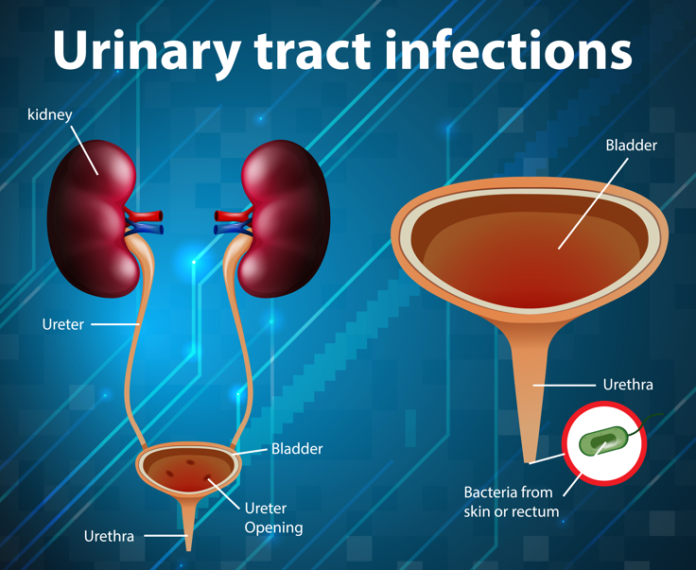
Check If It’s A Urinary Tract Infection
Symptoms of a UTI may include:
- pain or a burning sensation when peeing
- needing to pee more often than usual during the night
- pee that looks cloudy
- needing to pee suddenly or more urgently than usual
- needing to pee more often than usual
- lower tummy pain or pain in your back, just under the ribs
- a high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a very low temperature below 36C
Treatment For Recurrent Utis
You can typically get rid of a simple UTI with antibiotics, the Mayo Clinic explains. But, when you have chronic UTIs, your doctor may recommend the following, per the Mayo Clinic:
Low-dose antibiotics, for six months but maybe longer
Self-diagnosis and treatment, if you stay in touch with your doctor
A single dose of an antibiotic after sex, if your recurrent UTIs are related to sex
Vaginal estrogen therapy, if youre postmenopausal
Uti Causes And Risk Factors
The most common cause of a UTI in the urethra is a sexually transmitted disease. Chlamydia and gonorrhea are two STDs that can cause a UTI. STDs are also the most common cause of UTIs in younger men.
Prostate problems can also cause UTIs. An enlarged prostate is common in older men and can block the flow of urine. This can increase the odds that bacteria will build up and cause a UTI.
Prostatitis, which is an infection of the prostate, shares many of the same symptoms as UTIs.
Diabetes and other medical issues that affect your immune system can also make you more likely to get a UTI.
Don’t Miss: Can Bladder Cancer Be Detected By Blood Test
What Causes Recurrent Utis
Bacteria can enter the urinary tract from the outside to cause a UTI to come back, or a recurrent infection can be caused by bacteria that remain in the urinary tract after a previous infection. Symptoms of recurrent UTI in men and women include the frequent urge to urinate, burning pain or pressure, cloudy or discolored urine, bloody urine, and chills and fever. Children with UTIs are more likely to have fever without the other symptoms. Common conditions that can lead to recurrent UTIs include:
- Being in a nursing home or hospital
- Diabetes
- Having an infected or enlarged prostate
- Being born with an abnormality of the urinary tract
When To Get Medical Advice
It’s a good idea to see your GP if you think you might have a UTI, particularly if:
- you have symptoms of an upper UTI
- the symptoms are severe or getting worse
- the symptoms haven’t started to improve after a few days
- you get UTIs frequently
Your GP can rule out other possible causes of your symptoms by testing a sample of your urine and can prescribe antibiotics if you do have an infection.
Antibiotics are usually recommended because untreated UTIs can potentially cause serious problems if they’re allowed to spread.
You May Like: What Causes Weak Bladder In Males
Urinary Tract Infection Symptoms
Lower UTI symptoms may include the following:
-
Blood in the urine
-
Pain or burning during urination
-
Difficulty urinating
-
Strange sensations or pain in the pelvic region
-
Pain during sex
Upper UTI symptoms may include the following:
-
Upper back pain
-
Vomiting
-
Fever, chills or the shakes
*Note: Upper UTI infections shouldnt be ignored, as they can be life-threatening if bacteria pass from an infected kidney into the blood. If you have symptoms of a UTI, dont wait to see if theyll go away on their own, as theres always a chance they wont and could even get much worse. See a doctor.
