After Transitional Cell Cancer Of The Renal Pelvis And Ureter Has Been Diagnosed Tests Are Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Renal Pelvis And Ureter Or To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out if cancer has spread within the renal pelvis and ureter or to otherparts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from thestaging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to knowthe stage in order to plan treatment. The doctor will use results of the diagnostic tests to help find out the stage of the disease.
The following tests andprocedures may also be used in the staging process:
- Chest x-ray: An x-ray of the organs and bones inside the chest. An x-ray is a type of energy beam that can go through the body and onto film, making a picture of areas inside the body.
- PET scan : A procedure to find malignanttumorcells in the body. A small amount of radioactive glucose is injected into a vein. The PET scanner rotates around the body and makes a picture of where glucose is being used in the body. Malignant tumor cells show up brighter in the picture because they are more active and take up more glucose than normal cells do.
- Bone scan: A procedure to check if there are rapidly dividing cells, such as cancer cells, in the bone. A very small amount of radioactive material is injected into a vein and travels through the bloodstream. The radioactive material collects in the bones with cancer and is detected by a scanner.
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- What treatment do you think is best for me?
- Whats the goal of this treatment? Do you think it could cure the cancer?
- Will treatment include surgery? If so, who will do the surgery?
- What will the surgery be like?
- How will I pee after surgery?
- Will I have other types of treatment, too?
- Whats the goal of these treatments?
- What side effects could I have from these treatments?
- Is there a clinical trial that might be right for me?
- What about treatments like special vitamins or diets that friends tell me about? How will I know if they are safe?
- What should I do to be ready for treatment?
- Is there anything I can do to help the treatment work better?
- Whats the next step?
Dr David Samadi Is A Well
Dr. Samadi is one of the very few urologic surgeons in the United States trained in oncology, open, laparoscopic, and robotic surgery. He is also the first surgeon in the United States to successfully perform a robotic surgery redo. To date, Dr. Samadi has performed over 7,000+ prostate surgeries. This is more than any other prostate cancer surgeons in all of New York.
Make an appointment: 1-212-365-5000
You May Like: Bladder Cancer What To Expect
How Many People Died From Bladder Cancer In 2018
According to estimates from the American Cancer Society, the numbers related to bladder cancer cases in America, in 2018, will be: About 81,190 new diagnosed cases of bladder cancer, of which 76% will be diagnosed in men and 24% of them in women About 17,240 deaths from bladder cancer, of which 72% will occur in men and 28% in women.
Treatments For Kidney Infections
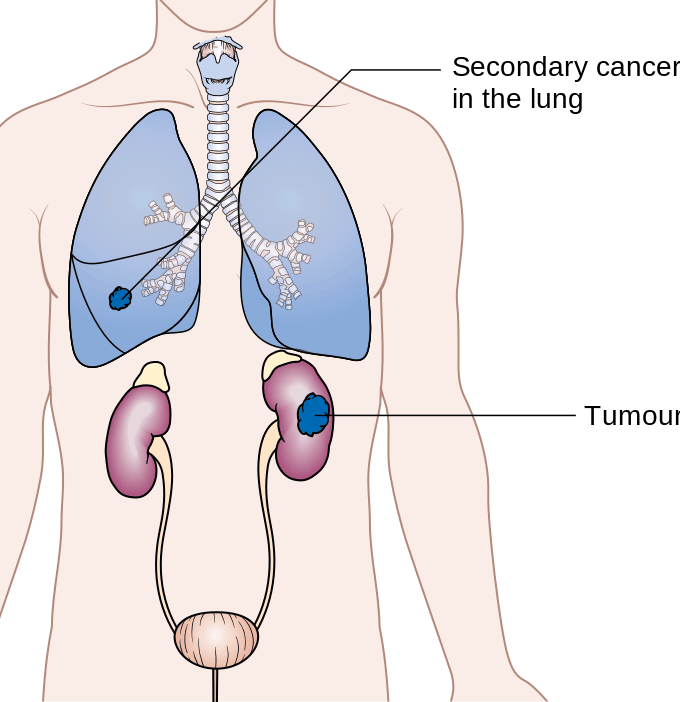
Kidney infections in men or women will typically require antibiotics. While home remedies exist, dont rely on them alone to take care of kidney infections. Delayed treatment can result in a very serious blood infection called sepsis.
Usually, doctors will prescribe empiric antibiotics to cover all the bases of potential bacteria that initially caused the infection until they can target the specific bacteria causing the infection.
