The Effect Of Treatment With Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis To Liver
Regardless of age at diagnosis, surgery alone was the optimal treatment option for patients with pancreatic cancer metastasis to liver, followed by surgery combined with chemotherapy , chemotherapy alone and no treatment . And the median survival time of patients with surgery alone was approximately 3.54 years. .
Kalpan Meier survival curve showing the effect of treatment with pancreatic cancer metastasis to liver.
Tests For Bladder Cancer
Your doctor may do some tests to check for bladder cancer:
- internal examination the doctor may check inside your bottom or vagina with their finger, using gloves
- urine tests your urine will be checked for signs of bladder cancer
- blood tests to check your general health
- ultrasound a scan on the outside of your abdomen to check for cancer
- cystoscopy the doctor puts a small camera into your bladder to see inside
- biopsy the doctor takes a small sample of the cells from the bladder to check for signs of cancer.
Your doctor might ask you to have further tests. These can include:
- CT scan and x-rays scans that take pictures of the inside of the body, sometimes also called a CT-IVP or a triple phase abdominal-pelvic CT scan
- MRI scan a scan that uses magnetism and radio waves to take pictures of the inside of the body
- bone scan a scan that uses dye to show changes in your bones
- FDG-PET scan a scan that uses an injection of liquid to show cancer cells.
Treating Metastatic Bladder Cancer
Treatment for metastatic bladder cancer is different for each person, depending on your specific situation. Your doctor and care team will discuss different options with you, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of each type of treatment option.
The goals of most types of treatment are to slow down how fast the cancer cells are growing and to shrink the tumor as much as possible. Other important goals of treatment are to help people with bladder cancer live as long as possible and to make sure they have the best possible quality of life. Palliative care can also help relieve symptoms and treatment side effects.4
Recommended Reading: Can You Bleed From A Bladder Infection
Study Variables And Endpoints
The variables including the age at diagnosis, sex, race, primary site, histologic type, grade, treatment, seventh edition of the AJCC Staging Manual tumor stage including Ta/Tis/T1/T2a/T2b/T3a/T4b/N0/N1/N2/N3/M0/M1 stage, sites of distant metastases and the number of distant metastatic sites were analysed in our research. We used the pathological grading standard according to the SEER database and previous studies., The data for metastasis to distant lymph nodes, liver, lung, bone, and brain were identified at the time of diagnosis. The overall survival was considered as the endpoint.
Review: Brain Metastases In Bladder Cancer
Article type: Review Article
Authors: Brenneman, Randall J.a | Gay, Hiram A.a | Christodouleas, John P.b | Sargos, Paulc | Arora, Vivekd | Fischer-Valuck, Benjamine | Huang, Jiayia | Knoche, Ericd | Pachynski, Russelld | Picus, Joeld | Reimers, Melissad | Roth, Bruced | Michalski, Jeff M.a | Baumann, Brian C.ab*
Affiliations: Department of Radiation Oncology, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO, USA | Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, PA, USA | Department of Radiation Oncology, Jewish General Hospital, Montreal, QC, Canada | Division of Medical Oncology, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO, USA | Department of Radiation Oncology, Emory University, Atlanta, GA, USA
Correspondence: Correspondence to: Dr. Brian Baumann, Assistant Professor, Chief of Genitourinary Radiation Oncology, Department of Radiation Oncology, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO, USA. Tel.: +1 314 747 7236 Fax: +1 314 362 7769 E-mail: .
Keywords: Urothelial carcinoma, urinary bladder neoplasms, radiotherapy, neoplasm metastasis, immune checkpoint blockade
DOI: 10.3233/BLC-200304
Journal: Bladder Cancer, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 237-248, 2020
Abstract
Recommended Reading: What Antibiotics Are Given For Bladder Infection
Signs And Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
Sometimes bladder cancer doesnt have many symptoms. Signs or symptoms can include:
- blood in your urine
- pain or burning when passing urine
- not being able to pass urine when you need to.
Not everyone with these symptoms has bladder cancer. If you have any of these symptoms or are worried, always see your doctor.
Also Check: How Can I Strengthen My Bladder
How Does The Robot
Sexual dysfunction following the RALP tends to be severe and difficult to treat. The RALP procedure can cause sexual dysfunction for the following several reasons:
- The RALP can damage the cavernosal nerves that are vital to the erection.
- The RALP can damage the blood supply to the penis.
- The RALP can cause scarring of the corpora cavernosa. The corpora are two long cylinders that run the length of the penis and they play a critical role in the erection.
- Scarring of the corpora cavernosa can also reduce the length of the penis
- The RALP completely removes the prostate. This results in a dry ejaculate no fluid comes out during orgasm.
