Prognosis Of Patients With Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Who Are Intolerable To Receive Any Anti
Muscle invasive bladder tumor has a high propensity for rapid growth and distant metastasis.
-
The aim of this retrospective study was to evaluate the prognosis of patients who had been diagnosed with muscle invasive bladder cancer and did not receive anti-cancer treatment because of their physical characteristics.
-
We evaluated 26 patients. Median overall survival was 12 months.
-
These results may assist in counseling older patients with MIBC if the disease is left untreated.
T Categories For Bladder Cancer
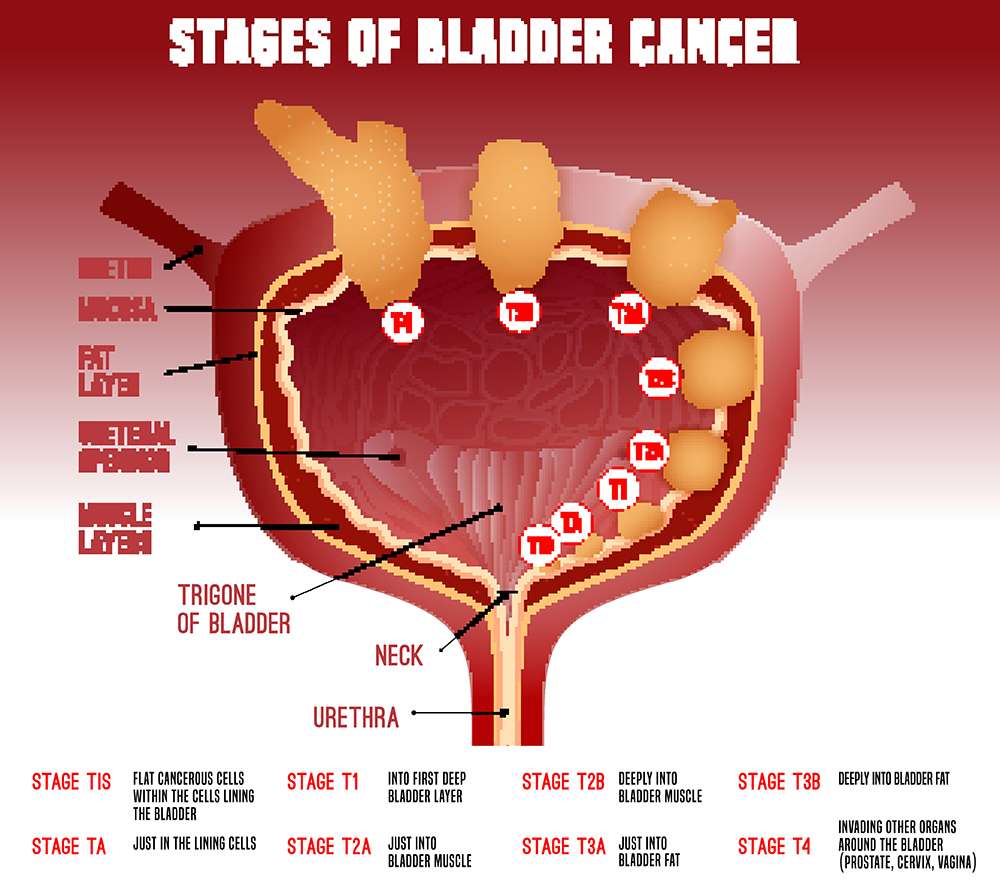
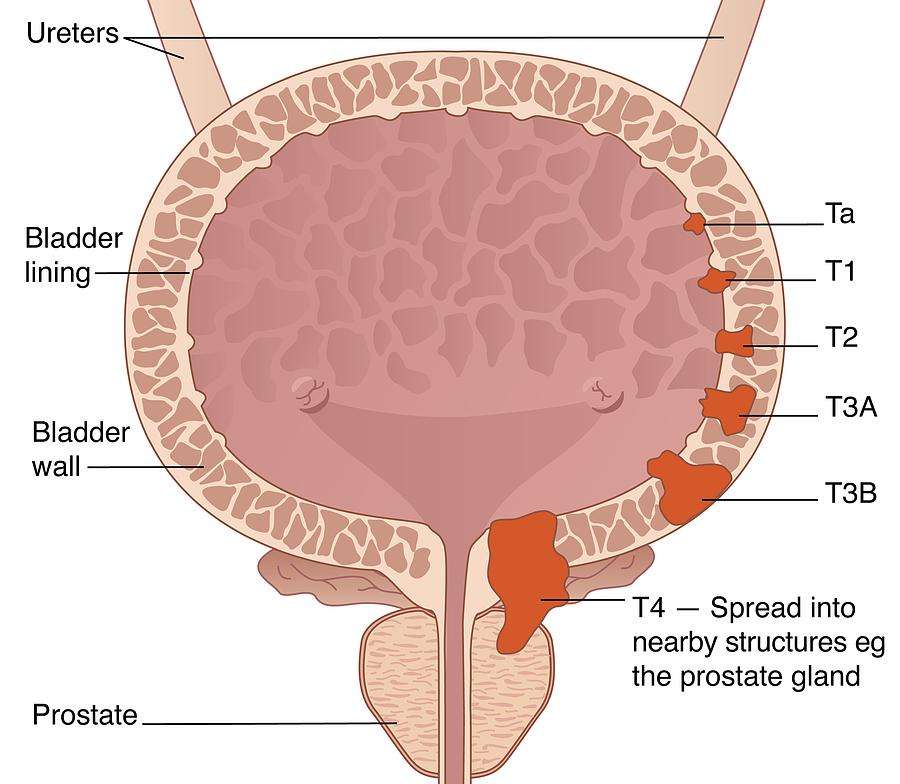
The T category describes how far the main tumor has grown into the wall of the bladder .
