And It Won’t Hurt To Try These
Like many women, you may have memorized the following age-old advice for preventing UTIs:
-
Wipe from front to back.
-
Urinate before and after sex.
-
Drink lots of water.
-
Avoid tight underpants and jeans.
These suggestions are directed at flushing the bladder and keeping E. coli from spreading into the urinary tract. Although studies have failed to show that they prevent either primary or recurrent UTIs, there’s no harm in trying them, Dr. Gupta says. “They can’t hurt, and if they help, you’re ahead of the game.”
Check If It’s A Urinary Tract Infection
Symptoms of a UTI may include:
- pain or a burning sensation when peeing
- needing to pee more often than usual during the night
- pee that looks cloudy
- needing to pee suddenly or more urgently than usual
- needing to pee more often than usual
- lower tummy pain or pain in your back, just under the ribs
- a high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a very low temperature below 36C
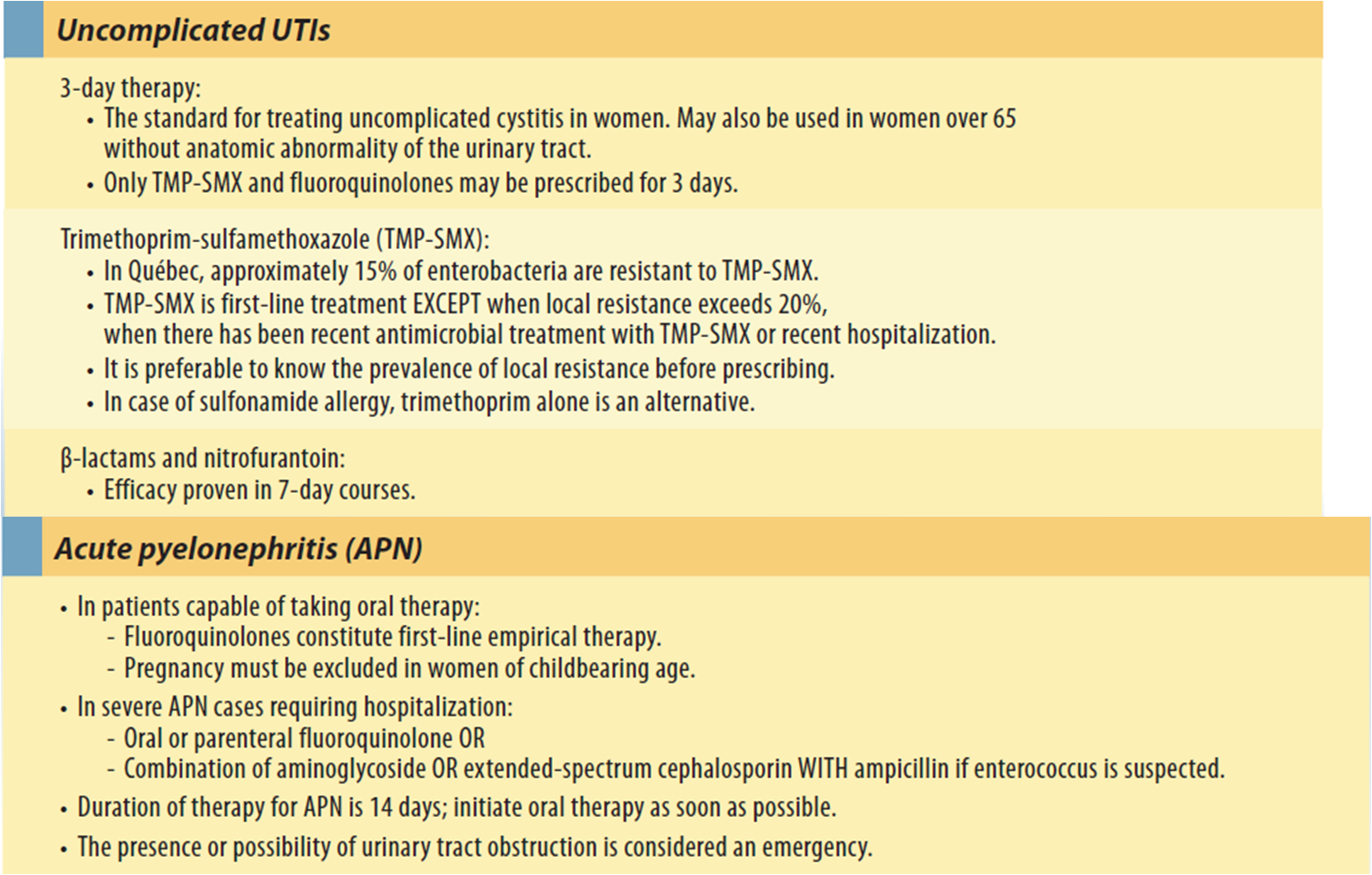
International Clinical Practice Guidelines
In 2010, a panel of international experts updated the 1999 Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines on the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women. The panel reviewed the literature, including the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, and provided an evidence-based guideline for women with uncomplicated bacterial cystitis and pyelonephritis.16,17 The IDSA collaborated with the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, and invited representation from diverse geographic areas and a wide variety of specialties, including urology, obstetrics and gynecology, emergency medicine, family medicine, internal medicine, and infectious diseases. Levels-of-evidence ratings were assigned to recommendations on the use of antimicrobials for the treatment of uncomplicated UTIs.
