Tests For Bladder Cancer
Your doctor may do some tests to check for bladder cancer:
- internal examination the doctor may check inside your bottom or vagina with their finger, using gloves
- urine tests your urine will be checked for signs of bladder cancer
- blood tests to check your general health
- ultrasound a scan on the outside of your abdomen to check for cancer
- cystoscopy the doctor puts a small camera into your bladder to see inside
- biopsy the doctor takes a small sample of the cells from the bladder to check for signs of cancer.
Your doctor might ask you to have further tests. These can include:
- CT scan and x-rays scans that take pictures of the inside of the body, sometimes also called a CT-IVP or a triple phase abdominal-pelvic CT scan
- MRI scan a scan that uses magnetism and radio waves to take pictures of the inside of the body
- bone scan a scan that uses dye to show changes in your bones
- FDG-PET scan a scan that uses an injection of liquid to show cancer cells.
Treating Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the pelvic or abdominal wall , may have spread to nearby lymph nodes , and/or have spread to distant parts of the body . Stage IV cancers are very hard to get rid of completely.
Chemotherapy is usually the first treatment if the cancer has not spread to distant parts of the body . The tumor is then rechecked. If it appears to be gone, chemo with or without radiation or cystectomy are options. If there are still signs of cancer in the bladder, chemo with or without radiation, changing to another kind of chemo, trying an immunotherapy drug, or cystectomy may be recommended.
Chemo is typically the first treatment when bladder cancer has spread to distant parts of the body . After this treatment the cancer is rechecked. If it looks like it’s gone, a boost of radiation to the bladder may be given or cystectomy might be done. If there are still signs of cancer, options might include chemo, radiation, both at the same time, or immunotherapy.
In most cases surgery cant remove all of the cancer, so treatment is usually aimed at slowing the cancers growth and spread to help people live longer and feel better. If surgery is a treatment option, it’s important to understand the goal of the operation whether it’s to try to cure the cancer, to help a person live longer, or to help prevent or relieve symptoms from the cancer.
Because treatment is unlikely to cure these cancers, many experts recommend taking part in a clinical trial.
Drugs To Treat Cancer Spread To Bone
If prostate cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it almost always goes to the bones first. These areas of cancer spread can cause pain and weak bones that might break. Medicines that can help strengthen the bones and lower the chance of fracture are bisphosphonates and denosumab. Sometimes, radiation, radiopharmaceuticals, or pain medicines are given for pain control.
Side effects of bone medicines
A serious side effect of bisphosphonates and denosumab is damage to the jaw, also called osteonecrosis of the jaw . Most people will need to get approval from their dentist before starting one of these drugs.
Also Check: Mild Bladder Infection Home Remedies
Expert Review And References
- Gallbladder cancer. American Cancer Society. Gallbladder Cancer. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society 2014.
- Hodgin MB. Gallbladder and bile duct cancer. Yarbro, CH, Wujcki D, & Holmes Gobel B. . Cancer Nursing: Principles and Practice. 7th ed. Sudbury, MA: Jones and Bartlett 2011: Chapter 55. pp: 1316-1333.
- Patel,T. and Borad, M.J.. Cancer of the biliary tree. DeVita VT Jr, Lawrence TS, & Rosenberg SA. Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2015: 53:715-733.
Take Charge Of Your Health With Cxbladder
Early detection saves lives and is a crucial factor when it comes to the treatment of bladder cancer. Cxbladder is a clinically proven cutting-edge genomic urine test that quickly and accurately detects or rules out bladder cancer in patients presenting with blood in the urine and those being monitored for recurrence. The test works at a molecular level, measuring five biomarker genes to detect the presence or absence of bladder cancer.
Cxbladder is discreet, quick, non-invasive and painless, typically giving you meaningful results within five working days. It comes as a suite of test options, each optimized for a different point in the patient journey.
- Triage: Incorporates known bladder cancer risk factors to help rapidly rule out the disease.
- Detect: Designed to work alongside other tests to improve overall detection accuracy.
- Monitor: Optimised for bladder cancer surveillance, reducing the need for further invasive tests
Cxbladder gives you peace of mind and will help your doctor make informed treatment decisions. Speak to your general practitioner or urologist to learn more about Cxbladder and which test might be right for you. You can also contact our Customer Service Team directly.Contact us for more information
Also Check: How Do Doctors Test For Bladder Infection
Treating Stage 0 Bladder Cancer
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma and flat non-invasive carcinoma . In either case, the cancer is only in the inner lining layer of the bladder. It has not invaded the bladder wall.
This early stage of bladder cancer is most often treated with transurethral resection with fulguration followed by intravesical therapy within 24 hours.
Living With Advanced Cancer
Advanced cancer usually means cancer that is unlikely to be cured. Some people can live for many months or years with advanced cancer. During this time palliative care services can help.
