What Is Bladder Augmentation
The bladder’s job is to store urine and release it when it’s full. It is one of the many organs located in the lower part of your abdomen. Sometimes the bladder isn’t large enough to hold the usual amount of urine made by the kidneys, so a bladder enlargement or augmentation may help.
What Happens under Normal Conditions?
The urinary tract is like a plumbing system with special ‘pipes’ for water and wastes to flow through. The urinary tract is made of the kidneys, 2 ureters, the bladder, and the urethra.
The kidneys act as a filter system for the blood. They remove toxins and keep the useful sugar, salts, and minerals. Urine is the waste product made by the kidneys. It flows from the kidneys down two, 10 to 12-inch-long tubes called ureters into the bladder.
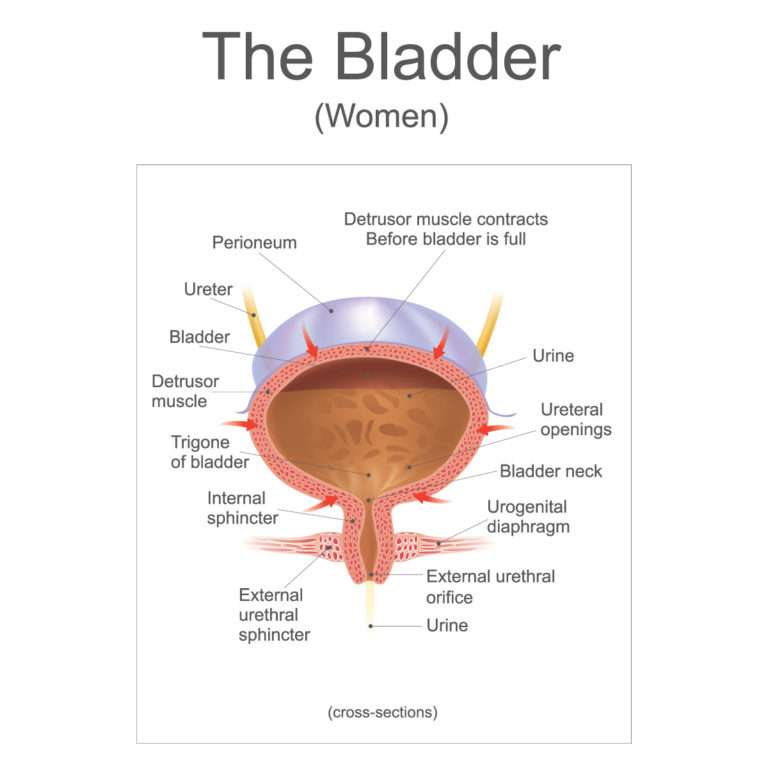
The bladder is a balloon-shaped organ that stores urine. It’s held in place by pelvic muscles in the lower part of your belly. When it isn’t full, the bladder is relaxed. Nerve signals in your brain let you know that your bladder is getting full. When full, you feel the need to urinate. The brain tells the bladder muscles to squeeze . This forces the urine out of your body through your urethra.
Your urethra has muscles called sphincters. They help keep the urethra closed so urine doesn’t leak out before you’re ready to go to the bathroom. These sphincters open up when the bladder contracts.
What is Bladder Augmentation?
Either of these conditions can cause wetting , urinary tract infections, or kidney damage.
Urinary Bladder Facts: 6
6. When empty, the inner lining of the Urinary Bladder makes folds and tucks in. When urine fills in, the lining and hence the bladder expands to accommodate urine flowing in through the Ureters.
7. When empty the muscle walls of the bladder becomes thick and the whole organ becomes firm. However, this is only temporary.
8. The moment the Kidneys process urine and send the liquid through the Ureters all the way down to the bladder, the muscle walls of the Urinary Bladder start thinning and the bladder starts expanding. One thing of note here is that the urine runs down the Ureters because of:
- Gravity.
- Peristalsis a wave-like movement of the Ureters.
9. As the bladder keeps expanding, it needs space. The growing bladder gradually moves upwards and fills in the space in the abdominal cavity.
10. There are two question that need to be asked. They are:
Bladder Diseases: Signs To Watch Out For
When something goes wrong with our bladder, we realize just how much our daily lives depend on this organ. While some symptoms are obvious, others are harder to detect and may go unnoticed. In most cases, the cause is not serious, but can sometimes hide more worrying disorders. Here are several signs to watch for if your bladder is malfunctioning along with some tips for preventative care.
