What Are The Treatment Options For Bladder Cancer
There are four types of treatment for patients with bladder cancer. These include:
- Surgery
Sometimes, combinations of these treatments will be used.
Surgical options
Surgery is a common treatment option for bladder cancer. The type of surgery chosen will depend on the stage of the cancer.
- Transurethral resection of the bladder is used most often for early stage disease . It is done under general or spinal anesthesia. In this procedure, a special telescope called a resectoscope is inserted through the urethra into the bladder. The tumor is then trimmed away with the resectoscope, using a wire loop, and the raw surface of the bladder is then fulgurated .
- Partial cystectomy is the removal of a section of the bladder. At times, it is used for a single tumor that invades the bladder wall in only one region of the bladder. This type of surgery retains most of the bladder. Chemotherapy or radiation therapy is often used in combination. Only a minority of patients will qualify for this bladder-sparing procedure.
- Radical cystectomy is complete removal of the bladder. It is used for more extensive cancers and those that have spread beyond the bladder .
This surgery is often done using a robot, which removes the bladder and any other surrounding organs. In men, this is the prostate and seminal vesicles. In women, the ovaries, uterus and a portion of the vagina may be removed along with the bladder.
Chemotherapy
- Methotrexate
Intravesical therapy
Radiation therapy
Pathology: Examining Tissue For Signs Of Cancer
When a polyp or other area of suspicious tissue is seen during a cancer screening test, the doctor may take a tissue sample called a biopsy right away, depending on the bodily location being examined, or at a later date, if doing so requires a second procedure. A pathologist then examines the tissue under a microscope to look for cancerous cells.
To better visualize the various parts of the tissue, the pathologist often stains it, sometimes with multiple dyes.
The pathologist looks for abnormalities in the shape and size of cells, shape and size of cell nuclei, and distribution of the cells in the tissue, indicating cancer.
Once the pathologist has confirmed that a biopsy shows cancer, other lab tests may be done to help classify the cancer, which can in turn help to guide treatment.
While much of the work of examining tissue samples is still done by individuals looking through microscopes, advances in automated detection and classification of cancer cells promise faster diagnosis and treatment.
What Are The Risk Factors For Bladder Cancer
Some factors increase the risk of bladder cancer:
- Cigarette smoking is the biggest risk factor it more than doubles the risk. Pipe and cigar smoking and exposure to second-hand smoking may also increase one’s risk.
- Prior radiation exposure is the next most common risk factor .
- Certain chemotherapy drugs also increase the risk of bladder cancer.
- Environmental exposures increase the risk of bladder cancer. People who work with chemicals, such as aromatic amines are at risk. Extensive exposure to rubber, leather, some textiles, paint, and hairdressing supplies, typically related to occupational exposure, also appears to increase the risk.
- Infection with a parasite known as Schistosoma haematobium, which is more common in developing countries and the Middle East.
- People who have frequent infections of the bladder, bladder stones, or other diseases of the urinary tract, or who have chronic need for a catheter in the bladder, may be at higher risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
- Patients with a previous bladder cancer are at increased risk to form new or recurrent bladder tumors.
Other risk factors include diets high in fried meats and animal fats, and older age. In addition, men have a three-fold higher risk than women.
Don’t Miss: What Can I Take For Bladder Control
Screening Of Significant Prognostic Factors For Os And Css Using Univariable And Multivariable Analyses
The Cox proportional hazards models were used to determine the independent prognostic factors in the prediction of OS and CSS. Univariable analyses showed that a total 10 factors were related to OS and CSS. These were as follows: age, gender, race, pathological grade, pT stage, pN stage, LNH, LNR, tumor size, and adjuvant chemotherapy .). Multivariable Cox analyses indicated that age, race, pT stage, pN stage, LNH, LNR, tumor size, and adjuvant chemotherapy were significant independent prognostic factors of OS . Except pathological grade, these comparable variables were also significant prognostic risk factors for CSS . Significant independent prognostic factors were integrated into the predictive models for nomogram and risk stratification systems.
