Bladder Cancer Can Cause Changes In Urination
In addition to blood in the urine, bladder cancer may cause urinary changes, such as:
- Pain or burning sensations during urination
- A need to urinate more frequently than usual
- Urinary urgency, even when the bladder is not full
- A weak urine stream
- A need to urinate many times during the night
Much like bloody urine, however, these symptoms are more likely to have other causes, such as a urinary tract infection, overactive bladder or enlarged prostate .
Treating Metastatic Bladder Cancer
Treatment for metastatic bladder cancer is different for each person, depending on your specific situation. Your doctor and care team will discuss different options with you, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of each type of treatment option.
The goals of most types of treatment are to slow down how fast the cancer cells are growing and to shrink the tumor as much as possible. Other important goals of treatment are to help people with bladder cancer live as long as possible and to make sure they have the best possible quality of life. Palliative care can also help relieve symptoms and treatment side effects.4
Treatment Of Stage I Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage I bladder cancer may include the following:
- Transurethral resection with fulguration. This may be followed by one of the following:
- Intravesicalchemotherapy given right after surgery.
- Intravesical chemotherapy given right after surgery and then regular treatments with intravesical BCG or intravesical chemotherapy.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Also Check: Bladder Infection Bleeding Like Period
Living With Advanced Cancer
Advanced cancer usually means cancer that is unlikely to be cured. Some people can live for many months or years with advanced cancer. During this time palliative care services can help.
Most people continue to have treatment for advanced cancer as part of palliative care, as it helps manage the cancer and improve their day-to-day lives. Many people think that palliative care is for people who are dying but palliative care is for any stage of advanced cancer. There are doctors, nurses and other people who specialise in palliative care.
Treatment may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy or another type of treatment. It can help in these ways:
- slow down how fast the cancer is growing
- shrink the cancer
- help you to live more comfortably by managing symptoms, like pain.
Treatment depends on:
- how far it has spread
- your general health
Needing To Urinate Urgently Or More Often
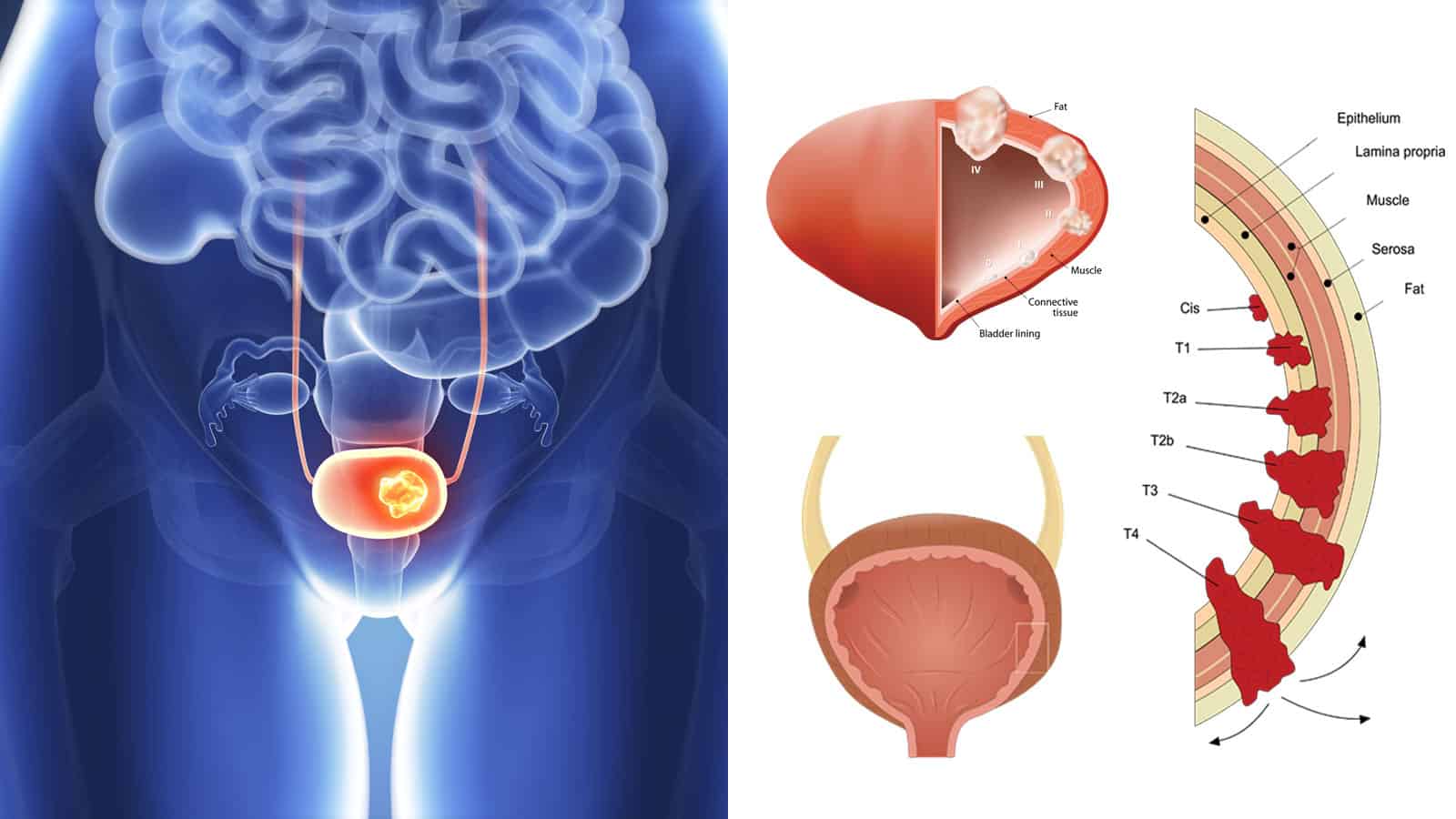
Bladder cancer can cause changes in how often you urinate, giving you the urge to urinate more often or more urgently even when your bladder isnt full. You may also find that you cant make it to the bathroom in time. A healthy person usually urinates four to eight times a day depending on the amount of water they drink every day. Think about whats normal for you and whether its changed recently.
Read Also: Home Remedies For Kidney And Bladder Infection
Early Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
The following are some of the early-stage bladder cancer symptoms you might experience:
1. Blood in the Urine
Blood in urine, often referred to as hematuria, is the most common symptom or sign of bladder cancer. With this symptom:
- You might have enough blood to change your urine color to pink, orange or, less often, dark red.
