How To Check For Cancer In Urine
When you pee in a cup at your doctors office, there are a number of things they and other health professionals can look for: 1 Urinalysis. Your doctor will check to see if theres any blood, or other substances, in your urine. 2 Urine cytology. Your doctor will use a microscope to check your urine for cancer cells. 3 Urine culture. Your doctor will send your urine to a lab. After a few days, lab technicians will check to see what kinds of germs grow in it. These results will tell your doctor if you have a bladder infection. 4 Urine tumor marker tests. These look for substances that are released by bladder cancer cells. Your doctor may use one or more of these along with a urine cytology to see if you have the disease.
Next Steps After Urine Lab Tests
Depending on the results of the patients physical examination and urine laboratory tests, healthcare providers may need to carry out further testing to help make a diagnosis.1,2 The tests can also be used in patients who have already been diagnosed with bladder cancer to help gather more information about the cancer and develop the patients treatment plan.
What Is The Best Treatment For Cancer
Radiation therapy, to destroy cancer cells, often as a primary treatment when surgery isnt an option or isnt desired. Immunotherapy, to trigger the bodys immune system to fight cancer cells, either in the bladder or throughout the body. Targeted therapy, to treat advanced cancer when other treatments havent helped.
Also Check: What Could Cause Bladder Leakage
Bladder And Other Urothelial Cancers Screening Patient Version
On This Page
Screening is looking for cancer before a person has any symptoms. This can help findcancer at an early stage. When abnormaltissue or cancer is found early, it maybe easier to treat. By the time symptoms appear, cancer may have begunto spread.
Scientists are trying to better understand whichpeople are more likely to get certain types of cancer. They also study the thingswe do and the things around us to see if they cause cancer. Thisinformation helps doctors recommend who should be screened for cancer, whichscreening tests should be used, and how often the tests should be done.
