Of Participation And Request For Credit
Fees for participating and receiving CME credit for this activity are as posted on The ObG Project website. During the period from Dec 31 2017 through Jan 25 2023, participants must read the learning objectives and faculty disclosures and study the educational activity.
If you wish to receive acknowledgment for completing this activity, please complete the post-test and evaluation. Upon registering and successfully completing the post-test with a score of 100% and the activity evaluation, your certificate will be made available immediately.
For Pharmacists: Upon successfully completing the post-test with a score of 100% and the activity evaluation form, transcript information will be sent to the NABP CPE Monitor Service within 4 weeks.
Considerations When Treating Oab
From the available data, it appears the strongest evidence is that anticholinergics increase the risk of cognitive impairment and potentially the development of dementia. Delaying the onset of dementia by only one year may prevent up to nine million cases of dementia by 2050.31 This is not only an important medical issue but also a socioeconomic issue. Therefore, it is important to consider which medication to use for treatment of OAB in our older adults.
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence advises that health care provider should take into account coexisting conditions , use of other drugs which affect anticholinergic load and the risk of adverse effects, including cognitive impairment.32 It recommends discussing with the patient that long-term effects of anticholinergic medicines for overactive bladder on cognitive function are uncertain. It states that immediate release oxybutynin should not be offered to older women who may be at higher risk of a sudden deterioration in their physical or mental health.
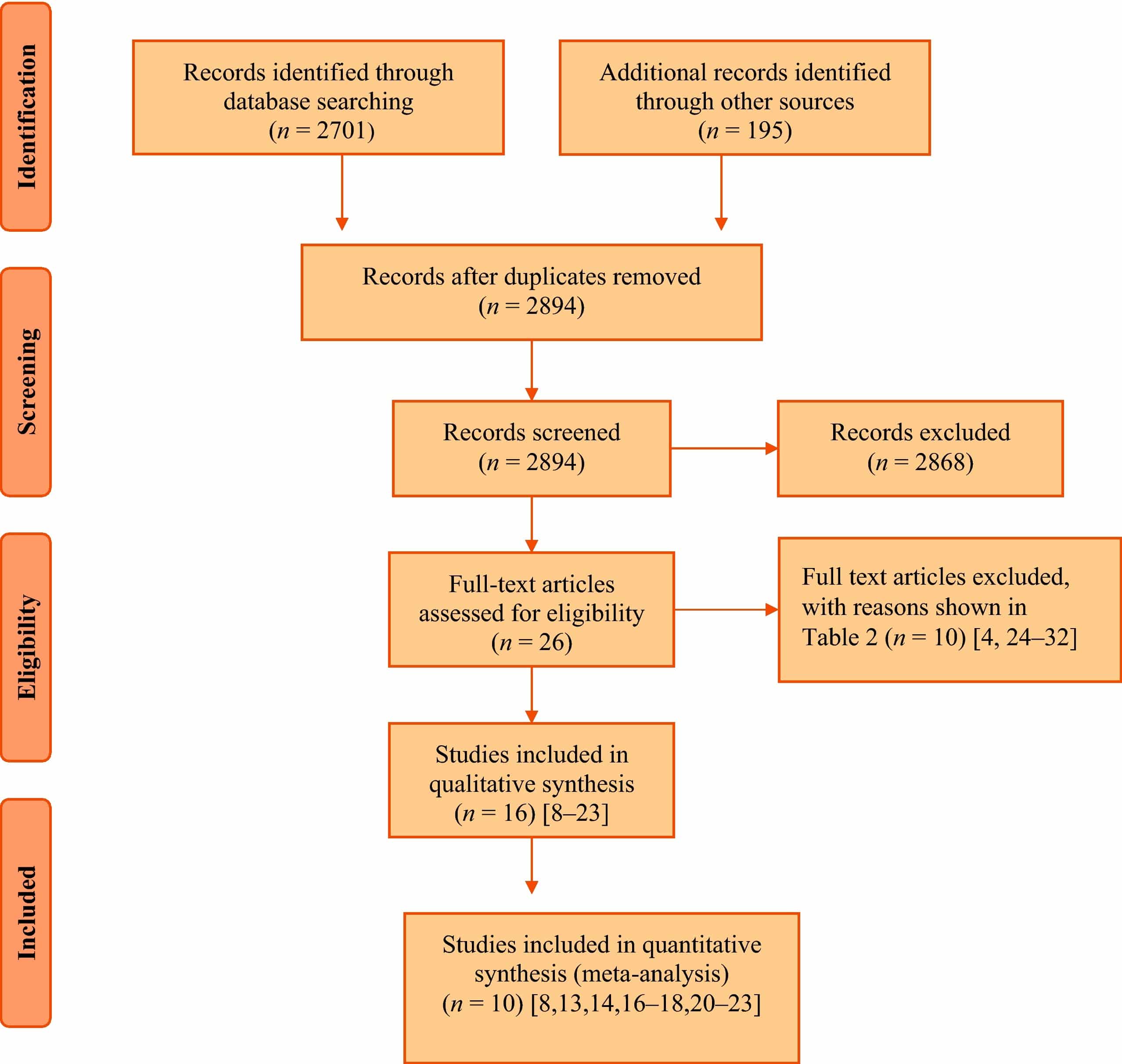
Risk Of Bias In Included Studies
The methodological quality of the published studies was assessed by looking at the methods of generation of random allocation, concealment of allocation, blinding of the trial participants and investigators, completeness of treatment, withdrawals and dropouts and loss to follow up.
Randomisation, allocation concealment and blinding
The method of group allocation was rarely described. Double blinding should adequately conceal group allocation but this is not guaranteed. For the purposes of the review, trials that stated group allocation was ‘doubleblind’ were coded as having adequate concealment. All trials but two were double blind and therefore considered to have adequate allocation concealment.