You May Like: Over The Counter Bladder Medication
How To Strengthen Your Bladder And Urinate Less Often
This article was medically reviewed by Allison Romero, PT, DPT. Dr. Allison Romero is a Pelvic Health Specialist, Physical Therapist, and the Owner of Reclaim Pelvic Therapy in the San Francisco Bay Area. With over a decade of experience, Allison specializes in comprehensive pelvic physical therapy treatments for pelvic floor dysfunction. She holds a Bachelor of Science in Kinesiology and Exercise Science from Sonoma State University and a Doctor of Physical Therapy from the University of Southern California. Allison is a board certified Physical Therapist in California and is a member of the American Physical Therapy Association-Section on Womens Health and the International Pelvic Pain Society.There are 19 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 100% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 963,372 times.
What Are The Symptoms Of An Overactive Bladder
Overactive bladder symptoms can include:
- Sudden and overwhelming urge to urinate This symptom can come on very quickly and without any warning.
- Urge incontinence This happens when you suddenly leak urine after feeling an urgent and immediate need to go to the toilet. Theres also a feeling of not being able to reach the toilet fast enough.
- Frequency This is the need to urinate more often than usual sometimes more than eight times within a 24 hour period. Often the need to urinate is ever-present whether fluid intake is limited or not.
- Nocturia This occurs when an overactive bladder wakes you to use the toilet several times during the night to the point where your sleep cycle is disrupted.
Also Check: Do I Have A Bladder Infection
What Are Normal Bladder Habits
A healthy bladder can hold one and a half to two cups of urine during the day and about four cups at night. It is normal to pass urine five or six times a day if you drink between 6-8 glasses of fluid. It is usual to empty your bladder when you get out of bed in the morning, three times during the day, and before you go to bed at night. As we age this pattern may change, as older people tend to make more urine at night.
Urinary Bladder Facts: 26
26. For a person with healthy urinary system, the Urinary Bladder is capable of holding urine for a period of up to 5 hours.
27. When a person pees, the Urinary Bladder will completely empty itself. This happens each and every time a person urinates.
28. The Urinary Bladder is said to be overactive if a person needs to pee more than 8 times in a day. Emptying the bladder up to 8 times a day is just fine.
29. Both genders males and females can suffer from bladder problems. However, the problems are far commoner in certain groups of people such as women who recently had children, men with prostate problems and older people.
30. Overactive Bladder is two types Dry and Wet. Dry means that a person gets sudden and urgent need for urinating many times a day. Wet means that a person has to pee and at the same time, his or her bladder leaks. The Wet Overactive Bladder goes by another name Urge Incontinence.
Hope you liked our urinary bladder facts article. If you want us to write more on similar topics, please drop a comment in the comment box.
Don’t Miss: Best Pills For Bladder Infection
Information For Healthcare Providers On Bladder Control Problems
The content on this page will be of most use to clinicians, such as nurses, doctors, pharmacists, specialists and other healthcare providers.
The following signs and symptoms are cause for concern and require referral to a specialist for further investigation:
| Red flags for referral in people with incontinence |
|
Males with urinary incontinence and any of the following factors should be referred to an appropriate specialist within 2 weeks:
|
|
Consideration for referral to a urologist should be given to patients with the following factors:
|
What Causes An Overactive Bladder
The exact cause of an overactive bladder is a mystery. However, several factors are known to contribute to the involuntary contraction of the bladder muscle, improper bladder function, and other symptoms associated with an overactive bladder.
Some nervous system abnormalities that can cause an overactive bladder include:
- Spinal cord injury
Other causes of overactive bladder can include:
- Nerve damage or trauma caused by surgery or certain therapies
- Trauma to the pelvis or abdomen
- Urinary Tract Infection
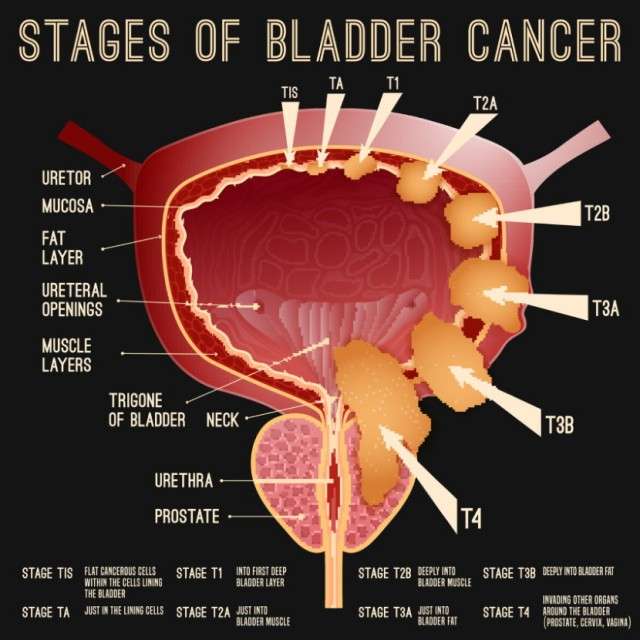
- Bladder cancer/tumours
- Enlarged prostate
There are also several risk factors that can increase the chances of an overactive bladder. These include:
- Age the risk of overactive bladder increases as you age
- Gender women tend to be more susceptible than men because menstruation, pregnancy and menopause all lead to a rise in oestrogen levels and weaker pelvic floor muscles. For men, an enlarged prostate or damage from prostate surgery can cause an overactive bladder.