Don’t Miss: Back Pain And Bladder Leakage
Latest Antibiotics For Utis
- Vabomere is a combination carbapenem antibiotic and beta-lactamase inhibitor. Vabomere was first approved in August of 2017.
- Vabomere is used for the treatment of adult patients with complicated urinary tract infections due to susceptible Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae species complex.
- Vabomere is given as an intravenous infusion every 8 hours. Dosage adjustments are required in patients with varying degrees of kidney impairment.
Zemdri
- Zemdri is an aminoglycoside antibacterial for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections, including pyelonephritis. Zemdri was first approved in February of 2015.
- Zemdri is used against certain Enterobacteriaceae in patients who have limited or no alternative treatment options. Zemdri is an intravenous infusion, administered once daily.
See also: Treatment Options for UTIs
Physical Examination And Diagnostic Testing
The physical examination of patients with acute uncomplicated cystitis is typically normal, except in the 10 to 20 percent of women with suprapubic tenderness.10 Acute pyelonephritis should be suspected if the patient is ill-appearing and seems uncomfortable, particularly if she has concomitant fever, tachycardia, or costovertebral angle tenderness.
Further studies beyond urinalysis and urine cultures are rarely needed to diagnose acute uncomplicated cystitis. Patients who present with atypical symptoms of acute uncomplicated cystitis and those who do not respond to appropriate antimicrobial therapy may need imaging studies, such as computed tomography or ultrasonography, to rule out complications and other disorders.
Recommended Reading: What Medication Is Good For A Bladder Infection
Does Cranberry Juice Prevent A Urinary Tract Infection
Many people say that cranberry juice can help treat, or even prevent, a UTI. Researchers are currently looking into the topic, but havent found a definitive answer yet. Healthcare providers recommend drinking lots of fluids if you have, or have a history of getting, a UTI. Adding a glass of unsweetened cranberry juice to your diet isnt a proven way to prevent a UTI, but it typically wont hurt you either.
Best Probiotics For Recurrent Utis
Using a special strand of probiotics was proven to restore the urogenital flora of healthy premenopausal women.
The Lactobacilli probiotic dominates most healthy womens urogenital flora, and many clinical studies show that its the most effective probiotic you can take to prevent recurring UTIs.
However:
Some strains are better than others. Here are the findings:
Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1 and L. reuteri RC-14 seemed to be the most effective among the studied lactobacilli for the prevention of UTIs. L. casei shirota and L. crispatus CTV-05 have also shown efficacy in some studies
Where Can You Find This Exact Probiotic?
I recommend the Jarrow Formulas Fem-Dophilus, which supports vaginal and Urinary Tract health you can purchase it from iHerb.
It contains the right strain of probiotics proven to prevent UTIs $29 at iHerb
What about you? what has worked best for you? Share your experience in the comments below.