- Your urine color is sometimes normal, but a urine test , which the doctor performs during a general medical checkup or if you have other symptoms, can still detect small traces of blood.
- You may have blood one day and not the next, with your urine staying clear for weeks or maybe even months at a time.
Generally, the earlier stages of bladder cancer when the cancer is small and confined to your bladder only cause bleeding with either no pain or little pain.
It’s important to note that blood in your urine doesn’t necessarily indicate bladder cancer. The cause of blood may be due to another factor. In fact, many healthy individuals may have some unseen blood in their urine at some stage . And, for most individuals, the cause isn’t cancer.
In many situations, the cause is due to other things like benign tumors, medications or foods, infection, bladder or kidney stones or another benign kidney disease. Still, you should have your doctor check it out.
If you’re concerned about cancer, ask them about Cxbladder, a non-invasive genomic urine test that quickly and accurately detects or rules out bladder cancer.
Where It Can Spread To
Not all bladder cancers will spread. But If it does it’s most likely to spread to the structures close to the bladder, such as the ureters, urethra, prostate, vagina, or into the pelvis. This is called local spread.
Bladder cancer can also spread to another part of the body. This is secondary cancer or metastasis. The places it’s most likely to spread to are your:
- lymph nodes in the pelvis and tummy
- lungs
Recommended Reading: Alka Seltzer For Bladder Infection
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- What treatment do you think is best for me?
- Whats the goal of this treatment? Do you think it could cure the cancer?
- Will treatment include surgery? If so, who will do the surgery?
- What will the surgery be like?
- How will I pee after surgery?
- Will I have other types of treatment, too?
- Whats the goal of these treatments?
- What side effects could I have from these treatments?
- Is there a clinical trial that might be right for me?
- What about treatments like special vitamins or diets that friends tell me about? How will I know if they are safe?
- What should I do to be ready for treatment?
- Is there anything I can do to help the treatment work better?
- Whats the next step?
How Can My Doctor Help
If they don’t know already, your doctor will need to figure out which type of testicular cancer you have. They’ll look for certain proteins in your blood to get that answer. Both seminomas and non-seminomas raise levels of a protein called HCG. Non-seminomas also cause a rise in something called alpha-fetoprotein .
Once they know which you have, they’ll use a variety of tests to see if and where your cancer has spread. They may order:
- X-rays
Also Check: Pumpkin Seed Oil For Bladder Control
Not Being Able To Empty Your Bladder Completely
Urinary retention is the inability to empty your bladder completely, even when its full. You may have lower abdominal pain, be unable to urinate at all and/or strain when trying to empty your bladder. You may also notice your urine stream is weak, have the urge to urinate again immediately after emptying your bladder and/or have urinary incontinence.
Surgery For Bladder Cancer
Surgery is done for most bladder cancers. The type you have depends on the stage of the cancer.