Few trials specifically stated that outcome assessors were blind to group allocation . Some trials stated the code was broken at the completion of the study and in some it was specified as after the analysis. This would imply that the final measurement was done blinded. A recent study by DuBeau et al suggests that doubleblind designs might not be adequate to blind participants to anticholinergic versus placebo allocation, emphasising the importance of blinded outcome assessors .
Withdrawals and dropouts
Read Also: Bladder Cancer Treatment With Tuberculosis Bacteria
Sufu White Paper On Overactive Bladder Anticholinergic Medications And Dementia Risk
Department of Urology, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, Virginia, USA
Glickman Urological & Kidney Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio, USA
Correspondence Dr. Jacqueline Zillioux, Department of Urology, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, VA, USA.
Department of Urology, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, Virginia, USA
Glickman Urological & Kidney Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio, USA
Correspondence Dr. Jacqueline Zillioux, Department of Urology, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, VA, USA.
Get access to the full version of this article.You previously purchased this article through ReadCube.
Institutional Login
Log in to Wiley Online Library
If you have previously obtained access with your personal account, please log in.
- View the article/chapter PDF and any associated supplements and figures for a period of 48 hours.
- Article/Chapter can not be printed.
- Article/Chapter can not be downloaded.
- Article/Chapter can not be redistributed.
- Unlimited viewing of the article/chapter PDF and any associated supplements and figures.
- Article/Chapter can not be printed.
- Article/Chapter can not be downloaded.
- Article/Chapter can not be redistributed.
- Unlimited viewing of the article/chapter PDF and any associated supplements and figures.
- Article/chapter can be printed.
Rationale For Anticholinergic Use
Detrusor muscle contractions are essential for normal micturition, but involuntary contractions produce the symptoms of overactive bladder. Contractions depend on the activation of muscarinic receptors in the bladder by acetylcholine. The M3 muscarinic receptor-subtype is thought to be the most important in regulating detrusor contractions.
Anticholinergic drugs block muscarinic receptor activation and inhibit the spontaneous detrusor contractions found in overactive bladder. Drug efficacy is dose-dependent, but effectiveness is often limited by unwanted antimuscarinic effects in distant organs where other acetylcholine receptor-subtypes predominate . These adverse effects are also dose-dependent. They commonly include dry mouth, dry eyes, confusion, constipation, somnolence, blurred vision and increased heart rate.