Chronic Urinary Tract Infection Symptoms may include the following:
-
Frequent urination
-
Pain or burning during urination
-
Kidney pain
-
Pain in your bladder region
-
Pain radiating to genitals
-
A constant urge to go to the bathroom
-
Premenstrual aggravation of symptoms
-
Urethral pain
What Causes Urinary Tract Infection
The vast majority of urinary tract infections are caused by the bacteria Escherichia coli , which is usually found in the digestive system. However, other pathogens may cause a UTI. These include:
- Klebsiella pneumonia
- Enterococcus faecalis
- Staphylococcus saprophyticus
The bacteria may infect any part of the urinary tract bladder, urethra or kidneys. Depending on where the infection occurs, the UTIs are often known as:
- Cystitis infection of the bladder
- Urethritis infection of the urethra
- Pyelonephritis infection of the kidneys
The infection in urethra and bladder is usually not very serious and clears up with treatment. Similarly, ureters very rarely get infected. However, if a UTI reaches the kidneys, it may lead to kidney infections and a person may have to go to the hospital for treatment.
Recommended Reading: Can You Have A Fever With A Bladder Infection
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections In Women: Diagnosis And Management
CHARLES M. KODNER, MD, University of Louisville School of Medicine, Louisville, Kentucky
EMILY K. THOMAS GUPTON, DO, MPH, Primary Care Medical Center, Murray, Kentucky
Am Fam Physician. 2010 Sep 15 82:638-643.
Recurrent urinary tract infections are common in women and associated with considerable morbidity and health care use. The clinical features, diagnostic testing, and causative organisms are often similar to those of single cases of UTI, although there are additional treatment strategies and prevention measures to consider with recurrent UTIs.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
A urine culture with greater than 102 colony-forming units per mL is considered positive in patients who have symptoms of UTI.
| Clinical recommendation | Evidence rating | References |
|---|---|---|
|
Continuous and postcoital antimicrobial prophylaxis have demonstrated effectiveness in reducing the risk of recurrent UTIs. |
||
|
Cranberry products may reduce the incidence of recurrent symptomatic UTIs. |
||
|
Use of topical estrogen may reduce the incidence of recurrent UTIs in postmenopausal women. |
||
|
Treatment of complicated UTIs should begin with broad-spectrum antibiotic coverage, with adjustment of antimicrobial coverage guided by culture results. |
||
|
Prophylactic antimicrobial therapy to prevent recurrent UTIs is not recommended for patients with complicated UTIs. |
UTI = urinary tract infection.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
UTI = urinary tract infection.
Reasons Why You Might Get Recurring Utis
Many women who get a urinary tract infection may get one again at some point in their lives. In fact, one in five women experience recurrent UTIsan infection that occurs two times or more within six months or at least three times in a year. Men can get recurrent UTIs too, but it is not as common and is often due to some type of urinary tract blockage.
Also Check: How Do Poise Bladder Supports Work
Why Do Utis Go Back In Spite Of Remedy
There are a few half-dozen oral antibiotics that deal with UTIs. From time to time a physician will prescribe one drug, then transfer to any other after a urine tradition identifies which micro organism is at paintings. Adjusting the medicine can take time, and recurrent infections might happen within the intervening time.
From time to time an individual begins to really feel higher and comes to a decision to stops taking the antibiotic opposite to the physicians directions and any other an infection quickly follows. Its by no means a good suggestion to forestall taking antibiotics sooner than your dosage is whole.
However even individuals who take drugs because the physician prescribes might get recurrent infections, Dr. Vasavada says.
In the event youre a more youthful girl whos sexually lively, your physician might prescribe an antibiotic to take sooner than and after sexual job. For post-menopausal ladies, a vaginal estrogen cream might assist cut back infections.
If infections persist, your physician might take a look at for different well being issues within the kidney, bladder or different portions of the urinary machine.
How Many Is Too Many Utis
Three or more UTIs in one year indicates a recurrent infection, according to the ACOG.
Recurrent urinary tract infections are treated with antibiotics. A week or two after you finish the antibiotic treatment, your doctor may perform a urine test to make sure the infection is cured.