Occurrence In The United States
The American Cancer Society estimates that 83,730 new cases of bladder cancer will be diagnosed in the United States in 2021 and that 17,200 people will die of the disease. The incidence of bladder cancer increases with age, with the median age at diagnosis being 73 years bladder cancer is rarely diagnosed before age 40 years.
Bladder cancer is about 3 times more common in men than in women. Over the past 2 decades, however, the rate of bladder cancer has been stable in men but has increased in women by 0.2% annually. The male predominance in bladder cancer in the United States reflects the prevalence of transitional cell carcinoma . With small cell carcinomain contrast to TCCthe male-to-female incidence ratio is 1:2.
Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men in the United States, after prostate, lung, and colorectal cancer, but it is not among the top 10 cancers in women. Accordingly, more men than women are expected to die of bladder cancer in 2021, with 12,260 deaths in men versus 4940 in women. Nevertheless, women generally have a worse prognosis than men.
The incidence of bladder cancer is twice as high in white men as in black men in the United States. However, blacks have a worse prognosis than whites.
Limited data indicate that small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder probably has the same epidemiologic characteristics as urothelial carcinoma. Patients are more likely to be male and older than 50 years.
Read Also: Bcg Used In Bladder Cancer
Bladder Cancer Clinical Trials
What about Clinical Trials?
You may hear about clinical trials for your bladder cancer. Clinical trials are research studies that test if a new treatment or procedure is safe and effective.
Through clinical trials, doctors find new ways to improve treatments and the quality of life for people with disease. Trials are available for all stages of cancer. The results of a clinical trial can make a major difference to patients and their families. Please visit our clinical trials research webpage to learn more.
Looking For More Of An Introduction
If you would like more of an introduction, explore this related item. Please note that this link will take you to another section on Cancer.Net.
- ASCO Answers Fact Sheet:Read a 1-page fact sheet that offers an introduction to bladder cancer. This free fact sheet is available as a PDF, so it is easy to print.
You May Like: Best Foods To Eat For Bladder Infection
About The Bladder Renal Pelvis And Ureter
The bladder is a hollow organ in the pelvis that stores urine before it leaves the body during urination. This function makes the bladder an important part of the urinary tract. The urinary tract is also made up of the kidneys, ureters, and urethra. The renal pelvis is a funnel-like part of the kidney that collects urine and sends it into the ureter. The ureter is a tube that runs from each kidney into the bladder. The urethra is the tube that carries urine out of the body. The prostate gland is also part of the urinary tract.
The bladder, like other parts of the urinary tract, is lined with a layer of cells called the urothelium. This layer of cells is separated from the bladder wall muscles, called the muscularis propria, by a thin, fibrous band called the lamina propria.
What Are The Types Of Malignant Neoplasms
Malignant neoplasms can develop anywhere in your body. There are five main types of malignant neoplasms , including:
- Carcinomas. Making up about 90% of all cancer cases, carcinomas originate in your epithelial tissue, such as the skin or linings of your organs. Common carcinomas include malignant neoplasms of your skin, breast, prostate, bladder, cervix, endometrium , lung, colon and rectum.
- Sarcomas. This type of cancer begins in your connective tissues, like your bones, cartilage, muscle, tendons and fat. Unlike many other types of cancer, sarcomas are more common in young adults. The most common type of sarcoma is soft tissue sarcoma.
- Myelomas. Also called multiple myeloma, this type of cancer forms in the plasma cells of your bone marrow. The two main types of myelomas are smoldering and active .
- Leukemias. Also called blood cancers, leukemias are cancers of bone marrow. This disease is often associated with the overproduction of immature blood cells, which leads to anemia, fatigue and blood clotting problems.
- Lymphomas. This type of cancer develops in the glands or nodes of your lymphatic system. Lymphomas can occur anywhere in your body, but theyre most commonly felt as lumps in your neck, underarm or groin areas.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get A Uti From Holding Your Bladder
Other Types Of Bladder Cancer
Approximately 2% of bladder cancers are adenocarcinomas. Nonurothelial primary bladder tumors are extremely rare and may include small cell carcinoma, carcinosarcoma, primary lymphoma, and sarcoma . Small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder accounts for only 0.3-0.7% of all bladder tumors. High-grade urothelial carcinomas can also show divergent histologic differentiation, such as squamous, glandular, neuroendocrine, and sarcomatous features.