- Obesity increased weight puts additional pressure on the bladder.
- Diabetes can affect the nerves that control bladder function.
- Pregnancy causes excess pressure on the bladder.
- Spinal injury damage to the spinal cord can disrupt signals sent to the bladder, causing involuntary contract of bladder muscles.
You May Like: What Is A Sling For The Bladder
Common Bladder Problems And When To Seek Help
Bladder problems can disrupt day-to-day life. When people have bladder problems, they may avoid social settings and have a harder time getting tasks done at home or at work. Common bladder problems include urinary tract infections, urinary incontinence, and urinary retention.
Some signs of a bladder problem may include:
- Inability to hold urine or leaking urine
- Needing to urinate more frequently or urgently
- Cloudy urine
- Pain or burning before, during, or after urinating
- Trouble starting or having a weak stream while urinating
- Trouble emptying the bladder
If you experience any of these symptoms, talk to your health care provider.
Treatment for bladder problems may include behavioral and lifestyle changes, exercises, medications, surgery, or a combination of these treatments and others. For more information on treatment and management of urinary incontinence, visit Urinary Incontinence in Older Adults.
Why Is The Bladder Important
Your urinary system or bladder is essential because it filters extra fluid and wastes from your bloodstream, removing them from your body. When your kidneys are functioning normally, they:
Prevent excess fluid and waste buildup in your body.
Produce blood pressure-regulating hormones.
Keep your electrolyte levels like phosphates and potassium stable.
Keep your bones strong.
Produce red blood cells.
Your bladder, urethra and ureters move your urine from your kidneys and then store it until it’s time to release it from your body.
Also Check: Bladder Ultrasound For Urinary Retention
How Do I Increase My Bladder Capacity
Problems with bladder capacity can come about due to several situations. A serious illness may negatively impact the normal function of the bladder, rendering the organ unable to hold the same amount of urine as in times past. Recent surgical procedures may temporarily lower the capacity of the bladder. There is even some evidence that emotional issues can impact the natural ability of the body to control bladder functions in what is considered a normal manner. Fortunately, there are ways to address each of these issues and restore a healthy bladder capacity.
One sign of a problem with bladder capacity is the need for frequent urination. For some reason, the bladder begins to sense the need to urinate long before it is full. When a doctor cannot identify any specific medical condition that is causing the decrease in capacity and control, the use of conditioning exercises can sometimes be helpful.
It should be noted that any exercises designed for use with bladders should only be undertaken under the advice and care of a trained medical professional. Further, the exercises should only be employed when the doctor is sure that there is no organic reason for the bladder capacity problem.
What Are Some Types Of Bladder Management
There are many types bladder management following SCI, each with various advantages and disadvantages. Several of the more common types of bladder management are listed below. It is important to speak with your health care provider to determine which option is best for you.
If you continue to have significant problems affecting your kidneys or bladder or your lifestyle despite non-surgical bladder management options, your doctor might in rare cases suggest a surgical option such as a urinary diversion. For more information on surgical management, see MSKTC factsheet entitled Surgical Alternatives for Bladder Management Following SCI. This factsheet will focus on some of the more common non-surgical options of bladder management.
Don’t Miss: Bladder Problems After Endometrial Ablation
What Else Can Be Done
For many people with IC, changes in diet can also help control symptoms. To learn more, check out the information about IC and food sensitivities. There are also over-the-counter products and prescription medicines that may help control symptoms of urinary urgency and frequency .
Revised Tuesday, May 26th, 2015
What Drinks Are Good For Your Bladder
When trying to figure out how to keep your urinary system healthy, consider these healthy drinks.
Water: You can help prevent incontinence by drinking enough water.