To your health and happiness,
Meital
Read Also: How Long Does Overactive Bladder Last
Do I Need To See A Doctor
Yes. Painful urination can be a symptom of a more serious problem. You should tell your doctor about your symptoms and how long youve had them. Tell your doctor about any medical conditions you have, such as diabetes mellitus or AIDS, because these could affect your bodys response to infection. Tell your doctor about any known abnormality in your urinary tract, and if you are or might be pregnant. Tell your doctor if youve had any procedures or surgeries on your urinary tract. He or she also need to know if you were recently hospitalized or stayed in a nursing home.
If your doctor thinks your pain may be from vaginal inflammation, he or she may wipe the lining of your vagina with a swab to collect mucus. The mucus will be looked at under a microscope to see if it has yeast or other organisms. If your pain is from an infection in your urethra , your doctor may swab it to test for bacteria. If an infection cant be found, your doctor may suggest other tests.
Get The Best Antibiotics For Uti Online
Those dealing with a UTI infection often ask, how can I get rid of UTI in 24 hours at home?
While most UTIs will not be completely resolved within a day, antibiotics for UTI may provide relief in a matter of hours.
Fortunately, PlushCare makes it easy for you to see a doctor immediately and have a prescription sent to the pharmacy of your choice.
If you think you are experiencing symptoms of a UTI, book an online appointment with a top PlushCare doctor to get an official diagnosis and discuss your treatment options in as little as 15 minutes.
Our doctors are selected exclusively from the top 50 medical schools in the country and are skilled at diagnosing and treating UTIs.
The average appointment with PlushCare takes just 15 minutes and same-day appointments are available.
See an online doctor and get a prescription for the best antibiotic for UTI treatment so you can start to feel better again.
Don’t Miss: Can Sugar Cause Bladder Infection
How Long Should I Take Antibiotics
Your doctor will let you know. Typically, for an uncomplicated infection, you’ll take antibiotics for 2 to 3 days. Some people will need to take these medicines for up to 7 to 10 days.
For a complicated infection, you might need to take antibiotics for 14 days or more.
If you still have symptoms after completing antibiotics, a follow-up urine test can show whether the germs are gone. If you still have an infection, you’ll need to take antibiotics for a longer period of time.
If you get UTIs often, you may need a prolonged course of antibiotics. And if sex causes your UTIs, you’ll take a dose of the medicine right before you have sex. You can also take antibiotics whenever you get a new UTI if youâre having symptoms and a positive urine culture.
Antibiotics For Urinary Tract Infections In Older People
Antibiotics are medicines that can kill bacteria. Health care providers often use antibiotics to treat urinary tract infections .
The main symptom of a UTI is a burning feeling when you urinate.
However, many older people get UTI treatment even though they do not have these symptoms. This can do more harm than good. Heres why:
Antibiotics usually dont help when there are no UTI symptoms.
Older people often have some bacteria in their urine. This does not mean they have a UTI. But health care providers may find the bacteria in a routine test and give antibiotics anyway.
The antibiotic does not help these patients.
- It does not prevent UTIs.
- It does not help bladder control.
- It does not help memory problems or balance.
Most older people should not be tested or treated for a UTI unless they have UTI symptoms. And if you do have a UTI and get treated, you usually dont need another test to find out if you are cured. You should also not be tested just in case there is a UTI.
You should only get tested or treated if UTI symptoms come back.
Antibiotics have side effects.
Antibiotics can have side effects, such as fever, rash, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, headache, tendon ruptures, and nerve damage.
Antibiotics can cause future problems.
Antibiotics can kill friendly germs in the body. This can lead to vaginal yeast infections. It can also lead to other infections, severe diarrhea, hospitalization, and even death.
When should older people take antibiotics for a UTI?
You May Like: Can A Ct Urogram Detect Bladder Cancer
Before Antibiotics Utis Often Equaled Death
8 million people visit the doctor every year because of a UTI. Fortunately, the infection is almost always cleared up with antibiotics. People in the past were not as lucky.
At least 50% of women and 12% of men will get a urinary tract infection, also known as a UTI, in their lifetime. To present a hypothetical case, it is 1852 and a young, married woman gets up to use the chamber pot and when she pees, it stings. The next day she keeps having the urge to urinate but very little or nothing comes out. When it does, the pain is worse than the day before.
Here are a few hints to what she might or might not be thinking.