Most people continue to have treatment for advanced cancer as part of palliative care, as it helps manage the cancer and improve their day-to-day lives. Many people think that palliative care is for people who are dying but palliative care is for any stage of advanced cancer. There are doctors, nurses and other people who specialise in palliative care.
Treatment may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy or another type of treatment. It can help in these ways:
- slow down how fast the cancer is growing
- shrink the cancer
- help you to live more comfortably by managing symptoms, like pain.
Treatment depends on:
- how far it has spread
- your general health
Also Check: How Quickly Does Bladder Cancer Grow
Selecting And Testing Gemcitabine
When Dr. Messing began research on gemcitabine as a possible way to reduce recurrences more than a decade ago, the drug was not widely used for bladder cancer. “We tried to pick an agent that we thought would be safe and effective,” he said.
The researchers decided to compare gemcitabine against placebo rather than mitomycin C, based on studies showing how infrequently patients received some form of chemotherapy following surgery despite guidelines recommending this approach.
“If the new procedure were adopted widely, we could spare patients a lot of suffering from repeated surgeries and save health care costs associated with those surgeries,” Dr. Messing said.
“Now that we have the results of the trial,” he went on, “we hope that patients and physicians will embrace this approach to treatment.”
Low Grade And High Grade
Bladder cancer can also be described as either low grade or high grade.
Low grade bladder cancer means that your cancer is less likely to grow, spread and come back after treatment. High grade means your cancer is more likely to grow spread and come back after treatment.
For example, if you have early bladder cancer but the cells are high grade, you’re more likely to need further treatment after surgery. This is to reduce the risk of your cancer coming back.
Low grade is the same as grade 1. High grade is the same as grade 3. Grade 2 can be split into either low or high grade. Carcinoma in situ tumours are high grade.
Also Check: Percentage Of Bladder Tumors That Are Cancerous
Do Benign Tumors Need To Be Removed
It depends, says Dr. Guru. Benign bladder masses usually grow very slowly and will not spread to other tissues or organs in the body. In some cases, we will just monitor patients on a regular basis. However, some benign masses can bleed or grow very large and cause problems by taking up too much space in your bladder or pressing on other organs in your body. In that case, we usually remove or treat benign masses, using a TURBT procedure.
If you are ever unsure about your bladder symptoms or your bladder tumor diagnosis, we recommend an appointment with our multidisciplinary cancer care experts at Roswell Park.
What Affects Survival Rate And What Treatment Options Are Available
After diagnosing bladder cancer, your doctor will try to determine if it has advanced and if it has, how far. Doctors use a staging process to describe how far the tumor has penetrated the surrounding tissue and muscle, and to what extent it has spread to other parts of the body or metastasized. The staging process helps the doctor decide on the best way to treat it.
The American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM system is the most widely used staging system for bladder cancer. It relies on three critical factors:
- T: The letter “T” stands for “tumor” and describes the degree to which the tumor has grown through the wall of your bladder and into neighboring tissue and muscles.
- N: The letter “N” stands for “nodes” and notes if the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are groups of immune system cells about the size of beans. When cancer starts to spread, it frequently spreads to the lymph nodes nearest the bladder first.
- M: The letter “M” stands for “metastasized,” which means the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver, lungs or other lymph nodes farther from the bladder.
The American Cancer Society provides a detailed breakdown of the TNM system. Letters or numbers after T, N and M offer more detail related to the progression of the cancer.
Recommended Reading: Why Do I Have A Bladder Infection
Risk Factors Of Bladder Cancer
By far, smoking is the biggest risk factor to be concerned about when it comes to bladder cancer. According to the National Institutes of Health, about 50% of women diagnosed with bladder cancer are smokers. Because the rate of occurrence is so much higher for smokers, if you notice any of the above symptoms and you smoke, let your doctor know as soon as possible.
Another major risk factor is previously having bladder cancer. Bladder cancer has a 50-80% recurrence rate, which is among the highest of any form of cancer. This is why it is imperative to continue to see your physician and be on the lookout for any symptoms of bladder cancer if youve had it before. When in doubt, get it checked out.
Age is another major factor. The average age of diagnosis in women is 73. Any woman over the age of 55 years old should keep an extra eye out for symptoms.