- The RALP can produce urinary incontinence. Leakage of urine can decrease libido and interfere with overall sexual function.
- The RALP procedure can produce climacteric the passage of urine during orgasm.
Recommended Reading: Does Medicare Cover Botox For Overactive Bladder
Stage Ii Bladder Cancer
Stage II cancer has invaded the muscle of the bladder wall but is still confined to the bladder. Depending on the extent and grade of the cancer, we may recommend a partial or total cystectomy. Some people may need chemotherapy before surgery. We may be able to remove the tumor with TUR followed by radiation and chemotherapy.
Testicular Cancers: How They Spread
Testicular cancer begins in your testes, the male reproductive organ. Which treatment your doctor will choose to treat it is based on the type of cancer you have and if it has spread.
The majority of testicular cancers start in germ cells. Germ cells in your testicles make sperm. When these cells begin to grow out of control, they form two main types of tumors: seminomas and non-seminomas.
They grow and spread at different rates.
Donât Miss: Yoga Exercises For Prolapsed Bladder
Recommended Reading: How To Reduce Bladder Inflammation Naturally
Simultaneous Insertion Of The Penile Implant And The Artificial Urinary Sphincter
Patients who undergo the RALP procedure may suffer from ED and urinary incontinence. Placement of both the 3 penile implant and the artificial urinary sphincter can be performed at the same time in patients who suffer from ED and urinary incontinence. The success rate of the simultaneous procedure is high. The main disadvantage is that the risk of penile implant infection increases in the presence of the artificial urinary sphincter.
Factors Influencing Survival Rates
The variability in survival rates highlights one key reality about stage 4 lung cancer: no two people have the same disease. Arguably more than any other stage of the disease, stage 4 lung cancer survival is influenced by multiple factors, some of which are fixed and others of which can be changed .