The wall of the bladder has 4 main layers.
- The innermost lining is called the urothelium or transitional epithelium.
- Beneath the urothelium is a thin layer of connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves.
- Next is a thick layer of muscle.
- Outside of this muscle, a layer of fatty connective tissue separates the bladder from other nearby organs.
Nearly all bladder cancers start in the lining or urothelium. As the cancer grows into or through the other layers in the bladder, it becomes more advanced .
The T categories are described in the table above, except for:
TX: Main tumor cannot be assessed due to lack of information
T0: No evidence of a primary tumor
What Is Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
Muscle invasive bladder cancer is a cancer that spreads into the detrusor muscle of the bladder. The detrusor muscle is the thick muscle deep in the bladder wall. This cancer is more likely to spread to other parts of the body.
In the U.S., bladder cancer is the third most common cancer in men. Each year, there are more than 83,000 new cases diagnosed in men and women. About 25% of bladder cancers are MIBC. Bladder cancer is more common as a person grows older. It is found most often in the age group of 75-84. Caucasians are more likely to get bladder cancer than any other ethnicity. But there are more African-Americans who do not survive the disease.
What is Cancer?
Cancer is when your body cells grow out of control. When this happens, the body cannot work the way it should. Most cancers form a lump called a tumor or a growth. Some cancers grow and spread fast. Others grow more slowly. Not all lumps are cancers. Cancerous lumps are sometimes called malignant tumors.
What is Bladder Cancer?
When cells of the bladder grow abnormally, they can become bladder cancer. A person with bladder cancer will have one or more tumors in his/her bladder.
How Does Bladder Cancer Develop and Spread?
The bladder wall has many layers, made up of different types of cells. Most bladder cancers start in the urothelium or transitional epithelium. This is the inside lining of the bladder. Transitional cell carcinoma is cancer that forms in the cells of the urothelium.
You May Like: Natural Remedies To Cure Bladder Infection
Subtleties And Future Questions
Several factors have to be carefully considered in interpreting the trial results, explained Dr. Apolo.
A major one is that the study did not directly compare survival between people who got avelumab immediately versus when their cancer progressed. Only about half of the participants who initially received supportive care alone went on to receive immunotherapy after their cancer got worse. There could be many reasons for this, including lack of access to these drugs in different countries, Dr. Apolo said.
But it also might be that, for some people, the cancer was progressing too rapidly, she added. When these tumors start growing, they start growing very quickly. So if you wait to start at the time of progression, maybe its too late, added Dr. Apolo.
Not all patients will be caught by the second-line safety net, agreed Dr. Plimack.
So, for now, said Dr. Balar, the takeaway message from the JAVELIN study is after chemotherapy, dont wait to give immunotherapy.
But more and more, studies are looking at whether some patients should receive immunotherapy as first-line treatment, he continued. Immunotherapy is one of the most important advances weve made in the last 30 years, Dr. Balar said.
The JAVELIN results cant provide any insight into which patients benefit from first-line treatment with a platinum-based chemotherapy, he added. This trial wasnt designed to ask: Is chemotherapy necessarily the best choice for every patient? he explained.
What Is Intermittent Adt
Researchers have investigated whether a technique called intermittent androgen deprivation can delay the development of hormone resistance. With intermittent androgen deprivation, hormone therapy is given in cycles with breaks between drug administrations, rather than continuously. An additional potential benefit of this approach is that the temporary break from the side effects of hormone therapy may improve a mans quality of life.
Randomized clinical trials have shown similar overall survival with continuous ADT or intermittent ADT among men with metastatic or recurrent prostate cancer, with a reduction in some side effects for intermittent ADT .
