Causes Of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections
The most common recurrent urinary tract infection causes in women are
- The female urethra is shorter than a mans, which means that bacteria has a shorter distance it needs to travel in order to get to the bladder, multiply, and cause infection.
- The proximity of the female urethra and rectum can result in a bacteria exchange from the rectum to the urethra, particularly if the patient wipes back to front instead of front to back after defecating.
They can be prevented by:
- Staying hydrated aka drinking plenty of water, ideally a gallon per day, to flush out bacteria.
- Being cautious when using a diaphragm during sex. Diaphragms can push up against the urethra, which makes it harder to fully empty the bladder during urination. The urine that doesnt empty is more likely to grow bacteria.
- Avoiding spermicides, vaginal douches, and certain oral antibiotics. They can change the bacterial makeup of the vagina, which increases the risk of developing a chronic UTI.
Causes And Symptoms Of A Uti
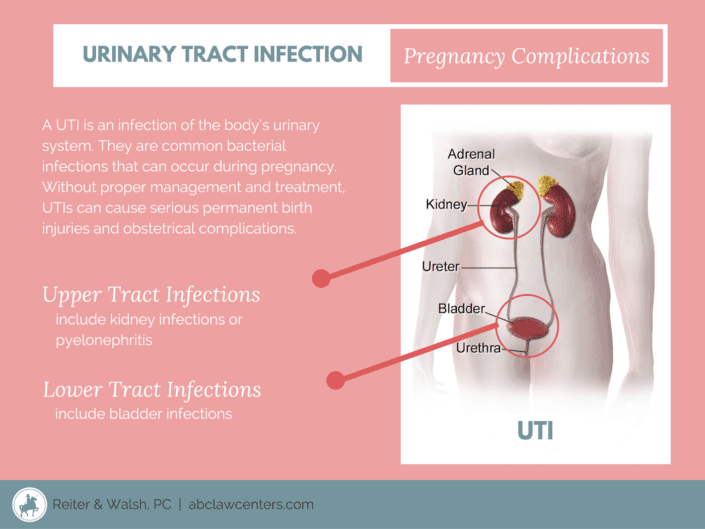
Many people refer to a UTI as a bladder infection, but you can get an infection anywhere along your urinary tract. That includes your:
- Bladder the sac that holds your urine.
- Urethra the tube that carries urine out of your body from your bladder.
- Ureters 2 tubes that send urine from your kidneys to your bladder.
- Kidneys the organs that filter your blood and remove wastes that become urine.
Most of the time, a UTI affects your bladder. It happens when bacteria enter your urethra and settle in your bladder. Once bacteria start to grow, they cause symptoms like:
- Pain or burning when you urinate.
- Urine thats cloudy, pink from blood, or has an odor.
- Feeling like you have to urinate frequently, even though your bladder is empty.
- Pressure or cramping in your lower abdomen.
A kidney infection is a less common UTI, but its more serious. With a kidney infection, your symptoms might include:
- A fever.
What Can I Do To Prevent Recurrent Utis
The majority of UTIs, about 90%, are caused by E. coli, a bacteria that naturally occurs in your intestines where its helpful. When this bacteria comes in contact with your urinary tract system, however, it can be harmful and lead to a UTI.
For most people, simple hygiene and lifestyle changes can help prevent recurrent UTIs. To help stop a UTI before it starts, try implementing these tips:
- Avoid spreading E. coli by washing your genitals with warm water and mild soap before and after sex.
- Drink plenty of fluids to flush out any wandering bacteria from the urinary system.
- Be sure to urinate after having sex to keep bacteria from lingering in the urethra.
- When you feel the urge to urinate, go postponing urination increases your risk of developing a UTI.
- Be sure to wipe from front to back to avoid spreading E. coli to the vagina.
Ready to learn more about UTIs and how they affect older women? Experiencing symptoms of a UTI? Contact our Littleton office or book an appointment online now and the help you need!
You May Like: Bcg Tx For Bladder Cancer
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections In Women: Diagnosis And Management
CHARLES M. KODNER, MD, University of Louisville School of Medicine, Louisville, Kentucky
EMILY K. THOMAS GUPTON, DO, MPH, Primary Care Medical Center, Murray, Kentucky
Am Fam Physician. 2010 Sep 15 82:638-643.