An Ounce Of Prevention

Unfortunately, most UTIs are not completely preventable, and are caused by differences in the structure or function of the urinary tract and immune system. But there are . For example, stay hydrated to increase urine production and flush out unwanted bacterial intruders. Good hygiene is also important, but scrubbing away at delicate genital tissues can damage them and create portals for bacteria. Clean your genital area gently with mild soap and water. Postmenopausal women may benefit from . Finally, eating cranberries and urinating after having sex havent been proven to have major benefits, but arent likely to hurt, either.
Follow me on Twitter
Also Check: Stage 2 Bladder Cancer Prognosis
Option #: Persistent Uti Symptoms After Treatment
Here is another option: they sent your urine sample to a lab and later told you that according to the test you have a UTI. However, antibiotics resolved some symptoms , but the urge to urinate or pain in the lower abdomen remained.
As you could imagine, there could be a scenario when not only you have a full-blown UTI, but also an inflamed bladder lining is causing additional symptoms, as discussed above.
In this case, you, most likely, will see a reduction in pain, and your urine will become clear. However, pain in the bladder area and slight irritation after urination might still linger.
Moreover, when patients mention they feel burning in the urethra rather than the bladder, its quite normal. In fact, the urethra has more nerve endings that could be easily irritated due to underlying inflammation.
What Are The Five Key Practice Changes Of The Uti Program
Obtain urine cultures only when residents have the indicated clinical signs and symptoms of a UTI.
Obtain and store urine cultures properly.
Prescribe antibiotics only when specified criteria have been met, and reassess once urine culture and susceptibility results have been received.
Do not use dipsticks to diagnose a UTI.
Discontinue routine annual urine screening and screening at admission if residents do not have indicated clinical signs and symptoms of a UTI.
Recommended Reading: How Can I Heal My Bladder Naturally
How Can I Get Instant Relief From A Uti
Because most UTIs are bacterial, antibiotics for UTI treatment are the fastest way to get rid of a UTI and get relief.
Not just any antibiotic will cure your UTI. Some antibiotics are processed in a way that they never even reach the urinary tract. Other antibiotics may be equipped to fight off another type of bacteria, but not the one causing your UTI.
So, how do you know which antibiotic for UTI treatment is best for you?
The two most important questions you and your doctor need to consider are:
- What is the most likely bacteria causing the infection?
- What antibiotic is known to combat that bacterium?
With this, you doctor will prescribe you an antibiotic for UTI treatment and you should start feeling better in a few days.
Other Ways To Prevent Recurring Utis
If you have more than 3 UTIs in 1 year, or 2 UTIs in 6 months, there are other things that may help prevent UTIs.
There is some evidence that women under 65 years old who keep getting UTIs may find it helpful to take:
- a supplement called D-mannose this is not recommended for pregnant women
- cranberry products, such as juice or tablets
Speak to your doctor before taking any of these during pregnancy.
Be aware that D-mannose and cranberry products can contain a lot of sugar.
Page last reviewed: 18 November 2020 Next review due: 18 November 2023
Recommended Reading: Drugs To Treat Bladder Infection
What Type Of Bacteria Usually Cause Urinary Tract Infections
The most common bacterial cause of UTIs are E coli. These bacteria usually live harmlessly in the gut of healthy people but can cause problems if they get into the bladder or other parts of the urinary tract. Uncomplicated infection of the bladder, also called cystitis, is common and can be very painful.