Your doctor may also ask you about factors that increase the risk of a recurrent UTI, including:
- Young age at first UTI
Read Also: Over The Counter Bladder Medication
Unpleasant Symptoms Of A Uti
Usually the first sign that something is amiss is a burning sensation when you urinate. Many times you rush to the bathroom only to discover you have urinated very little. Your urine can be cloudy, red, pink, or brown, and many times it has an unpleasant odor. In addition, there will be pain right near your pelvic bone.
The infection itself can be located in your urethra where urine is eliminated, and where bacteria from your bowels is supposed to be flushed out. Sometimes the infection can stay in the urethra or in the bladder.
If a UTI is not treated quickly, it can spread to your kidneys. When that occurs, you will experience a high fever, vomiting, chills, nausea, and pain in your upper abdomen.
Causes Of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections In Women Are:
- Sexual intercourse after long time: During sexual intercourse bacteria from genital region, and anus can easily enter into female urinary system. Women are also prone to get urinary tract infection after first intercourse ,after frequent intercourse and intercourse after a long gap.
- Use of diaphragm as a birth control device: The diaphragm presses down on and narrows the urinary passage. This results in incomplete bladder emptying and recurrent urinary tract infections
- Recurrent urinary tract infection in post menopausal women: The female hormone estrogen maintains an acidic pH of the female genital region which prevents rampant growth of germs. This protection is lowered after this hormone is lowered as part of menopausal hormonal changes.
While conventional medicines will help take care of the infection, homoeopathic treatment for recurrent UTI offers great hope. Homoeopathic medicines reduce the frequency of attacks and help build up your immunity against the bacteria. Contact us today to know how homoeopathic treatment for UTI at LifeForce can help you. You may use the form below to get in touch with us. Alternately you could reach us at via a phone call on + 91-22-66-888888, or visit us at or email us at
| Rating |
You May Like: Can A Bladder Infection Cause Dizziness
Can You Test For Biofilms In The Bladder
The presence of biofilms in the bladder is not far-fetched science.
The National Institutes of Health estimates around 80% of all bacterial infections in humans involve biofilms.
Although the existence of biofilms in human infection has been accepted in medicine for decades, it is much more recently that attention has turned to their involvement in chronic UTI.
| In my opinion it’s pretty clear that biofilms and IBCs are a true phenomenon, and it would explain why a given patient can get what seems like a perfectly appropriate antibiotic based on antibiotic susceptibility testing from cultured bacteria. Then as soon they stop taking the antibiotic, the same exact bacterial isolate comes roaring back with the same antibiotic susceptibility. Why wasnt it wiped out? Well, I think sometimes it’s IBCs, or biofilms. And then in other cases, it may be that they’ve reseeded themselves from their distal guts or their vagina as well.” |
Traditionally, testing labs have focused on culturing and testing free-floating pathogens. If free-floating pathogens are identified, their susceptibility to antibiotics is also tested while they are in a free-floating state.
Once the susceptibility has been tested, it is possible to prescribe the right treatment.
The problem with these types of tests is that they do not specifically detect biofilm formations in the bladder. And therefore, they are not helpful in deciphering which treatments may be effective against microbes within a biofilm.
What Should You Do If You Keep Getting Recurring Utis
If you continue to have UTIs, you should consult your primary care doctor at the earliest to manage the condition and prevent it from worsening. After discussing with you, your doctor will either propose therapies or refer you to a urologist.
Request an appointment at MI Express Primary Care today if you are facing any symptoms of UTIs. Our medical team is well-experienced in treating UTIs and can provide a personalized treatment plan for you.
Read Also: How To Train A Weak Bladder
What Causes Chronic Urinary Tract Infections
- Bacteria from the rectum and vagina
- Bacteria entering the urethra during sexual intercourse
- Urinary tract problems
- Problems emptying the bladder completely due to blockage, muscle or nerve problems
- Kidney or bladder stones
- Altered estrogen levels during menopause
- Genetic predisposition
Women are at an increased risk of getting urinary tract infections if they:
- Have had a UTI before
- Have had several children
How To Avoid The Recurrence Of Utis
Drinking lots of water, urinating before and after sexual intercourse, and not waiting to urinate can all help reduce your incidence of urinary tract infections. Other remedies include wiping from front to back after urinating, wearing cotton underwear, and seeking treatment at the first sign of a UTI.