C679 Malignant Neoplasm Of Bladder Unspecified
NEC Not elsewhere classifiableThis abbreviation in the Tabular List represents other specified. When a specific code is not available for a condition, the Tabular List includes an NEC entry under a code to identify the code as the other specified code.
NOS Not otherwise specifiedThis abbreviation is the equivalent of unspecified.
This note further define, or give examples of, the content of the code or category.
List of terms is included under some codes. These terms are the conditions for which that code is to be used.The terms may be synonyms of the code title, or, in the case of other specified codes, the terms are a list of the various conditions assigned to that code.The inclusion terms are not necessarily exhaustive. Additional terms found only in the may also be assigned to a code.
Certain conditions have both an underlying etiology and multiple body system manifestations due to the underlying etiology.For such conditions, the ICD-10-CM has a coding convention that requires the underlying condition be sequenced first, if applicable, followed by the manifestation.Wherever such a combination exists, there is a use additional code note at the etiology code, and a code first note at the manifestation code.These instructional notes indicate the proper sequencing order of the codes, etiology followed by manifestation.
Don’t Miss: Can Spinal Stenosis Cause Bladder Problems
How To Prevent Bladder Cancer
The study on bladder cancer is still going on. Moreover, the doctors do not know its causes so you can try out some of the common preventing ideas by professionals. You should avoid smoking as it can kill immunity and decreases the life of a person. Also, you should drink plenty of water every day so the system of your body works properly.
If you feel the symptoms of even slight pain, you should never take it lightly. Bladder cancer can be deadly for you and it can spread quickly if not taken care of.
Dont Miss: Cat Food To Prevent Bladder Stones
What Is Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
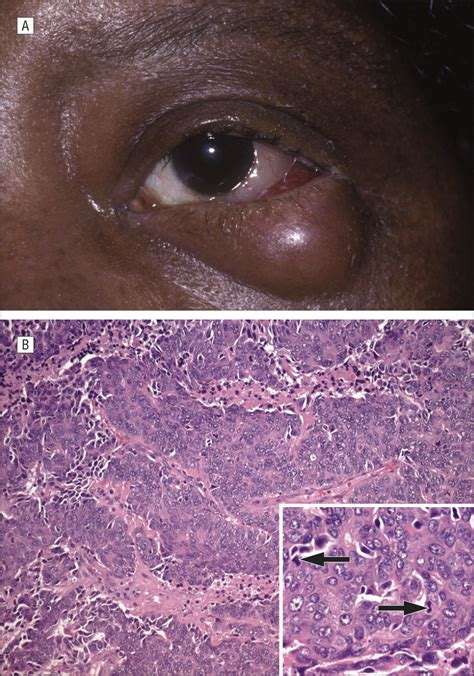
Muscle invasive bladder cancer is a cancer that spreads into the detrusor muscle of the bladder. The detrusor muscle is the thick muscle deep in the bladder wall. This cancer is more likely to spread to other parts of the body.
In the U.S., bladder cancer is the third most common cancer in men. Each year, there are more than 83,000 new cases diagnosed in men and women. About 25% of bladder cancers are MIBC. Bladder cancer is more common as a person grows older. It is found most often in the age group of 75-84. Caucasians are more likely to get bladder cancer than any other ethnicity. But there are more African-Americans who do not survive the disease.
What is Cancer?
Cancer is when your body cells grow out of control. When this happens, the body cannot work the way it should. Most cancers form a lump called a tumor or a growth. Some cancers grow and spread fast. Others grow more slowly. Not all lumps are cancers. Cancerous lumps are sometimes called malignant tumors.
What is Bladder Cancer?
When cells of the bladder grow abnormally, they can become bladder cancer. A person with bladder cancer will have one or more tumors in his/her bladder.
How Does Bladder Cancer Develop and Spread?