There are seven factors known to influence survival times in people with stage 4 NSCLC.
Read Also: Can Fibroids Cause Bladder Leakage
Recommended Reading: What Can I Use For Bladder Infection
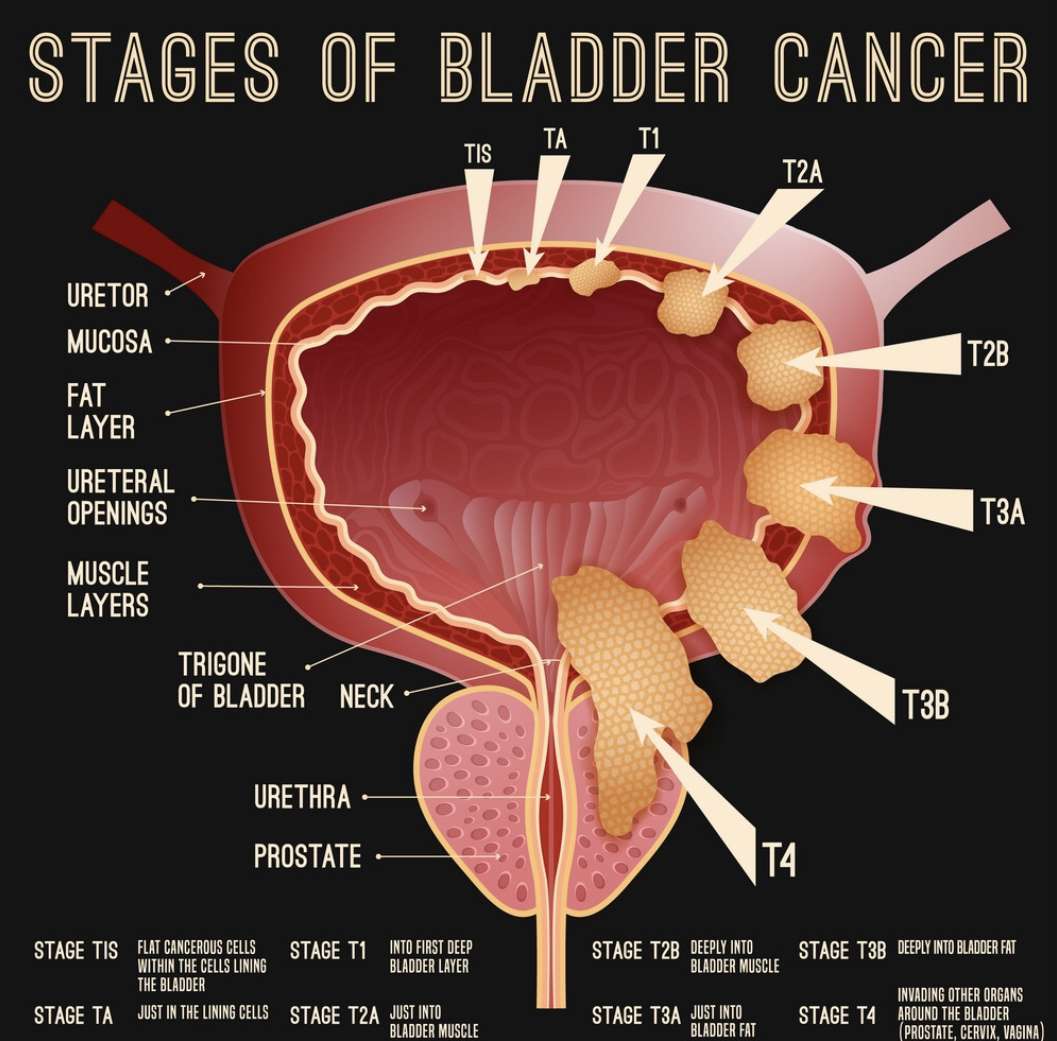
How Is Bladder Cancer Staged
Cancer staging describes how much the cancer has grown and invaded the area, explaining the extent of the disease. Bladder cancer is often found at an early stage, as hematuria starts early in the course of the disease. Sometimes bladder cancer can advance to invasive disease before causing symptoms. To best understand staging, you need to know how cancer spreads and advances in stage.
Cancers can spread and disrupt how normal organs work. Bladder cancers often begin very superficially, involving only the lining of the bladder. Bladder cancers can invade the bladder wall, involving the muscular layers of the wall. As bladder cancer grows it can invade the entire way through the wall and into the fat surrounding the bladder or even into other organs . This local extension is the most common way bladder cancer spreads.
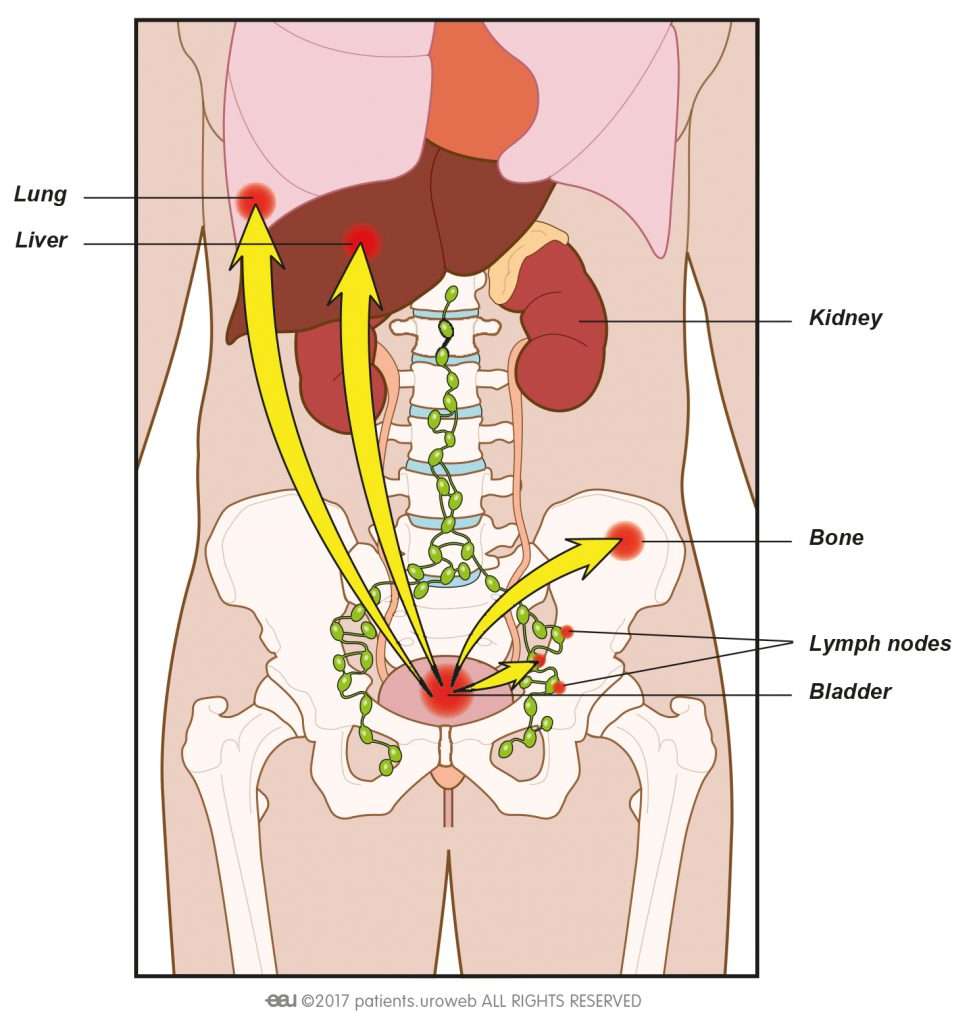
When cancer spreads to another area in the body, that area is called metastasis. Cancer can also spread through the lymph system and the bloodstream. Bladder cancer often spreads locally or to lymph nodes before spreading distantly, though this is not always the case. The lungs and bones are the most common areas for metastases to develop. When bladder cancer spreads to another area, it is still bladder cancer. For instance, if it spreads to the lung, it is not called lung cancer, but bladder cancer that has metastasized to the lung. If we look at the affected lung tissue under a microscope, it will look like bladder cancer cells.
