or nerve damage.
As described in the section above on causes of urinary incontinence, common conditions may contribute to chronic urinary incontinence, including: urinary tract infection , constipation, interstitial cystitis or other bladder conditions, nerve damage that affects bladder control, side effects from a prior surgery, and neurological disorders.
Recommended Reading: How To Train Bladder To Hold More Urine
Should I Drink Less Water Or Other Fluids If I Have Urinary Incontinence
No. Many people with urinary incontinence think they need to drink less to reduce how much urine leaks out. But you need fluids, especially water, for good health.
Women need 91 ounces of fluids a day from food and drinks.11 Getting enough fluids helps keep your kidneys and bladder healthy, prevents urinary tract infections, and prevents constipation, which may make urinary incontinence worse.
After age 60, people are less likely to get enough water, putting them at risk for dehydration and conditions that make urinary incontinence worse.12
Recommended Reading: Can A Bladder Infection Make You Feel Tired
When Should I See A Health Care Professional
See a health care professional if you have symptoms of a bladder problem, such as trouble urinating, a loss of bladder control, waking to use the bathroom, pelvic pain, or leaking urine.
Bladder problems can affect your quality of life and cause other health problems. Your health care professional may be able to treat your UI by recommending lifestyle changes or a change in medicine.
Causes Of Loss Of Bladder And Bowel Control
Causes of Bowel Incontinence
Causes of Urine Incontinence
It is not always necessary to have a noticeable cause of loss of bladder and bowel control, but your doctor can help you identify the best treatment in this case. Certain conditions can cause urinary incontinence. For instance, it may happen due to poor overall health, vaginal childbirth, and any damage to the nervous system.
Dont Miss: What Causes Bladder Pain And Pressure
Read Also: How To Do A Bladder Scan
How The Bladder Works
To understand the different causes for bladder problems and the differences faced by between men and women, it is essential to understand how a healthy bladder functions. The bladder is a balloon-shaped organ a muscle in fact — that sits in the pelvis, supported and held in place, by the pelvic floor muscles. Its purpose is to store and release urine. A tube, called the urethra, connects the bladder to the genitals, from where the urine is passed. Ring-like muscles, called sphincters, control the urethra, keeping it closed so urine doesnt leak from the bladder before its ready to be released while hormones help keep the lining of the bladder and urethra healthy. The bladder muscle relaxes when it fills with urine and contracts when its time to urinate. Nerves carry signals from the bladder to the brain to let the brain know when the bladder is full – and from the brain to the bladder to let the bladder know when its time to urinate. For the urinary system to do its job effectively, muscles and nerves must work together to hold urine in the bladder and then release it at the right time. If either the muscles or the nerves are impaired, this could lead to incontinence.
Weak muscles
Weak pelvic muscles cause most bladder control problems. If the bladder sags out of position, it can stretch the opening to the urethra.
Nerve damage
As well as weak muscles and nerve damage, bladder control problems can be caused when medicines dull the nerves.