Contact Cleveland Urology Associates at if you are experiencing early signs of a urinary tract infection.
Don’t Miss: Antibiotics For Uti Or Bladder Infection
How Are Recurrent Utis Treated
Treatment for recurrent UTIs depends on what’s causing them. Sometimes the answer is as simple as teaching a child to empty their bladder as soon as they have the urge to go.
If a condition like VUR is causing the infections, the solution is a bit more complicated. Kids with VUR must be watched closely, because it can lead to kidney infection and kidney damage. Most kids outgrow the condition. Some might need surgery to correct the reflux.
Some kids with VUR benefit from daily treatment with a small amount of antibiotics, which can also make surgery unnecessary. Kids with VUR should see a pediatric urologist, who can decide if antibiotic treatment is the best option.
In some cases, surgery is needed to correct VUR. The most common procedure is ureteral reimplantation, in which one or both of the ureters are repositioned to correct the backflow of urine from the bladder. This procedure requires only a small incision and, in some children, can be done using robotic-assisted laparoscopy. When surgery is necessary, the success rate is high, but not everyone is a good candidate for it.
Kids may be candidates for ureteral reimplantation if they:
- have an intolerance to antibiotics
- get recurrent infections while on antibiotic treatment
- have severe, or “high-grade,” reflux
- are older kids and teens with reflux
How To Help Your Loved One Avoid Utis
Do you give the older adult in your life cranberry juice or probiotics to prevent a UTI? These products wont hurt them, but whether theyll help is unclear.
We dont have enough research to support their effectiveness in UTI prevention, although their medical benefits cant be ruled out completely, says Dr. Goldman.
Instead, he recommends these tried-and-true prevention strategies:
- Encourage sufficient fluid intake
- Promote genital and urinary hygiene
- Ask the doctor about low-dose vaginal cream for postmenopausal women
Dr. Goldman says researchers are also studying D-Mannose for UTI prevention. The supplement, which has few side effects, sticks to bladder receptors that normally attract the E. coli bacteria usually responsible for UTIs.
Researchers also believe D-Mannose may keep bad bacteria from colonizing the digestive tract, which can harbor the bacteria responsible for UTIs in women.
Following these tips should help your aging relative stay healthy, productive and out of the hospital.
You May Like: What Causes Weak Bladder In Females
How Are Antibiotics For Uti Selected
If you arrive at a clinic with a UTI, there are three things your doctor doesnt yet know:
Which pathogen is causing your infection
Which classes of antibiotic will effectively treat that bacterium
The resistance of that bacterium to different antibiotic classes
Your doctor may send your urine sample to a lab for testing, but if you are in a lot of discomfort in the meantime, they may prescribe according to a few common guidelines on how UTI antibiotics are selected, along with their best-educated guess.
If your antibiotics arent working, there are a few possible reasons why:
-
It might not be the right antibiotic
-
Your symptoms may be caused by more than one organism – so your antibiotic might not be treating the entire bacterial community
-
Your symptoms may not be caused by bacteria
-
You may have an embedded infection that requires longer term treatment.
Ineffective antibiotic treatment may in fact contribute to the recurrence of UTI by allowing bacteria to increase their resistance to that type of antibiotic.
Utis And Sexually Transmitted Diseases
A number of sexually transmitted infections are known to cause UTIs, including trichomoniasis and chlamydia. Oftentimes a person will assume that the UTI is bacterial in nature and fail to identify the underlying STI.
It is, therefore, vital to consider your risk of STIs when any infection of the genitals or urinary tract is involved. This is especially true if you have multiple sex partners or have gotten a UTI after having sex with a new partner.
Current pediatric guidelines recommend that doctors take a comprehensive sexual history of any adolescent with urinary tract complaints and routinely test them for STIs.
Sexually active men under the age of 35 who don’t use condoms can experience a condition called epididymitis. It is an infection of the epididymis, the coiled tube to the back of the testicles, that can be caused either by bacteria or an STI, most often gonorrhea or chlamydia. Treatment varies based on the cause and severity.
Safer sex practices, which include the consistent use of condoms, are always the best plan for reducing the risk of these and other STIs.
You May Like: What Side Is The Bladder On