There are no currently available drugs with pure selectivity for the muscarinic receptors in the detrusor. To try to improve the benefit:harm ratio a number of anticholinergics have been developed with greater selectivity for the detrusor or the M3 receptor, or with extended release properties.
Recommended Reading: Heavy Feeling In Bladder And Frequent Urination
Study Characteristics For Reference
Summary
> With regards to the above reference, we believe that the study > characteristics quoted on pages 27?28 do not appear to correlate to > those in the published paper. Whereas the study cited in the review > investigated only solifenacin, with tolterodine as a comparator, the > characteristics quoted include details about another anticholinergic > compound, darifenacin, implying that this compound was included for > comparison in the study. > seems possible that a second paper by Chapple et al, reporting on the > efficacy of darifenacin, has been included in the description of the > study characteristics by mistake :9931001), discusses two doses of darifenacin versus placebo ). > > We would therefore like to request a review of the text on pages 27 ? > 28, > and a potential amendment to the study characteristics as necessary. > In addition, as quality of life data is not discussed in either > of the above papers by Chapple et al, statements such as ?QoL data > reported favours solifenacin? in the table of study characteristics > are potentially misleading to the reader. > We look forward to your review of the text and modification of the > study characteristics table.
the info in characteristics of studies table has now been changed
Contributors
Nabi Ghulam, Peter Herbison, June Cody
How Anticholinergic Bladder Medications Work
Anticholinergic drugs are often prescribed to treat OAB. These drugs work by relaxing your bladder muscles. They also help prevent urine leaks by controlling bladder spasms.
Most of these drugs come as oral tablets or capsules. They also come in transdermal patches and topical gels. Most are only available as prescriptions, but the patch is available over the counter.
Oxybutynin is an anticholinergic drug for overactive bladder. Its available in the following forms:
- transdermal patch
You take this drug on a daily basis. Its available in several strengths. The oral tablet comes in immediate-release or extended-release forms. Immediate-release drugs release into your body right away, and extended-release drugs release into your body slowly. You may need the take the immediate-release form up to three times per day.
Recommended Reading: What’s Good For Bladder Control
Anticholinergic Drugs For Overactive Bladder: A Review Of The Literature And Practical Guide
Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology
Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology North Middlesex University Hospital London N18 1QX
William Wong M Pharm MRPharm
Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology
North Middlesex University Hospital London N18 1QX
Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology
Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology North Middlesex University Hospital London N18 1QX
Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology
Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology North Middlesex University Hospital London N18 1QX
William Wong M Pharm MRPharm
Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology
North Middlesex University Hospital London N18 1QX
Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology
Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology North Middlesex University Hospital London N18 1QX
Which Anticholinergic Drug For Overactive Bladder Symptoms In Adults
Many adults have symptoms of overactive bladder. A person with overactive bladder syndrome feels a very strong urge to pass urine and they may not make it to the toilet before they leak urine. Other common problems are a feeling of needing to urinate often during the day or night, or both. This problem seems to be caused by an overactive bladder muscle, and it becomes more common with ageing. Treatments are conservative measures, such as bladder training or drugs. Anticholinergic drugs can reduce the overactivity of the bladder muscle and the feeling of urgency. The review found that there are several anticholinergic drugs prescribed for adults with overactive bladder symptoms. The two most studied drugs are oxybutynin and tolterodine. These two drugs have similar effects but, on average, those taking oxybutynin were more likely to withdraw from the studies because of adverse effects, mainly dry mouth. However, both drugs can give dry mouth and this problem is less likely if an extended release formulation of either drug is used. Two newer drugs are solifenacin and fesoterodine. Solifenacin has a better effect and less risk of dry mouth compared to tolterodine. Fesoterodine has a better effect than extended release tolterodine but withdrawal from studies due to adverse effects and dry mouth was more likely.
To compare the effects of different anticholinergic drugs for overactive bladder symptoms.
Read Also: Difference Between Uti And Overactive Bladder
Topical Oestrogen In Postmenopausal Women
Postmenopausal women with dry vaginal and urethral tissues can also be treated with local vaginally inserted oestrogen cream. This is not the same as a hormone tablet or patch that is designed to raise blood levels of oestrogen.