Recurrent urinary tract infections are common in women and associated with considerable morbidity and health care use. The clinical features, diagnostic testing, and causative organisms are often similar to those of single cases of UTI, although there are additional treatment strategies and prevention measures to consider with recurrent UTIs.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
A urine culture with greater than 102 colony-forming units per mL is considered positive in patients who have symptoms of UTI.
| Clinical recommendation | Evidence rating | References |
|---|---|---|
|
Continuous and postcoital antimicrobial prophylaxis have demonstrated effectiveness in reducing the risk of recurrent UTIs. |
||
|
Cranberry products may reduce the incidence of recurrent symptomatic UTIs. |
||
|
Use of topical estrogen may reduce the incidence of recurrent UTIs in postmenopausal women. |
||
|
Treatment of complicated UTIs should begin with broad-spectrum antibiotic coverage, with adjustment of antimicrobial coverage guided by culture results. |
||
|
Prophylactic antimicrobial therapy to prevent recurrent UTIs is not recommended for patients with complicated UTIs. |
UTI = urinary tract infection.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
UTI = urinary tract infection.
How Do I Know If The Treatment Isnt Working
If the treatment isnt working, your symptoms will stay the same, get worse, or you will develop new symptoms. Call your doctor if you have a fever , chills, lower stomach pain, nausea, and vomiting. You should also call your doctor if, after taking medicine for 3 days, you still have a burning feeling when you urinate. If you are pregnant, you should also call your doctor if you have any contractions.
Also Check: Men’s Overactive Bladder Treatment
How Do Utis Affect Pregnancy
Changes in hormone levels during pregnancy raise your risk for UTIs. UTIs during pregnancy are more likely to spread to the kidneys.
If you’re pregnant and have symptoms of a UTI, see your doctor or nurse right away. Your doctor will give you an antibiotic that is safe to take during pregnancy.
If left untreated, UTIs could lead to kidney infections and problems during pregnancy, including:
- Premature birth
- Low birth weight
Can Recurrent Utis Be A Sign Of Cancer
Both UTIs and bladder cancer can cause similar symptoms, such as a frequent need to urinate and even blood in the urine, according to the University of Rochester Medical Center.
According to the American Cancer Society, urinary tract infections, kidney and bladder stones, and other causes of chronic bladder irritation have been linked to bladder cancer. However, its not clear whether recurrent urinary or bladder infections can actually cause bladder cancer or whether they constitute a true risk factor for bladder cancer.
The biggest known risk factor for bladder cancer is smoking. The risk of bladder cancer also increases with age. Most people who get bladder cancer are over the age of 55.
If you think you may have chronic or recurrent UTIs, its best to get checked out by your doctor. Your provider can rule out other health issues, including bladder cancer, and get you the treatment you need to get rid of chronic UTIs.
Recommended Reading: Can You Use A Drain Bladder On A Toilet
Causes Of Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs are usually caused by bacteria from poo entering the urinary tract.
The bacteria enter through the tube that carries pee out of the body .
Women have a shorter urethra than men. This means bacteria are more likely to reach the bladder or kidneys and cause an infection.
Things that increase the risk of bacteria getting into the bladder include:
- having sex
-
do not use scented soap
-
do not hold your pee in if you feel the urge to go
-
do not rush when going for a pee try to fully empty your bladder
-
do not wear tight, synthetic underwear, such as nylon
-
do not drink lots of alcoholic drinks, as they may irritate your bladder
-
do not have lots of sugary food or drinks, as they may encourage bacteria to grow
-
do not use condoms or diaphragms with spermicidal lube on them try non-spermicidal lube or a different type of contraception
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection Treatments
Here are some treatments that are commonly used for successful treatment of chronic UTIs. Keep in mind that treatments employed will depend on the cause of the UTI:
- The primary treatment for UTIs is a course of antibiotics delivered over one week however, for chronic UTIs, if the patient takes low dose antibiotics long term or after sexual intercourse, it will help to prevent future UTIs.
- Along with prescribing antibiotics, the doctor may want to monitor the urinary system more closely using home urine tests. These are easy to do, and they are very effective at properly diagnosing the problem.
- Drinking cranberry juice and taking Vitamin C supplements can make your urine more acidic, which decreases the potential for bacteria growth while also keeping your heart and immune system healthy.