A variety of available antibiotics are usually prescribed for at least a full week. Normally, you wont require a stay at a hospital for a kidney infection if you can move around and consistently keep down oral antibiotics.
Suppose you exhibit severe symptoms, including kidney infection symptoms or back pain, or cannot keep down the medication due to constant vomiting. In that case, you may be hospitalized so that your doctor may administer antibiotics and fluids intravenously. Pregnant women are most at risk of needing such additional care, and may be recommended to stay in the hospital for careful monitoring.
Other people who may require hospital stays due to kidney infections include those with sickle cell anemia, people aged 60 or over, patients in severe pain, and those experiencing severe vomiting. In addition, if the kidney infection progresses enough to create an abscess in the kidney, you may require more serious treatment.
Also Check: Does Cranberry Help Bladder Infections
Read Also: How Do You Know If Bladder Cancer Has Spread
Does The Cystoscopy Hurt
The cystoscopy doesnt usually hurt, but you might feel a slight urination sensation. If the sensation doesnt disappear shortly, you can tell your doctor or your nurse. The anesthesia is local so you will likely be awake. However, you will be given a sedative, so be sure you have someone to take you home after the procedure. People usually fear this procedure, but its a standard one, with minimal risks.
Stage Groups For Bladder Cancer
Doctors assign the stage of the bladder cancer by combining the T, N, and M classifications .
Bladder cancer
Stage 0a: This is an early cancer that is only found on the surface of the inner lining of the bladder. Cancer cells are grouped together and can often be easily removed. The cancer has not invaded the muscle or connective tissue of the bladder wall. This type of bladder cancer is also called noninvasive papillary urothelial carcinoma .
Stage 0is: This stage of cancer, also known as a flat tumor or carcinoma in situ , is found only on the inner lining of the bladder. It has not grown in toward the hollow part of the bladder, and it has not spread to the thick layer of muscle or connective tissue of the bladder . This is always a high-grade cancer and is considered an aggressive disease because it can lead to muscle-invasive disease.
Stage I: The cancer has grown through the inner lining of the bladder and into the lamina propria. It has not spread to the thick layer of muscle in the bladder wall or to lymph nodes or other organs .
Stage II: The cancer has spread into the thick muscle wall of the bladder. It is also called invasive cancer or muscle-invasive cancer. The tumor has not reached the fatty tissue surrounding the bladder and has not spread to the lymph nodes or other organs .
Stage IV: The tumor has spread into the pelvic wall or abdominal wall, or the cancer has spread to lymph nodes outside of the pelvis or to other parts of the body.
Recurrent cancer
Recommended Reading: How To Strengthen Weak Bladder Muscles
What Is Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the kidney. The most common type of kidney cancer is renal cell carcinoma , accounting for about 90% of all cases. Usually only one kidney is affected, but in rare cases the cancer may develop in both kidneys.
Other less common types include:
- Urothelial carcinoma which can begin in the ureter or renal pelvis where the kidney and ureter meet. It is generally treated like bladder cancer.
- Wilms tumour, which is most common in younger children although it is still rare.
It is estimated that 4377 people in Australia will be diagnosed with kidney cancer in 2021. Kidney cancer is more common in men – the risk of being diagnosed by age 85 is 1 in 47 for men compared to 1 in 100 for women.
The five year survival rate for kidney cancer is 79%.
What Is The Prostate
The prostate is a gland that is located just below a mans bladder. The tube that carries urine from the bladder and out of the body travels through the prostate. The main purpose of the prostate gland is reproductive. It is responsible for adding nutrients to sperm to help with fertilization of an egg.
By Genevra Pittman, Reuters Health
4 Min Read
NEW YORK Men who are treated for prostate cancer with hormone-targeted therapy have a higher risk of developing kidney problems, a new study suggests.
The treatment, known as androgen deprivation therapy, lowers the risk of death among men with advanced, aggressive prostate cancer.
However, researchers said its increasingly being used to treat possible recurrences among men with less advanced disease for whom the benefits are less clear, and the risks more worrisome.
Our study does raise the concern that perhaps we should be more careful in prescribing androgen deprivation therapy in patients who do not have the clear indication for it, said Laurent Azoulay, who worked on the research at McGill University in Montreal.
Its all about the balance, finding the right population for which the benefits clearly outweigh the risks, he told Reuters Health.