Also Check: What Are The Chances Of Getting Prostate Cancer
Read Also: Malignant Neoplasm Of Bladder Unspecified
After Bladder Cancer Has Been Diagnosed Tests Are Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Bladder Or To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out if cancer has spread within thebladder lining and muscle or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment. The following tests and procedures may be used in the staging process:
Treatment Of Recurrent Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of recurrentbladder cancer depends on previous treatmentand where the cancer has recurred. Treatment for recurrent bladder cancer mayinclude the following:
- Radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- A clinical trial of a new treatment.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Also Check: Why Does My Bladder Feel Full
Treating Stage 0 Bladder Cancer
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma and flat non-invasive carcinoma . In either case, the cancer is only in the inner lining layer of the bladder. It has not invaded the bladder wall.
This early stage of bladder cancer is most often treated with transurethral resection with fulguration followed by intravesical therapy within 24 hours.
Tnm Staging System For Bladder Cancer
The TNM staging system uses letters and numbers to describe the bladder cancer.
- T is how far the tumour has grown into the bladder, and how far it has spread into the surrounding tissues.
- N is whether the tumour has spread to the nearby lymph nodes.
- M is whether the tumour has spread to another part of the body .
Non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer means the cancer cells are only in the inner lining of the bladder. This means non-muscle-invasive bladder cancers are always N0 and M0.
Non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer can be staged as CIS, Ta or T1.
Recommended Reading: Can A Bladder Infection Make You Sick
What To Do Before And After Treatment
Talk with your doctors about whether you need to do anything to prepare for treatment and help your recovery. Some things they may suggest are to:
- Stop smoking if you smoke, aim to quit before starting treatment. If you keep smoking, you may not respond as well to treatment and you may have more treatment-related side effects. Continuing to smoke also increases your risk of cancer returning.
- Begin or continue an exercise program exercise will help build up your strength for treatment and recovery. It can also help you deal with side effects of treatment.
- Improve diet aim to eat a balanced diet with a variety of fruit, vegetables, wholegrains and protein. Eating well can improve your strength and you may respond better to treatment.
- See a physiotherapist they can teach you exercises to strengthen your pelvic floor muscles, which help control how your bladder and bowel work. These exercises are useful if you have a neobladder, a partial cystectomy, or radiation therapy.
Certain Factors Affect Prognosis And Treatment Options
The prognosis depends on the following:
- The stage of the cancer . Bladder cancer in the early stages can often be cured.
- The type of bladder cancer cells and how they look under a microscope.
- Whether there is carcinoma in situ in other parts of the bladder.
- The patients age and general health.
If the cancer is superficial, prognosis also depends on the following:
- How many tumors there are.
- The size of the tumors.
- Whether the tumor has recurred after treatment.
Treatment options depend on the stage of bladder cancer.
Read Also: Prognosis Of Bladder Cancer In Females
Treatment Of Stage I Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage I bladder cancer may include the following:
- Transurethral resection with fulguration. This may be followed by one of the following:
- Intravesicalchemotherapy given right after surgery.
- Intravesical chemotherapy given right after surgery and then regular treatments with intravesical BCG or intravesical chemotherapy.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Radiotherapy With A Radiosensitiser
Radiotherapy is given by a machine that beams the radiation at the bladder . Sessions are usually given on a daily basis for 5 days a week over the course of 4 to 7 weeks. Each session lasts for about 10 to 15 minutes.
A medicine called a radiosensitiser should also be given alongside radiotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. This medicine affects the cells of a tumour, to enhance the effect of radiotherapy. It has a much smaller effect on normal tissue.
As well as destroying cancerous cells, radiotherapy can also damage healthy cells, which means it can cause a number of side effects. These include:
- diarrhoea
- tightening of the vagina , which can make having sex painful
- erectile dysfunction
- tiredness
- difficulty passing urine
Most of these side effects should pass a few weeks after your treatment finishes, although there’s a small chance they’ll be permanent.
Having radiotherapy directed at your pelvis usually means you’ll be infertile .
After having radiotherapy for bladder cancer, you should be offered follow-up appointments every 3 months for the first 2 years, then every 6 months for the next 2 years, and every year after that. At these appointments, your bladder will be checked using a cystoscopy.
You may also be offered CT scans of your chest, abdomen and pelvis after 6 months, 1 year and 2 years. A CT scan of your urinary tract may be offered every year for 5 years.
Don’t Miss: How To Stop Bladder Infection Pain
Understanding Your Bladder Cancer Stage
A staging system is a standard way for the cancer care team to describe how far a cancer has spread. The staging system most often used for bladder cancer is the American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM system, which is based on 3 key pieces of information:
- T describes how far the main tumor has grown through the bladder wall and whether it has grown into nearby tissues.