The bladder wall has many layers, made up of different types of cells. Most bladder cancers start in the urothelium or transitional epithelium. This is the inside lining of the bladder. Transitional cell carcinoma is cancer that forms in the cells of the urothelium.
Recommended Reading: Can Endometriosis Affect Your Bladder
What Is The Icd
The code is valid for the year 2020 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions. The ICD-10-CM code Z80.42 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like family history of malignant neoplasm of genital structure or family history of prostate cancer or fh: neoplasm of male genital organ.
Prognosis In Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Tumor stage, lymph node involvement, and tumor grade have been shown to be of independent prognostic value in SCC. However, pathologic stage is the most important prognostic factor. In one relatively large series of 154 cases, the overall 5-year survival rate was 56% for pT1 and 68% for pT2 tumors. However, the 5-year survival rate for pT3 and pT4 tumors was only 19%.
Several studies have demonstrated grading to be a significant morphologic parameter in SCC. In one series, 5-year survival rates for grade 1, 2, and 3 SCC was 62%, 52%, and 35%, respectively. In the same study of patients undergoing cystectomy, the investigators suggested that a higher number of newly formed blood vessels predicts unfavorable disease outcome.
In SCC, the survival rate appears to be better with radical surgery than with radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy. In locally advanced tumors, however, neoadjuvant radiation improves the outcome. Sex and age have not been prognostically significant in SCC.
Also Check: Ways To Treat Bladder Infection At Home
What Is A C67 Neoplasm Of The Bladder
Malignant neoplasm of bladder C67- > . A primary or metastatic malignant neoplasm involving the bladder. The bladder is a hollow organ in your lower abdomen that stores urine. Bladder cancer occurs in the lining of the bladder. People with a family history of bladder cancer or who are older, white, or male have a higher risk.treatments
Recommended Reading: Botox Injections For Bladder Control
License For Use Of Current Dental Terminology
End User License Agreement:These materials contain Current Dental Terminology , copyright © 2021 American Dental Association . All rights reserved. CDT is a trademark of the ADA.
The license granted herein is expressly conditioned upon your acceptance of all terms and conditions contained in this agreement. By clicking below on the button labeled I accept, you hereby acknowledge that you have read, understood and agreed to all terms and conditions set forth in this agreement.
If you do not agree with all terms and conditions set forth herein, click below on the button labeled I do not acceptand exit from this computer screen.
If you are acting on behalf of an organization, you represent that you are authorized to act on behalf of such organization and that your acceptance of the terms of this agreement creates a legally enforceable obligation of the organization. As used herein, you and your refer to you and any organization on behalf of which you are acting.
by Adam Smith | Jul 26, 2021 | Uncategorized |
Also Check: Why Do I Have Bladder Leakage
Personal History Of Malignant Neoplasm Unspecified
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific CodePOA Exempt
- bladder Z85.51
Z85.51 Personal history of malignant neoplasm of bladder
Reimbursement claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015 require the use of ICD-10-CM codes.
Other Ways Of Describing Bladder Cancer
In addition to its cell type, bladder cancer may be described as noninvasive, non-muscle-invasive, or muscle-invasive.
-
Noninvasive. Noninvasive bladder cancer includes noninvasive papillary carcinoma and carcinoma in situ . Noninvasive papillary carcinoma is a growth found on a small section of tissue that is easily removed. This is called stage Ta. CIS is cancer that is found only on or near the surface of the bladder, which is called stage Tis. See Stages and Grades for more information.
-
Non-muscle-invasive. Non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer typically has only grown into the lamina propria and not into muscle, also called stage I. Non-muscle-invasive cancer may also be called superficial cancer, although this term is being used less often because it may incorrectly suggest that the cancer is not serious.
-
Muscle-invasive. Muscle-invasive bladder cancer has grown into the bladder’s wall muscle and sometimes into the fatty layers or surrounding tissues or organs outside the bladder.
It is important to note that non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer has the possibility of spreading into the bladder muscle or to other parts of the body. Additionally, all cell types of bladder cancer can spread beyond the bladder to other areas of the body through a process known as metastasis.
Also Check: Recurrent Bladder Infections And Cancer