Local or topical oestrogen pessaries aim to treat only the dry vaginal tissues, which can contribute to overactive bladder symptoms in some women . Ovestin® cream or Vagifem Low® pessaries are prescribed twice weekly for this purpose.
Dr. Karen McKertich
Criteria For Considering Studies For This Review
Types of studies
All randomised or quasirandomised controlled trials of anticholinergic drugs versus placebo or no treatment of overactive bladder syndrome.
Types of participants
All adult men and women with a symptomatic diagnosis of overactive bladder syndrome or a urodynamic diagnosis of detrusor overactivity , or both.
Types of interventions
At least one arm of the study had to use an anticholinergic drug and one other was a placebo or no treatment arm. To be included, the drug had to be a muscarinic anticholinergic antagonist given for the purpose of decreasing symptoms of overactive bladder. The group of drugs included: emepronium bromide or carrageenate, darifenacin, dicyclomine chloride, oxybutynin chloride, propantheline bromide, propiverine, tolterodine, and trospium chloride. Terodiline, an anticholinergic drug previously used in the treatment of overactive bladder, was excluded because it has been withdrawn from the market. Trials with intravesical anticholinergic medication administration were excluded in this updated version of the review.
Other drugs with less direct anticholinergic effects were also excluded, .
Types of outcome measures
Both subjective and objective outcome measures were included in this review.
Primary outcomes of interest:
A. Patient observations, e.g. symptom scores, perception of cure or improvement, satisfaction with outcome
B. Quantification of symptoms, e.g. number of leakage episodes, frequency and volume
Read Also: How To Train A Weak Bladder
Disclosure Of Conflicts Of Interest
Postgraduate Institute for Medicine requires faculty, planners, and others in control of educational content to disclose all their financial relationships with ineligible companies. All identified conflicts of interest are thoroughly vetted and mitigated according to PIM policy. PIM is committed to providing its learners with high quality accredited continuing education activities and related materials that promote improvements or quality in healthcare and not a specific proprietary business interest of an ineligible company.
The PIM planners and others have nothing to disclose. The OBG Project planners and others have nothing to disclose.
Faculty: Susan J. Gross, MD, receives consulting fees from Cradle Genomics, and has financial interest in The ObG Project, Inc.
Planners and Managers: The PIM planners and managers, Trace Hutchison, PharmD, Samantha Mattiucci, PharmD, CHCP, Judi Smelker-Mitchek, MBA, MSN, RN, and Jan Schultz, MSN, RN, CHCP have nothing to disclose.
Data Management And Statistics
The validity of the anonymized submission data was checked for plausibility and completeness. Missing data on patient and physician assessments of treatment efficacy and tolerability and variables describing OAB symptoms at the last visit was replaced by the corresponding data collected at the interim visit in cases where the time difference between the first and the interim visit was at least 10 days. Adverse events were classified using the MedDRA coding system V19.1.
Transformation, preparation and exploratory analyses of data were carried out using the statistical software package SAS® V9.3 and 9.4, respectively. Since direct calculation of the exact confidence interval of the median was not possible with SAS, it was done using the DescTools package in R-version 3.3.1. The IML module was used to call R from SAS.
Data was analysed using descriptive statistical methods. The distributions of the qualitative and discrete quantitative variables were described in terms of absolute and relative frequencies based on sample size of the respective collective and were presented by three age classes and gender separately, and globally for all patients. The distributions of the continuous variables and quantitative discrete variables with a lot of values were described by sample size, number of missing values, minimum, 1. quartile , median, 3. quartile , maximum, and confidence interval of the median.
Recommended Reading: Chinese Herbs For Prolapsed Bladder
Drugs For Overactive Bladder
In people with overactive bladder, muscles in the bladder wall contract at the wrong time. A group of drugs called anticholinergics combat this problem by blocking the nerve signals related to bladder muscle contractions. Research suggests that these drugs also might increase bladder capacity and decrease the urge to go.