It is important to remember that your doctor does not necessarilythink you have cancer if he or she suggests a screening test. Screeningtests are given when you have no cancer symptoms.
If a screening test result is abnormal, you may need to have more tests done to find out if you have cancer. These are called diagnostic tests.
Common Tests & Procedures
Most doctors feel that cystoscopy is still the best way to find bladder cancer. Some of these tests are more helpful for finding bladder cancer that has come back in someone who has already had it, rather than first diagnosing it. Cystoscopy. If bladder cancer is suspected, most doctors will recommend a cystoscopy. .
You May Like: Small Cell Bladder Cancer Survival Rate
What Is A Cxbladder Triage
Cxbladder Triage. If you have blood in your urine, you or your doctor may wish to quickly rule out bladder cancer. Cxbladder Triage analyzes the gene expression of urine-based biomarkers alongside information on known blad der cancer risk factors like age, gender and smoking history to rule out patients with a low risk of having the disease.
Urine Cytology Tests After A Cystoscopy
Urine cytology tests can also be used after a procedure called cystoscopy, in which a sterile liquid is injected into the bladder to allow the bladder to expand so it can be adequately examined. When the liquid is removed from the bladder it may be analyzed with cytology testing to check for the presence of cancer or pre-cancer cells.
Read Also: Why Does My Bladder Feel Sore
Patients Can Enter Clinical Trials Before During Or After Starting Their Cancer Treatment
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCIs clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
How Is Bladder Cancer Removed From The Body
· A test, which uses patented technology to detect MCM5 in urine, could help urologists rule out bladder cancer in as little as two hours. At a time when experts from the Institute for Public Policy Research are warning that up to 7,200 excess deaths from cancer could occur due to delays in diagnosis because of COVID-19, it is vital that urologists have the tools
You May Like: Will Cranberry Juice Help A Bladder Infection
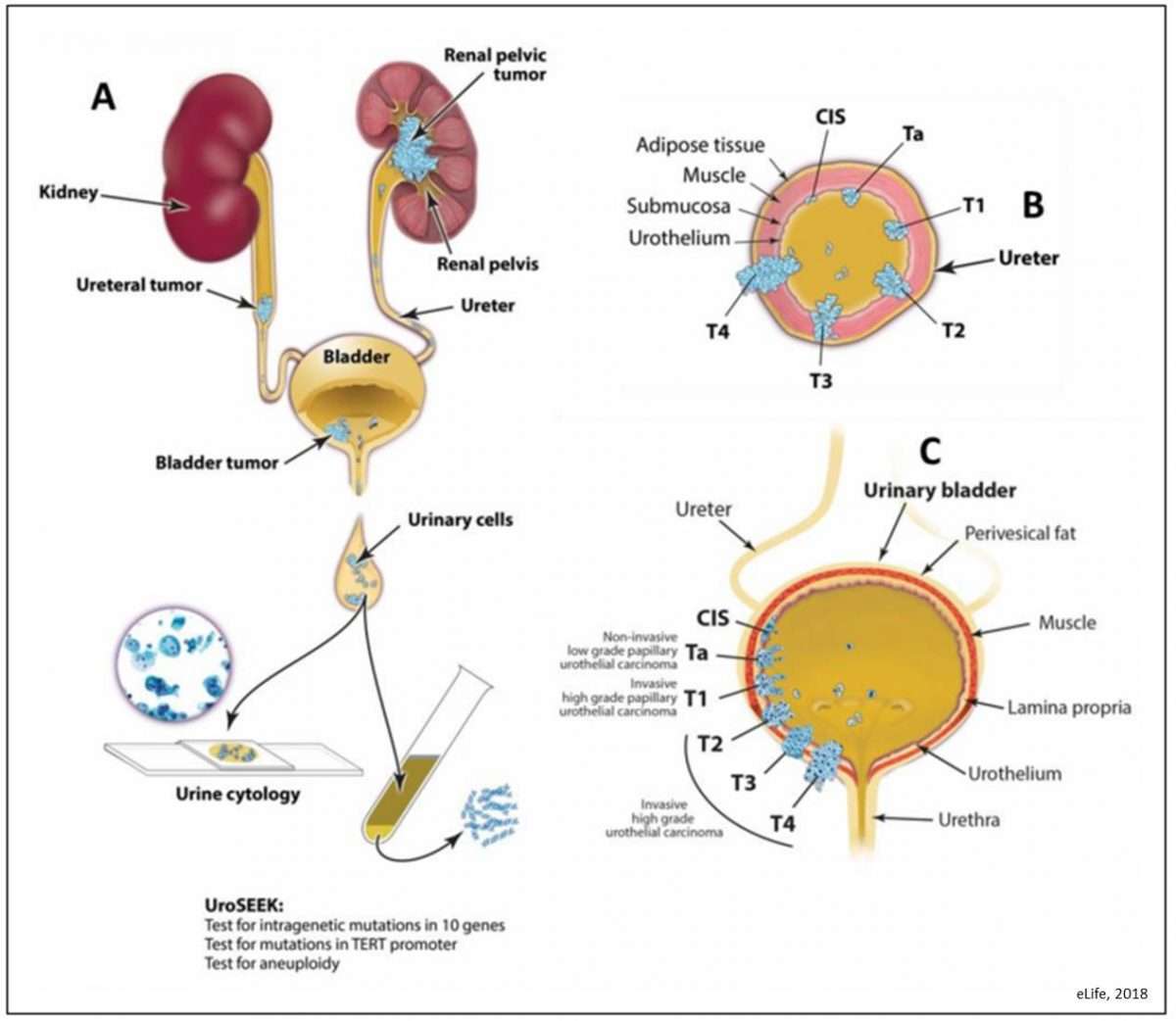
Bladder Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Bladder
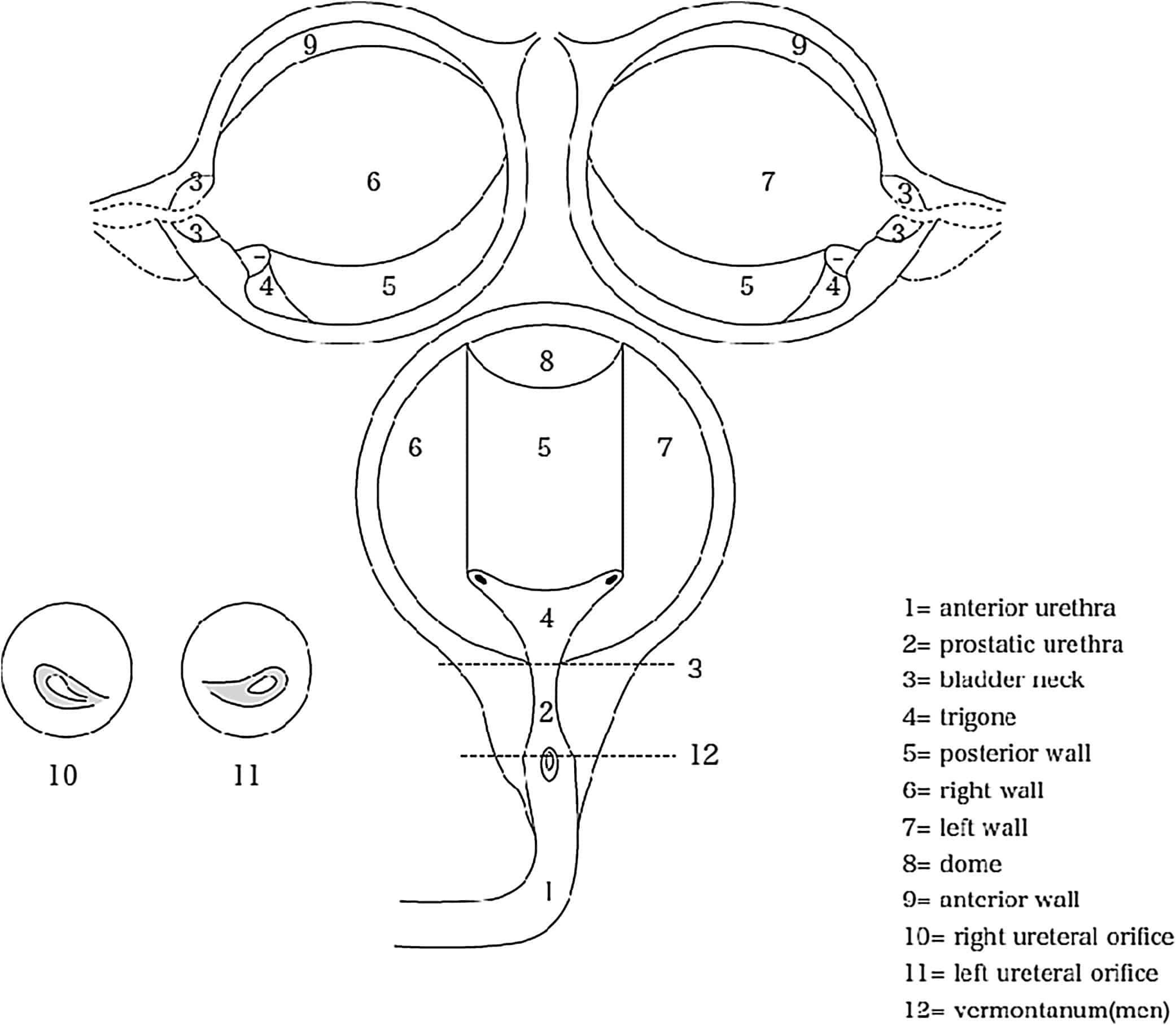