What Tests Will I Have If My Doctor Suspects Bladder Cancer Or Another Urinary Problem
Your doctor will want to analyze your urine to determine if an infection could be a cause of your symptoms. A microscopic examination of the urine, called cytology, will look for cancer cells.
A cystoscopy is the main procedure to identify and diagnose bladder cancer. In this procedure, a lighted telescope is inserted into your bladder from the urethra to view the inside of the bladder and, when done under anesthesia, take tissue samples , which are later examined under a microscope for signs of cancer. When this procedure is done in the doctors office, local anesthesia gel is placed into the urethra prior to the procedure to minimize the discomfort.
If the diagnosis of bladder cancer is made, then the next step is to remove the tumor for detailed staging and diagnosis.
Transurethral resection is a procedure done under general or spinal anesthesia in the operating room. A telescope is inserted into the bladder and the tumor is removed by scraping it from the bladder wall , using a special cystoscope . This procedure is diagnostic as well as therapeutic.
This often can be done as an outpatient procedure, with patients discharged from hospital the same day. After removal, the tumor is analyzed by a pathologist, who will determine the type of tumor, the tumor grade and the depth of invasion. The purpose of the procedure is to remove the tumor and obtain important staging information .
Don’t Miss: What Are The Chances Of Surviving Bladder Cancer
Intrahepatic Chemotherapy And Chemoembolisation
Intrahepatic chemotherapy and chemoembolisation involve giving chemotherapy directly into the liver. This is done through a thin tube, called a catheter, into the main blood supply to the liver.
Giving chemotherapy directly into the liver means a higher concentration of the drug can be delivered to the area of cancer.
In chemoembolisation, the chemotherapy is delivered along with an oily liquid or foam which blocks the blood supply to the cancer. The cancer is deprived of oxygen and nutrients, and the chemotherapy stays in the area for longer. The liver continues to be supplied with blood in the normal way.
These treatments may not be routinely available on the NHS but may be offered as part of a clinical trial.
Also Check: How Long Does It Take Azo Bladder Control To Work
Prognosis And Survival For Bladder Cancer
If you have bladder cancer, you may have questions about your prognosis. A prognosis is the doctors best estimate of how cancer will affect someone and how it will respond to treatment. Prognosis and survival depend on many factors. Only a doctor familiar with your medical history, the type and stage and other features of the cancer, the treatments chosen and the response to treatment can put all of this information together with survival statistics to arrive at a prognosis.
A prognostic factor is an aspect of the cancer or a characteristic of the person that the doctor will consider when making a prognosis. A predictive factor influences how a cancer will respond to a certain treatment. Prognostic and predictive factors are often discussed together. They both play a part in deciding on a treatment plan and a prognosis.
The following are prognostic and predictive factors for bladder cancer.
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Overactive Bladder
Also Check: Icd 10 Incontinence Of Bowel And Bladder
Bladder Reconstructions And Stomas
If you have had your bladder removed, the way you pass urine will change. There are several options that your treatment team will talk to you about:
- Urostomy is where doctors create a new hole in your abdomen called a stoma. Urine drains from the stoma to the outside of your abdomen into a special bag.
- Neobladder is where a new bladder made from your small bowel forms a pouch inside your body to store urine. You will pass urine by squeezing your abdominal muscles. You will also pass a small tube into the neobladder each day to help drain the urine.
- Continent urinary diversion is a pouch made from your small bowel inside your body to store urine. The urine empties through a hole called a stoma to the outside of your abdomen into a special bag.
A bladder reconstruction is a big change in your life. You can speak with a continence or stomal therapy nurse for help, support and information. You can also call Cancer Council . You may be able to speak with a trained Cancer Council volunteer who has had cancer for tips and support.