Removing the tumor from the inside bladder is the most common surgery for early bladder cancer. This can be done during a cystoscopy. A a cystoscope with a looped wire on the end is used to remove the tumor.
When the cancer is more invasive, the cancer is removed along with part of the bladder or the entire bladder.
If only part of the bladder is removed, you’ll still be able to hold and release urine as normal, though in smaller amounts. If the entire bladder is removed, you’ll need another way to store and pass urine. Your doctor can explain the options for this.
Side effects of surgery
Any type of surgery can have some risks and side effects. For instance, removing the bladder not only changes how your body passes urine, but it can also cause sexual side effects. If you have these or any other problems, let your doctors know. There are ways to help deal with many side effects.
Don’t Miss: Can Hernia Mesh Cause Bladder Problems
What Are The Risks Of Bladder Cancer
No single factor is directly connected to bladder cancer, but factors that can increase the risk include:
- Age: Bladder cancer typically affects people age 55 and older.
- Smoking: Carcinogens from tobacco smoke come in contact with the lining of the bladder. Smokers are three times as likely as non-smokers to get bladder cancer.
- Family history: There is evidence that bladder cancer may have a genetic component.
- Industrial chemicals: Chemicals known as aromatic amines are often used in the dye industry. Workers who have daily exposure to them, such as painters, machinists and hairdressers, may be at a higher risk for bladder cancer.
- Drinking contaminated water: This includes water that has been treated with chlorine or drinking water with a naturally high level of arsenic, which occurs in many rural communities in the United States,.
- Taking certain herb: Supplements such as Aristolochia fangchi, a Chinese herb, sometimes used for weight loss has been linked to higher rates of bladder cancer.
Risk Factor: Chemical Exposure
Research suggests that certain jobs may increase your risk for bladder cancer. Metal workers, mechanics, and hairdressers are among those who may be exposed to cancer-causing chemicals. If you work with dyes, or in the making of rubber, textiles, leather, or paints, be sure to follow safety procedures to reduce contact with dangerous chemicals. Smoking further increases risk from chemical exposure.
Anyone can get bladder cancer, but these factors put you at greater risk:
- Gender: Men are three times more likely to get bladder cancer.
- Age: Nine out of 10 cases occur over age 55.
- Race: Whites have twice the risk of African-Americans.
Other factors at play include a family history of bladder cancer, previous cancer treatment, certain birth defects of the bladder, and chronic bladder irritation.
Read Also: Natural Ways To Control Overactive Bladder
Bladder Cancer Treatment: Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is given in some cases before surgery to shrink bladder cancer tumors. It can also be used after surgery to destroy any remaining tumor cells. Chemotherapy may be given intravenously or administered directly into the bladder . Intravesical chemotherapy is effective in decreasing the recurrence rate of superficial bladder cancers on a short-term basis, but not effective against bladder cancer that has already invaded the muscular walls. Systemic or intravenous chemotherapy is required when the cancer has deeply penetrated the bladder, lymph nodes, or other organs.
Chemotherapy Side Effects
Side effects vary from patient to patient. Common side effects of systemic chemotherapy include the following:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sores on the inside of the mouth or in the digestive tract
- Feeling tired or lacking energy
- Increased susceptibility to infection
Radiotherapy With A Radiosensitiser
Radiotherapy is given by a machine that beams the radiation at the bladder . Sessions are usually given on a daily basis for 5 days a week over the course of 4 to 7 weeks. Each session lasts for about 10 to 15 minutes.
A radiosensitiser should also be given alongside radiotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. This is a medicine which affects the cells of a tumour, to enhance the effect of radiotherapy. It has a much smaller effect on normal tissue.
As well as destroying cancerous cells, radiotherapy can also damage healthy cells, which means it can cause a number of side effects. These include:
- tightening of the vagina , which can make having sex painful
- erectile dysfunction
- tiredness
- difficulty passing urine
Most of these side effects should pass a few weeks after your treatment finishes, although there’s a chance they’ll be permanent.
Having radiation directed at your pelvis usually means you’ll be infertile for the rest of your life. However, most people treated for bladder cancer are too old to have children, so this isn’t usually a problem.
After having radiotherapy for bladder cancer, you should be offered follow-up appointments every 3 months for the first 2 years, then every 6 months for the next 2 years, and every year after that. At these appointments, your bladder will be checked using a cystoscopy.
Read Also: The Most Frequent Initial Symptom Of Bladder Cancer Is
New And Experimental Treatments
Several new treatments may prove useful in treating bladder cancer. Photodynamic therapy, used in early stage cancers, uses a laser light to activate a chemical that kills cancer cells. Some gene therapies use lab-created viruses to fight cancer. And targeted therapies aim to control the growth of cancer cells. You may be eligible to participate in a clinical trial of these or other cutting-edge treatments.