The bladder is a hollow organ in the lower part of the abdomen. It is shaped like a small balloon and has a muscular wall that allows it to get larger or smaller to store urine made by the kidneys. There are two kidneys, one on each side of the backbone, above the waist. Tiny tubules in the kidneys filter and clean the blood. They take out waste products and make urine. The urine passes from each kidney through a long tube called a ureter into the bladder. The bladder holds the urine until it passes through the urethra and leaves the body.
There are three types of bladder cancer that begin in cells in the lining of the bladder. These cancers are named for the type of cells that become malignant :
- Transitional cell carcinoma: Cancer that begins in cells in the innermost tissue layer of the bladder. These cells are able to stretch when the bladder is full and shrink when it is emptied. Most bladder cancers begin in the transitional cells. Transitional cell carcinoma can be low-grade or high-grade:
- Low-grade transitional cell carcinoma often recurs after treatment, but rarely spreads into the muscle layer of the bladder or to other parts of the body.
- High-grade transitional cell carcinoma often recurs after treatment and often spreads into the muscle layer of the bladder, to other parts of the body, and to lymph nodes. Almost all deaths from bladder cancer are due to high-grade disease.
See the following PDQ summaries for more information:
How Do You Confirm Bladder Cancer
Cystoscopy. Cystoscopy is the key diagnostic procedure for bladder cancer. It allows the doctor to see inside the body with a thin, lighted, flexible tube called a cystoscope. Flexible cystoscopy is performed in a doctors office and does not require anesthesia, which is medication that blocks the awareness of pain.
Also Check: Can Second Hand Smoke Cause Bladder Cancer
Treatment Of Bladder Cancer By Stage
Most of the time, treatment of bladder cancer is based on the tumors clinical stage when it’s first diagnosed. This includes how deep it’s thought to have grown into the bladder wall and whether it has spread beyond the bladder. Other factors, such as the size of the tumor, how fast the cancer cells are growing , and a persons overall health and preferences, also affect treatment options.