- If the chronic UTI occurs in combination with menopause, the patient may want to consider vaginal estrogen therapy in order to limit risk for future UTIs.
Consult your doctor before starting a treatment regimen. Chronic Urinary Tract Infections can be very painful, but with a little bit of time, the proper diagnosis, and patience, they can be a thing of the past.
Don’t Miss: What Medications Cause Overactive Bladder
Whats The Difference Between A Urinary Tract Infection And Bladder Infection
A urinary tract infection is a more general type of infection. There are many parts of your urinary tract. A UTI is a term for an infection that takes place throughout the urinary tract. A bladder infection, also called cystitis, is a specific infection. In this infection, bacteria makes its way into the bladder and causes inflammation.
Not all urinary tract infections become bladder infections. Preventing the spread of the infection is one of the most important reasons to treat a UTI quickly when you have symptoms. The infection can spread not only to the bladder, but also into your kidneys, which is a more complicated type of infection than a UTI.
Role Of Urinary Testing In Diagnosing Symptomatic Utis In Older Adults
The utility of urinary dipstick testing, urinalysis, and urine culture is challenging in the older adult because of the high prevalence of bacteriuria and pyuria that may not be clinically important. As in the case of Mrs M, all urinary studies to evaluate for leukocyte esterase, nitrites, pyuria, and bacteriuria over a 2-year period were positive.
The urinary dipstick, although easy and convenient, has variable test characteristics. Sensitivity and specificity for urinary dipstick testing to evaluate for leukocyte esterase, nitrites, or both vary in older adults by the age of study participants, clinical suspicion of UTI, and laboratory definition for UTI used . The sensitivity and specificity for a positive dipstick test in older patients with was 82% and 71% , respectively. Other studies of elderly patients showed the negative predictive value for dipstick testing ranges from 92% to 100%., Urinary dipstick analysis should be performed in the out-patient setting primarily to rule out and not to establish a diagnosis of UTI. In a patient with a low pretest probability of UTI, if the dipstick is negative for leukocyte esterase and nitrites, it excludes the presence of infection and mitigates the need to obtain urinalysis and urine culture . High false-positive rates limit dipstick testing effectiveness. Further urinary studies are warranted for patients with a high pretest probability of UTI.
Recommended Reading: Why Does My Bladder Feel Full
Why Do Women Get Urinary Tract Infections More Often Than Men
Women tend to get urinary tract infections more often than men because bacteria can reach the bladder more easily in women. The urethra is shorter in women than in men, so bacteria have a shorter distance to travel.
The urethra is located near the rectum in women. Bacteria from the rectum can easily travel up the urethra and cause infections. Bacteria from the rectum is more likely to get into the urethra if you wipe from back to front after a bowel movement. Be sure to teach children how to wipe correctly.
Having sex may also cause urinary tract infections in women because bacteria can be pushed into the urethra. Using a diaphragm can lead to infections because diaphragms push against the urethra and make it harder to completely empty your bladder. The urine that stays in the bladder is more likely to grow bacteria and cause infections.
Frequent urinary tract infections may be caused by changes in the bacteria in the vagina. Antibacterial vaginal douches, spermicides, and certain oral antibiotics may cause changes in vaginal bacteria. Avoid using these items, if possible. Menopause can also cause changes in vaginal bacteria that increase your risk for urinary tract infection. Taking estrogen usually corrects this problem but may not be for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questionsexpand All
- How common are urinary tract infections ?
Urinary tract infections are common infections. Many women get them at some point in their lives. Some women have repeat infections and may have them often. But most UTIs are not serious. These infections can be treated with antibiotics, and symptoms usually can be relieved quickly.
- What is the urinary tract?
The urinary tract has a lower part and an upper part. The upper urinary tract consists of the ureters and kidneys. The lower tract is made up of the urethra and the bladder. The organs work together in the following ways:
-
The two kidneys produce urine.
-
The two tubes called ureters carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
-
The bladder stores urine.
-
The urethra carries urine from the bladder out of the body.
Most UTIs start in the lower urinary tract. Bacteria enter through the urethra and spread upward to the bladder. This can cause cystitis, a bladder infection. In some cases, an infection of the urethra called urethritis can develop at the same time.
Bacteria that have infected the bladder may travel up the ureters to the kidneys. This can cause pyelonephritis, a kidney infection. An infection in the upper tract may cause a more severe illness than infection in the lower tract.