- N indicates any cancer spread to lymph nodes near the bladder. Lymph nodes are bean-sized collections of immune system cells, to which cancers often spread first.
- M indicates if the cancer has spread to distant sites, such as other organs, like the lungs or liver, or lymph nodes that are not near the bladder.
Numbers or letters after T, N, and M provide more details about each of these factors. Higher numbers mean the cancer is more advanced. Once a persons T, N, and M categories have been determined, usually after surgery, this information is combined in a process called stage grouping to assign an overall stage.
The earliest stage cancers are called stage 0 , and then range from stages I through IV .
As a rule, the lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, such as stage IV, means a more advanced cancer. And within a stage, an earlier letter means a lower stage. Cancers with similar stages tend to have a similar outlook and are often treated in much the same way.
Bladder Cancer Clinical Trials
What about Clinical Trials?
You may hear about clinical trials for your bladder cancer. Clinical trials are research studies that test if a new treatment or procedure is safe and effective.
Through clinical trials, doctors find new ways to improve treatments and the quality of life for people with disease. Trials are available for all stages of cancer. The results of a clinical trial can make a major difference to patients and their families. Please visit our clinical trials research webpage to learn more.
Read Also: Bladder Control Products By Mail
Patients Can Enter Clinical Trials Before During Or After Starting Their Cancer Treatment
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCIs clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
The Tnm System Of Bladder Cancer Staging
The size of the tumor and whether it has spread are used to ascertain the stage. Cancer staging specifics are determined by guidelines set by the American Joint Committee on Cancers system, named the TNM staging system.
The TNM system has three parts:
- T stands for tumor. This number indicates how large the tumor is and how much it has grown into nearby tissues.
- N stands for nodes. This number indicates if the tumor has spread to lymph nodes, where the lymph nodes are located, and how many lymph nodes are impacted.
- M stands for metastasis. This number indicates if the tumor has spread to other organs.
Recommended Reading: Women’s Bladder Falling Out
Genetic Factors In Pathogenesis
Divergent, yet interconnected and overlapping, molecular pathways are likely responsible for the development of noninvasive and invasive bladder tumors. Somatic mutations in fibroblast growth receptor3 and tumor protein p53 in tumor cells appear to be important early molecular events in the noninvasive and invasive pathways, respectively.
FGFR-3, Ras, and PIK3CA mutations occur with high frequency in noninvasive tumors, leading to upregulation of Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase . Loss of heterozygosity on chromosome 9 is among the most frequent genetic alterations in bladder tumors and is considered an early event.
Large numbers of genomic changes have been detected using karyotyping and comparative genomic hybridization analysis in urothelial carcinoma. Numerically common are losses of 2q, 5q, 8p, 9p, 10q, 18q, and Y. Gains of 1q, 5p, 8q, and 17q are frequently present, and high-level amplifications can be found however, the target genes in the regions of amplifications have not been conclusively identified.
Alterations in the TP53 gene are noted in approximately 60% of invasive bladder cancers. Progression-free survival is significantly shorter in patients with TP53 mutations and is an independent predictor of death among patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
Treating Stage Iii Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the outside of the bladder and might have grown into nearby tissues or organs and/or lymph nodes . They have not spread to distant parts of the body.
Transurethral resection is often done first to find out how far the cancer has grown into the bladder wall. Chemotherapy followed by radical cystectomy is then the standard treatment.Partial cystectomy is rarely an option for stage III cancers.
Chemotherapy before surgery can shrink the tumor, which may make surgery easier. Chemo can also kill any cancer cells that could already have spread to other areas of the body and help people live longer. It can be especially useful for T4 tumors, which have spread outside the bladder. When chemo is given first, surgery to remove the bladder is delayed. The delay is not a problem if the chemo shrinks the cancer, but it can be harmful if it continues to grow during chemo. Sometimes the chemo shrinks the tumor enough that intravesical therapy or chemo with radiation is possible instead of surgery.
Some patients get chemo after surgery to kill any cancer cells left after surgery that are too small to see. Chemo given after cystectomy may help patients stay cancer-free longer, but so far its not clear if it helps them live longer. If cancer is found in nearby lymph nodes, radiation may be needed after surgery. Another option is chemo, but only if it wasn’t given before surgery.
Recommended Reading: Bladder Leakage Pads For Men
Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
Stage IV cancer has metastasized or spread to major organs in other parts of the body. This is often called metastatic cancer. About 5% of bladder cancer cases are diagnosed after theyve already spread to distant organs, according to SEER.
Stage IV bladder cancer is divided into stage IVA and IVB. IVA cancer has spread either:
- Into the wall of the abdomen or pelvis
- Into multiple lymph nodes near the major arteries of the pelvis
IVB bladder cancer has spread to other organs, which can include the lungs, bones, and liver.