How Do Healthcare Providers Diagnose Bladder Cancer
Healthcare providers do a series of tests to diagnose bladder cancer, including:
- Urinalysis: Providers use a variety of tests to analyze your pee. In this case, they may do urinalysis to rule out infection.
- Cytology: Providers examine cells under a microscope for signs of cancer.
- Cystoscopy: This is the primary test to identify and diagnose bladder cancer. For this test, providers use a pencil-sized lighted tube called a cystoscope to view the inside of your bladder and urethra. They may use a fluorescent dye and a special blue light that makes it easier to see cancer in your bladder. Providers may also take tissue samples while doing cystoscopies.
If urinalysis, cytology and cystoscopy results show you have bladder cancer, healthcare providers then do tests to learn more about the cancer, including:
Healthcare providers then use what they learn about the cancer to stage the disease. Staging cancer helps providers plan treatment and develop a potential prognosis or expected outcome.
Bladder cancer can be either early stage or invasive .
The stages range from TA to IV . In the earliest stages , the cancer is confined to the lining of your bladder or in the connective tissue just below the lining, but hasnt invaded the main muscle wall of your bladder.
Stages II to IV denote invasive cancer:
A more sophisticated and preferred staging system is TNM, which stands for tumor, node involvement and metastases. In this system:
Read Also: Bladder Sling Lawsuit Settlement Amount
Permission To Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as NCIs PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: .
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Bladder Cancer Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated < MM/DD/YYYY> . Available at: . Accessed < MM/DD/YYYY> .
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author, artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
Complete Blood Count And Chemistry Panel
On the complete blood count , the presence of anemia or an elevated white blood cell count warrants further investigation for an explanation.
The chemistry panel should include liver function studies. Although BCG is administered intravesically, systemic absorption of this agent can produce acute hepatitis. Performing baseline liver function tests before initiating therapy and repeating these tests during the course of therapy is important to help prevent serious adverse events and to determine when therapy should be stopped. In patients with suspected metastasis to liver or bone, liver function tests and measurement of the bony fraction of alkaline phosphatase should be performed.
Kidney function should be evaluated prior to the initiation of therapy because patients with marginal or abnormal kidney function may have an obstruction or some type of renal disease that may worsen with intravesical therapy. Kidney function can be evaluated with serum creatinine measurements or technetium scans of the kidneys.
You May Like: Treatment Of Overactive Bladder In Females
What To Expect During Your Visit With The Urological Oncologist
Your specialist will conduct a physical exam, feeling the abdomen and pelvis for possible tumors, and will review various test results. You also will be given a local anesthetic and undergo a cystoscopy, a procedure in which the doctor uses a thin, flexible scope to look in your bladder. If an abnormality is seen in your bladder during the cystoscopy, arrangements will be made for a surgical appointment to confirm your diagnosis.
Smoking Can Affect The Risk Of Bladder Cancer
Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesn’t mean that you will not get cancer. Talk to your doctor if you think you may be at risk for bladder cancer.
Risk factors for bladder cancer include the following:
- Using tobacco, especially smoking cigarettes.
- Having a family history of bladder cancer.
- Having certain changes in the genes that are linked to bladder cancer.
- Being exposed to paints, dyes, metals, or petroleum products in the workplace.
- Past treatment with radiation therapy to the pelvis or with certain anticancer drugs, such as cyclophosphamide or ifosfamide.
- Taking Aristolochia fangchi, a Chinese herb.
- Drinking water from a well that has high levels of arsenic.
- Drinking water that has been treated with chlorine.
- Having a history of bladder infections, including bladder infections caused by Schistosoma haematobium.
- Using urinarycatheters for a long time.
Older age is a risk factor for most cancers. The chance of getting cancer increases as you get older.
You May Like: What Causes A Cyst On Your Bladder
Treating Stage 0 Bladder Cancer
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma and flat non-invasive carcinoma . In either case, the cancer is only in the inner lining layer of the bladder. It has not invaded the bladder wall.
This early stage of bladder cancer is most often treated with transurethral resection with fulguration followed by intravesical therapy within 24 hours.
How Do Ultrasounds Help Detect And Monitor Bladder Cancer
An ultrasound of the urinary tract can help assess the size of a bladder tumor and whether a bladder cancer has spread. Ultrasound is able to differentiate between fluid-filled cysts and solid tumors, however, it cannot determine if a tumor is cancerous. Ultrasound can also be used to guide a biopsy needle to sample a suspected cancer.