What Stages Have To Do With Cancer Spread
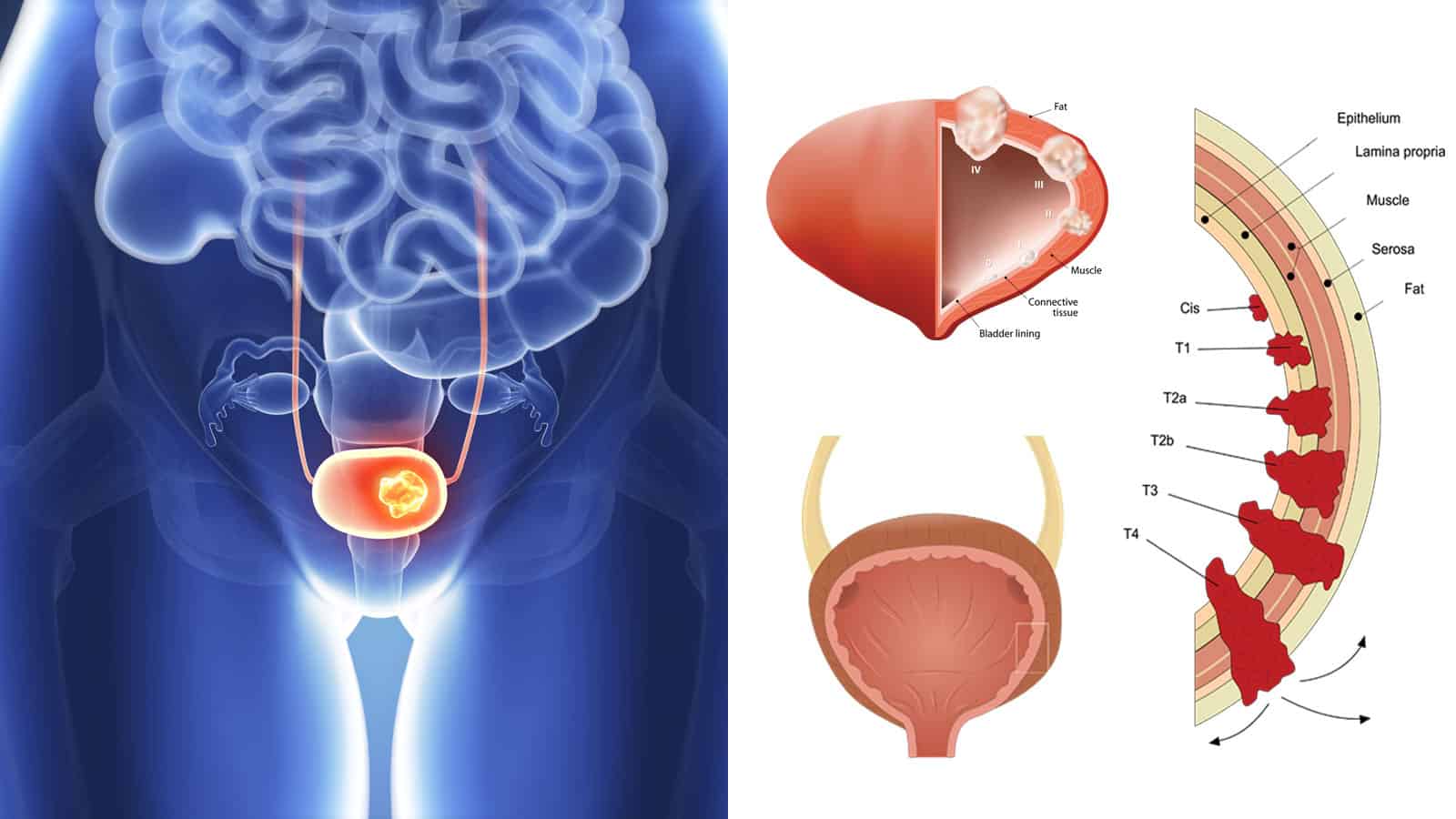
Cancers are staged according to tumor size and how far it has spread at the time of diagnosis. Stages help doctors decide which treatments are most likely to work and give a general outlook.
There are different types of staging systems and some are specific to certain types of cancer. The following are the basic stages of cancer:
- In situ. Precancerous cells have been found, but they havent spread to surrounding tissue.
- Localized. Cancerous cells havent spread beyond where they started.
- Regional. Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes, tissues, or organs.
- Distant. Cancer has reached distant organs or tissues.
- Unknown. Theres not enough information to determine the stage.
- Stage 0 or CIS. Abnormal cells have been found but have not spread into surrounding tissue. This is also called precancer.
- Stages 1, 2, and 3. The diagnosis of cancer is confirmed. The numbers represent how large the primary tumor has grown and how far the cancer has spread.
- Stage 4. Cancer has metastasized to distant parts of the body.
Your pathology report may use the TNM staging system, which provides more detailed information as follows:
T: Size of primary tumor
- TX: primary tumor cant be measured
- T0: primary tumor cant be located
- T1, T2, T3, T4: describes the size of the primary tumor and how far it may have grown into surrounding tissue
N: Number of regional lymph nodes affected by cancer
M: Whether cancer has metastasized or not
Don’t Miss: How To Empty Bladder With Uti
Evaluating A Bladder Mass
To assess a bladder mass, urologists perform a physical examination, and blood and urine tests to evaluate for the presence of blood in the urine. You may also have a bladder wash to obtain cells from your bladder for a pathologist to analyze. But ultimately, the urologist needs to look inside your bladder via a procedure called cystoscopy.