Kohli tea: This tea is an extract from a subtropical plant that grows in southern China. It’s a sweet tea sold over the counter in Japan for its antioxidant benefits. It also has a protective effect on your bladder. A study on kohli tea found it had a substantial protective effect in rabbits with partial bladder obstruction in terms of contractile responses and bladder function.
Cranberry juice: Researchers report cranberry juice could help prevent bacteria from turning into a urinary tract infection within
Pear or apple juice: If you drink fruit juice, switch it to a less acidic juice like pear or apple juice and dilute it with water.
Barley water
Diluted squash: You can take diluted squash, but try and avoid squash and blackcurrant containing sugar alternatives like saccharin and aspartame, which can irritate the bladder.
Fruit and herbal teas: Fruit and herbal teas come in many varieties and are typically free of caffeine. Ginseng, however, can stimulate the bladder and could increase the urgency and frequency of urination.
Lemon water: Lemon is vitamin C-rich and a powerful antioxidant that alkalizes your body. It helps hinder bacterial growth. Additionally, it acts like a diuretic agent, flushing harmful toxins out from your urinary tract, helping prevent UTI recurrence.
Recommended Reading: Natural Remedies For Cystitis Bladder Infection
What Foods Are Good For The Urinary System
Along with beverages, it’s also a good idea to know the foods for a healthy bladder and kidneys. If your bladder is sensitive, there are still foods you can enjoy without irritating it. You already know the foods you should avoid. Here are some bladder-cleansing foods you may want to eat.
Pears: Pears are a great source of fiber and usually start to ripen sometime in September or October, depending on where you live.
Bananas: You’ll find bananas in your local grocery store pretty much all year long. They’re perfect for topping cereals, eating as snacks or putting in smoothies.
Winter squash: Despite its name, you can find squash year-round as well, particularly in the fall and winter. Squash varieties include butternut, acorn and spaghetti.
Green beans: Add a little color to your plate with green beans. Put them in salads, eat them raw or roast them with a bit of olive oil.
Potatoes: Both potatoes and sweet potatoes are bladder-friendly foods.
Whole grains: Rice, quinoa and oats are whole grains and just a few examples of the many varieties you’ll find. They’re not typically expensive, either.
Lean proteins: Low-fat chicken, pork, turkey, beef and fish are examples of lean proteins. They’re not likely to bother your bladder, particularly when you steam, broil or bake them.
Nuts: Cashews and peanuts make perfect protein-rich and bladder-healthy snacks.
Breads: Bread makes a great addition to any meal and is overall bladder-friendly.
Surgical Treatment Of Neurogenic Bladder Dysfunction
To increase bladder capacity, options include bladder augmentation and an ileal conduit. Bladder augmentation is used for patients with detrusor hyperactivity, reduced compliance, and decreased functional storage capacity that do not respond to medical therapy. An ileal conduit used as a urinary diversion strategy is recommended for conditions in which the bladder cannot be preserved. To increase bladder contractility, electrical stimulation with electrodes implanted on the bladder wall, pelvic nerves, sacral roots, and conus is used to elicit detrusor contraction. To increase bladder outlet resistance, options include injection therapy into the bladder neck and urethra to increase tissue bulk under and around the bladder neck, a fascial sling, or an artificial sphincter. To decrease bladder outlet resistance, sphincterotomy is usually indicated in patients with SCI who are unable or unwilling to perform self-catheterization, with bladder neck obstruction resulting from primary hyperactivity or bladder wall hypertrophy that occurs because of chronic striated sphincter dyssynergia. After the procedure, obstruction from recurrence of the stricture or dyssynergia may occur. A urethral stent is used after failed sphincterotomy or as a substitute for sphincterotomy.
Mitesh Parekh MD, in, 2006
Read Also: How To Increase Bladder Capacity Naturally
Blood And Lymph Supply
The bladder receives blood by the vesical arteries and drained into a network of vesical veins. The superior vesical artery supplies blood to the upper part of the bladder. The lower part of the bladder is supplied by the inferior vesical artery, both of which are branches of the internal iliac arteries. In females, the uterine and vaginal arteries provide additional blood supply. Venous drainage begins in a network of small vessels on the lower lateral surfaces of the bladder, which coalesce and travel with the lateral ligaments of the bladder into the internal iliac veins.
The lymph drained from the bladder begins in a series of networks throughout the mucosal, muscular and serosal layers. These then form three sets of vessels: one set near the trigone draining the bottom of the bladder one set draining the top of the bladder and another set draining the outer undersurface of the bladder. The majority of these vessels drain into the external iliac lymph nodes.