Recommended Reading: Why Have I Lost Control Of My Bladder
Cxbladder Is A Genomic Urine Test That Improves Bladder Cancer Detection Accuracy
Cxbladder is a non-invasive and easy-to-use genomic urine test optimized for the detection and management of bladder cancer.
Cxbladder is a non-invasive genomic urine test optimized for the detection and management of bladder cancer. The test combines clinical risk factors with gene expression markers to quickly and accurately detect the presence or absence of bladder cancer.
You should consider a Cxbladder test when youve seen blood in your urine, when tests reveal you have blood in your urine, or when youve had bladder cancer and are being monitored for recurrence. Cxbladder provides greater certainty, resolving diagnostic ambiguity and improving overall detection accuracy. As a non-invasive surveillance alternative, the test can reduce the frequency of cystoscopy required in many patients.
Cxbladders proven accuracy makes it a reliable choice. With performance validated in over 20 peer-reviewed studies, Cxbladder is covered by Medicare and trusted by over 2,000 urologists in more than 80,000 patients. In New Zealand, the test is available to 70% of the population through public healthcare.
Take control of your care. Cxbladder comes with the option of in-home sampling for comfort and convenience, and provides reliable results that will help you and your doctor make informed diagnosis and management decisions.Learn more about Cxbladder Contact us for more information
Can You See Blood In Urine
Many patients diagnosed with bladder cancer have the symptom of blood in the urine that is easily visible, but in some patients the amount of blood is so small that it is not visible to the naked eye. Urinalysis can detect very small amounts of blood in the urine, which can sometimes help to diagnose bladder cancer at an earlier stage,
You May Like: Bladder Medication Over The Counter
What Causes Bladder Cancer
Healthcare providers and researchers dont know exactly why certain bladder cells mutate and become cancerous cells. Theyve identified many different risk factors that may increase your chance of developing bladder cancer, including:
- Cigarette smoke: Smoking cigarettes more than doubles your risk of developing bladder cancer. Smoking pipes and cigars and being exposed to second-hand smoke may also increase your risk.
- Radiation exposure: Radiation therapy to treat cancer may increase your risk of developing bladder cancer.
- Chemotherapy: Certain chemotherapy drugs may increase your risk.
- Exposure to certain chemicals: Studies show that people who work with certain chemicals used in dyes, rubber, leather, paint, some textiles and hairdressing supplies may have an increased risk.
- Frequent bladder infections: People who have frequent bladder infections, bladder stones or other urinary tract infections may be at an increased risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
- Chronic catheter use: People who have a chronic need for a catheter in their bladder may be at risk for squamous cell carcinoma.
What Is Renal Ultrasound
Renal ultrasound is the least invasive way to evaluate the kidneys. It does not require radiation and avoids contrast. It may be used in lower risk patients and those with contrast allergies or poor renal function. Unfortunately, it can miss small kidney stones and tumors. Also, it will not detect tumors in the ureter unless they are causing a blockage leading to hydronephrosis.
You May Like: Nerve Stimulation For Overactive Bladder
Ask Your Doctor For A Referral To A Urologist
For women diagnosed with a UTI, Dr. Donat has this advice: Make sure your doctor sends a urine culture for testing, she says. If you did have a culture, make sure it came back positive to confirm that you actually have an infection. If the culture was negative or your bladder symptoms continue despite treatment, dont be afraid to ask your doctor for a referral to a urologist to get a formal evaluation.
Tests can sometimes distinguish the bleeding associated with bladder cancer from postmenopausal uterine bleeding, but the results are not always clear-cut. Your gynecologist can send a catheterized urine sample for testing to determine the source of the blood and to evaluate for gynecologic causes of the bleeding, Dr. Donat explains. If your gynecologic exam fails to identify the source of the bleeding or is inconclusive, or if your irritative bladder symptoms persist, you should also seek out the expertise of a urologist.
Hematuria may originate in the bladder or the kidneys, says Dr. Donat, so a urologist needs to check both. This is best done with a special CT scan of the urinary tract called a CT urogram and by looking in the bladder with a lighted telescope called a cystoscope. This procedure, called a cystoscopy, is usually done in an office in just a few minutes and does not require anesthesia, says Dr. Donat. A urine test called a cytology may also be sent to check for cancer cells in the urine.