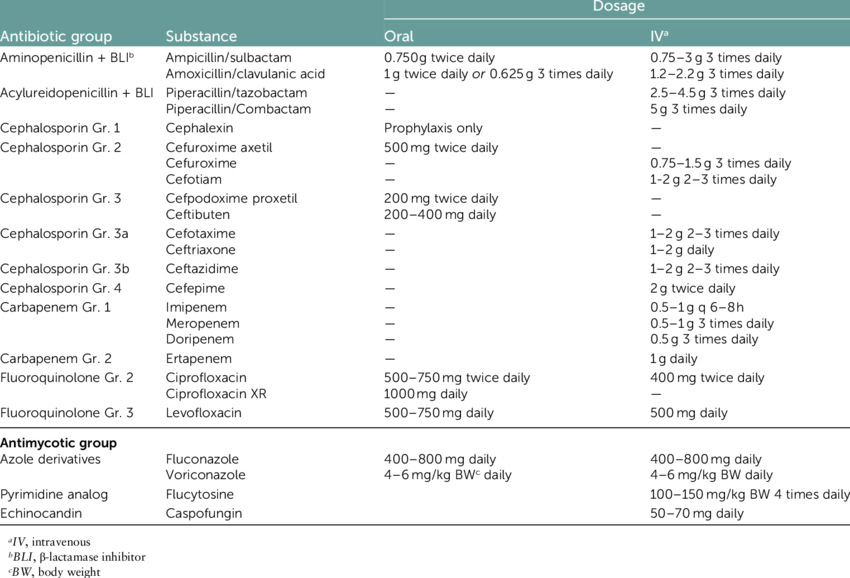
Some strains of E. coli bacteria have begun to produce enzymes called extended-spectrum beta-lactamases . These can make the bacteria resistant to certain antibiotics, and so the bacteria continue to multiply and spread. This causes more severe infection which becomes much more difficult to treat. Another type of bacteria which often causes antibiotic resistant UTIs is ESBL klebsiella pneumoniae. You can read more about extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing bacteria here.
E. coli belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family of Gram-negative bacteria. This family of bacteria also include klebsiella pneumoniae and enterobacter cloacae. The Enterobacteriaceae family can all cause UTIs and are often treated with the beta-lactam antibiotic, carbapenem, for which there are specific ESBL enzymes. The carbapenem resistant Enterobacteriaceae that have developed, have become a real risk to health as the main antibiotic becomes useless and their presence increases in hospitals and care settings.
Treatment For Recurrent Infections
Women who have 2 or more symptomatic UTIs within a 6-month period, or 3 or more episodes over the course of a year, may need preventive antibiotics. All women should use lifestyle measures to prevent recurrences.
Intermittent Self Treatment
Many, if not most, women with recurrent UTIs can effectively self-treat recurrent UTIs without going to a doctor. In general, this requires the following steps:
- As soon as the person develops symptoms, she takes the antibiotic. Infections that occur less than twice a year are usually treated as if they were an initial attack, with single-dose or 3-day antibiotic regimens.
- In some cases, she also performs a clean-catch urine test before starting antibiotics and sends it to the doctor for culturing to confirm the infection.
A woman should consult a doctor under the following circumstances:
- If symptoms have not gone away within 48 hours of starting the antibiotic treatment
- If there is a change in symptoms
- If the person suspects that she is pregnant
- If the person has more than 4 infections a year
Women who are not good candidates for self-treatment are those with impaired immune systems, previous kidney infections, structural abnormalities of the urinary tract, or a history of infection with antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Postcoital Antibiotics
Continuous Preventive Antibiotics
Recommended Reading: Antibiotics Given For Bladder Infection
Amoxicillin/potassium Clavulanate Cefdinir Or Cephalexin
How it Works: is another combination drug that belongs to the penicillin class of antibiotics. and belong to a different class of antibiotics thats closely related to penicillins.
All three antibiotics kill bacteria by destroying one of its most important components: the cell wall, which normally keeps bacteria structurally intact.
Common doses:
-
Amoxicillin/clavulanate: 500 twice a day for 5 to 7 days
-
Cefdinir: 300 mg twice a day for 5 to 7 days
-
Cephalexin: 250 mg to 500 mg every 6 hours for 7 days
Notable side effects: Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and rash are common side effects of these antibiotics. In rare cases, all three have the potential to cause the dangerous skin reactions, SJS and TEN.
If you have a penicillin allergy, your healthcare provider wont prescribe amoxicillin/clavulanate. They may or may not prescribe cefdinir or cephalexin since there is a small chance that a person with a penicillin allergy may also be allergic to these two.
Took Antibiotics Some Uti Symptoms Resolved Other Symptoms Still Linger
So why if it wasnt a UTI, the prescribed antibiotics worked and you did feel a relief? Well, there could be at least three reasons:
Dr. Hawes hypothesizes that it could be due to some sort of a side-effect from Cipro: perhaps, the medicine does something else to the body besides killing bacteria that could indeed reduce UTI-like symptoms.
You May Like: Does Apple Cider Vinegar Help With Bladder Infection