Anticholinergic drugs include:
Oxytrol for women is the only drug available over the counter. Overall, these drugs work about the same in treating overactive bladder, and generally people tolerate all of them well. The main side effect is dry mouth, but anticholinergics also can cause constipation, blurred vision, and increased heartbeat.
Anticholinergics aren’t right for everyone. Some people with glaucoma, urinary retention, or gastrointestinal disease should avoid using anticholinergic drugs.
The drugs mirabegron and vibegron called beta-3 adrenergic agonists. These medications work by activating a protein receptor in bladder muscles that relaxes them and helps the bladder fill and store urine.
Another type of drug for overactive bladder is the tricyclic antidepressantimipramine hydrochloride , which also relaxes bladder muscles.
Doctors also treat men with drugs that relax a muscle at the bladder neck and prostate to help with emptying. They include:
Medications For Unspecified Oab
If your doctor cant find a cause for your OAB, dont worry. Drugs can still help ease your symptoms. Some of these drugs work by relaxing your bladder. They stop involuntary contractions that bring on the urge to urinate. Other drugs help strengthen the tissues around your bladder that may have become weak. The stronger tissue can help improve your bladder control.
Read Also: How Do You Fix Nerve Damage In The Bladder
Anticholinergic Meds For Overactive Bladder May Up Dementia Risk
Among patients with overactive bladder , anticholinergic medication use appears to be associated with an increased risk of new onset dementia when compared with beta-3 agonist use, according to the findings of a retrospective population-based cohort study.
The study utilized linked administrative data from Ontario, Canada, to determine whether OAB patients initiating an anticholinergic medication had an increased risk of dementia compared with those initiating a beta-3 agonist. A group of new users of anticholinergic medications used to treat OAB were matched to new users of the beta-3 agonist medication, mirabegron . After matching, the groups were similar across all 75 measured baseline variables . The primary outcome of the analysis was dementia.
Findings of the study revealed tolterodine, oxybutynin, and solifenacin to be the most common anticholinergic medications used . The median prescription duration was found to be 30 days for anticholinergic medications compared with 64 days for mirabegron.
The study authors reported that users of anticholinergic medications were found to have an increased risk of new onset dementia compared with beta-3 agonist users . Anticholinergics may affect cognitive function by increasing amyloid plaques, or by directly inhibiting specific muscarinic receptors in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus, the authors hypothesized.
Anticholinergics Could Be Sidelined As First
In March, a US study published in the International Urogynecology Journal highlighted a shift in prescribing patterns for overactive bladder .
In March, a US study published in the International Urogynecology Journal highlighted a shift in prescribing patterns for overactive bladder .
Responses obtained from 222 American Urogynecologic Society members reveal that urogynecology providers are becoming more hesitant to prescribe anticholinergic drugs because of concerns they may increase the risk of dementia. This is good news for Astellas and Urovant Sciences, which are likely to see increased uptake of their respective beta 3 adrenergic receptor agonists, Myrbetriq and Gemtesa , in OAB.
Anticholinergics are used to inhibit involuntarily muscle movements across a range of indications. They can improve the symptoms of OAB, a symptom complex characterized by urinary urgency with or without incontinence, by suppressing involuntarily bladder contractions.
You May Like: Heating Pad For Bladder Infection
Post Hoc Subgroup Analysis
After the statistical analysis was finished as laid down in the study protocol, a subgroup of the efficacy analysis set consisting of two treatment groups according to the dosage regime 1 times a day 45 mg of TC or 3 times a day 15 mg of TC documented over the whole treatment period, was used to compare treatment outcomes in relation to the two administration schemes . All analyses were descriptive and explorative in nature.
Fig. 1
For between-group comparisons relating the main variables, we used effect size measures for evaluating the strength of the observed result. We calculated Cohens r for the median change of average number of voids/24 h between Visit 1 and the last evaluable visit and Cramérs V for the combination in the occurrence of incontinence episodes at Visit 1 to the last evaluable visit, as well as for the assessments of efficacy and tolerability by physicians and patients. For facilitating the interpretation of effect sizes, we used the defined reference values by Cohen and Ellis .