Infections also can develop when the bladder does not empty completely. This may be caused by the following:
A problem with the nerves or muscles of the pelvis.
nausea
Also Check: Is Green Tea Good For Bladder Infection
What Can I Do To Help Prevent Cystitis
Unfortunately there is no evidence that any lifestyle changes really help to prevent cystitis. Traditionally, doctors have advised drinking plenty of fluids to ‘flush out’ the germs , and drinking cranberry juice. However, there is no evidence this makes any difference. Researchers are also studying the effects of probiotics on preventing cystitis but currently there isn’t enough evidence to know if they are of any use either. Other changes, such as the way you clean yourself and which underwear you wear, have also not been found to make any difference. If recurring cystitis is a problem, you may need to discuss one of the options below with your doctor.
Can I Prevent Recurrent Utis
There are steps you can take to help reduce UTIs. The most basic is to drink plenty of fluids. This encourages frequent urination and helps flush out bacteria.
For women, following good hygiene practices is especially important:
- After a bowel movement, wipe from front to back to reduce the chance of moving E. coli bacteria from the rectal area to the urethra.
- Pee immediately before and after sex.
- Dont douche or use feminine deodorants on your genitals.
- Wear cotton underwear.
For older adults, take care to deal with retention problems, which are especially an issue as you age.
I tell them to double-void urinate and then go back and urinate again, Dr. Vasavada says.
What about drinking cranberry juice to fight UTIs?
Thats one of the most commonly asked questions, Dr. Vasavada says. Theres conflicting data. Its not going to cure an infection, but it could help prevent one, so we dont discourage it.
You May Like: How To Take Care Of A Bladder Infection At Home
Bladder Cancer And Radiation Treatment
While urine containing blood is a more common symptom of bladder cancer, some women with this condition also feel the need to urinate more often. If a tumor is present in the bladder, it takes up space that could otherwise be filled with urine, thereby leading to an increased need to pee frequently. Not only can cancer cause more frequent urination, but the treatments for cancer can cause this as well. For example, radiation is often used to treat cancer and can cause the side effect of frequent urination. This is especially true if the radiation therapy is targeted at the pelvic area.
Can I Become Immune To The Antibiotics Used To Treat A Uti
Your body can actually get used to the antibiotics typically used to treat a urinary tract infection . This happens in people who have very frequent infections. With each UTI and use of antibiotics to treat it, the infection adapts and becomes harder to fight. This is called an antibiotic-resistant infection. Because of this, your healthcare provider may suggest alternative treatments if you have frequent UTIs. These could include:
- Waiting: Your provider may suggest that you watch your symptoms and wait. During this time, you may be encouraged to drink plenty of fluids in an effort to flush out your system.
- Intravenous treatment: In some very complicated cases, where the UTI is resistant to antibiotics or the infection has moved to your kidneys, you may need to be treated in the hospital. The medicine will be given to you directly in your vein . Once youre home, you will be prescribed antibiotics for a period of time to fully get rid of the infection.
You May Like: Used Marine Fuel Bladder For Sale
Common Questions About Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections In Women
JAMES J. ARNOLD, DO LAURA E. HEHN, MD and DAVID A. KLEIN, MD, MPH, National Capital Consortium Family Medicine Residency, Fort Belvoir, Virginia
Am Fam Physician. 2016 Apr 1 93:560-569.
Patient information: See related handout on recurrent urinary tract infections, written by the authors of this article.
Urinary tract infections are the most common bacterial infection in women of all ages.1 An estimated 30% to 44% of women will have a second UTI within six months of an initial infection.24 Healthy women with normal urologic anatomy account for most patients who have recurrent UTIs.15
UTI = urinary tract infection.
A = consistent, good-quality patient-oriented evidence B = inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence C = consensus, disease-oriented evidence, usual practice, expert opinion, or case series. For information about the SORT evidence rating system, go to .
Recurrent UTI is typically defined as three or more UTIs in 12 months, or two or more infections in six months.25 Recurrence is thought to occur by ascent of uropathogens in fecal flora along the urogenital tract and by reemergence of bacteria from intracellular bacterial colonies in uroepithelial cells. In either mechanism, the same species that caused the initial infection is typically the reinfecting agent.5