Cystoscopy involves passing a cystoscope through the urethra and into the bladder, allowing the urologist to see what is there.
If your cystoscopy or imaging scans reveal a suspicious mass or any irregularity, such as a lesion, we will obtain a biopsy or tissue sample through an incisionless surgical procedure called Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor . During a TURBT, the surgeon inserts a tool called a resectoscope through the urethra to reach the inside of your bladder and remove a piece of tumor tissue or the entire tumor from your bladder.
A pathologist will then examine the tissue to determine whether it is benign or cancerous.
At Roswell Park, our pathologists are fully trained for all disease sites, but also specialize in diagnosing tumors of specific sites, such as the urinary tract, says Dr. Guru. As a high-volume cancer center, Roswell Park has pathologists who examine bladder mass tissue samples every day.
Is A Mass In The Bladder Always Cancer
If youve been told that you have a mass in your bladder, you need to have it evaluated by experts uniquely qualified to determine whether or not it is cancer.
While there are several types of benign masses that can grow in the bladder, these are uncommon and account for fewer than 1% of bladder masses,” says Khurshid Guru, MD, Chair of Roswell Parks Department of Urology.
Also Check: Antibiotics For Bladder And Kidney Infection
What Is Bladder Cancer
Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the bladder is called bladder cancer. It starts when cells in the bladder grow out of control and crowd out normal cells. This makes it hard for the body to work the way it should.
Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body. For instance, cancer cells in the bladder can travel to the bone and grow there. When cancer cells spread, its called metastasis.
Cancer is always named for the place where it starts. So when bladder cancer spreads to the bone , it’s still called bladder cancer. Its not called bone cancer unless it starts in the bone.
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- What treatment do you think is best for me?
- Whats the goal of this treatment? Do you think it could cure the cancer?
- Will treatment include surgery? If so, who will do the surgery?
- What will the surgery be like?
- How will I pee after surgery?
- Will I have other types of treatment, too?
- Whats the goal of these treatments?
- What side effects could I have from these treatments?
- Is there a clinical trial that might be right for me?
- What about treatments like special vitamins or diets that friends tell me about? How will I know if they are safe?
- What should I do to be ready for treatment?
- Is there anything I can do to help the treatment work better?
- Whats the next step?
Read Also: Harmony Urinary Tract And Bladder Support
Stages Of Cervical Cancer
Stage 0: Cervical dysplasia or Precancerous cells are detected. A biopsy is initially performed to identify any abnormalities. If found, surgery is performed to remove all of the precancerous cells.
Stage 1: Cancer has not spread outside the cervix.
Stage 2: The cancer has spread but is within the pelvic wall. The cancer is not in present in the lower third of the vagina.
Stage 3: Cancer has spread to either further than the pelvic wall or to the lower third of the vagina.
Stage 4: The cancer has spread beyond the pelvis, or into the bladder or rectum.
Further categorizations such as an A or B are used based on the exact size of the primary tumor and exact location of metastasis.
For the earliest stages of cervical cancer, either surgical procedure or radiation mixed with chemo may be used. For advanced stages, radiation combined with chemo is normally the principle treatment method. If first-line treatments are unsuccessful, clinical trials are a viable option for many patients.
What Are The Treatment Options For Bladder Cancer
There are four types of treatment for patients with bladder cancer. These include:
- Surgery
Sometimes, combinations of these treatments will be used.
Surgical options
Surgery is a common treatment option for bladder cancer. The type of surgery chosen will depend on the stage of the cancer.
- Transurethral resection of the bladder is used most often for early stage disease . It is done under general or spinal anesthesia. In this procedure, a special telescope called a resectoscope is inserted through the urethra into the bladder. The tumor is then trimmed away with the resectoscope, using a wire loop, and the raw surface of the bladder is then fulgurated .
- Partial cystectomy is the removal of a section of the bladder. At times, it is used for a single tumor that invades the bladder wall in only one region of the bladder. This type of surgery retains most of the bladder. Chemotherapy or radiation therapy is often used in combination. Only a minority of patients will qualify for this bladder-sparing procedure.
- Radical cystectomy is complete removal of the bladder. It is used for more extensive cancers and those that have spread beyond the bladder .
This surgery is often done using a robot, which removes the bladder and any other surrounding organs. In men, this is the prostate and seminal vesicles. In women, the ovaries, uterus and a portion of the vagina may be removed along with the bladder.
Chemotherapy
- Methotrexate
Intravesical therapy
Radiation therapy
Recommended Reading: Bladder Cancer Ct Scan With Contrast