21) Carol & Mike Werner / Visuals Unlimited / Corbis
American Urological Association: “Bladder Cancer.”
American Urological Association Foundation: “Hematuria.”
Journal of the American Medical Association: Association Between Smoking and Risk of Bladder Cancer Among Men and Women.
Occupational & Environmental Medicine: Bladder cancer among hairdressers: a meta-analysis.
British Journal of Cancer: Occupation and bladder cancer: a cohort study in Sweden.
National Cancer Institute: “Staging,” “Bladder Cancer Treatment,” “Drugs Approved for Bladder Cancer,” “SEER Stat Fact Sheets: Bladder.”
NIH Research Matters: “Smoking and Bladder Cancer.”
ScienceDaily: “Cigarette Smoking Implicated in Half of Bladder Cancers in Women Bladder Cancer Risk from Smoking Is Higher Than Previously Estimated, Study Confirms.”
Stanford Cancer Institute: “Information About Bladder Cancer.”
World Health Organization: “Tobacco Free Initiative — Cancer.”
Bladder Cancer Diagnosis: Testing
There is no single lab test that can specifically screen for and diagnose bladder cancer, even though urine tests may suggest that cancer is present. If a cancer is present, several tests may be abnormal, including urine cytology and tests for tumor marker proteins.
Cystoscopy
A type of endoscopy, cystoscopy, is a procedure that allows visualization of the inside of the bladder through a thin, lighted tube that contains a camera. The instrument can also take small samples if abnormal areas are seen. A tissue biopsy is the most reliable way to diagnose bladder cancer.
Urinalysis and Urine Cytology
An analysis of the urine is a very useful test in the diagnosis of and screening for many diseases and conditions. The urinalysis will detect any abnormalities in the urine such as blood, protein, and sugar . A urine cytology is the examination of urine under a microscope while looking for abnormal cells that might indicate bladder cancer.
You May Like: Bladder Control Products By Mail
Advanced Bladder Cancer Warning Signs
Not everyone with early-stage bladder cancer will have symptoms. In some people, the first warning signs appear when the cancer has already grown too big or has spread beyond the bladder.
Warning signs of advanced bladder cancer include:
Advanced Bladder Cancer Symptoms
In its later stages, bladder cancer symptoms are much more severe. For example, a growth or mass may appear in the patients pelvis, which is close to the bladder. Swelling often occurs in the lower leg area and many patients experience kidney pain that is felt in the lower back. When bladder cancer continues to spread to other parts of the body, the patient is likely to lose weight and suffer from significant pain in the pelvic area, bones and rectum.
You May Like: Can You Treat A Bladder Infection At Home
Bladder Cancer Treatment: Surgery
Transurethral Resection
Early-stage cancers are most commonly treated by transurethral surgery. An instrument with a small wire loop is inserted through the urethra and into the bladder. The loop removes a tumor by cutting or burning it with electrical current, allowing it to be extracted from the bladder.
Partial and Radical Cystectomy
Partial cystectomy includes the removal of part of the bladder. This operation is usually for low-grade tumors that have invaded the bladder wall but are limited to a small area of the bladder. In a radical cystectomy, the entire bladder is removed, as well as its surrounding lymph nodes and other areas that contain cancerous cells. If the cancer has metastasized outside of the bladder and into neighboring tissue, other organs may also be removed such as the uterus and ovaries in women and the prostate in men.
Patients Can Enter Clinical Trials Before During Or After Starting Their Cancer Treatment
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCIs clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Also Check: Types Of Pessaries For Bladder Prolapse
How Long Will You Live If You Have Bladder Cancer
The survival rate depends on the stage of cancer at diagnosis and other health issues.
Overall, 70 to 90 percent of people with localized bladder cancer will live for at least five years or more. The physician calculates this with the help of survival rates. Survival rates indicate the percentage of people who live with a certain type of cancer for a specific time. The physician often uses an overall five-year survival rate. Factors that may affect survival rate include
Table. Five-year survival rates of different stages of bladder cancer
| Bladder cancer SEER stages | Five-year relative survival rate |
|---|---|
| In situ alone | 96 |
| All SEER stages combined | 77 |
The surveillance, epidemiology, and end results stages are taken from the SEER database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute. SEER database groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages.
- Localized: There is no indication that cancer has spread outside the bladder.
- Regional: Cancer has invaded the nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: Cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, such as the lungs, liver, or bones.
Thus, bladder cancer, if detected in the early stage is treatable and has higher survival rates. However, if the cancer is detected in the advanced stages, treatment becomes difficult and the survival rate is low.