If you find it difficult to adjust after your bladder reconstruction, it may help to be referred to a psychologist or counsellor.
Note: If you have a stoma, you can join a stoma association for support and free supplies. For more information about stoma associations, visit the Australian Council of Stoma Associations.
What Is The Bladder
The bladder is an organ found in the lower part of the belly near the pelvic bones. It acts as a holding area for urine. The bladder expands and can hold about half of a liter of urine, but a person usually feels the urge to urinate when the bladder is 25% full. The bladder will contract and become smaller when it is empty. The ureters are two tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder. They empty urine from the kidneys into the bladder. The urethra is a tube that connects the bladder to the outside of the body and releases urine.
The bladder wall consists of 4 main layers of tissue.
- The innermost layer is called the urothelium, or transitional epithelium. It is made up of cells called urothelial or transitional cells.
- Beneath the urothelium is a thin layer called the lamina propria, made up of connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves.
- The next layer is called the muscularis propria, made of muscle.
- The last layer is a layer of fatty tissue that separates the bladder from other surrounding organs.
Read Also: Can Diabetes Cause Bladder Problems
Side Effects Of Prostate Surgery
The major possible side effects of radical prostatectomy are urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction . These side effects can also occur with other forms of prostate cancer treatment.
Urinary incontinence: You may not be able to control your urine or you may have leakage or dribbling. Being incontinent can affect you not only physically but emotionally and socially as well. These are the major types of incontinence:
- Men with stress incontinence might leak urine when they cough, laugh, sneeze, or exercise. Stress incontinence is the most common type after prostate surgery. Itâs usually caused by problems with the valve that keeps urine in the bladder . Prostate cancer treatments can damage this valve or the nerves that keep the valve working.
- Men with overflow incontinence have trouble emptying their bladder. They take a long time to urinate and have a dribbling stream with little force. Overflow incontinence is usually caused by blockage or narrowing of the bladder outlet by scar tissue.
- Men with urge incontinencehave a sudden need to urinate. This happens when the bladder becomes too sensitive to stretching as it fills with urine.
- Rarely after surgery, men lose all ability to control their urine. This is called continuous incontinence.
After surgery for prostate cancer, normal bladder control usually returns within several weeks or months. This recovery usually occurs slowly over time.
There are several options for treating erectile dysfunction:
How Will My Cancer Be Monitored
Your doctor will talk to you about how often you should have check-ups. At some hospitals, you may not have many appointments at the hospital itself. Instead, you may talk to your doctor or nurse over the telephone. You might hear this called self-management.
You will have regular PSA tests. This is often a useful way to check how well your treatment is working. Youll also have regular blood tests to see whether your cancer is affecting other parts of your body, such as your liver, kidneys or bones.
You might have more scans to see how your cancer is responding to treatment and whether your cancer is spreading.
Your doctor or nurse will also ask you how youre feeling and if you have any symptoms, such as pain or tiredness. This will help them understand how youre responding to treatment and how to manage any symptoms. Let them know if you have any side effects from your treatment. There are usually ways to manage these.
Read Also: How Many Radiation Treatments For Bladder Cancer
Potential Long Noncoding Rna Biomarkers In Cancer And Other Diseases
lncRNAs play important regulatory roles in transcription, translation, chromatin modification, and cellular organization. Misregulation of lncRNAs is found associated with various human diseases. Though lncRNAs are only recently discovered, at least 321 experimentally verified lncRNAs associated with 221 various types of diseases, which are most related to cancer . The lncRNAs represent another group of potential biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and prognosis.
Prostate cancer antigen 3 is a well-studied lncRNA and the most specific to prostate cancer as it is not expressed in other normal human tissues. PROGENSA PCA3 test is the first urine-based molecular diagnostic test approved by the Food and Drug Administration . The sensitivity and specificity of urine PCA3 expression for PCa diagnosis reach 62 and 75%, respectively, supporting PCA3 as a reasonable marker for prostate cancer diagnosis .
HOX transcript antisense RNA is another well-studied lncRNA. In cervical cancers, high serum levels of HOTAIR were significantly correlated with tumor recurrence and shorter overall survival .
Dong et al. found that the combination of CUDR, LSINCT-5, and PTENP1 provided the best diagnostic value in GC with an AUC of 0.92, a sensitivity of 74.1%, and a specificity of 100%. They were also sufficiently sensitive and specific for early GC detection and distinguishing benign peptic ulcers from GC .
For reference, more potential lncRNA biomarkers are listed in Table 18.3.
| LncRNAs |
|---|