Hormone-targeted treatment has been linked to a higher risk of diabetes and heart disease.
You May Like: Period Underwear For Bladder Leakage
What Does Your Bladder Do
Your bladder is part of your urinary system. The job of the urinary system is to filter waste products from your blood and transport the waste products or urine, out of your body. The diagram below shows the organs of the urinary system.
Most of the urinary tract is lined with a special layer of cells called transitional cells. The primary machines in the human filtering system are the two kidneys located close to the backbone and protected by the ribs. The kidneys work independently. They have the significant task of filtering approximately 20% of total blood volume each minute and removing the by-products of digestion and of other body functions.
Once produced, the urine is stored in the central part of the kidney called the renal pelvis. At regular intervals, the renal pelvis contracts and propels the urine through the ureters. These narrow, thin-walled tubes extend from inside the renal pelvis to the bladder. The bladder is a thick-walled structure, consisting of a relatively thin inner layer with a thick muscle covering.
How Does Bladder Cancer Spread
Bladder cancer spreads when cancerous cells reproduce and invade surrounding healthy tissues. This is known as metastasis. Usually, metastatic bladder cancer refers to cancer that has spread to distant organs, but metastasis can occur locally in the muscles and connective tissues that are directly adjacent to the bladder as well.
Don’t Miss: What To Take For Overactive Bladder
Treatment Of Bladder Cancer By Stage
Most of the time, treatment of bladder cancer is based on the tumors clinical stage when it’s first diagnosed. This includes how deep it’s thought to have grown into the bladder wall and whether it has spread beyond the bladder. Other factors, such as the size of the tumor, how fast the cancer cells are growing , and a persons overall health and preferences, also affect treatment options.
How Will I Feel
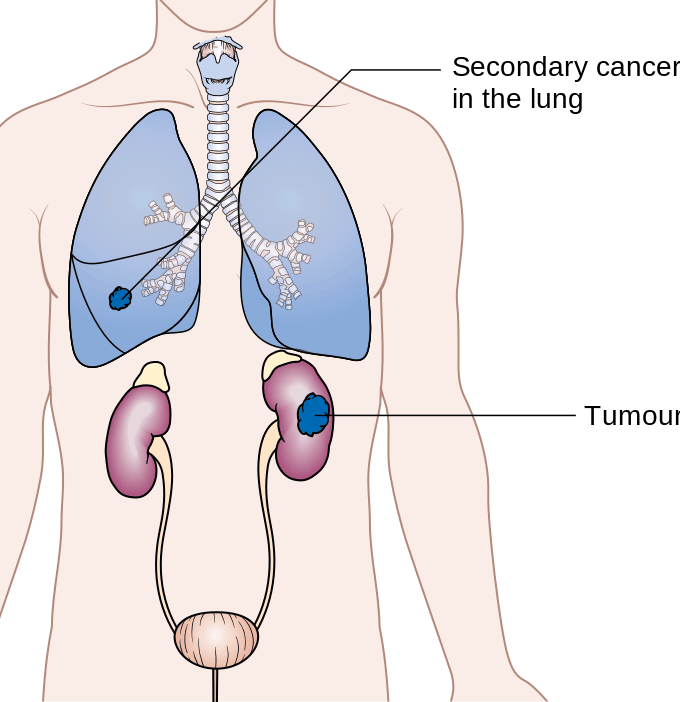
The symptoms of kidney cancer are different for each person. In most cases, youâll see blood in your pee. You may feel generally sick, tired, and like you donât want to eat much. And you may have:
- A fever that comes and goes
- A lump in your belly
- Night sweats, so much that you need to change your clothes or sheets
- Pain in your back or side that wonât go away
- Weight loss for no reason
You might also get symptoms where the cancer spreads. If itâs in one of your bones, you might feel pain there. In your lungs, it can give you a cough or trouble breathing.
Don’t Miss: Does Oxybutynin Cure Overactive Bladder
How Does Kidney Cancer Spread
As the tumor grows, it spreads into fat or major blood vessels around the kidney. It may also creep into the adrenal gland, which sits right on top of the organ.
From there, it can spread farther through your:
- Blood. Cancer cells that get into a blood vessel can travel to many body parts through your veins and arteries.
- Lymph system. This is a network that runs throughout your body, much like your blood vessels. It helps you fight disease. But cancer cells that get into lymph nodes can hitch a ride to other organs.
Kidney cancer most often spreads to the lungs and bones, but it can also go to the brain, liver, ovaries, and testicles.
Because it has no symptoms early on, it can spread before you even know you have it. If you do find it early, but treatment doesnât get rid of all the cancer cells, it can come back in your kidney or somewhere else.
How Do Healthcare Providers Diagnose Bladder Cancer
Healthcare providers do a series of tests to diagnose bladder cancer, including:
- Urinalysis: Providers use a variety of tests to analyze your pee. In this case, they may do urinalysis to rule out infection.
- Cytology: Providers examine cells under a microscope for signs of cancer.
- Cystoscopy: This is the primary test to identify and diagnose bladder cancer. For this test, providers use a pencil-sized lighted tube called a cystoscope to view the inside of your bladder and urethra. They may use a fluorescent dye and a special blue light that makes it easier to see cancer in your bladder. Providers may also take tissue samples while doing cystoscopies.
If urinalysis, cytology and cystoscopy results show you have bladder cancer, healthcare providers then do tests to learn more about the cancer, including:
Healthcare providers then use what they learn about the cancer to stage the disease. Staging cancer helps providers plan treatment and develop a potential prognosis or expected outcome.
Bladder cancer can be either early stage or invasive .
The stages range from TA to IV . In the earliest stages , the cancer is confined to the lining of your bladder or in the connective tissue just below the lining, but hasnt invaded the main muscle wall of your bladder.
Stages II to IV denote invasive cancer:
A more sophisticated and preferred staging system is TNM, which stands for tumor, node involvement and metastases. In this system:
Don’t Miss: Panty Liners For Light Bladder Leakage
Treatment For Bladder Cancer
Treatment for bladder cancer depends on how quickly the cancer is growing. Treatment is different for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer and muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
You might feel confused or unsure about your treatment options and decisions. Its okay to ask your treatment team to explain the information to you more than once. Its often okay to take some time to think about your decisions.
When deciding on treatment for bladder cancer, you may want to discuss your options with a urologist, radiation oncologist and medical oncologist. Ask your GP for referrals.
Are Bladder Cancer And Kidney Cancer Related
Unfortunately, there is no any cancer treatment that can guarantee you will not get another cancer. Again, there is still a chance for cancer survivors to have the recurrence of the disease or even the risk of having an unrelated, new cancer .
Statistics show that kidney cancer may be related to the increased risk of certain cancers. One of them is bladder cancer. Other second cancers that may occur include:
Having bladder cancer may also be related to the increased risk of kidney cancer. It may also increase the risk of the following other cancers:
It seems that there is a link between kidney cancer and bladder. But this issue still remains puzzling, more comprehensive studies are required.
The exact cause of how kidney cancer may increase the risk of bladder cancer is not fully known! But there are some possible explanations. These include:
Read Also: How To Help Cat With Bladder Infection
Treating Stage Ii Bladder Cancer
These cancers have invaded the muscle layer of the bladder wall , but no farther. Transurethral resection is typically the first treatment for these cancers, but it’s done to help determine the extent of the cancer rather than to try to cure it.
When the cancer has invaded the muscle, radical cystectomy is the standard treatment. Lymph nodes near the bladder are often removed as well. If cancer is in only one part of the bladder, a partial cystectomy may be done instead. But this is possible in only a small number of patients.
Radical cystectomy may be the only treatment for people who are not well enough to get chemo. But most doctors prefer to give chemo before surgery because it’s been shown to help patients live longer than surgery alone. When chemo is given first, surgery is delayed. This is not a problem if the chemo shrinks the bladder cancer, but it might be harmful if the tumor continues to grow during chemo.
If cancer is found in nearby lymph nodes, radiation may be needed after surgery. Another option is chemo, but only if it wasn’t given before surgery.
For people who have had surgery, but the features of the tumor show it is at high risk of coming back, the immunotherapy drug, nivolumab, might be offered. When given after surgery, nivolumab is given for up to one year.
For patients who cant have surgery because of other serious health problems, TURBT, radiation, chemotherapy, or some combination of these may be options.
Signs And Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
Sometimes bladder cancer doesnt have many symptoms. Signs or symptoms can include:
- blood in your urine
- pain or burning when passing urine
- not being able to pass urine when you need to.
Not everyone with these symptoms has bladder cancer. If you have any of these symptoms or are worried, always see your doctor.
Also Check: What Should I Take For A Bladder Infection